Abstract
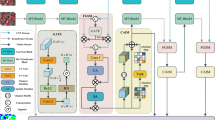
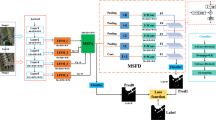
Dual-branch networks serve a crucial role in real-time semantic segmentation. During feature extraction, sequential downsampling frequently results in the loss of fine details, while existing methods often underutilize contextual information. Traditional spatial domain fusion approaches cannot fully integrate local and global information, limiting the network’s expressive capability. To address these challenges, a Context-Guided Detail Fusion Network (CGDFNet) is developed based on existing dual-branch frameworks to enhance feature representation while preserving image details. Specifically, a Semantic Refinement Module (SRM) is implemented in the context branch, where global semantic information is captured through adaptive pooling, and local and global features undergo parallel processing. In the detail branch, high-frequency detail features are guided and reinforced by a Context-Guided Detail Module (CGDM), which leverages semantic information and implements detail-enhanced convolution. Additionally, a Fourier-Domain Adaptive Fusion Module (FDAFM) is developed to achieve efficient fusion of contextual and detail features. This module extracts global frequency information through a Fourier transform, and dynamically fuses features from both branches via an adaptive gating mechanism, enabling effective integration of dual-branch features. CGDFNet achieves 77.8% mIoU with an inference speed of 87.6 FPS on the Cityscapes test set, while attaining 77.9% mIoU at 128.7 FPS on the CamVid test set. Experimental evaluations indicate that CGDFNet balances segmentation quality with real-time inference speed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets used in this study are publicly available. The Cityscapes dataset can be accessed at https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com/. The CamVid dataset is available at https://mi.eng.cam.ac.uk/research/projects/VideoRec/CamVid/. No datasets were generated during the current study.
References
Fan, J. et al. Segtransconv: Transformer and cnn hybrid method for real-time semantic segmentation of autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 25, 1586–1601 (2023).
Song, Q., Mei, K. & Huang, R. Attanet: Attention-augmented network for fast and accurate scene parsing. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence vol. 35, pp. 2567–2575 (2021).
Long, J., Shelhamer, E. & Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 3431–3440 (2015).
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X. & Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2881–2890 (2017).
Zhang, Q., Wu, J., Miao, D., Zhao, C. & Zhang, Q. Attentive multi-granularity perception network for person search. Inf. Sci. 681, 121191 (2024).
Chen, L.-C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K. & Yuille, A. L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected crfs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.7062 (2014).
Simonyan, K. & Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014).
Chen, L.-C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K. & Yuille, A. L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40, 834–848 (2017).
Chen, L.-C., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F. & Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.05587 (2017).
Li, H., Xiong, P., Fan, H. & Sun, J. Dfanet: Deep feature aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 9522–9531 (2019).
Gao, G. et al. Mscfnet: A lightweight network with multi-scale context fusion for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23, 25489–25499 (2021).
Fan, M. et al. Rethinking bisenet for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 9716–9725 (2021).
Xu, G. et al. Lightweight real-time semantic segmentation network with efficient transformer and cnn. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 24, 15897–15906 (2023).
Xu, G., Jia, W., Wu, T., Chen, L. & Gao, G. Haformer: Unleashing the power of hierarchy-aware features for lightweight semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. (2024).
Zhou, Q. et al. Boundary-guided lightweight semantic segmentation with multi-scale semantic context. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 26, 7887–7900 (2024).
Weng, X. et al. Deep multi-branch aggregation network for real-time semantic segmentation in street scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23, 17224–17240 (2022).
Peng, J. et al. Pp-liteseg: A superior real-time semantic segmentation model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.02681 (2022).
Li, W., Liao, M., Hua, G., Zhang, Y. & Zou, W. Contextual guidance network for real-time semantic segmentation of autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. (2025).
Yoo, J., Ko, D. & Kim, G. Ccaseg: Decoding multi-scale context with convolutional cross-attention for semantic segmentation. In 2025 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 9479–9488 (IEEE, 2025).
Chen, G., Li, H., Li, Y., Zhang, W. & Song, T. Parallel segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 148, 110487 (2025).
Yu, C. et al. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 325–341 (2018).
Yu, C. et al. Bisenet v2: Bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vision 129, 3051–3068 (2021).
Zhao, H., Qi, X., Shen, X., Shi, J. & Jia, J. Icnet for real-time semantic segmentation on high-resolution images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 405–420 (2018).
Saksena, S. CABiNet: Efficient Context Aggregation Network for Low-Latency Semantic Segmentation. Master’s thesis, (University of Twente, 2020).
Pan, H., Hong, Y., Sun, W. & Jia, Y. Deep dual-resolution networks for real-time and accurate semantic segmentation of traffic scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 24, 3448–3460 (2022).
Xu, J., Xiong, Z. & Bhattacharyya, S. P. Pidnet: A real-time semantic segmentation network inspired by pid controllers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 19529–19539 (2023).
Guo, Z. et al. Dsnet: A novel way to use atrous convolutions in semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. (2024).
Dong, Y. et al. Afpn: Alignment feature pyramid network for real-time semantic segmentation. Pattern Recogn. 112019 (2025).
Dong, Y., Mao, C., Zheng, L. & Wu, Q. Dmanet: Dual-branch multiscale attention network for real-time semantic segmentation. Neurocomputing 617, 128991 (2025).
Zhang, Q. et al. Learning adaptive shift and task decoupling for discriminative one-step person search. Knowl.-Based Syst. 304, 112483 (2024).
Zhang, Q. et al. Iris recognition based on adaptive optimization log-gabor filter and rbf neural network. In Chinese Conference on Biometric Recognition 312–320 (Springer, 2019).
Chen, Z., He, Z. & Lu, Z.-M. Dea-net: Single image dehazing based on detail-enhanced convolution and content-guided attention. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 33, 1002–1015 (2024).
Mathieu, M., Henaff, M. & LeCun, Y. Fast training of convolutional networks through ffts. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.5851 (2013).
Sun, H. et al. Fourier convolution block with global receptive field for mri reconstruction. Med. Image Anal. 99, 103349 (2025).
Zhang, Q. et al. Dynamic frequency selection and spatial interaction fusion for robust person search. Inf. Fusion 103314 (2025).
Zhou, J., Liu, Y., Peng, B., Liu, L. & Li, X. Madinet: Mamba diffusion network for sar target detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. (2025).
Chen, L., Yang, M.-H., Pu, J. & Zheng, Z. Triplenet: Exploiting complementary features and pseudo-labels for semi-supervised salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. (2025).
Cordts, M. et al. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 3213–3223 (2016).
Brostow, G. J., Shotton, J., Fauqueur, J. & Cipolla, R. Segmentation and recognition using structure from motion point clouds. In European Conference on Computer Vision 44–57 (Springer, 2008).
Brar, D. S., Aggarwal, A. K., Nanda, V., Saxena, S. & Gautam, S. Ai and cv based 2d-cnn algorithm: Botanical authentication of Indian honey. Sustain. Food Technol. 2, 373–385 (2024).
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I. & Hinton, G. E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60, 84–90 (2017).
Goyal, P. et al. Accurate, large minibatch sgd: Training imagenet in 1 hour. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.02677 (2017).
Contributors, M. Openmmlab semantic segmentation toolbox and benchmark (Tech. Rep, Shanghai, China, 2020).
Russakovsky, O. et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vision 115, 211–252 (2015).
Ouyang, D. et al. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning. In ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) 1–5 (IEEE, 2023).
Cai, H., Li, J., Hu, M., Gan, C. & Han, S. Efficientvit: Multi-scale linear attention for high-resolution dense prediction. arxiv 2022. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.14756 (2022).
Liu, X., Liu, J., Tang, J. & Wu, G. Catanet: Efficient content-aware token aggregation for lightweight image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference 17902–17912 (2025).
Zhang, T. et al. Cas-vit: Convolutional additive self-attention vision transformers for efficient mobile applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.03703 (2024).
Selvaraju, R. R. et al. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision 618–626 (2017).
Elhassan, M. A. et al. \(s^{2}\)-fpn: Scale-ware strip attention guided feature pyramid network for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.07298 (2022).
Shi, M. et al. Lmffnet: A well-balanced lightweight network for fast and accurate semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 34, 3205–3219 (2022).
Zhang, W. et al. Topformer: Token pyramid transformer for mobile semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 12083–12093 (2022).
Dong, B., Wang, P. & Wang, F. Head-free lightweight semantic segmentation with linear transformer. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence vol. 37, pp. 516–524 (2023).
Xu, Z. et al. Sctnet: Single-branch cnn with transformer semantic information for real-time segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 38, 6378–6386 (2024).
Wei, C. et al. Hyperseg: Towards universal visual segmentation with large language model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.17606 (2024).
Gao, G. et al. Fbsnet: A fast bilateral symmetrical network for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 25, 3273–3283 (2022).
Shi, M. et al. Lightweight context-aware network using partial-channel transformation for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 25, 7401–7416 (2024).
Ye, B. & Xue, R. Dual attention dual-resolution networks for real-time semantic segmentation of street scenes. IEEE Access (2024).
Xiao, X. et al. Baseg: Boundary aware semantic segmentation for autonomous driving. Neural Netw. 157, 460–470 (2023).
Li, S. et al. Ndnet: Spacewise multiscale representation learning via neighbor decoupling for real-time driving scene parsing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 35, 7884–7898 (2022).
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62472145) the Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research Project (No. 252102211015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated in the conception and design of the study. Shan Zhao, Wenjing Fu, and Jiajia Gao were responsible for material preparation, data collection, and analysis. Fukai Zhang and Zhanqiang Huo handled software development and project management. The initial manuscript draft was prepared by Wenjing Fu, with all authors providing feedback on earlier versions. Every author reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Fu, W., Gao, J. et al. CGDFNet: a dual-branch real-time semantic segmentation network with context-guided detail fusion. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39370-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39370-1