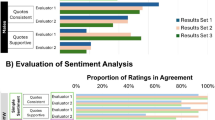
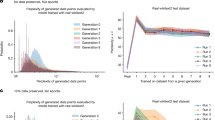
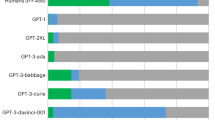
Abstract
This work aims to answer one central question: to what extent can open-source generative text models be used in a workflow to approximate steps in thematic analysis in social science research? To answer this question, we present the Generative AI-enabled Theme Organization and Structuring (GATOS) workflow, which uses open-source machine learning techniques, natural language processing tools, and generative text models to facilitate aspects of thematic analysis. To establish evidence of validity of the method, we present three case studies applying the GATOS workflow, leveraging these models and techniques to inductively create codebooks similar to traditional procedures using thematic analysis. We show that the GATOS workflow can identify themes in the text that were used to generate the original synthetic datasets. We conclude with a discussion of relevant considerations, the implications of this work for social science research, and the tradeoffs of using open-source generative text models to facilitate scalable qualitative data analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The simulated data for this study will be made available in the corresponding author’s GitHub repository: https://github.com/andrewskatz.
References
Argyle LP, Busby EC, Fulda N, Gubler JR, Rytting C, Wingate D (2023) Out of one, many: using language models to simulate human samples. Political Anal 31(3):337–351
Anakok I, Katz A, Chew K J, Matusovich H (2025) Leveraging Generative Text Models and Natural Language Processing to Perform Traditional Thematic Data Analysis. Int J Qual Methods 24:16094069251338898
Belotto MJ (2018) Data analysis methods for qualitative research: managing the challenges of coding, interrater reliability, and thematic analysis. Qual Rep 23(11):2622–2633
Benoit K, Watanabe K, Wang H, Nulty P, Obeng A, Müller S, Matsuo A (2018) quanteda: an R package for the quantitative analysis of textual data. J Open Source Softw 3(30):774–774
Bird C, Ungless E, Kasirzadeh A (2023) Typology of risks of generative text-to-image models. In Proceedings of the 2023 AAAI/ACM conference on AI, ethics, and society, 396–410
Blei DM, Ng AY, Jordan MI (2003) Latent Dirichlet allocation. J Mach Learn Res 3(Jan):993–1022
Braun V, Clarke V (2006) Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol 3(2):77–101
Burton A, Altman DG, Royston P, Holder RL (2006) The design of simulation studies in medical statistics. Stat Med 25(24):4279–4292
Clonts JG (1992) The concept of reliability as it pertains to data from qualitative studies
Cope DG (2014) Computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software. Oncol Nurs Forum 41:322–323
Davison RM, Chughtai H, Nielsen P, Marabelli M, Iannacci F, van Offenbeek M et al (2024) The ethics of using generative AI for qualitative data analysis. Inf Syst J 34:1433–1439
DeBode JD, Armenakis AA, Feild HS, Walker AG (2013) Assessing ethical organizational culture: refinement of a scale. J Appl Behav Sci 49(4):460–484
De Paoli S (2024) Performing an inductive thematic analysis of semi-structured interviews with a large language model: an exploration and provocation on the limits of the approach. Soc Sci Comput Rev 42(4):997–1019
Dickerson DA, Masta S, Ohland MW, Pawley AL (2024) Is Carla grumpy? Analysis of peer evaluations to explore microaggressions and other marginalizing behaviors in engineering student teams. J Eng Educ 113(3):603–634
Dominick PG, Reilly RR, McGourty JW (1997) The effects of peer feedback on team member behavior. Group Organ Manag 22(4):508–520
Donia M, O’Neill TA, Brutus S (2015) Peer feedback increases team member performance, confidence and work outcomes: a longitudinal study. Acad Manag Proc 2015(1):12560
Dubey A, Jauhri A, Pandey A, Kadian A, Al-Dahle A, Letman A, et al. (2024) The llama 3 herd of models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.21783
Elliott V (2018) Thinking about the coding process in qualitative data analysis. Qual Rep 23 (11)
Gao J, Guo, Y, Lim G, Zhang T, Zhang Z, Li, TJJ, Perrault ST (2024) Collabcoder: a lower-barrier, rigorous workflow for inductive collaborative qualitative analysis with large language models. In Proceedings of the CHI conference on human factors in computing systems 1–29
Gao C, Lan X, Li N, Yuan Y, Ding J, Zhou Z, Li Y (2024) Large language models empowered agent-based modeling and simulation: a survey and perspectives. Hum Soc Sci Commun 11(1):1–24
Gery W, Bernard HR (2000) Data management and analysis methods. Handb Qual Res 32(3):125–139
Gibson CB, Gilson LL, Griffith TL, O’Neill TA (2023) Should employees be required to return to the office?. Organ Dyn 52(2):100981
Golafshani N (2003) Understanding reliability and validity in qualitative research. Qual Rep 8(4):597–607
Grix J (2002) Introducing students to the generic terminology of social research. Politics 22(3):175–186
Grootendorst M (2022) Bertopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based tf-idf procedure. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.05794
Guba EG, Lincoln YS et al (1994) Competing paradigms in qualitative research. Handb Qual Res 2(163-194):105
Halfpenny P (1979) The analysis of qualitative data. Sociol Rev 27(4):799–827
Hamilton L, Elliott D, Quick A, Smith S, Choplin V (2023) Exploring the use of ai in qualitative analysis: a comparative study of guaranteed income data. Int J Qual Methods 22: 16094069231201504
Hou H, Remøy H, Jylhä T, Vande Putte H (2021) A study on office workplace modification during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Netherlands. J Corp Real Estate 23(3):186–202
Iooss B, Lemaître P (2015) A review on global sensitivity analysis methods. Uncertainty management in simulation-optimization of complex systems: algorithms and applications 101–122
Johnson B., Main J. B., Katz A (2023) How participating in extracurricular activities supports dimensions of student wellness. In Proceedings of the IEEE frontiers in education conference (FIE) (pp 1–10). IEEE
Kaptein M (2011) Understanding unethical behavior by unraveling ethical culture. Hum Relat 64(6):843–869
Katz A, Gerhardt M, Soledad M (2024) Using generative text models to create qualitative codebooks for student evaluations of teaching. Int J Qual Methods 23:16094069241293283
Katz A, Shakir U, Chambers B (2023) The utility of large language models and generative AI for education research. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.18125
Kelle U, Bird K (1995) Computer-aided qualitative data analysis: Theory, methods and practice. Sage
Key S (1999) Organizational ethical culture: real or imagined?. J Bus Ethics 20:217–225
Kuye O, Uche C, Akaighe G (2013) Organizational culture and ethical behaviour: a strategic standpoint. J Hum Soc Sci Creative Arts 8(1):1–12
Liang PP, Wu C, Morency LP, Salakhutdinov R (2021) Towards understanding and mitigating social biases in language models. In International conference on machine learning 6565–6576
Liesenfeld A, Dingemanse M (2024) Rethinking open source generative AI: open-washing and the EU AI Act. In Proceedings of the 2024 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (pp. 1774–1787)
Lincoln YS, Lynham SA, Guba EG et al (2011) Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences, revisited. Sage Handbook on Qualitative Research 4(2):97–128
Liu Z, Van Egdom D, Flin R, Spitzmueller C, Adepoju O, Krishnamoorti R (2020) I don’t want to go back: examining the return to physical workspaces during covid-19. J Occup Environ Med 62(11):953–958
Morris TP, White IR, Crowther MJ (2019) Using simulation studies to evaluate statistical methods. Stat Med 38(11):2074–2102
Ott S, Barbosa-Silva A, Blagec K, Brauner J, Samwald M (2022) Mapping global dynamics of benchmark creation and saturation in artificial intelligence. Nat Commun 13(1):6793
Paul K, Kim J, Diekman A, Godwin A, Katz A, Maltese A (2022) Collateral damage: Investigating the impacts of COVID on STEM professionals with caregiving responsibilities. In Proceedings of the ASEE annual conference & exposition
Perkins M, Roe J (2024) The use of generative AI in qualitative analysis: inductive thematic analysis with ChatGPT. J Appl Learn Teach 7(1)
Potosky D, Godé C, Lebraty JF (2022) Modeling the feedback process in teams: a field study of teamwork. Group Organ Manag 47(6):1218–1258
Prescott MR, Yeager S, Ham L, Rivera Saldana CD, Serrano V, Narez J et al (2024) Comparing the efficacy and efficiency of human and generative AI: qualitative thematic analyses. JMIR AI 3:e54482
Qiao S, Fang X, Garrett C, Zhang R, Li X, Kang Y (2024) Generative ai for qualitative analysis in a maternal health study: coding in-depth interviews using large language models (LLMs). medRxiv 2024–09
Roy A, Newman A, Round H, Bhattacharya S (2024) Ethical culture in organizations: a review and agenda for future research. Bus Ethics Q 34(1):97–138
Salah M, Al Halbusi H, Abdelfattah F (2023) May the force of text data analysis be with you: unleashing the power of generative AI for social psychology research. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans 100006
Saldaña J (2011) Fundamentals of qualitative research. Oxford University Press
Saldaña J (2021) The coding manual for qualitative researchers
Salomon G (1991) Transcending the qualitative-quantitative debate: the analytic and systemic approaches to educational research. Educ Res 20(6):10–18
Saltelli A, Tarantola S, Campolongo F (2000) Sensitivity analysis as an ingredient of modeling. Stat Sci 377–395
Silge J, Robinson D (2016) tidytext: Text mining and analysis using tidy data principles in R. J Open Source Softw 1(3):37
Tai RH, Bentley LR, Xia X, Sitt JM, Fankhauser SC, Chicas-Mosier AM, Monteith BG (2024) An examination of the use of large language models to aid analysis of textual data. Int J Qual Methods 23: 16094069241231168
Wang Y, Liu Y, Cui W, Tang J, Zhang H, Walston D, Zhang D (2021) Returning to the office during the COVID-19 pandemic recovery: early indicators from China. In Extended abstracts of the 2021 CHI Conference on human factors in computing systems 1–6
Wu CH, Parker SK, De Jong JP (2014) Feedback seeking from peers: a positive strategy for insecurely attached team-workers. Hum Relat 67(4):441–464
Xu C, Sun Q, Zheng K, Geng X, Zhao P, Feng J, et al (2023) WizardLM: Empowering large language models to follow complex instructions. In The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation under EEC 2107008 and a grant from the Virginia Tech Academy of Data Science Discovery Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK wrote the prompts to generate the simulated data; analyzed the data; created the figures; and wrote the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion sections of the paper. GCF wrote the background section. JBM contributed to editing and conceptualizing. All authors reviewed the full paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not obtained because the research does not involve human participants or their data. The study used simulated data.
Informed consent
Not obtained because the research does not involve human participants or their data. The study used simulated data.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Katz, A., Fleming, G.C. & Main, J.B. Thematic analysis with open-source generative AI and machine learning: a new method for inductive qualitative codebook development. Humanit Soc Sci Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-026-06508-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-026-06508-5