Abstract
The reversibility of South Asian summer monsoon (SASM) precipitation under the CO2 removal scenario is critical for climate mitigation and adaptation. In the idealized CO2 ramp-up (from 284.7 to 1138.8 ppm) and symmetric ramp-down experiments, SASM precipitation is largely reversible while exhibiting strong asymmetry: it may overshoot the unperturbed level when CO2 recovers. Such asymmetric response is mainly due to the enhanced El Niño-like and Indian Ocean dipole-like warming during the ramp-down period. The uneven sea surface warming weakens Walker circulation, with anomalous sinking over the SASM region. Meanwhile, the warming also affects the rainfall over the Maritime Continent and tropical western Indian Ocean. The suppressed rainfall over the Maritime Continent triggers the equatorial Rossby wave, which weakens the ascent over the SASM region; the increased rainfall over the tropical western Indian Ocean excites the equatorial Kelvin wave, which reduces moisture transport. Additionally, tropic-wide warming reduces the land-sea thermal contrast and weakens monsoonal circulation. Consequently, the combined effects of the weakened ascent and moisture transport lead to the overshooting of SASM rainfall. Our results suggest that symmetric CO2 removal, although unlikely in the foreseeable future, may result in a risk of local drought over the SASM region.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The concentration of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere has been increasing since the Industrial Revolution. It exerts severe, widespread, and irreversible influences on climate and human society1. To avoid or lower these influences, the Paris Agreement proposed a strict target, i.e., holding the increase in the global average temperature to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial (PI) level and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5 °C above PI. Such long-term temperature goals call for reaching the global peak of greenhouse gas emissions as soon as possible to achieve a climate-neutral world by the middle of the 21st century. Achieving this target requires Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) methods to decrease atmospheric CO2 concentration in the future1,2,3,4,5,6. Due to its huge heat capacity, the ocean acts as heat storage which absorbs most of the redundant energy arising from the CO2 concentration increases1,7. In particular, the response of the ocean is much slower, with a timescale of decades to millennia8,9,10. If CDR methods are applied, the excess heat accumulated in the ocean would affect the climate response during the CO2 ramp-down period11,12,13. At present, the climate effect of CDR is still inconsistent and inadequately understood in the scientific community14,15.
The South Asian summer monsoon (SASM), a crucial component of the global monsoon system, directly affects the lives of more than one billion people. Slight changes in SASM precipitation can cause tremendous socioeconomic impacts, including impacts on agricultural production, water resources, and basic human needs16,17. Hence, understanding the response of SASM precipitation to climate change is of great importance. Under a global warming scenario where the CO2 concentration increases monotonically, SASM precipitation is projected to increase in nearly all models, despite a weakening of SASM circulation18,19. Previous studies have reported that enhanced atmospheric water vapor content and the larger moisture convergence into the SASM region20,21,22,23 are responsible for the increased rainfall, which is consistent with the “wet-get-wetter” mechanism24,25,26. However, the positive contribution of the thermodynamic effect is partially offset by the dynamic effect due to the weakened circulation, which results in a lower increase in SASM precipitation than water vapor content27,28. The enhanced upper-tropospheric warming over the tropical Indian Ocean29, as well as the mean advection of the stratification change mechanism30, may all contribute to the weakened SASM circulation.
Under the CDR scenario, SASM precipitation displays an overshooting relative to that during the CO2 ramp-up period31, namely, SASM precipitation may fully recover and exhibit drought when the CO2 concentration recovers. This is significantly different from that of the global hydrological cycle12,13,32,33,34,35. In the idealized experiment in which the CO2 rise is followed by a symmetric decline, global precipitation continues to rise for decades after CO2 peaks and cannot return to the initial level when CO2 recovers. Such an asymmetric response of global precipitation originates mainly from the ocean, and precipitation on land is nearly symmetrical11,36. The response of rainfall at the regional scale has a similar response to global precipitation, including the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)37, East Asia34, and the Korean Peninsula35. For example, the location of the ITCZ changes minimally during the CO2 ramp-up period; in contrast, it shifts rapidly to the south during the CO2 ramp-down period and resides in the south when the CO2 concentration recovers to the initial level, leading to the asymmetric responses of the ITCZ-related precipitation37. Researchers have inferred that both the accumulated heat in the deep ocean during the CO2 ramp-up period11,13 and the rainfall sensitivity to CO2 forcing through tropospheric adjustment processes33 are responsible for such asymmetric responses. For the distinct response of SASM precipitation, the HadCM3 output suggested that it may result from the lag recovery of Pacific and Indian Ocean Sea Surface Temperature (SST)31. The weakened moisture flux convergence related to the southward ITCZ shift during the CO2 ramp-down period compared to the ramp-up period also plays a role38. As a part of Coupled Model Intercomparison Project phase six (CMIP6), the Carbon Dioxide Removal Model Intercomparison Project (CDRMIP) was sponsored15. To date, eight models have participated in this project and have conducted CDR experiments (see “Methods”). The evolution of CO2 concentration of these experiments is presented in Fig. 1a, which increases for 140 years and then gradually decreases to the initial level. It is a good opportunity to verify the robustness of the response of SASM precipitation under the CDR scenario. Moreover, there is the possibility of uncovering other process responsible for the asymmetric response. Therefore, this study aims to address the following two scientific questions: (a) How does SASM rainfall respond to CDR in multiple models? How is the inter-model consistency? (b) What major processes are responsible for this response?
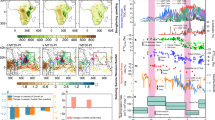
a The evolution of the atmospheric CO2 concentration (unit: ppm) in CDR experiments. b The global mean surface temperature (GMST; unit: K) and precipitation (GMP; unit: mm day−1) responses in CO2 ramp-up and ramp-down experiments relative to the PI from the MME. Time series of the CO2 concentration (black line; unit: ppm), annual GMST (red line), and GMP (blue line) anomalies. A 3-point (1/4,1/2,1/4) filter with 40 times is used to remove interannual variability. The vertical dashed line denotes Year 140 when CO2 peaks.
Results
Asymmetric response of temperature and rainfall
The global mean surface temperature (GMST) and precipitation (GMP) responses during the CO2 ramp-up and ramp-down experiments from the Multi-Model Ensemble (MME) are presented in Fig. 1b. Both the GMST and GMP respond asymmetrically and show hysteresis concerning symmetric CO2 forcing, which is consistent with previous studies33,35,37. The GMST and GMP increase consistently with CO2 but continue to increase for about 10 and 20 years, respectively, after CO2 peaks and show significant positive anomalies after CO2 recovers. Such GMST and GMP hysteresis can be interpreted by the release of heat stored in the deep ocean11,13,31. The brief increase in GMP after CO2 peaks is a consequence of rainfall sensitivity to CO2 forcing through tropospheric adjustment processes33.
However, compared to the GMP, SASM precipitation evolves quite differently. SASM precipitation is the area average of land rainfall over the domain (7.5–30.5°N, 73–90°E; see the red rectangles in Fig. 3). It increases during the CO2 ramp-up period; after CO2 peaks, it continues to increase for approximately a decade before diminishing rapidly; it overshoots an unperturbed level before CO2 recovers to the PI (Fig. 2). We select two 40-year periods with the same CO2 concentration to analyze the reversibility of SASM precipitation: year 21–60 in the CO2 ramp-up period (hereafter RU) and year 220–259 in the CO2 ramp-down period (hereafter RD; gray bands in Fig. 2). Precipitation increases consistently across the SASM region relative to the PI during the RU period (Fig. 3a), which agrees with the results under the global warming scenario18,19,39. During the RD period, precipitation over South Asia (SA) displays a “decreased-increased-decreased” tripolar response from southwest to northeast relative to the PI (Fig. 3b). Overall, despite the CO2 concentration being the same in both periods, SA is significantly drier in the RD period than in the RU period (Fig. 3c). If we change the length of the two periods with equivalent CO2 concentration levels to 30 years and 50 years, the asymmetric response of precipitation is still significant (Supplementary Fig. 1). Thus, the model simulations imply that if CDR is applied, SASM precipitation may gradually decline to a level below the unperturbed level when CO2 recovers to the PI.
Time series of the CO2 concentration (blue line; unit: ppm) and rainfall (red line; unit: mm day−1) anomaly compared to PI. Pink shadings indicate the ensemble spread of the seven models. A 3-point (1/4,1/2,1/4) filter with 40 times is used to remove interannual variability. The vertical dotted line denotes the CO2 peak year (Year 140). Two gray shadings in Year 21–60 (RU) and Year 220–259 (RD) indicate the two 40-year periods with the same average CO2 concentration during the ramp-up and ramp-down periods.
The RU (a) and RD (b) periods rainfall anomalies compared to PI. c Difference in rainfall between the RU (20–60) and RD (220–259) periods. Black dots in (a, b) denotes the regions where more than 70% ensemble members agree with the sign of the MME. The regions denoted by the black dots in (c) indicate where the rainfall difference between the RU and RD periods are statistically significant at a 90% confidence level and more than 70% ensemble members agree with the sign of the MME. The red rectangles highlight the SASM region.
Under global warming scenario, the precipitation change mainly comes from the contribution of the dynamic term related to the circulation and the thermodynamic term related to the moisture according to the moisture budget. To understand the asymmetric response of SASM precipitation, the simplified moisture budget equation is employed40:
Where ∆ represents the departure from the PI; P, ω and q are precipitation, pressure velocity at 500 hPa, and surface specific humidity, respectively. Horizontal moisture advection and quadratic (nonlinear processes) terms were omitted because they are insignificant compared with the thermodynamic and dynamic components in the tropics25,40,41. The sum of the thermodynamic and dynamic terms (Fig. 4c) resembles the contemporary precipitation distribution (Fig. 3c) with a small difference in magnitude, which indicates that the linear approximation of the moisture budget (Eq. 1) can well represent the total precipitation change. The thermodynamic component (\(- \Delta q \cdot \omega\), Fig. 4a) shows increased precipitation over the region where ascent prevails climatologically. This can be explained by the “wet-get-wetter” mechanism. According to the Classius–Clapeyron equation, a higher GMST may lead to more water vapor in the atmosphere during the RD period than during the RU period (Fig. 1; Fig. 4d). Supposing that the ascent remained fixed, more water vapor may contribute to a wetter SA during the RD period (Fig. 4a). The results of the dynamic component (\(- \Delta \omega \cdot q\), Fig. 4b) indicate that the weakening of the ascent (Fig. 4e) in SA leads to less precipitation during the RD period relative to the RU period, which is partly offset by the thermodynamic effect. Moreover, the spatial pattern of the dynamic component (Fig. 4b) resembles the contemporary precipitation change (Fig. 3c; Fig. 4c). This indicates that the asymmetric response of SASM precipitation is mainly the result of the dynamic component, which is dominated by changes in vertical motion.
The difference in thermodynamic term (a), dynamic term (b), and both of them (c) between the RU and RD periods (unit: mm day−1). d, e The same as in (a−c), but for the integration of specific humidity from the surface to 1 hPa (unit: kg m−2) and pressure velocity at 500 hPa (unit: 10−2 Pa s−1). The black dots denote the region in which at least 70% of models agree on the sign of the MME. The red rectangles highlight the SASM region.
Atmospheric circulation change and its driving mechanisms
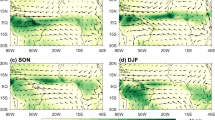
We found that the asymmetric response of SASM precipitation mainly comes from the contribution of vertical circulation; therefore, the causes of change in vertical velocity are further explored. Figure 5 displays the difference in upper-level (200 hPa) velocity potential and divergence winds between the RU and RD periods. The large-scale circulation features a weakened Walker circulation. Over SA and MC, anomalous upper-level convergence favors local precipitation suppression (Fig. 3c). Divergence anomalies exist over the tropical central Pacific. The TWIO has increased rainfall (Fig. 3c) due to anomalous rising motion, and the delayed response of moisture (Fig. 4d) further strengthens such positive rainfall anomalies.
In the lower troposphere, an anomalous anticyclone is evident with its center in the northeastern part of SA during the RD period relative to the RU period (Fig. 6a). Via the effect of Ekman downwelling, the anomalous anticyclone contributes to a weakened ascent on the top of the planetary boundary layer, which also favors rainfall suppression over the SASM region. In addition, the anomalous easterlies (Fig. 6a) over southern SA hinder local southwesterly water vapor transport. Since the moisture is mainly confined in the lower troposphere, the pattern of the vertically integrated moisture flux (vectors in Fig. 6b) highly resembles the horizontal wind pattern at 850 hPa. The responses of atmospheric horizontal wind and vertical velocity over the SASM region are well coupled, which corresponds to the divergence of moisture flux suppressing rainfall (shadings in Fig. 6b).
a The difference in the pattern of the 850 hPa wind (vectors; unit: m s−1) and vorticity (shadings; unit: 10−6 s−1) between the RU and RD periods. b The same as in (a), but for vertically integrated moisture fluxes from the surface to 1 hPa (vectors; unit: 102 kg m−1 s−1) and their divergence (shadings; unit: 10−5 kg m−2 s−1). The black dots denote the region in which at least 70% of models agree on the sign of the MME. Vectors only exceeding 70% of model consistency are shown. The red rectangles highlight the SASM region.
What causes the asymmetric response of the SASM horizontal circulation? As shown in Fig. 3c, the decreased precipitation over the MC and the enhanced precipitation over the TWIO are hypothesized to be responsible. The suppressed precipitation over the MC induces an equatorial Rossby wave response with an anomalous anticyclone over SA21,42. The positive rainfall over the TWIO may induce an equatorial Kelvin wave response with easterly anomalies over southern SA. To test these hypotheses, we employed the LBM, which is widely used in studying tropical dynamics43,44. The climatology of the RU period is set as the model basic state since we focus on the asymmetric response between the RU and RD periods. The LBM is forced by (1) cooling over the MC (−10°S–0°, 90–130°E, Fig. 7a), with a maximum cooling rate of −2.67 K day−1, and (2) heating over the TWIO (−10°S–10°N, 50–70°E, Fig. 7c), with a maximum heating rate of 2.67 K day−1. The vertical profiles of atmospheric diabatic heating (cooling) follow the gamma distribution, and their maximum (minimum) is at σ = 0.45 (Fig. 7b, d).
The response of the 850 hPa wind (vectors; unit: m s−1) in the LBM, which is forced by the atmospheric diabatic heating (shadings; unit: K day−1) over the MC (a), TWIO (c) and the sum of the two (e). b, d The vertical distribution of atmospheric diabatic heating over the TWIO and atmospheric diabatic cooling over the MC (unit: K day−1). Wind speed changes less than 0.095 in (a), 0.075 in (c), and 0.085 in (e) are omitted.
The forced results of the LBM reproduced the key features of lower-level horizontal wind over SA well in the CMIP6 results (Fig. 7e). The cooling over the MC excites an equatorial Rossby wave response to its northwest. Over northeastern SA, a pronounced anomalous anticyclone occurs (Fig. 7a). The Rossby wave response is substantially stronger north than south of the equator due to the effects of monsoon easterly vertical shear mean flows45,46. The warming over the TWIO triggers an equatorial Kelvin wave response to its east. Easterly anomalies as part of the Kelvin wave response exist over southern SA (Fig. 7c). According to the theories of Matsuno47 and Gill48, in a resting basic state without mean flow, the Kelvin wave response is confined to the vicinity of the equator and shows remarkable symmetry with respect to the equator. However, because of the strong monsoon circulation, the low-level circulation shows a stronger response north of the equator, with a remarkable asymmetry49. Equatorial symmetry strengthens in the upper level (Supplementary Fig. 2). Therefore, the two numerical experiments support the hypothesis that the rainfall responses over the MC and TWIO induce weakened SASM circulation, including the anomalous anticyclone and easterly winds, which leads to drier condition over SA.
In addition to the forcings over the equatorial regions, the land–sea contrast may be responsible for the asymmetric responses of SASM precipitation during the two periods. Previous studies suggested that the land–sea thermal contrast plays a crucial role in SASM circulation changes21,50. Following their definitions, we use thicknesses between 200 and 500 hPa to represent the thermal conditions. The thickness anomalies center over the tropical western and central Indian Ocean (Fig. 8a). The stronger warming over the Indian Ocean leads to a weaker land–sea thermal contrast over the Indian Ocean and SA sector. We defined the land–sea thermal contrast index (TCupper) as the difference of 200–500 hPa thickness between northern SA (20.5–40.5°N, 55–100°E; northern box in Fig. 8a) and the TWIO (10.5°S–10.5°N, 40–85°E; southern box in Fig. 8a). TCupper decreases as the CO2 concentration increases and shows noticeable inertia after CO2 peaks (Fig. 8b). The inertia may be due to the strong warming over the TWIO during the RD period led by local enhanced latent heating (Fig. 3c). TCupper during the RD period is markedly weaker than that in the RU period. The weaker land–sea thermal contrast decreases the baroclinicity in the troposphere and decreases the low-tropospheric westerly (Fig. 6a) and the upper-tropospheric easterly51. Finally, the weakened circulation leads to drier conditions over the SASM region during the RD period relative to the RU period.
a The difference in 200–500 hPa thickness (shadings; unit: m) between the RU (21–60) and RD (220–259) periods. b Time series of the land–sea thermal contrast (TCupper; red line; unit: m) and CO2 concentration (blue line; unit: ppm). The 200–500 hPa thickness difference between the land (northern blue box in (a), 20.5°–40.5°N, 55°–100°E) and ocean (southern blue box in (a), −10.5°–10.5°N, 40°–85°E) is defined as the land–sea contrast index. A 3-point (1/4,1/2,1/4) filter with 40 times is performed on the land-sea contrast index. The atmospheric CO2 concentration is multiplied by −1 to facilitate comparison.
The tropical SST response in the CO2 ramp-up and ramp-down experiments
Under global warming scenario, the rainfall change over the Asian monsoon regions mainly consists of two components: the rapid adjustment associated with CO2 radiative forcing and the slow response associated with the SST changes52,53. The rapid adjustment has a timescale of less than one year and the slow response has a timescale of decades to millennia1,8,54. Under the scenario that the CO2 concentration evolves symmetrically (1%CO2 and 1%CO2-CDR experiments), the rapid adjustment largely follows the evolution of the CO2 concentration10, making it difficult to produce the asymmetric response of SASM precipitation. In contrast, the contribution of the slow response lags the evolution of CO2 concentration remarkably and dominates the total climate response during the CO2 ramp-down period10. In particular, the ocean continues to absorb heat after the CO2 peaks11,13. Therefore, to understand the asymmetric response, it is necessary to analyze the SST response in the CO2 ramp-up and ramp-down experiments.
The tropical Pacific and Indian Ocean SSTs all warmed (left panel in Fig. 9) and featured El Niño-like and Indian Ocean dipole (IOD)-like warming patterns (right panel in Fig. 9), respectively, in the RU and RD periods. Furthermore, the magnitude of SST warming over the tropics, as well as El Niño-like and IOD-like warming, is larger during the RD period than during the RU period (Fig. 9c, f). This indicates that the tropical SST displays an asymmetric response in the CO2 ramp-up and ramp-down experiments, consistent with previous studies12,55,56,57.
a, b The SST anomalies during the RU (a) and RD (b) periods compared to PI, respectively. c The difference between the RU and RD periods. The right panel (d–f) is the same as the left panel, but with the tropical mean SST removed. The black dots denote the region in which at least 70% of models agree on the sign of the MME.
For the asymmetric response of El Niño-like warming in the tropical Pacific Ocean, the continued accumulation of heat in the ocean after the CO2 peaks plays an important role11,13. During the RU period, the Walker circulation weakens due to temperature and precipitation constraints, accompanied by the decrease in upwelling intensity, which ultimately results in an El Niño-like warming in the tropical Pacific25,26. In addition, the upper ocean warms faster than the deep ocean (Fig. 10), resulting in a sharp increase in vertical temperature stratification; it transmits heat downward by thermal diffusion or other ocean dynamic processes, allowing the deep ocean to warm and accumulate heat. The faster warming in the upper ocean and the climatological upwelling contribute to a cooling in the central and eastern Pacific. But this effect is overwhelmed by the warming effect led by Walker circulation (its slowdown leads to anomalous westerlies and results in an anomalous warm horizontal advection)34. Thus, an El Niño-like warming occurs in the tropical Pacific. After the CO2 peaks, the upper ocean continues to warm for about a decade and then begins to cool. In contrast, the deep ocean response is much slower, which continues to warm for about 70 years before it begins to cool. During the RD period, the deep ocean continues to warm and warms stronger than the upper (Fig. 10), which generally weakens the vertical temperature gradient and hence reduces the cooling effect led by the climatological upwelling in the central and eastern Pacific58. It contributes to an enhanced El Niño-like warming pattern during the RD period compared to the RU period.
Time evolution of tropical Pacific Ocean mean (−10.5°S–10.5°N, 180°–100°W) potential temperature change (\(\Delta PT\); unit: °C) profile in CO2 ramp-up and ramp-down experiments at all depths, based on repeated application of 3-point (1/4, 1/2, 1/4) filter with 40 times. \(\Delta PT\) is relative to the PI. The black dashed line indicates the CO2 peak year (Year 140). Black dots indicate more than 70% ensemble members agree with the sign of the MME. Note that the vertical depth coordinate is logarithmic.
The asymmetric response of the tropical SST affects the SASM rainfall via atmospheric circulation, showing drought in the RD period. During the RD period, the warmer SST (Fig. 9c) leads to more water vapor in the atmosphere (Fig. 4d) and a larger contribution of the thermodynamic component (Fig. 4a). Following an approximately moist adiabatic lapse rate, tropic-wide warming increases with height in the atmosphere30,59,60, which leads to the enhanced warming center in the middle-to-upper troposphere over the Indian Ocean (Fig. 8a). Meanwhile, the enhanced El Niño-like and IOD-like warming patterns (Fig. 9f) cause the Walker circulation to weaken during the RD period (Fig. 5). Therefore, on the one hand, the decreased Walker circulation directly weakens the ascent in SA; on the other hand, it influences the rainfall in the MC and TWIO through anomalous convergence and divergence motion, thereby indirectly affecting SASM circulation. The contribution of the weakened circulation is stronger than the positive contribution of the thermodynamic component, which leads to the drier condition over the SASM region during the RD period compared to the RU period.
Discussion
We investigated the response of SASM precipitation based on CO2 ramp-up (1%CO2) and ramp-down (1%CO2-CDR) experiments in CMIP6. The results show that if CDR is applied, SASM precipitation is largely reversible although it exhibits asymmetry about symmetric CO2 forcing. Despite the CO2 concentration being the same in the RU and RD periods, precipitation over the SASM region is significantly reduced during the RD period relative to the RU period. The diagnosis reveals that thermodynamic and dynamic components contribute oppositely: the thermodynamic effect favors the increased rainfall, while the dynamic effect favors the decreased rainfall. The asymmetric response of SASM precipitation in the CO2 ramp-up and ramp-down experiments mainly originates from the dynamic effect (i.e., atmospheric circulation) rather than the thermodynamic effect (i.e., moisture change), which is different from that under the global warming scenario.
Subsequently, the possible mechanisms of anomalous atmospheric circulation are revealed. Figure 11 is a schematic diagram illustrating the key processes. Owning to the continued accumulation of heat in the ocean after the CO2 peaks, which feedback to the surface ocean causing the asymmetric response of the SST12,56,58. Relative to the RU period, the tropical Pacific and Indian Ocean show stronger warming during the RD period, featuring an enhanced El Niño-like and IOD-like warming pattern, respectively. Following the moist adiabatic lapse rate, tropical-wide warming increases with height. The enhanced warming center over the Indian Ocean weakens the SA-Indian Ocean thermal and thus SASM circulation. The uneven enhanced warming leads to anomalous sinking, as well as decreased precipitation over the SASM region directly. Additionally, over the Pacific and Indian Ocean sectors, the weakened Walker circulation affects SASM circulation indirectly. It suppresses the rainfall over the MC and increases the rainfall over the TWIO. The suppressed precipitation over the MC triggers an equatorial Rossby wave response to generate an anomalous lower-level anticyclone, which weakens the ascent on the top of the planetary boundary layer, via the effect of Ekman downwelling. The increased rainfall over the TWIO triggers an equatorial Kelvin wave response to hinder water vapor transport to SA. The enhanced IOD-like warming pattern may reinforce the anomalous easterly over the tropical Indian Ocean and further weaken water vapor transport. The combination of the weakened ascent and water vapor transport caused by the enhanced uneven SST warming leads to the asymmetric response of SASM precipitation.
In the present study, our results are mainly based on the MME of seven models participating in the 1%CO2 and 1%CO2-CDR experiments. Compared to studies based on a single model, the MME analysis can partially exclude the model-dependent response and the role of internal variabilities in the climate system, indicating the robustness of the asymmetric response to SASM precipitation. This study systematically reveals the prominent dynamic processes (e.g., equatorial waves) in the formation of the asymmetric response of SASM precipitation. In particular, we highlight the role of atmospheric thermal forcings on SASM circulation induced by uneven tropical SST warming. These important thermal forcings, including rainfall anomalies over the MC and TWIO, have not been mentioned by previous studies concerning the asymmetric response of SASM precipitation. However, we cannot completely eliminate model dependence due to the limited number of models, which may disturb the response of SASM precipitation under the CDR scenario. The internal variabilities of the climate system, such as the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation and Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation, are associated with the SASM61,62,63. Despite this, it is necessary to understand the sources of model uncertainty and the effects of internal variabilities in future studies. In addition to this, the detailed processes leading to an enhanced IOD-like warming pattern during the RD period compared to the RU period remain to be understood. We infer that this may be related to the slow recovery of Walker circulation and the enhanced El Niño-like warming pattern during the RD period.
Although the scenario used in this study is idealized, it is useful for exploring the reversibility and hysteresis of the climate system, especially in providing insight into the CDR scenario. It is noteworthy that SASM precipitation overshoots the unperturbed level before the CO2 concentration returns to PI. This indicates that the symmetric CDR may increase the risk of drought and may affect water management in the SASM region. This gives us a hint that one should consider the side effects of climate mitigation when making climate change policies.
Methods
Observation and reanalysis datasets
The observational and reanalysis data used in the present study include (1) the Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) monthly precipitation dataset64; (2) the National Centers for Environmental Prediction-Department of Energy (NCEP-DOE) reanalysis65; and (3) the Hadley Center Global Sea Surface Temperature (HadISST) dataset66. All the above datasets cover 1979–2014.
CMIP6 model datasets
The present study is mainly based on the monthly outputs of the following experiments (Supplementary Table 1) of CMIP6: (1) historical experiment, in which time-dependent observed anthropogenic and natural forcings are specified to reflect observational estimates valid for the historical period (i.e., 1850–2014)67; (2) pre-industrial control (piControl) experiment (global mean atmospheric CO2 concentration of 284.7 ppm), started from initial conditions obtained from a spin-up with the same, which should ideally represent a near-equilibrium state of the climate system under imposed year 1850 conditions67; (3) 1%CO2 experiment, in which the climate (including CO2 concentration) initiates from the end of the piControl experiment and the CO2 concentration gradually increases at a rate of 1% per year for 140 years until it quadruples (i.e., 1138.8 ppm; all other forcing is kept at that of the year 1850)67, which is named the ramp-up period; and (4) 1%CO2-CDR experiment, in which the climate (including CO2 concentration) initiates from the end of the 1%CO2 experiment and the evolution of CO2 concentration is the mirror of that in the 1%CO2 experiment (all other forcing is kept at that of the year 1850), which is named the ramp-down period15. The evolution of the CO2 concentration in the 1%CO2 and 1%CO2-CDR experiments is displayed in Fig. 1a. The total time of these two experiments is 280 years (140 years for ramp-up and 140 years for ramp-down). Seven models (ACCESS-ESM1-5, CanESM5, CNRM-ESM2-1, GFDL-ESM4, MIROC-ES2L, NorESM1-LM, and UKESM1-0-LL) participated in the present study (Supplementary Table 2). CESM2 is excluded because the differences between ramp-down and ramp-up periods are exaggerated (Supplementary Fig. 3). If it is involved in the calculation, the MME is dominated by the results of CESM2. UKESM1-0-LL does not participate in vertical-velocity-associated calculations due to data unavailability.
To obtain the MME, the outputs are regridded to a common 1° × 1° grid. We consider the results to be robust when more than 70% of the models (5 out of 7) agree on the sign of the MME. For convenience, we defined the 1st year of the 1%CO2 experiments as Year 1. To examine the reversibility of SASM precipitation, we select two periods during which the mean CO2 concentration is identical: CO2 ramp-up (year 21–60; RU) and ramp-down (year 220–259; RD) periods. It is reasonable to choose the periods at the beginning of the CO2 ramp-up and the end of the CO2 ramp-down. However, to increase the magnitude of the response signal, we shift these two periods to the middle by 20 years. A repeated application of the 3-point filter is used to remove interannual variability, and the results do not fundamentally change when the 21-year running mean is applied. The two-sided Student’s t-test is used to evaluate the statistical significance of the difference. The climatology of the last 100 years in the piControl experiment is defined as the baseline (PI). The analysis focuses on the average boreal summer (June–August) because the precipitation over South Asia is mainly concentrated in summer68.
Model evaluation
Before analyzing the response of SASM precipitation to CO2 forcing, we examine the performance of models based on the CMIP6 MME. SASM precipitation and its associated variables are compared and examined (Supplementary Fig. 4). The CMIP6 MME can grasp the spatial distribution of variables, but with slight differences in magnitude. The spatial correlation coefficients of the individual models with reanalysis all exceed 0.71, and those of the CMIP6 MME all exceed 0.84 (Supplementary Fig. 5). Overall, the CMIP6 MME is capable of investigating the SASM response to CO2 forcing.
The Linear Baroclinic Model
To investigate the effects of heat forcing on the atmosphere, the Linear Baroclinic Model (LBM) is employed. This model has 20 vertical levels based on the sigma coordinate system and a horizontal resolution of T42. The horizontal diffusion has an e-folding decay time of 6 h for the largest wavenumber. The Rayleigh friction and Newtonian damping have a time-scale of 1 day−1 for sigma levels below 0.9, 5 day−1 for sigma levels of 0.89, 15 day−1 for sigma levels of 0.83, 30 day−1 for sigma levels between 0.83 and 0.03, and 1 day−1 for sigma levels above 0.03. Further information on the model is given in Watanabe and Kimoto (2000)69. In the present study, the model is integrated for 36 days, and the average from 25 to 35 days is displayed.
Data availability
The CMIP6 outputs are available online at https://esgf-node.llnl.gov/projects/cmip6/. The observational and reanalysis data that examine the performance of models are openly available at https://psl.noaa.gov/data/gridded/data.gpcp.html (GPCP), https://psl.noaa.gov/data/gridded/data.ncep.reanalysis2.pressure.html (NCEP-DOE) and https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/hadobs/hadisst/data/download.html (HadISST). The LBM is available online at https://ccsr.aori.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~lbm/sub/lbm_4.html.
References
IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (eds Masson-Delmotte, V. et al.) (Cambridge University Press, 2021).
Field, C. B. & Mach, K. J. Rightsizing carbon dioxide removal. Science 356, 706–707 (2017).
Fuss, S. et al. Betting on negative emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 4, 850–853 (2014).
Realmonte, G. et al. An inter-model assessment of the role of direct air capture in deep mitigation pathways. Nat. Commun. 10, 3277 (2019).
Rogelj, J. et al. Scenarios towards limiting global mean temperature increase below 1.5 °C. Nat. Clim. Change 8, 325–332 (2018).
Zickfeld, K., Azevedo, D., Mathesius, S. & Matthews, H. D. Asymmetry in the climate-carbon cycle response to positive and negative CO2 emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 11, 613–617 (2021).
von Schuckmann, K. et al. An imperative to monitor Earth’s energy imbalance. Nat. Clim. Change 6, 138–144 (2016).
Zappa, G., Ceppi, P. & Shepherd, T. G. Time-evolving sea-surface warming patterns modulate the climate change response of subtropical precipitation over land. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 4539–4545 (2020).
Monerie, P.-A., Pohl, B. & Gaetani, M. The fast response of Sahel precipitation to climate change allows effective mitigation action. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 4, 1–8 (2021).
Zhou, S., Huang, P., Xie, S.-P., Huang, G. & Wang, L. Varying contributions of fast and slow responses cause asymmetric tropical rainfall change between CO2 ramp-up and ramp-down. Sci. Bull. 67, 1702–1711 (2022).
Yeh, S. W., Song, S. Y., Allan, R. P., An, S. I. & Shin, J. Contrasting response of hydrological cycle over land and ocean to a changing CO2 pathway. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 4, 1–8 (2021).
Chadwick, R., Wu, P., Good, P. & Andrews, T. Asymmetries in tropical rainfall and circulation patterns in idealised CO2 removal experiments. Clim. Dyn. 40, 295–316 (2012).
Wu, P., Wood, R., Ridley, J. & Lowe, J. Temporary acceleration of the hydrological cycle in response to a CO2 rampdown. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37, L12705 (2010).
Huang, G. et al. Critical climate issues toward carbon neutrality targets. Fundam. Res. 2, 396–400 (2022).
Keller, D. P. et al. The Carbon Dioxide Removal Model Intercomparison Project (CDRMIP): rationale and experimental protocol for CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 11, 1133–1160 (2018).
Singh, D., Tsiang, M., Rajaratnam, B. & Diffenbaugh, N. S. Observed changes in extreme wet and dry spells during the South Asian summer monsoon season. Nat. Clim. Change 4, 456–461 (2014).
Turner, A. G. & Annamalai, H. Climate change and the South Asian summer monsoon. Nat. Clim. Change 2, 587–595 (2012).
Li, G., Xie, S. P., He, C. & Chen, Z. S. Western Pacific emergent constraint lowers projected increase in Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Nat. Clim. Change 7, 708–712 (2017).
Rajesh, P. V. & Goswami, B. N. A new emergent constraint corrected projections of Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 49, e2021GL096671 (2022).
Douville, H. & Royer, J.-F. Impact of CO2 doubling on the Asian summer monsoon robust cersus model-dependent responses. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 78, 421–439 (2000).
Li, Z. B., Sun, Y., Li, T., Chen, W. & Ding, Y. H. Projections of South Asian summer monsoon under Global Warming from 1.5 degrees to 5 degrees C. J. Clim. 34, 7913–7926 (2021).
Maharana, P., Dimri, A. P. & Choudhary, A. Future changes in Indian summer monsoon characteristics under 1.5 and 2 °C specific warming levels. Clim. Dyn. 54, 507–523 (2019).
Ueda, H., Iwai, A., Kuwako, K. & Hori, M. E. Impact of anthropogenic forcing on the Asian summer monsoon as simulated by eight GCMs. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L06703 (2006).
Endo, H. & Kitoh, A. Thermodynamic and dynamic effects on regional monsoon rainfall changes in a warmer climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 1704–1711 (2014).
Held, I. M. & Soden, B. J. Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming. J. Clim. 19, 5686–5699 (2006).
Vecchi, G. A. & Soden, B. J. Global warming and the weakening of the tropical circulation. J. Clim. 20, 4316–4340 (2007).
Ma, J. & Yu, J.-Y. Paradox in South Asian summer monsoon circulation change: lower tropospheric strengthening and upper tropospheric weakening. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 2934–2940 (2014).
Wang, B., Yim, S.-Y., Lee, J.-Y., Liu, J. & Ha, K.-J. Future change of Asian-Australian monsoon under RCP 4.5 anthropogenic warming scenario. Clim. Dyn. 42, 83–100 (2013).
Sun, Y., Ding, Y. H. & Dai, A. G. Changing links between South Asian summer monsoon circulation and tropospheric land-sea thermal contrasts under a warming scenario. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37, L02704 (2010).
Ma, J., Xie, S. P. & Kosaka, Y. Mechanisms for tropical tropospheric circulation change in response to global warming. J. Clim. 25, 2979–2994 (2012).
Wu, P., Ridley, J., Pardaens, A., Levine, R. & Lowe, J. The reversibility of CO2 induced climate change. Clim. Dyn. 45, 745–754 (2014).
Abe, M., Shiogama, H., Yokohata, T., Emori, S. & Nozawa, T. Asymmetric impact of the physiological effect of carbon dioxide on hydrological responses to instantaneous negative and positive CO2 forcing. Clim. Dyn. 45, 2181–2192 (2015).
Cao, L., Bala, G. & Caldeira, K. Why is there a short-term increase in global precipitation in response to diminished CO2 forcing? Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, L06703 (2011).
Song, S. Y. et al. Asymmetrical response of summer rainfall in East Asia to CO2 forcing. Sci. Bull. 67, 213–222 (2022).
Sun, M.-A. et al. Reversibility of the hydrological response in East Asia from CO2-derived climate change based on CMIP6 simulation. Atmosphere 12, 72 (2021).
Boucher, O. et al. Reversibility in an Earth System model in response to CO2 concentration changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 7, 024013 (2012).
Kug, J. S. et al. Hysteresis of the intertropical convergence zone to CO2 forcing. Nat. Clim. Change 12, 47–53 (2022).
Oh, H. et al. Contrasting hysteresis behaviors of Northern hemisphere land monsoon precipitation to CO2 pathways. Earth’s Future 10, e2021EF002623 (2022).
Bhowmick, M., Mishra, S. K., Kravitz, B., Sahany, S. & Salunke, P. Response of the Indian summer monsoon to global warming, solar geoengineering and its termination. Sci. Rep. 11, 9791 (2021).
Huang, P., Xie, S. P., Hu, K. M., Huang, G. & Huang, R. H. Patterns of the seasonal response of tropical rainfall to global warming. Nat. Geosci. 6, 357–361 (2013).
Seager, R., Naik, N. & Vecchi, G. A. Thermodynamic and dynamic mechanisms for large-scale changes in the hydrological cycle in response to global warming. J. Clim. 23, 4651–4668 (2010).
Wang, B., Wu, R. G. & Li, T. Atmosphere-warm ocean interaction and its impacts on Asian-Australian monsoon variation. J. Clim. 16, 1195–1211 (2003).
Hu, K. M., Huang, G., Xie, S. P. & Long, S. M. Effect of the mean flow on the anomalous anticyclone over the Indo-Northwest Pacific in post-El Nino summers. Clim. Dyn. 53, 5725–5741 (2019).
Hu, P. et al. Close linkage of the South China sea summer monsoon onset and extreme rainfall in May over Southeast Asia: role of the synoptic-scale systems. J. Clim. 35, 4347–4362 (2022).
Wang, B. & Xie, X. Low-frequency equatorial waves in vertically sheared zonal flow. Part I: Stable waves. J. Atmos. Sci. 53, 449–467 (1996).
Xie, X. & Wang, B. Low-frequency equatorial waves in vertically sheared zonal flow. Part II: Unstable waves. J. Atmos. Sci. 53, 3589–3605 (1996).
Matsuno, T. Quasigeostrophic motions in the equatorial area. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 44, 25–43 (1966).
Gill, A. E. Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 106, 447–462 (1980).
Xie, S. P. et al. Indian Ocean capacitor effect on Indo-Western Pacific climate during the summer following El Nino. J. Clim. 22, 730–747 (2009).
Dai, A. G. et al. The relative roles of upper and lower tropospheric thermal contrasts and tropical influences in driving Asian summer monsoons. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 118, 7024–7045 (2013).
Luo, X. Q., Xu, J. J. & Li, K. Discrepancies oft upper troposphere summer thermal contrast between Tibetan Plateau and tropical Indian Ocean in multiple data. Front. Environ. Sci. 9, 655521 (2021).
Endo, H., Kitoh, A. & Ueda, H. A unique feature of the Asian summer monsoon response to global warming: the role of different land-sea thermal contrast change between the lower and upper troposphere. Sci. Online Lett. Atmos. 14, 57–63 (2018).
Li, X. Q. & Ting, M. F. Understanding the Asian summer monsoon response to greenhouse warming: the relative roles of direct radiative forcing and sea surface temperature change. Clim. Dyn. 49, 2863–2880 (2017).
Bony, S. et al. Robust direct effect of carbon dioxide on tropical circulation and regional precipitation. Nat. Geosci. 6, 447–451 (2013).
An, S.-I. et al. Intensity changes of Indian Ocean dipole mode in a carbon dioxide removal scenario. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 5, 1–8 (2022).
Long, S.-M., Xie, S.-P., Zheng, X.-T. & Liu, Q. Fast and slow responses to global warming: sea surface temperature and precipitation patterns. J. Clim. 27, 285–299 (2014).
Ohba, M., Tsutsui, J. & Nohara, D. Statistical parameterization expressing ENSO variability and reversibility in response to CO2 concentration changes. J. Clim. 27, 398–410 (2014).
Long, S. M. et al. Effects of ocean slow response under low warming targets. J. Clim. 33, 477–496 (2020).
Chen, X. L. & Zhou, T. J. Distinct effects of global mean warming and regional sea surface warming pattern on projected uncertainty in the South Asian summer monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 9433–9439 (2015).
Knutson, T. R. & Manabe, S. Mean response over the tropical Pacific to increased CO2 in a coupled ocean-atmosphere model. J. Clim. 8, 2181–2199 (1995).
Chinta, V., Chen, Z. S., Du, Y. & Chowdary, J. S. Influence of the interdecadal Pacific Oscillation on South Asian and East Asian summer monsoon rainfall in CMIP6 models. Clim. Dyn. 58, 1791–1809 (2022).
Huang, X. et al. South Asian summer monsoon projections constrained by the interdecadal Pacific oscillation. Sci. Adv. 6, eaay6546 (2020).
Sandeep, N. et al. On the weakening association between South Asian Monsoon and Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation. Clim. Dyn. 59, 2531–2547 (2022).
Adler, R. F. et al. The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979-present). J. Hydrometeorol. 4, 1147–1167 (2003).
Kanamitsu, M. et al. NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 83, 1631–1643 (2002).
Rayner, N. A. et al. Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 108, 4407 (2003).
Eyring, V. et al. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 9, 1937–1958 (2016).
Bollasina, M. A. HYDROLOGY Probing the monsoon pulse. Nat. Clim. Change 4, 422–423 (2014).
Watanabe, M. & Kimoto, M. Atmosphere-ocean thermal coupling in the North Atlantic: a positive feedback. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 126, 3343–3369 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the World Climate Research Program, which, through its Working Group on Coupled Modeling, coordinated and promoted CMIP6. We thank the climate modeling groups for producing and making available their model output, the Earth System Grid Federation (ESGF) for archiving the data and providing access, and the multiple funding agencies who support CMIP6 and ESGF. Suqin Zhang thanks Hongyu Hou of the Institute of Atmospheric Physics for helping to solve the LBM-related problems. The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC; 42141019, 42175055, 41831175), the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research program (2019QZKK0102), and project of Key Laboratory of Meteorological Disaster, Ministry of Education & Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology (KLME202111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.Z.: Investigation, data Curation, formal analysis, drafted the manuscript, writing review, and editing. X.Q.: Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing review, and editing. G.H.: Conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, project administration. P.H.: Methodology, formal analysis, writing review, and editing. All authors contributed to the discussion.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Qu, X., Huang, G. et al. Asymmetric response of South Asian summer monsoon rainfall in a carbon dioxide removal scenario. npj Clim Atmos Sci 6, 10 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-023-00338-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-023-00338-x
This article is cited by
-
Asymmetric response of the Western North Pacific tropical cyclone genesis to symmetric CO2 pathway
npj Climate and Atmospheric Science (2025)
-
Role of the Pacific-Japan Pattern in Shaping Sri Lanka Rainfall
Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences (2025)
-
Asian–Pacific Summer Monsoon Variability and Atmospheric Teleconnection Patterns: Review and Outlook
Journal of Meteorological Research (2025)
-
Summer precipitation responses to CO2 removal scenario over the transitional climate zone in East Asia and the driving mechanisms
Climate Dynamics (2025)
-
Exploring causes of distinct regional and subseasonal Indian summer monsoon precipitation responses to CO2 removal
npj Climate and Atmospheric Science (2024)