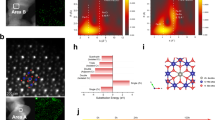
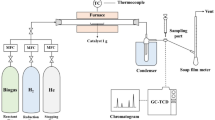
Abstract
Catalytic syngas conversion has the potential to improve the sustainability of chemical products. However, balancing high catalytic activity with selectivity is challenging because the complex interactions among intermediates across various active sites can trigger competing reactions. To address this challenge, we introduce a catalytic shunt strategy that redirects intermediates in a multifunctional catalytic system to guide interdependent reaction pathways. The key to this catalytic shunt strategy is modulating the adsorption of the intermediates across different activity domains. By tuning Mo–O coordination numbers of single atoms in a bifunctional catalyst, we achieve over 80% selectivity for aromatics and a carbon monoxide conversion surpassing 70%, with aromatics yields of over 40%. By absorbing the intermediates on the first activity domain, the shunt pathway prevents their participation in subsequent reactions, thereby boosting methane production with selectivity above 93% and carbon monoxide conversion exceeding 50%. This catalytic shunt strategy also showcases versatility across other bifunctional systems for producing gasoline and light olefins. Overall, this study provides a viable approach for tackling the activity–selectivity trade-off in catalytic syngas conversion, removing a major barrier preventing its practical implementation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available in the manuscript or the Supplementary Information. Additional data are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request. The structure part of ZnCrOx can be found at https://legacy.materialsproject.org/.
References
Guan, Q. et al. Bimetallic monolayer catalyst breaks the activity–selectivity trade-off on metal particle size for efficient chemoselective hydrogenations. Nat. Catal. 4, 840–849 (2021).
Gu, J. et al. Synergizing metal–support interactions and spatial confinement boosts dynamics of atomic nickel for hydrogenations. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1141–1149 (2021).
Xie, J. et al. Atomically-thin molybdenum nitride nanosheets with exposed active surface sites for efficient hydrogen evolution. Chem. Sci. 5, 4615–4620 (2014).
Ozden, A. et al. Carbon-efficient carbon dioxide electrolysers. Nat. Sustain. 5, 563–573 (2022).
Chen, Y. et al. Cooperative catalysis coupling photo-/photothermal effect to drive Sabatier reaction with unprecedented conversion and selectivity. Joule 5, 3235–3251 (2021).
Chang, X. et al. Designing single-site alloy catalysts using a degree-of-isolation descriptor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 611–616 (2023).
Pérez-Ramírez, J. & López, N. Strategies to break linear scaling relationships. Nat. Catal. 2, 971–976 (2019).
Craig, M. J. et al. Universal scaling relations for the rational design of molecular water oxidation catalysts with near-zero overpotential. Nat. Commun. 10, 4993 (2019).
Sun, G. et al. Breaking the scaling relationship via thermally stable Pt/Cu single atom alloys for catalytic dehydrogenation. Nat. Commun. 9, 4454 (2018).
Zhao, Z.-J. et al. Theory-guided design of catalytic materials using scaling relationships and reactivity descriptors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 4, 792–804 (2019).
Jiao, F. et al. Disentangling the activity-selectivity trade-off in catalytic conversion of syngas to light olefins. Science 380, 727–730 (2023).
Zhai, P. et al. Development of direct conversion of syngas to unsaturated hydrocarbons based on Fischer–Tropsch route. Chem 7, 3027–3051 (2021).
Lee, J. W. et al. Systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms for natural and non-natural chemicals. Nat. Chem. Biol. 8, 536–546 (2012).
Schuster, S., Fell, D. A. & Dandekar, T. A general definition of metabolic pathways useful for systematic organization and analysis of complex metabolic networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 326–332 (2000).
Zhao, Q. et al. A severe leakage of intermediates to shunt products in acarbose biosynthesis. Nat. Commun. 11, 1468 (2020).
Fait, A., Fromm, H., Walter, D., Galili, G. & Fernie, A. R. Highway or byway: the metabolic role of the GABA shunt in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 13, 14–19 (2008).
Dolan, S. K. & Welch, M. The glyoxylate shunt, 60 years on. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 72, 309–330 (2018).
Ahn, S., Jung, J., Jang, I.-A., Madsen, E. L. & Park, W. Role of glyoxylate shunt in oxidative stress response. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 11928–11938 (2016).
Walsh, K. & Koshland, D. E. Determination of flux through the branch point of two metabolic cycles. The tricarboxylic acid cycle and the glyoxylate shunt. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 9646–9654 (1984).
Cronan Jr., J. E. & Laporte, D. Tricarboxylic acid cycle and glyoxylate bypass. EcoSal Plus https://doi.org/10.1128/ecosalplus.3.5.2 (2005).
Ji, Y. et al. Oxygenate-based routes regulate syngas conversion over oxide–zeolite bifunctional catalysts. Nat. Catal. 5, 594–604 (2022).
Yang, J., Pan, X., Jiao, F., Li, J. & Bao, X. Direct conversion of syngas to aromatics. Chem. Commun. 53, 11146–11149 (2017).
Wang, A., Li, J. & Zhang, T. Heterogeneous single-atom catalysis. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2, 65–81 (2018).
Li, M. et al. Single-atom tailoring of platinum nanocatalysts for high-performance multifunctional electrocatalysis. Nat. Catal. 2, 495–503 (2019).
Mao, J. et al. Direct conversion of methane with O2 at room temperature over edge-rich MoS2. Nat. Catal. 6, 1052–1061 (2023).
Hu, J. et al. Sulfur vacancy-rich MoS2 as a catalyst for the hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol. Nat. Catal. 4, 242–250 (2021).
Hu, J. et al. Edge-rich molybdenum disulfide tailors carbon-chain growth for selective hydrogenation of carbon monoxide to higher alcohols. Nat. Commun. 14, 6808 (2023).
Huang, R. et al. Acetylene hydrogenation to ethylene by water at low temperature on a Au/α-MoC catalyst. Nat. Catal. 6, 1005–1015 (2023).
Michailovski, A. et al. Studying the solvothermal formation of MoO3 fibers by complementary in situ EXAFS/EDXRD techniques. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44, 5643–5647 (2005).
Huang, Z. et al. Ceria‐zirconia/zeolite bifunctional catalyst for highly selective conversion of syngas into aromatics. ChemCatChem 10, 4519–4524 (2018).
Liu, C. et al. Insights into the key factor of zeolite morphology on the selective conversion of syngas to light aromatics over a Cr2O3/ZSM-5 catalyst. ACS Catal. 10, 15227–15237 (2020).
Xiong, H. et al. In situ imaging of the sorption-induced subcell topological flexibility of a rigid zeolite framework. Science 376, 491–496 (2022).
Yang, X., Su, X., Chen, D., Zhang, T. & Huang, Y. Direct conversion of syngas to aromatics: a review of recent studies. Chin. J. Catal. 41, 561–573 (2020).
Kasipandi, S. & Bae, J. W. Recent advances in direct synthesis of value‐added aromatic chemicals from syngas by cascade reactions over bifunctional catalysts. Adv. Mater. 31, 1803390 (2019).
Zhang, L. et al. Direct conversion of CO2 to a jet fuel over CoFe alloy catalysts. Innovation 2, 100170 (2021).
Yao, B. et al. Transforming carbon dioxide into jet fuel using an organic combustion-synthesized Fe-Mn-K catalyst. Nat. Commun. 11, 6395 (2020).
Arslan, M. T. et al. Highly selective conversion of CO2 or CO into precursors for kerosene-based aviation fuel via an aldol–aromatic mechanism. ACS Catal. 12, 2023–2033 (2022).
Tan, M. et al. Probing hydrophobization of a Cu/ZnO catalyst for suppression of water–gas shift reaction in syngas conversion. ACS Catal. 11, 4633–4643 (2021).
Zhu, P. et al. Direct conversion of methane to aromatics and hydrogen via a heterogeneous trimetallic synergistic catalyst. Nat. Commun. 15, 3280 (2024).
Wang, C. et al. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis to olefins boosted by MFI zeolite nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 714–720 (2022).
Bai, B. et al. Tuning the crystal phase to form MnGaOx‐spinel for highly efficient syngas to light olefins. Angew. Chem. 135, e202217701 (2023).
Wang, M. et al. Spinel nanostructures for the hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol and hydrocarbon chemicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 14528–14538 (2024).
D’Andria, M., Krumeich, F., Yao, Z., Wang, F. R. & Güntner, A. T. Structure–function relationship of highly reactive CuOx clusters on Co3O4 for selective formaldehyde sensing at low temperatures. Adv. Sci. 11, 2308224 (2024).
Chen, X.-M. et al. In situ DRIFTS study on the partial oxidation of ethylene over Co-ZSM-5 catalyst. Catal. Commun. 10, 428–432 (2009).
Ma, R. et al. Insights into the nature of selective nickel sites on Ni/Al2O3 catalysts for propane dehydrogenation. ACS Catal. 12, 12607–12616 (2022).
Yang, L. et al. Stabilizing the framework of SAPO-34 zeolite toward long-term methanol-to-olefins conversion. Nat. Commun. 12, 4661 (2021).
Li, N. et al. High‐quality gasoline directly from syngas by dual metal oxide–zeolite (OX‐ZEO) catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 7400–7404 (2019).
Kim, H.-S. et al. Oxygen vacancies enhance pseudocapacitive charge storage properties of MoO3–x. Nat. Mater. 16, 454–460 (2017).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169 (1996).
Kresse, G. & Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 59, 1758 (1999).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996).
Ma, S., Huang, S.-D. & Liu, Z.-P. Dynamic coordination of cations and catalytic selectivity on zinc–chromium oxide alloys during syngas conversion. Nat. Catal. 2, 671–677 (2019).
NIST Chemistry WebBook. NIST https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ (2025).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFA1203301 to F.W.), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22278238 to C.Z., 22238004 to F.W., 22275110 and 22322203 to X.C. and 52402053 to H.M.), the Key Research and Development Program of Inner Mongolia and Ordos (20211140095 to C.Z.) and the China National Petroleum Corporation Innovation Funds (2020990028 to C.Z.). This research was sponsored by the Tsinghua–Toyota Joint Research Fund (X.C. and F.W.). We acknowledge L. Song and S. Chen from the National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, Chinese Academy of Sciences Center for Excellence in Nanoscience at the University of Science and Technology of China for their discussions on the synchrotron X-ray absorption spectra data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.T., C.Z., X.C. and F.W. designed the study. G.T., X.F. and D.L. synthesized the catalysts. G.T. and X.F. performed the catalytic tests. G.T., Z.L., D.L., X.F., K.S., N.W., X. Liang, H.X., H.M., S.Q., X.C., Z.L., H.-j.P., B.Y. and T.Y. conducted the characterizations. G.T., X. Liu and H.-j.P. contributed to the DFT calculations. G.T. wrote the paper. All the authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Sustainability thanks Jong Wook Bae, José Antonio Odriozola and Feng-Shou Xiao for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–56, Tables 1–8 and References 1–42.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, G., Li, Z., Liao, D. et al. Efficient syngas conversion via catalytic shunt. Nat Sustain 8, 508–519 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-025-01551-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-025-01551-7
This article is cited by
-
“Next-Generation ZIF-90/Nb2C@GQD nanohybrids for integrated energy storage and hydrogen evolution”
Ionics (2025)
-
Clove oil and surfactant-based green synthesis and characterization of nano calcium hydrates for application in stone conservation
Applied Physics A (2025)
-
Controlled Synthesis Approaches for Tuning the Structural, Optical, and Morphological Features of Chemo-catalytically Active Covellite (CuS) Nanostructures
Brazilian Journal of Physics (2025)