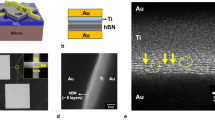
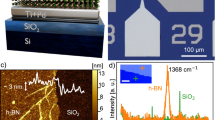
Abstract
Radiofrequency switches that drive or block high-frequency electromagnetic signals—typically, a few to tens of gigahertz—are essential components in modern communication devices. However, demand for higher data transmission rates requires radiofrequency switches capable of operating at frequencies beyond 100 GHz, which is challenging for current technologies. Here we report ambipolar memristive radiofrequency switches that are based on multilayer hexagonal boron nitride and can operate at frequencies up to 260 GHz. The ambipolar behaviour, which could help reduce peripheral hardware requirements, is due to a Joule-effect-assisted reset. We show switching in 21 devices with low-resistance states averaging 294 Ω and endurances of 2,000 cycles. With further biasing optimization, we reduce the resistance to 9.3 ± 3.7 Ω over more than 475 cycles, and achieve an insertion loss of 0.9 dB at 120 GHz. We also build a series–shunt device configuration with an isolation of 35 dB at 120 GHz.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The minimum set of data needed to evaluate the conclusions in this work is available via Zenodo at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11181165 (ref. 49). Additional related data supporting the findings in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ielmini, D. & Waser, R. (eds) Resistive Switching: From Fundamentals of Nanoionic Redox Processes to Memristive Device Applications (Wiley-VCH, 2016).
Pearson, A. D., Northover, W., Dewald, J. F. & Peck, W. Jr Chemical, physical, and electrical properties of some unusual inorganic glasses. Adv. Glass Technol. 2, 357–365 (1962).
Lanza, M. et al. Memristive technologies for data storage, computation, encryption, and radio-frequency communication. Science 376, eabj9979 (2022).
Pazos, S. et al. Hardware implementation of a true random number generator integrating a hexagonal boron nitride memristor with a commercial microcontroller. Nanoscale 15, 2171–2180 (2023).
Zhu, K. et al. Inkjet-printed h-BN memristors for hardware security. Nanoscale 15, 9985–9992 (2023).
Carboni, R. & Ielmini, D. Stochastic memory devices for security and computing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 5, 1900198 (2019).
Aguirre, F. et al. Hardware implementation of memristor-based artificial neural networks. Nat. Commun. 15, 1974 (2024). .
Kim, M. et al. Monolayer molybdenum disulfide switches for 6G communication systems. Nat. Electron. 5, 367–373 (2022).
Wainstein, N., Adam, G., Yalon, E. & Kvatinsky, S. Radiofrequency switches based on emerging resistive memory technologies – a survey. Proc. IEEE 109, 77–95 (2021).
Kim, D. et al. Emerging memory electronics for non-volatile radiofrequency switching technologies. Nat. Rev. Electr. Eng. 1, 10–23 (2024).
Sobolewski, J. & Yashchyshyn, Y. State of the art sub-terahertz switching solutions. IEEE Access 10, 12983–12999 (2022).
Ma, L.-Y., Soin, N., Mohd Daut, M. H. & Wan Muhamad Hatta, S. F. Comprehensive study on RF-MEMS switches used for 5G scenario. IEEE Access 7, 107506–107522 (2019).
Yu, B. et al. Ultra-wideband low-loss switch design in high-resistivity trap-rich SOI with enhanced channel mobility. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 65, 3937–3949 (2017).
Li, C. et al. 5G mm-Wave front-end-module design with advanced SOI process. In 2017 IEEE 12th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON) 1017–1020 (IEEE, 2017).
Slovin, G., El-Hinnawy, N., Moen, K. & Howard, D. Phase-change material RF switches and monolithic integration in 180 nm RF-SOI CMOS processes. Tech. Dig. - Int. Electron Devices Meet. IEDM 2021, 4.4.1–4.4.4 (2021).
Kim, M. et al. Zero-static power radio-frequency switches based on MoS2 atomristors. Nat. Commun. 9, 2524 (2018).
Singh, T. & Mansour, R. R. Ultra-compact phase-change GeTe-based scalable mmWave latching crossbar switch matrices. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 70, 938–949 (2022).
Amin, F. et al. Wideband SPDT and SP4T RF switches using phase-change material in a SiGe BiCMOS process. IEEE MTT- Int. Microw. Symp. Dig. 2021, 431–434 (2021).
El-Hinnawy, N. et al. A four-terminal, inline, chalcogenide phase-change RF switch using an independent resistive heater for thermal actuation. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 34, 1313–1315 (2013).
Wang, M. & Rais-Zadeh, M. Directly heated four-terminal phase change switches. In 2014 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS) 1–4 (IEEE, 2014).
Young, R. M. et al. Improvements in GeTe-based phase change RF switches. In 2018 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS) 832–835 (IEEE, 2018).
Singh, T. & Mansour, R. R. Experimental investigation of performance, reliability, and cycle endurance of nonvolatile DC–67 GHz phase-change RF switches. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 69, 4697–4710 (2021).
Moon, J. S. et al. Phase-change RF switches with robust switching cycle endurance. IEEE Radio Wirel. Symp. RWS 2018, 231–233 (2018).
Bettoumi, I., Le Gall, N. & Blondy, P. Phase change material (PCM) RF switches with integrated decoupling bias circuit. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 32, 52–55 (2022).
Leon, A. et al. RF power-handling performance for direct actuation of germanium telluride switches. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 68, 60–73 (2020).
El-Hinnawy, N., Slovin, G., Rose, J. & Howard, D. A 25 THz FCO (6.3 fs R_ON*C_OFF) phase-change material RF switch fabricated in a high volume manufacturing environment with demonstrated cycling > 1 billion times. In 2020 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS) 45–48 (IEEE, 2020).
El-Hinnawy, N. et al. Substrate agnostic monolithic integration of the inline phase-change switch technology. In 2016 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS) 1–4 (IEEE, 2016).
Nessel, J. A. et al. A novel nanoionics-based switch for microwave applications. In 2008 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest 1051–1054 (IEEE, 2008).
Vena, A. et al. A fully passive RF switch based on nanometric conductive bridge. In 2012 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest 1–3 (IEEE, 2012).
Pi, S., Ghadiri-Sadrabadi, M., Bardin, J. C. & Xia, Q. Nanoscale memristive radiofrequency switches. Nat. Commun. 6, 7519 (2015).
Kim, G. H. et al. Improved endurance of resistive switching TiO2 thin film by hourglass shaped Magnéli filaments. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 262901 (2011).
Xu, Z. R. et al. Conductive bridging-based memristive RF switches on a silicon substrate. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 70, 24–34 (2022).
Singh, T., Hummel, G., Vaseem, M. & Shamim, A. Recent advancements in reconfigurable mmWave devices based on phase-change and metal insulator transition materials. IEEE J. Microw. 3, 827–851 (2023).
Kim, M. et al. Analogue switches made from boron nitride monolayers for application in 5G and terahertz communication systems. Nat. Electron. 2020 38 3, 479–485 (2020).
Yang, S. J. et al. Reconfigurable low-voltage hexagonal boron nitride nonvolatile switches for millimeter-wave wireless communications. Nano Lett. 23, 1152–1158 (2023).
Ge, R. et al. Atomristor: nonvolatile resistance switching in atomic sheets of transition metal dichalcogenides. Nano Lett. 18, 434–441 (2018).
Zhu, K. et al. Hybrid 2D–CMOS microchips for memristive applications. Nature 618, 57–62 (2023).
Liu, S. et al. Eliminating negative-SET behavior by suppressing nanofilament overgrowth in cation-based memory. Adv. Mater. 28, 10623–10629 (2016).
Shen, Y. et al. Variability and yield in h-BN-based memristive circuits: the role of each type of defect. Adv. Mater. 33, 2103656 (2021).
Palumbo, F. et al. A review on dielectric breakdown in thin dielectrics: silicon dioxide, high‐k, and layered dielectrics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1900657 (2019).
Pazos, S. et al. High-temporal-resolution characterization reveals outstanding random telegraph noise and the origin of dielectric breakdown in h-BN memristors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34, 2213816 (2023).
Yuan, Y. et al. On the quality of commercial chemical vapour deposited hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Commun. 15, 4518 (2024).
PE42525 – UltraCMOS SPDT RF Switch. pSemi https://www.psemi.com/products/rf-switches/broadband-rf-switches/pe42525 (2023).
Razavi, B. RF Microelectronics 2nd edn (Prentice Hall, 2011).
Puyal, V., Leti, C., Cnrs, L. & Titz, D. in Handbook of Mems for Wireless and Mobile Applications (ed. Uttamchandani, D.) 136–175 (Woodhead Publishing, 2013).
Chakraborty, A. & Gupta, B. Paradigm phase shift: RF MEMS phase shifters: an overview. IEEE Microw. Mag. 18, 22–41 (2017).
Moon, J. S. et al. 5 THz figure-of-merit reliable phase-change RF switches for millimeter-wave applications. In 2018 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium – IMS 836–838 (IEEE, 2018).
Singh, T. & Mansour, R. R. Miniaturized DC-60 GHz RF PCM GeTe-based monolithically integrated redundancy switch matrix using T-Type switching unit cells. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 67, 5181–5190 (2019).
Pazos, S et al. Memristive circuits based on multilayer hexagonal boron nitride for millimetre-wave radiofrequency applications - Source data. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11181165 (2024).
Acknowledgements
M.L. acknowledges support from the generous Baseline funding programme and the Opportunity Fund Project 2023 under PID URF/1/5578-01-01 of King Abdullah University of Science and Technology. D.A. acknowledges the Cockrell Family Regents Chair Endowment. D.P. acknowledges support from the Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) under grant no. 20/RP/8334. J.V. and P.d.P. acknowledge the support by the Spanish Secretaría de Estado de Investigación, Desarrollo e Innovación under grant no. PID2021-127203OB-I00. M.L. acknowledges the platform Web Of Talents (https://weboftalents.com) for support on the recruitment of talented students and postdocs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.L., P.d.P. and S.P. designed the project. Y.S., O.A., Y.P., W.Z. and Y.Y. fabricated the samples and performed focused-ion-beam and cross-section TEM. S.P. designed and programmed the scripts for instrumentation control and data post-processing and measured the d.c. electrical characteristics of the devices. H.Z. and S.P. measured the high-frequency characteristics assisted by J.V., L.A. and E.G. A.F and D.P. aided with the simulations of the proof-of-concept application. A.S., D.P., D.A. and M.L. provided access to the required facilities. S.P. and M.L. wrote the article. All the authors discussed the results and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Electronics thanks Joanna Symonowicz, Lin-Sheng Wu and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–22 and Notes 1–7 with details of the design, fabrication, measurement and modelling protocols.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pazos, S., Shen, Y., Zhang, H. et al. Memristive circuits based on multilayer hexagonal boron nitride for millimetre-wave radiofrequency applications. Nat Electron 7, 557–566 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01192-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01192-2
This article is cited by
-
Synthesis of hexagonal boron arsenide nanosheets for low-power consumption flexible memristors
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Boron nitride for applications in microelectronics
Nature Reviews Electrical Engineering (2025)