Abstract
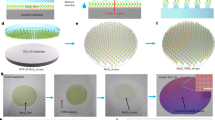
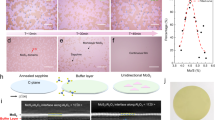
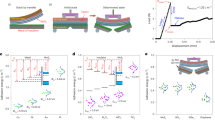
Two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors have the potential to replace silicon in next-generation electronic devices. However, despite advances in proof-of-concept device demonstrations and wafer-scale crystal synthesis, the lack of a compatible residue-free patterning technology has hindered industrialization. Here we describe a metal-stamp imprinting method for patterning 2D films into high-quality wafer-scale arrays without introducing chemical or polymer residues. A metal stamp with a three-dimensional morphology is used to form a local contact at the stamp–2D interface. The process selectively exfoliates some of the 2D material while leaving 2D arrays on the growth substrate. Microscopy and spectroscopy characterizations confirmed the clean surface and undamaged crystal structure. A statistical analysis of 100 back-gated molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) transistors and 500 top-gated logic circuits found a 20-times-lower variation of the threshold voltage compared to a reactive-ion-etching-based patterning process. The device yield on a 2-inch wafer was 97.6%.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data that support the plots within this paper and other findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Chhowalla, M., Jena, D. & Zhang, H. Two-dimensional semiconductors for transistors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1, 16052 (2016).
Qiu, H. et al. Two-dimensional materials for future information technology: status and prospects. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 67, 160400 (2024).
International Roadmap Committee. International Roadmap for Devices and Systems (IEEE, accessed 2023); https://irds.ieee.org/
Liu, Y. et al. Promises and prospects of two-dimensional transistors. Nature 591, 43–53 (2021).
Liu, Y., Huang, Y. & Duan, X. Van der Waals integration before and beyond two-dimensional materials. Nature 567, 323–333 (2019).
Li, W. et al. Approaching the quantum limit in two-dimensional semiconductor contacts. Nature 613, 274–279 (2023).
Tan, C. et al. 2D fin field-effect transistors integrated with epitaxial high-k gate oxide. Nature 616, 66–72 (2023).
Xia, Y. et al. 12-inch growth of uniform MoS2 monolayer for integrated circuit manufacture. Nat. Mater. 22, 1324–1331 (2023).
Li, T. et al. Epitaxial growth of wafer-scale molybdenum disulfide semiconductor single crystals on sapphire. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1201–1207 (2021).
Qin, B. et al. Interfacial epitaxy of multilayer rhombohedral transition-metal dichalcogenide single crystals. Science 385, 99–104 (2024).
Liu, L. et al. Transferred van der Waals metal electrodes for sub-1-nm MoS2 vertical transistors. Nat. Electron. 4, 342–347 (2021).
Li, W. et al. Monolayer black phosphorus and germanium arsenide transistors via van der Waals channel thinning. Nat. Electron. 7, 131–137 (2023).
Pham, P. et al. 2D heterostructures for ubiquitous electronics and optoelectronics: principles, opportunities, and challenges. Chem. Rev. 122, 6514–6613 (2022).
Min-Dianey, K., Le, T., Choi, J. & Pham, P. Advanced optical detection through the use of a deformably transferred nanofilm. Nanomaterials 11, 816 (2021).
Liu, S. et al. Nanopatterning technologies of 2D materials for integrated electronic and optoelectronic devices. Adv. Mater. 34, e2200734 (2022).
Mondal, A. et al. Low ohmic contact resistance and high on/off ratio in transition metal dichalcogenides field-effect transistors via residue-free transfer. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 34–43 (2024).
Zhao, Y. et al. A clean transfer approach to prepare centimetre-scale black phosphorus crystalline multilayers on silicon substrates for field-effect transistors. Nat. Commun. 15, 6795 (2024).
Nakatani, M. et al. Ready-to-transfer two-dimensional materials using tunable adhesive force tapes. Nat. Electron. 7, 119–130 (2024).
Shu, Z. et al. Near-zero-adhesion-enabled intact wafer-scale resist-transfer printing for high-fidelity nanofabrication on arbitrary substrates. Int. J. Extreme Manuf. 6, 015102 (2024).
Pham, P. et al. Transfer of 2D films: from imperfection to perfection. ACS Nano 18, 14841–14876 (2024).
Mao, H., Wu, D., Wu, W., Xu, J. & Hao, Y. The fabrication of diversiform nanostructure forests based on residue nanomasks synthesized by oxygen plasma removal of photoresist. Nanotechnology 20, 445304 (2009).
Franquet, A. et al. Characterization of post-etched photoresist and residues by various analytical techniques. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 1408–1411 (2008).
Choi, A. et al. Residue-free photolithographic patterning of graphene. Chem. Eng. J. 429, 132504 (2022).
Poddar, P. K. et al. Resist-free lithography for monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides. Nano Lett. 22, 726–732 (2022).
Garcia, R., Knoll, A. W. & Riedo, E. Advanced scanning probe lithography. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 577–587 (2014).
Albisetti, E. et al. Thermal scanning probe lithography. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2, 32 (2022).
Wei, Z. et al. Scratching lithography for wafer-scale MoS2 monolayers. 2D Mater. 7, 045028 (2020).
Hummel, A. W. Movable type printing in China: a brief survey. Q. J. Curr. Acquis. 1, 18–24 (1944).
Maruyama, N. et al. Advances and applications in nanoimprint lithography. In Proc. Novel Patterning Technologies 2023 124970D (SPIE, 2023).
Asano, T. et al. The advantages of nanoimprint lithography for semiconductor device manufacturing. In Proc. SPIE 11178 111780I (SPIE, 2019).
Huang, Y. et al. Universal mechanical exfoliation of large-area 2D crystals. Nat. Commun. 11, 2453 (2020).
Liu, F. et al. Disassembling 2D van der Waals crystals into macroscopic monolayers and reassembling into artificial lattices. Science 367, 903–906 (2020).
Ding, S. et al. Ag-assisted dry exfoliation of large-scale and continuous 2D monolayers. ACS Nano 18, 1195–1203 (2024).
Fu, Q. et al. One-step exfoliation method for plasmonic activation of large-area 2D crystals. Adv. Sci. 9, e2204247 (2022).
Li, Z. et al. Dry exfoliation of large-area 2D monolayer and heterostructure arrays. ACS Nano 15, 13839–13846 (2021).
Kim, K. et al. van der Waals heterostructures with high accuracy rotational alignment. Nano Lett. 16, 1989–1995 (2016).
Cao, Y. et al. Tunable correlated states and spin-polarized phases in twisted bilayer-bilayer graphene. Nature 583, 215–220 (2020).
Shen, P. C. et al. Ultralow contact resistance between semimetal and monolayer semiconductors. Nature 593, 211–217 (2021).
Lian, Z. et al. Valley-polarized excitonic Mott insulator in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattice. Nat. Phys. 20, 34–39 (2024).
Tan, Q. et al. Layer-dependent correlated phases in WSe2/MoS2 moiré superlattice. Nat. Mater. 22, 605–611 (2023).
Kim, K. S. et al. Non-epitaxial single-crystal 2D material growth by geometric confinement. Nature 614, 88–94 (2023).
Li, J. et al. General synthesis of two-dimensional van der Waals heterostructure arrays. Nature 579, 368–374 (2020).
Lu, D. et al. Monolithic three-dimensional tier-by-tier integration via van der Waals lamination. Nature 630, 340–345 (2024).
Guo, Y. F. et al. Van der Waals polarity-engineered 3D integration of 2D complementary logic. Nature 630, 346–352 (2024).
Jayachandran, D. et al. Three-dimensional integration of two-dimensional field-effect transistors. Nature 625, 276–281 (2024).
Kim, K. S. et al. The future of two-dimensional semiconductors beyond Moore’s law. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 895–906 (2024).
Milana, S. The lab-to-fab journey of 2D materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 919–921 (2019).
Satterthwaite, P. et al. Van der Waals device integration beyond the limits of van der Waals forces using adhesive matrix transfer. Nat. Electron. 7, 17–28 (2024).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by A*STAR (Grant Nos. M21K2c0116 and M24M8b0004), the Singapore National Research Foundation (Grant Nos. NRF-CRP22-2019-0004, NRF-CRP30-2023-0003, NRF2023-ITC004-001 and NRF-MSG-2023-0002) and the Singapore Ministry of Education (MOE) Tier 2 Grant (Grant No. MOE-T2EP50222-0018). H.C. acknowledges the support from the robotic AI-Scientist platform of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Anhui Outstanding Young Scientist Fund (2408085J005). Z. Liu acknowledges the support from the National Research Foundation, Singapore, under its Competitive Research Programme (CRP) (NRF-CRP22-2019-0007). This work is also supported by A*STAR MTC Programmatic Grant M23M2b0056. T.L. acknowledges the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 62322408 and 62204113). X.R.W. acknowledges support from the Singapore MOE Academic Research Fund (AcRF) Tier 3 (Grant No. MOE-MOET32023-0003) ‘Quantum Geometric Advantage’ and Tier 1 (Grant Nos. RG82/23 and RG155/24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.G. and Z. Li conceived the project. Z. Li performed the experiments and data analysis. X.L. contributed to the PL and transistor measurements. J.S. contributed to the photolithography and logic-gate fabrication. X.C. contributed to the STEM characterization. Y.Z. contributed to drawing the schematics. W.C., Y.J., H.J., C.Z., Y.D., Y.L., X.R.W., H.C. and Z. Liu contributed to device fabrication. S.Y.K. and J.L. contributed to the atomistic modelling. T.L. provided the wafer monolayer MoS2 film. W.G. and Z. Li co-wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the paper. Z. Li and X.L. contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Electronics thanks Huigao Duan, Phuong V. Pham and Yanbo Xie for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–12.
Supplementary Video
The process of imprinting 2D materials.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Statistical source data for Fig. 1.
Source Data Fig. 2
Statistical source data for Fig. 2.
Source Data Fig. 3
Statistical source data for Fig. 3.
Source Data Fig. 4
Statistical source data for Fig. 4.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Liu, X., Shi, J. et al. Residue-free wafer-scale direct imprinting of two-dimensional materials. Nat Electron 8, 571–577 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-025-01408-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-025-01408-z
This article is cited by
-
Metal stamp method for residue-free two-dimensional semiconductor patterning
Nature Reviews Electrical Engineering (2025)