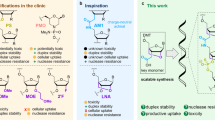
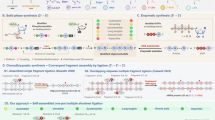
Abstract
The optimisation and further expansion of methods for the synthesis of oligonucleotide conjugates is receiving increased attention due to their importance for further advancement of therapeutic and diagnostic nucleic acid-based applications. Current methodologies, particularly those relying on maleimide-type linkers, are often hampered by linker instability. Herein, we present a versatile method for the direct functionalisation of readily available amino-modified oligonucleotides (AONs), where a 5-hydroxy-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-ones (5HP2O) Michael acceptor is directly formed in a rapid and efficient manner on a free primary amine. The methodology demonstrates broad applicability, tolerating various amino-modifiers and their positions within different oligonucleotide types, including DNA, LNA, PNA, and phosphorothioate-modified oligonucleotide strands. Most importantly, the possibility to introduce an additional second orthogonal reactive handle uniquely enables a direct single-site dual-functionalisation (Michael acceptor and click handle) of AONs for the assembly of complex constructs, as exemplified by the synthesis of a fluorescent peptide-oligonucleotide construct.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the main data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Information files. Extra data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Fàbrega, C. et al. Lipid and peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates for therapeutic purposes: from simple hybrids to complex multifunctional assemblies. Pharmaceutics 15, 320 (2023).
Østergaard, M. E. et al. Conjugation to a transferrin receptor 1-binding Bicycle peptide enhances ASO and siRNA potency in skeletal and cardiac muscles. Nucleic Acids Res. 53, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf270 (2025).
Knerr, L. et al. Glucagon Like Peptide 1 receptor agonists for targeted delivery of antisense oligonucleotides to pancreatic beta cell. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 3416–3429 (2021).
Mullard, A. Antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates enter the clinic. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 21, 6–8 (2022).
Dovgan, I., Koniev, O., Kolodych, S. & Wagner, A. Antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates as therapeutic, imaging, and detection agents. Bioconjugate Chem. 30, 2483–2501 (2019).
Benizri, S. et al. Bioconjugated oligonucleotides: recent developments and therapeutic applications. Bioconjugate Chem. 30, 366–383 (2019).
Chung, K. K. H. et al. Fluorogenic DNA-PAINT for faster, low-background super-resolution imaging. Nat. Methods 19, 554–559 (2022).
Nieves, D. J., Gaus, K. & Baker, M. A. B. DNA-based super-resolution microscopy: DNA-PAINT. Genes 9, 621 (2018).
Ryazantsev, D. Y., Voronina, D. V. & Zavriev, S. K. Immuno-PCR: achievements and perspectives. Biochemistry 81, 1754–1770 (2016).
Klabenkova, K., Fokina, A. & Stetsenko, D. Chemistry of peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates: a review. Molecules 26, https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175420 (2021).
Zavoiura, O. et al. Nanobody-siRNA conjugates for targeted delivery of siRNA to cancer cells. Mol. Pharm. 18, 1048–1060 (2021).
Rudchenko, M. et al. Autonomous molecular cascades for evaluation of cell surfaces. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 580–586 (2013).
Cuellar, T. L. et al. Systematic evaluation of antibody-mediated siRNA delivery using an industrial platform of THIOMAB-siRNA conjugates. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 1189–1203 (2015).
Fischer, A. et al. A quantitative real-time immuno-PCR approach for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins. J. Mol. Med. 85, 461–469 (2007).
Fan, Z. et al. Rapid fluorescence immunoassay of benzo[a]pyrene in mainstream cigarette smoke based on a dual-functional antibody–DNA conjugate. RSC Adv. 8, 29562–29569 (2018).
Sánchez, A., Pedroso, E. & Grandas, A. Conjugation reactions involving maleimides and phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Bioconjugate Chem. 23, 300–307 (2012).
Sánchez, A., Pedroso, E. & Grandas, A. Maleimide-Dimethylfuran exo Adducts: Effective Maleimide Protection in the Synthesis of Oligonucleotide Conjugates. Org. Lett. 13, 4364–4367 (2011).
Osawa, T., Ren, Q. & Obika, S. Development of phosphoramidite reagents for the synthesis of base-labile oligonucleotides modified with a linear Aminoalkyl and Amino-PEG Linker at the 3′-End. Molecules 27, 8501 (2022).
Ravasco, J. M. J. M., Faustino, H., Trindade, A. & Gois, P. M. P. Bioconjugation with maleimides: a useful tool for chemical biology. Chem. Eur. J. 25, 43–59 (2019).
Kjærsgaard, N. L., Hansen, R. A. & Gothelf, K. V. Preparation of maleimide-modified oligonucleotides from the corresponding amines using N-Methoxycarbonylmaleimide. Bioconjugate Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00144 (2022).
Fontaine, S. D., Reid, R., Robinson, L., Ashley, G. W. & Santi, D. V. Long-term stabilization of maleimide-thiol conjugates. Bioconjugate Chem. 26, 145–152 (2015).
Ou, L. et al. Assessment of crosslinkers between peptide antigen and carrier protein for fusion peptide-directed vaccines against HIV-1. Vaccines 10, https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111916 (2022).
Rocha Tapia, A. et al. Site-directed conjugation of single-stranded DNA to affinity proteins: quantifying the importance of conjugation strategy. Chem. Sci. 15, 8982–8992 (2024).
Cochran, M. et al. Structure-activity relationship of antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates: evaluating bioconjugation strategies for antibody-siRNA conjugates for drug development. J. Med. Chem. 67, 14852–14867 (2024).
Shen, L., Wu, Y., Xie, W., Chen, G. & Xing, H. Chemical biology approaches toward precise structure control of IgG-based antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates. ChemBioChem 24, https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.202300077 (2023).
Shen, B.-Q. et al. Conjugation site modulates the in vivo stability and therapeutic activity of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 30, 184–189 (2012).
Tumey, L. N. et al. Mild method for succinimide hydrolysis on ADCs: impact on ADC potency, stability, exposure, and efficacy. Bioconjugate Chem. 25, 1871–1880 (2014).
Peeters, J. M., Hazendonk, T. G., Beuvery, E. C. & Tesser, G. I. Comparison of four bifunctional reagents for coupling peptides to proteins and the effect of the three moieties on the immunogenicity of the conjugates. J. Immunol. Methods 120, 133–143 (1989).
Kafi, K. et al. Maleimide conjugation markedly enhances the immunogenicity of both human and murine idiotype-KLH vaccines. Mol. Immunol. 46, 448–456 (2009).
De Geyter et al. 5-Hydroxy-pyrrolone based building blocks as maleimide alternatives for protein bioconjugation and single-site multi-functionalization. Chem. Sci. 12, 5246–5252 (2021).
Kalaitzakis, D., Kouridaki, A., Noutsias, D., Montagnon, T. & Vassilikogiannakis, G. Methylene blue as a photosensitizer and redox agent: synthesis of 5-Hydroxy-1H-pyrrol-2(5H)-ones from Furans. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 6283–6287 (2015).
Halila, S., Velasco, T., De Clercq, P. & Madder, A. Fine-tuning furan toxicity: fast and quantitative DNA interchain cross-link formation upon selective oxidation of a furan containing oligonucleotide. Chem. Commun. 7, 936–938 (2005).
Op de Beeck, M. & Madder, A. Sequence specific DNA cross-linking triggered by visible light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 10737–10740 (2012).
Schneider, Anne-Fleur E. et al.Using muscle homing peptide CyPep10 to deliver phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers in the mdx mouse. Molecular Therapy: Nucleic Acids. 36, 102625 (2025).
Desmet, J. et al. Structural basis of IL-23 antagonism by an Alphabody protein scaffold. Nat. Commun. 5, 5237 (2014).
Acknowledgements
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Grant Agreement No. 956070 (OLIGOMED) (J.H.M., M.L., A.M., M.B.). E.C. acknowledges a FWO fellowship (12B1923N). We thank Dr. Chloe Howells and Prof. Eugen Stulz for LCMS measurement of crude functionalisation reactions. We thank Pieter Surmont and Prof. Frederic Lynen for HRMS Orbitrap measurement of purified oligonucleotide constructs. We thank Jan Goeman for LCMS measurements and Stijn Tanghe for general lab support. We thank the NMR expertise centre (Ghent University) for providing support and access to its NMR infrastructure. The 400 MHz NMR used in this work has been funded by a grant/project of the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO I006920N) and the ‘Bijzonder Onderzoeksfonds’ (BOF.BAS.2022.0023.01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jan H. Meffert was responsible for the overall conceptualisation of the study, designed and conducted all experiments including condition screening, oligonucleotide mono- and dual-functionalisation, product analysis and small molecule synthesis, and wrote the manuscript, with support from the other authors. Enrico Cadoni provided PNA constructs (P1 to P4). Mónica Lopes, Martin Bollmark and UIf Tedebark provided phosphorothioated amine oligonucleotides (D2-4). Annemieke Madder was responsible for the funding and overall guidance, contributed to the conceptualisation and assisted in manuscript writing, proofreading and correction.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Annemieke Madder has a pending patent application relating to 5HP2Os application for bioconjugation (Bioconjugation reagent and methods, WO2020174086A2, Annemieke MADDER, Ewout DE GEYTER, Eirini ANTONATOU, Sabina SMOLEN, Dimitris Kalaitzakis, Georgios VASSILIKOGIANNAKIS, Europe&US). All other authors declare no competing interest.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Chemistry thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Meffert, J.H., Lopes, M., Cadoni, E. et al. Versatile introduction of multifunctional Michael-acceptor moieties on amino-oligonucleotides for bioconjugation purposes. Commun Chem (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-025-01882-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-025-01882-8