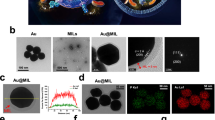
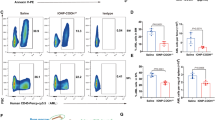
Abstract
Endometriosis is a chronic inflammatory gynecological condition that affects millions of women and people with uteri globally, with limited available treatments. In this work, we explore using ionic liquid (IL)-coated gold core polymeric nanoparticles (NPs), Au-PLGA-IL NPs, for selective neutrophil co-localization for the eventual development of targeted treatment of endometriosis via photothermal therapy. These NPs were synthesized by a modified solvent evaporation method and functionalized with ILs that confer neutrophil selectivity. In vitro biocompatibility was demonstrated using endometrial 12Z cells and a hemolysis assay with human female blood. Ex vivo studies confirmed superior neutrophil targeting ability in human female whole blood, quantified using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) to visualize the NP co-localization. Upon near-infrared irradiation (1 W/cm², 5 min), the Au-PLGA-IL NPs induced significant apoptosis in 12Z cells through localized hyperthermia. This study introduces the first system integrating the plasmonic properties of AuNPs with PLGA’s biocompatibility, enhanced by functional versatility of ILs, providing a promising platform for endometriosis treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballard, K., Lowton, K. & Wright, J. What’s the delay? A qualitative study of women’s experiences of reaching a diagnosis of endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 86, 1296–1301 (2006).
Mikhaleva, L. M. et al. Current knowledge on endometriosis etiology: A systematic review of literature. Int. J. Women’s Health.13, 525–537 (2021).
Yuxue, J., Ran, S., Minghui, F. & Minjia, S. Applications of nanomaterials in endometriosis treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1184155 (2023).
Bougie, O., Yap, M. I., Sikora, L., Flaxman, T. & Singh, S. Influence of race/ethnicity on prevalence and presentation of endometriosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG: Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 126, 1104–1115 (2019).
Nisolle, M. & Donnez, J. Peritoneal endometriosis, ovarian endometriosis, and adenomyotic nodules of the rectovaginal septum are three different entities. Fertil. Steril. 68, 585–596 (1997).
Klemmt, P. A. & Starzinski-Powitz, A. Molecular and cellular pathogenesis of endometriosis. Curr. women’s. health Rev. 14, 106–116 (2018).
Wang, Y., Nicholes, K. & Shih, I.-M. The origin and pathogenesis of endometriosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol.: Mechanisms Dis. 15, 71–95 (2020).
Johnson, N. P. et al. Consensus on current management of endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 28, 1552–1568 (2013).
Alimi, Y., Iwanaga, J., Loukas, M. & Tubbs, R. S. The clinical anatomy of endometriosis: a review. Cureus 10 (2018).
Mariani, A., Webb, M. J., Keeney, G. L. & Podratz, K. C. Routes of lymphatic spread: a study of 112 consecutive patients with endometrial cancer. Gynecologic Oncol. 81, 100–104 (2001).
Hunsche, E., Gauthier, M., Witherspoon, B., Rakov, V. & Agarwal, S. K. Endometriosis symptoms and their impacts on the daily lives of US women: Results from an interview study. Int. J.Women’s Health. 15, 893–904 (2023).
Bulletti, C., Coccia, M. E., Battistoni, S. & Borini, A. Endometriosis and infertility. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 27, 441–447 (2010).
Kolanska, K. et al. Endometriosis with infertility: A comprehensive review on the role of immune deregulation and immunomodulation therapy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 85, e13384 (2021).
Berlanda, N. et al. Surgery versus hormonal therapy for deep endometriosis: is it a choice of the physician?. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 209, 67–71 (2017).
Jensen, J. T., Schlaff, W. & Gordon, K. Use of combined hormonal contraceptives for the treatment of endometriosis-related pain: a systematic review of the evidence. Fertil. Steril. 110, 137–152.e131 (2018).
Tosti, C. et al. Hormonal therapy for endometriosis: from molecular research to bedside. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 209, 61–66 (2017).
Comptour, A. et al. Patient quality of life and symptoms after surgical treatment for endometriosis. J. Minim. invasive Gynecol. 26, 717–726 (2019).
Singh, S. S. & Suen, M. W. Surgery for endometriosis: beyond medical therapies. Fertil. Steril. 107, 549–554 (2017).
Bozdag, G. Recurrence of endometriosis: risk factors, mechanisms and biomarkers. Women’s. Health 11, 693–699 (2015).
Chiu, C.-C. et al. Maintenance Therapy for Preventing Endometrioma Recurrence after Endometriosis Resection Surgery–A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 29, 602–612 (2022).
Volpini, C. et al. The nano-revolution in the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. Nanoscale 15, 17313–17325 (2023).
Acharya, B., Behera, A., Behera, S. & Moharana, S. Recent advances in nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the diagnosis and treatment of reproductive disorders. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 7, 1336–1361 (2024).
Shandilya, R., Pathak, N., Lohiya, N. K., Sharma, R. S. & Mishra, P. K. Nanotechnology in reproductive medicine: Opportunities for clinical translation. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 47, 245 (2020).
Guo, X. et al. Specific photothermal ablation therapy of endometriosis by targeting delivery of gold nanospheres. Small 13, 1603270 (2017).
Ling, C., Wang, X. & Shen, Y. Advances in hollow inorganic nanomedicines for photothermal-based therapies. Int. J. Nanomed. 16, 493–513 (2021).
Paciotti, G. F. et al. Colloidal gold: a novel nanoparticle vector for tumor directed drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 11, 169–183 (2004).
Dykman, L. & Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 2256–2282 (2012).
Vashisth, P. et al. Choline Carboxylic Acid Ionic Liquid-Stabilized Anisotropic Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 7, 26332–26343 (2024).
Singh, G. et al. Good’s buffer based highly biocompatible ionic liquid modified PLGA nanoparticles for the selective uptake in cancer cells. Mater. Chem. Front. 7, 6213–6228 (2023).
Nichols, I. R. et al. The Impact of Water on Choline-2-Octenoic Ionic Liquid-Facilitated Transdermal Transport. Adv. Therapeutics 6, 2200096 (2023).
Darlington, D. S. et al. Selective Near-Infrared Blood Detection Driven by Ionic Liquid–Dye–Albumin Nanointeractions. Langmuir 39, 10806–10819 (2023).
Chism, C. M. et al. Antimicrobial effects of anion manipulation with biocompatible choline carboxylic acid-based ionic liquids. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 1, 23–31 (2022).
Dasanayake, G. S. et al. Glyco Ionic Liquids as Novel Nanoparticle Coatings to Enhance Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Drug Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 14, 2500592 (2025).
Dasanayake, G. S. et al. Imidazolium-based zwitterionic liquid-modified PEG–PLGA nanoparticles as a potential intravenous drug delivery carrier. Nanoscale 16, 5584–5600 (2024).
Hamadani, C. M. et al. Development of ionic liquid-coated PLGA nanoparticles for applications in intravenous drug delivery. Nat. Protoc. 18, 2509–2557 (2023).
Hamadani, C. M., Goetz, M. J., Mitragotri, S. & Tanner, E. E. Protein-avoidant ionic liquid (PAIL)–coated nanoparticles to increase bloodstream circulation and drive biodistribution. Sci. Adv. 6, eabd7563 (2020).
Hamadani, C. M. et al. Ionic Liquid Coating-Driven Nanoparticle Delivery to the Brain: Applications for NeuroHIV. Adv. Sci. 11, 2305484 (2024).
Hamadani, C. M. et al. Selective blood cell hitchhiking in whole blood with ionic liquid-coated PLGA nanoparticles to redirect biodistribution after intravenous injection. Res. Sq. rs. 3. rs-3146716 (2023).
Hamadani, C. M. et al. Insights into the physicochemical interactions of ionic liquid-coated polymeric nanoparticles with red blood cells. Nanoscale Adv. 7, 5273–5283 (2025).
Cuzytek, A., Hrycek, A., Stasiura, H. & Stadnicki, A. Peripheral blood neutrophils in patients with internal endometriosis in light of enzymatic tests. Wiadomosci Lekarskie (Wars., Pol.: 1960) 50, 75–80 (1997).
Symons, L. K. et al. Neutrophil recruitment and function in endometriosis patients and a syngeneic murine model. FASEB J. 34, 1558–1575 (2020).
Berkes, E., Oehmke, F., Tinneberg, H.-R., Preissner, K. T. & Saffarzadeh, M. Association of neutrophil extracellular traps with endometriosis-related chronic inflammation. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 183, 193–200 (2014).
Armstrong, G. M. et al. Endometrial apoptosis and neutrophil infiltration during menstruation exhibits spatial and temporal dynamics that are recapitulated in a mouse model. Sci. Rep. 7, 17416 (2017).
Salamonsen, L. A. & Lathbury, L. J. Endometrial leukocytes and menstruation. Hum. Reprod. update 6, 16–27 (2000).
King, A. E., Critchley, H. O. & Kelly, R. W. Innate immune defences in the human endometrium. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 1, 1–8 (2003).
Jones, R. L., Hannan, N. J., Kaitu’u, T.uJ., Zhang, J. & Salamonsen, L. A. Identification of chemokines important for leukocyte recruitment to the human endometrium at the times of embryo implantation and menstruation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 6155–6167 (2004).
Clare, B., Sirwardana, A. & MacFarlane, D. R. Synthesis, purification and characterization of ionic liquids. (Springer, 2010).
Ferraz, R. et al. Ionic liquids synthesis–methodologies. Organic Chem. Curr. Res. 46, 1–2 (2015).
Kimling, J. et al. Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 15700–15707 (2006).
Shen, J.-J. et al. Preliminary quality criteria of citrate-protected gold nanoparticles for medicinal applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 1, 2120–2128 (2018).
Fathy, M. M. et al. An insight into synthesis and antitumor activity of citrate and gallate stabilizing gold nanospheres. Sci. Rep. 13, 2749 (2023).
Faid, A. H., Shouman, S. A., Badr, Y. A. & Sharaky, M. Enhanced photothermal heating and combination therapy of gold nanoparticles on a breast cell model. BMC Chem. 16, 66 (2022).
O’Donnell, P. B. & McGinity, J. W. Preparation of microspheres by the solvent evaporation technique. Adv. drug Deliv. Rev. 28, 25–42 (1997).
Jin, J., Li, X., Geng, J. & Jing, D. Insights into the complex interaction between hydrophilic nanoparticles and ionic surfactants at the liquid/air interface. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 15223–15235 (2018).
Jain, P. K., Lee, K. S., El-Sayed, I. H. & El-Sayed, M. A. Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 7238–7248 (2006).
Link, S. & El-Sayed, M. A. Size and temperature dependence of the plasmon absorption of colloidal gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 4212–4217 (1999).
Mustafa, D. E. et al. Surface plasmon coupling effect of gold nanoparticles with different shape and size on conventional surface plasmon resonance signal. Plasmonics 5, 221–231 (2010).
Hang, Y., Wang, A. & Wu, N. Plasmonic silver and gold nanoparticles: shape-and structure-modulated plasmonic functionality for point-of-caring sensing, bio-imaging and medical therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 53, 2932–2971 (2024).
París Ogáyar, M. et al. Luminescence Fingerprint of Intracellular NIR-II Gold Nanocluster Transformation: Implications for Sensing and Imaging. ACS Nano 19, 7821–7834 (2025).
Jia, P. et al. Integration of IR-808 and thiol-capped Au–Bi bimetallic nanoparticles for NIR light mediated photothermal/photodynamic therapy and imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 9, 101–111 (2021).
Quintanilla, M., Henriksen-Lacey, M., Renero-Lecuna, C. & Liz-Marzán, L. M. Challenges for optical nanothermometry in biological environments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 51, 4223–4242 (2022).
Chen, J. et al. Collective plasmon coupling in gold nanoparticle clusters for highly efficient photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 16, 910–920 (2022).
Ding, X. et al. Surface plasmon resonance enhanced light absorption and photothermal therapy in the second near-infrared window. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 15684–15693 (2014).
Zhang, Y. et al. Temperature-dependent cell death patterns induced by functionalized gold nanoparticle photothermal therapy in melanoma cells. Sci. Rep. 8, 8720 (2018).
Kim, M. et al. Numerical study on effective conditions for the induction of apoptotic temperatures for various tumor aspect ratios using a single continuous-wave laser in photothermal therapy using gold nanorods. Cancers 11, 764 (2019).
Pérez-Hernández, M. et al. Dissecting the molecular mechanism of apoptosis during photothermal therapy using gold nanoprisms. ACS Nano 9, 52–61 (2015).
Minea, A. A. & Sohel Murshed, S. Ionic liquids-based nanocolloids—A review of progress and prospects in convective heat transfer applications. Nanomaterials 11, 1039 (2021).
Yu, M. & Zheng, J. Clearance pathways and tumor targeting of imaging nanoparticles. ACS Nano 9, 6655–6674 (2015).
Ng, C. T. et al. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis of gold nanoparticles in vitro. Anat. Rec. 298, 418–427 (2015).
Li, Y. & Monteiro-Riviere, N. A. Mechanisms of cell uptake, inflammatory potential and protein corona effects with gold nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 11, 3185–3203 (2016).
Chen, Y.-Q. et al. Uncovering the importance of ligand mobility on cellular uptake of nanoparticles: Insights from experimental, computational, and theoretical investigations. ACS Nano 18, 6463–6476 (2024).
Noblett, A. D., Baek, K. & Suggs, L. J. Controlling nucleopeptide hydrogel self-assembly and formation for cell-culture scaffold applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 7, 2605–2614 (2021).
Gong, N. & Mitchell, M. J. Rerouting nanoparticles to bone marrow via neutrophil hitchhiking. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 548–549 (2023).
Yuan, S. & Hu, Q. Convergence of nanomedicine and neutrophils for drug delivery. Bioact. Mater. 35, 150–166 (2024).
Melamed, J. R., Edelstein, R. S. & Day, E. S. Elucidating the fundamental mechanisms of cell death triggered by photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 9, 6–11 (2015).
Kim, S., Jun, D. H., Kim, H. J., Jeong, K.-C. & Lee, C.-H. Development of a high-content screening method for chemicals modulating DNA damage response. J. Biomolecular Screen. 16, 259–265 (2011).
Amin, K. & Dannenfelser, R. M. In vitro hemolysis: guidance for the pharmaceutical scientist. J. Pharm. Sci. 95, 1173–1176 (2006).
Yedgar, S., Barshtein, G. & Gural, A. Hemolytic activity of nanoparticles as a marker of their hemocompatibility. Micromachines 13, 2091 (2022).
Brenner, J. S. et al. Red blood cell-hitchhiking boosts delivery of nanocarriers to chosen organs by orders of magnitude. Nat. Commun. 9, 2684 (2018).
https://www.biolegend.com/en-gb/products/fitc-anti-human-cd15-ssea-1-antibody-3700, F. a.-h. C. S.-A. a.-C.-W. D. B. c. &. FITC anti-human CD15 SSEA-1 Antibody anti-CD15 - W6D3. (2021). Biolegend.com. https://www.biolegend.com/en-gb/products/fitc-anti-human-cd15-ssea-1-antibody-3700, 2021).
Anti-Human CD66b Antibody, C. G. F. S. T. S. c. Anti-Human CD66b Antibody, Clone G10F5 | STEMCELL Technologies. (2015). Stemcell.com. https://www.stemcell.com/products/anti-human-cd66b-antibody-clone-g10f5.html#section-protocols-and-documentation, 2015).
Chen, X. & Gao, C. Influences of surface coating of PLGA nanoparticles on immune activation of macrophages. J. Mater. Chem. B 6, 2065–2077 (2018).
Garanina, A. et al. The Internalization Pathways of Liposomes, PLGA, and Magnetic Nanoparticles in Neutrophils. Biomedicines 12, 2180 (2024).
Acknowledgements
E.E.L.T. acknowledges the College of Liberal Arts at the University of Mississippi and the NSF (#2236629) for funding. The abstract graphic and Fig. 1 were created with BioRender.com. A portion of this work was presented as an oral presentation at the American Chemical Society (ACS) Spring 2024 national meeting held in New Orleans, Louisiana on March 18, 2024. Ionic liquid-coated gold core polymeric nanoparticles for selective neutrophil hitchhiking and targeted endometriosis treatment Date March 18, 2024.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: P.V., E.E.L.T., C.M.H., W.J.; Au-PLGA-IL NP synthesis, optimization, characterization and methodology: P.V., L.T.D.C., G.S., C.M.H., B.G., N.W., T.G.; IL synthesis and characterization: C.M.C., P.V.; Photothermal efficiency measurement and ICP-MS, TEM Imaging and analysis: T.S., P.V., N.F.; Cytotoxicity assay: P.V., L.T.D.C., A.C.W., D.H.; In vitro photothermal experiments: P.V., L.T.D.C., A.C.W., D.H.; Live cell imaging for In vitro experiments: P.V., L.T.D.C., G.D.; FACS experimental setup (gating, optimization): C.M.H., P.V., G.D.; Ex vivo experiments with whole blood : PV, C.M.H., S.X.E., M.P.; Live cell confocal microscopy of white blood cells: C.M.H.; Supervision and funding: E.E.L.T.; Writing the original draft: P.V., E.E.L.T., L.T.D.C., D.H.; Manuscript review: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
E.E.L.T. and C.M.H. have filed intellectual property disclosures describing some aspects of this technology. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Chemistry thanks Hakan Erdoğan and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Vashisth, P., Clerc, L.T.D., Hu, D. et al. Ionic liquid-coated gold core polymeric nanoparticles for selective neutrophil hitchhiking towards endometriosis treatment. Commun Chem (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-026-01909-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-026-01909-8