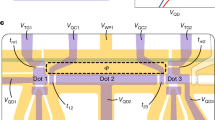
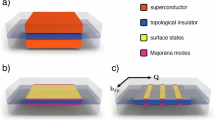
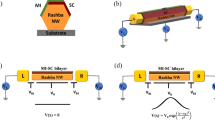
Abstract
Fusing Majorana zero modes (MZMs) leads to multiple outcomes, a property unique to non-Abelian anyons. The successful demonstration of this nontrivial fusion rule would be a hallmark for the development of topological quantum computation. Here, we propose that such fusion can be achieved by simply attaching a fermionic mode to a single Majorana zero mode. By modulation of the energy level of the fermionic mode (FM) as well as its coupling with MZM in different sequences, we show that a zero or integer charge pumping can be realized when different fusion loops are chosen. Such fusion loops are intimately related with the nontrivial fusion rule of Majorana modes and are solely determined by the crossings at zero energy in the parameter space. Finally, we demonstrate our proposal in a nanowire-based topological superconductor coupled to a quantum dot. We show that charge pumping is robust for MZMs in the realistic system irrespective of the initial condition of FM state.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available in the article and in its Supplementary Information. Additional data are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Code availability
The code that is deemed central to the conclusions is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Kitaev, A. Y. Unpaired Majorana fermions in quantum wires. Physics 44, 131 (2001).
Nayak, C., Simon, S. H., Stern, A., Freedman, M. & Das Sarma, S. Non-Abelian anyons and topological quantum computation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 1083–1159 (2008).
Fu, L. & Kane, C. L. Superconducting proximity effect and Majorana fermions at the surface of a topological insulator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 096407 (2008).
Sau, J. D., Lutchyn, R. M., Tewari, S. & Das Sarma, S. Generic new platform for topological quantum computation using semiconductor heterostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 040502 (2010).
Fujimoto, S. Topological order and non-Abelian statistics in noncentrosymmetric s-wave superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 77, 220501(R) (2008).
Sato, M., Takahashi, Y. & Fujimoto, S. Non-Abelian topological orders and Majorana fermions in spin-singlet superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 82, 134521 (2010).
Alicea, J. Majorana fermions in a tunable semiconductor device. Phys. Rev. B 81, 125318 (2010).
Lutchyn, R. M., Sau, J. D. & Das Sarma, S. Majorana fermions and a topological phase transition in semiconductor-superconductor heterostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 077001 (2010).
Hell, M., Leijnse, M. & Flensberg, K. Two-dimensional platform for networks of Majorana bound states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 107701 (2017).
Pientka, F. et al. Topological superconductivity in a planar Josephson junction. Phys. Rev. X 7, 021032 (2017).
Mourik, V. et al. Signatures of Majorana fermions in hybrid superconductor-semiconductor nanowire devices. Science 336, 1003–1007 (2012).
Deng, M. T. et al. Anomalous zero-bias conductance peak in a Nb-InSb nanowire-Nb hybrid device. Nano Lett. 12, 6414–6419 (2012).
Das, A. et al. Zero-bias peaks and splitting in an Al-InAs nanowire topological superconductor as a signature of Majorana fermions. Nat. Phys. 8, 887–895 (2012).
Gül, Ö. et al. Ballistic Majorana nanowire devices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 192–197 (2018).
Albrecht, S. M. et al. Exponential protection of zero modes in Majorana islands. Nature 531, 206–209 (2016).
Deng, M. T. et al. Majorana bound state in a coupled quantum-dot hybrid-nanowire system. Science 354, 1557–1562 (2016).
Nadj-Perge, S. et al. Observation of Majorana fermions in ferromagnetic atomic chains on a superconductor. Science 346, 602–607 (2014).
Feldman, B. E. et al. High-resolution studies of the Majorana atomic chain platform. Nat. Phys. 13, 286–291 (2017).
Sun, H. H. et al. Majorana zero mode detected with spin selective Andreev reflection in the vortex of a topological superconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 257003 (2016).
Wang, D. F. et al. Evidence for Majorana bound states in an iron-based superconductor. Science 362, 333–335 (2018).
Zhang, P. et al. Observation of topological superconductivity on the surface of an iron-based superconductor. Science 360, 182–186 (2018).
Fornieri, A. et al. Evidence of topological superconductivity in planar Josephson junctions. Nature 569, 89–92 (2019).
Ren, H. C. et al. Topological superconductivity in a phase-controlled Josephson junction. Nature 569, 93–98 (2019).
Liu, J., Potter, A. C., Law, K. T. & Lee, P. A. Zero-bias peaks in the tunneling conductance of spin-orbit-coupled superconducting wires with and without Majorana end-states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 267002 (2012).
Kells, G., Meidan, D. & Brouwer, P. W. Near-zero-energy end states in topologically trivial spin-orbit coupled superconducting nanowires with a smooth confinement. Phys. Rev. B 86, 100503(R) (2012).
Prada, E., San-Jose, P. & Aguado, R. Transport spectroscopy of NS nanowire junctions with Majorana fermions. Phys. Rev. B 86, 180503(R) (2012).
Liu, C. X., Sau, J. D. & Das Sarma, S. Distinguishing topological Majorana bound states from trivial Andreev bound states: proposed tests through differential tunneling conductance spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 97, 214502 (2018).
Moore, C., Stanescu, T. D. & Tewari, S. Two-terminal charge tunneling: Disentangling Majorana zero modes from partially separated Andreev bound states in semiconductor-superconductor heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B 97, 165302 (2018).
Vuik, A., Nijholt, B., Akhmerov, A. R. & Wimmer, M. Reproducing topological properties with quasi-Majorana states. SciPost Phys. 7, 061 (2019).
Penaranda, F., Aguado, R., San-Jose, P. & Prada, E. Quantifying wave-function overlaps in inhomogeneous Majorana nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 98, 235406 (2018).
Pan, H. N. & Das Sarma, S. Physical mechanisms for zero-bias conductance peaks in Majorana nanowires. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 013377 (2020).
Fleckenstein, C., Dominguez, F., Ziani, N. T. & Trauzettel, B. Decaying spectral oscillations in a Majorana wire with finite coherence length. Phys. Rev. B 97, 155425 (2018).
Cao, Z., Chen, S. M., Zhang, G. & Liu, D. E. Recent progress on Majorana in semiconductor-superconductor heterostructures-engineering and detection. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 66, 267003 (2023).
Ivanov, D. A. Non-Abelian statistics of half-quantum vortices in p-wave superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 268 (2001).
Alicea, J., Oreg, Y., Refael, G., von Oppen, F. & Fisher, M. P. A. Non-Abelian statistics and topological quantum information processing in 1D wire networks. Nat. Phys. 7, 412–417 (2011).
van Heck, B., Akhmerov, A. R., Hassler, F., Burrello, M. & Beenakker, C. W. J. Coulomb-assisted braiding of Majorana fermions in a Josephson junction array. New J. Phys. 14, 035019 (2012).
Liu, J., Chen, W. Q., Gong, M., Wu, Y. J. & Xie, X. C. Minimal setup for non-Abelian braiding of Majorana zero modes. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 64, 117811 (2021).
Mishmash, R. V., Bauer, B., von Oppen, F. & Alicea, J. Dephasing and leakage dynamics of noisy Majorana-based qubits: topological versus Andreev. Phys. Rev. B 101, 075404 (2020).
Fulga, I. C., van Heck, B., Burrello, M. & Hyart, T. Effects of disorder on Coulomb-assisted braiding of Majorana zero modes. Phys. Rev. B 88, 155435 (2013).
Manousakis, J. et al. Weak measurement protocols for Majorana bound state identification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 096801 (2020).
Vijay, S. & Fu, L. Teleportation-based quantum information processing with Majorana zero modes. Phys. Rev. B 94, 235446 (2016).
Karzig, T. et al. Scalable designs for quasiparticle-poisoning-protected topological quantum computation with Majorana zero modes. Phys. Rev. B 95, 235305 (2017).
Schrade, C. & Fu, L. Majorana superconducting qubit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 267002 (2018).
Oreg, Y. & von Oppen, F. Majorana zero modes in networks of cooper-pair boxes: topologically ordered states and topological quantum computation. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 11, 397–420 (2020).
Amorim, C. S., Ebihara, K., Yamakage, A., Tanaka, Y. & Sato, M. Majorana braiding dynamics in nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 91, 174305 (2015).
Harper, F., Pushp, A. & Roy, R. Majorana braiding in realistic nanowire Y-junctions and tuning forks. Phys. Rev. Res. 1, 033207 (2019).
Flensberg, K. Non-Abelian operations on Majorana fermions via single-charge control. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 090503 (2011).
Pandey, B., Okamoto, S. & Dagotto, E. Nontrivial fusion of Majorana zero modes in interacting quantum-dot arrays. Phys. Rev. Res. 6, 033314 (2024).
Aasen, D. et al. Milestones toward Majorana-based quantum computing. Phys. Rev. X 6, 031016 (2016).
Zhou, T. et al. Fusion of Majorana bound states with mini-gate control in two-dimensional systems. Nat. Commun. 13, 1738 (2022).
Pandey, B., Mohanta, N. & Dagotto, E. Nontrivial fusion of Majorana zero modes in interacting quantum-dot arrays. Phys. Rev. Res. 6, 033314 (2024).
Gong, M., Wu, Y. J., Jiang, H., Liu, J. & Xie, X. C. Unveiling non-Abelian statistics of vortex Majorana bound states in iron-based superconductors using fermionic modes. Phys. Rev. B 105, 014507 (2022).
Dvir, T. et al. Realization of a minimal Kitaev chain in coupled quantum dots. Nature 614, 445–450 (2023).
Levajac, V. et al. Subgap spectroscopy along hybrid nanowires by nm-thick tunnel barriers. Nat. Commun. 14, 6647 (2023).
Gao, Y. C. et al. Hard superconducting gap in pbte nanowires. Chin. Phys. Lett. 41, 038502 (2024).
Munk, M. I. K., Schulenborg, J., Egger, R. & Flensberg, K. Parity-to-charge conversion in Majorana qubit readout. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 033254 (2020).
Microsoft Azure Quantum et al. Interferometric single-shot parity measurement in InAs-Al hybrid devices. Nature 638, 651–655 (2025).
Sun, D. H. & Liu, J. Quench dynamics of the Josephson current in a topological Josephson junction. Phys. Rev. B 97, 035311 (2018).
Wang, L., Troyer, M. & Dai, X. Topological charge pumping in a one-dimensional optical lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 026802 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 92265103, and No. 12574056), Quantum Science and Technology -National Science and Technology Major Project (Grant No. 2021ZD0302400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L. conceived the idea that fusion can be achieved by attaching a fermionic mode to a single Majorana zero mode after a discussion with X.C.X., Y.Z., and C.-H.L performed calculations with assistance from J.L., X.-Y.Z., and J.-T.S. Y.Z. and J.L. wrote the manuscript with contributions from all authors. J.L. and X.C.X. supervised the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Physics thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhu, X., Li, C. et al. Unveiling nontrivial fusion rule of Majorana zero mode using a fermionic mode. Commun Phys (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-026-02504-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-026-02504-y