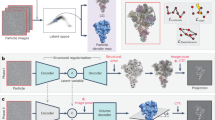
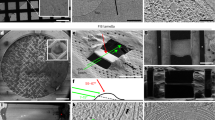
Abstract
In the life sciences, cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has revolutionized structure determination by providing atomic-resolution structures of biomolecules in their native environment and in multiple conformational states. The applications of cryo-EM techniques have been extended from structural biology, which mainly focuses on structural information, to materials science, where chemical and physical information are equally important. In this Technical Review, we focus on sample preparation methods and imaging strategies to enable high-resolution imaging of beam-sensitive materials while avoiding electron-beam damage. We also survey emerging methods and applications, with an emphasis on energy materials.
Key points
-
Effective sample preparation is crucial for maintaining the native state of materials and preventing phase transitions or chemical reactions during imaging.
-
Advanced fast freezing techniques have demonstrated the potential of cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to capture intermediate states in energy-related processes by slowing or halting these processes at cryogenic temperatures. Applying external fields (electric, magnetic or light) during freezing could allow for even more precise control over these states.
-
The effect of electron radiation damage on cryo-EM imaging and spectroscopy can be mitigated by minimizing the beam dose using low-dose techniques, maximizing the signal-to-noise ratio with a direct electron detector, and optimizing imaging conditions based on specific material type and properties of the sample.
-
Analytical scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) techniques such as energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and electron energy-loss spectroscopy at cryogenic temperatures, along with 4D-STEM and ptychography for detailed structural mapping, greatly expand the utility of cryo-EM in materials science.
-
The development of cryo-electron tomography and advanced data and image processing methods has further enabled 3D imaging and analysis of materials, opening new avenues for studying complex materials systems.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui, Y. & Kourkoutis, L. Imaging sensitive materials, interfaces, and quantum materials with cryogenic electron microscopy. Acc. Chem. Res. 54, 3619–3620 (2021).
Cressey, D. & Callaway, E. Cryo-electron microscopy wins chemistry Nobel. Nature 550, 167 (2017).
Taylor, K. A. & Glaeser, R. M. Electron diffraction of frozen, hydrated protein crystals. Science 186, 1036–1037 (1974).
Dubochet, J., Chang, J.-J., Freeman, R., Lepault, J. & McDowall, A. W. Frozen aqueous suspensions. Ultramicroscopy 10, 55–61 (1982).
Chiu, W., Downing, K. H. & Dubochet, J. Cryoprotection in electron microscopy. J. Microsc. 141, 385–391 (1986).
Li, X. et al. Electron counting and beam-induced motion correction enable near-atomic-resolution single-particle cryo-EM. Nat. Methods 10, 584–590 (2013).
De Rosier, D. J. & Klug, A. Reconstruction of three dimensional structures from electron micrographs. Nature 217, 130 (1968).
Henderson, R. et al. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 213, 899–929 (1990).
Sigworth, F. J. A. Maximum-likelihood approach to single-particle image refinement. J. Struct. Biol. 122, 328–339 (1998).
Chiu, W. Electron microscopy of frozen, hydrated biological specimens. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 15, 237–257 (1986).
Nogales, E. The development of cryo-EM into a mainstream structural biology technique. Nat. Methods 13, 24–27 (2016).
Li, Y. et al. Atomic structure of sensitive battery materials and interfaces revealed by cryo-electron microscopy. Science 358, 506–510 (2017).
Li, Y. et al. Unravelling degradation mechanisms and atomic structure of organic-inorganic halide perovskites by cryo-EM. Joule 3, 2854–2866 (2019).
Li, Y. et al. Cryo-EM structures of atomic surfaces and host-guest chemistry in metal-organic frameworks. Matter 1, 428–438 (2019).
Li, Y. et al. Correlating structure and function of battery interphases at atomic resolution using cryoelectron microscopy. Joule 2, 2167–2177 (2018).
Huang, W. et al. Nanostructural and electrochemical evolution of the solid-electrolyte interphase on CuO nanowires revealed by cryogenic-electron microscopy and impedance spectroscopy. ACS Nano 13, 737–744 (2019).
Huang, W. et al. Evolution of the solid-electrolyte interphase on carbonaceous anodes visualized by atomic-resolution cryogenic-electron microscopy. Nano Lett. 19, 5140–5148 (2019).
Zachman, M. J., Tu, Z., Choudhury, S., Archer, L. A. & Kourkoutis, L. F. Cryo-STEM mapping of solid−liquid interfaces and dendrites in lithium-metal batteries. Nature 560, 345–349 (2018).
Li, X. et al. Electron counting and beam- induced motion correction enable near-atomic-resolution single-particle cryo-EM. Nat. Methods 10, 584–590 (2013).
Levin, B. D. A. et al. Characterization of sulfur and nanostructured sulfur battery cathodes in electron microscopy without sublimation artifacts. Microsc. Microanal. 23, 155–162 (2017).
Parent, L. R. et al. Directly observing micelle fusion and growth in solution by liquid-cell transmission electron microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 17140–17151 (2017).
Ianiro, A. et al. Liquid−liquid phase separation during amphiphilic self-assembly. Nat. Chem. 11, 320–328 (2019).
Patterson, J. P. et al. Observing the growth of metal−organic frameworks by in situ liquid cell transmission electron microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 7322–7328 (2015).
Sood, A. et al. Electrochemical ion insertion from the atomic to the device scale. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 847–867 (2021).
Bazant, M. Z., Thornton, K. & Ajdari, A. Diffuse-charge dynamics in electrochemical systems. Phys. Rev. E 70, 021506 (2004).
Bazant, M. Z. Theory of chemical kinetics and charge transfer based on nonequilibrium thermodynamics. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 1144–1160 (2013).
Alia, S. M. et al. Activity and durability of iridium nanoparticles in the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, F3105 (2016).
Cherevko, S., Geiger, S., Kasian, O., Mingers, A. & Mayrhofer, K. J. Oxygen evolution activity and stability of iridium in acidic media. Part 2. Electrochemically grown hydrous iridium oxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 774, 102–110 (2016).
Tang-Kong, R., Chidsey, C. E. & McIntyre, P. C. Reversible decay of oxygen evolution activity of iridium catalysts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 166, H712 (2019).
Xu, K. Electrolytes and interphases in Li-ion batteries and beyond. Chem. Rev. 114, 11503–11618 (2014).
Li, Y. et al. Electrified operando-freezing of electrocatalytic CO2 reduction cells for cryogenic electron microscopy. Nano Lett. 24, 10409–10417 (2024).
Pennycook, S. J. & Nellist, P. D. (eds) Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy: Imaging and Analysis (Springer, 2011).
Ophus, C. Four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy (4D-STEM): from scanning nanodiffraction to ptychography and beyond. Microsc. Microanal. 25, 563–582 (2019).
Chen, Z. et al. Electron ptychography achieves atomic-resolution limits set by lattice vibrations. Science 372, 826–831 (2021).
Lovejoy, T. C., Corbin, G. C., Dellby, N., Hoffman, M. V. & Krivanek, O. L. Advances in ultra-high energy resolution STEM-EELS. Microsc. Microanal. 24, 446–447 (2018).
Woodford, W. H., Carter, W. C. & Chiang, Y.-M. Design criteria for electrochemical shock resistant battery electrodes. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 8014–8024 (2012).
Gan, L. & Jensen, G. J. Electron tomography of cells. Q. Rev. Biophys. 45, 27–56 (2012).
Schmid, M. F. in Recent Advances in Electron Cryomicroscopy, Part B (eds Ludtke, S. J. & Venkataram, P. B. V.) 37–65 (Elsevier, 2011).
Hovden, R. & Muller, D. A. Electron tomography for functional nanomaterials. MRS Bull. 45, 298–304 (2020).
Scott, M. C. et al. Electron tomography at 2.4-ångström resolution. Nature 483, 444–447 (2012).
Zhang, P. Correlative cryo-electron tomography and optical microscopy of cells. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 23, 763–770 (2013).
Chang, Y.-W. et al. Correlated cryogenic photoactivated localization microscopy and cryo-electron tomography. Nat. Methods 11, 737–739 (2014).
Villa, E., Schaffer, M., Plitzko, J. M. & Baumeister, W. Opening windows into the cell: focused-ion-beam milling for cryo-electron tomography. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 23, 771–777 (2013).
Egerton, R. F. Radiation damage to organic and inorganic specimens in the TEM. Micron 119, 72–87 (2019).
Zhang, Z. et al. Resolving three-dimensional nanoscale heterogeneities in lithium metal batteries with cryoelectron tomography. Matter 8, 102266 (2025).
Dubochet et al. Cryo-electron microscopy of vitrified specimens. Q. Rev. Biophys. 21, 129–228 (1988).
Brüggeller, P. & Mayer, E. Complete vitrification in pure liquid water and dilute aqueous solutions. Nature 288, 569–571 (1980).
Mayer, E. Vitrification of pure liquid water. J. Microsc. 140, 3–15 (1985).
Dubochet, J. & McDowall, A. W. Vitrification of pure water for electron microscopy. J. Microsc. 124, 3–4 (1981).
Dubochet, J. On the development of electron cryo-microscopy (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 10842–10846 (2018).
Grassucci, R. A., Taylor, D. J. & Frank, J. Preparation of macromolecular complexes for cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2, 3239–3246 (2007).
Weissenberger, G., Henderikx, R. J. M. & Peters, P. J. Understanding the invisible hands of sample preparation for cryo-EM. Nat. Methods 18, 463–471 (2021).
Huang, W. et al. Evolution of the solid–electrolyte interphase on carbonaceous anodes visualized by atomic-resolution cryogenic electron microscopy. Nano Lett. 19, 5140–5148 (2019).
Huang, W. et al. Dynamic structure and chemistry of the silicon solid-electrolyte interphase visualized by cryogenic electron microscopy. Matter 1, 1232–1245 (2019).
Zhang, Z. et al. Cathode-electrolyte interphase in lithium batteries revealed by cryogenic electron microscopy. Matter 4, 302–312 (2021).
Zhang, Z. et al. Capturing the swelling of solid-electrolyte interphase in lithium metal batteries. Science 375, 66–70 (2022).
Russo, C. J., Scotcher, S. & Kyte, M. A precision cryostat design for manual and semi-automated cryo-plunge instruments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87, 114302 (2016).
Wang, C. et al. Trapping and imaging dynamic battery nanointerfaces via electrified cryo-EM. Sci. Adv. 11, eadv3191 (2025).
Cheng, D., Lu, B., Raghavendran, G., Zhang, M. & Meng, Y. S. Leveraging cryogenic electron microscopy for advancing battery design. Matter 5, 26–42 (2022).
Zachman, M. J., Asenath-Smith, E., Estroff, L. A. & Kourkoutis, L. F. Site-specific preparation of intact solid–liquid interfaces by label-free in situ localization and cryo-focused ion beam lift-out. Microsc. Microanal. 22, 1338–1349 (2016).
Cheng, D. et al. Unveiling the stable nature of the solid electrolyte interphase between lithium metal and LiPON via cryogenic electron microscopy. Joule 4, 2484–2500 (2020).
Zachman, M. J., Tu, Z., Archer, L. A. & Kourkoutis, L. F. Nanoscale elemental mapping of intact solid–liquid interfaces and reactive materials in energy devices enabled by cryo-FIB/SEM. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 1224–1232 (2020).
Li, G. et al. Atomically resolved imaging of radiation-sensitive metal-organic frameworks via electron ptychography. Nat. Commun. 16, 914 (2025).
Shen, B. et al. A single molecule van der Waals compass. Nature 592, 541–544 (2021).
Xiong, H. et al. In situ imaging of the sorption-induced sub-cell topological flexibility of a rigid zeolite framework. Science 376, 491–496 (2022).
Wu, M. et al. Seeing structural evolution of organic molecular nano-crystallites using 4D scanning confocal electron diffraction (4D-SCED). Nat. Commun. 13, 2911 (2022).
Liu, L. et al. Direct imaging of atomically dispersed molybdenum that enables location of aluminum in the framework of zeolite ZSM-5. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 819–825 (2020).
Li, G. et al. Unraveling various stacking modes and local structures in poly(triazine imide) materials via low-dose electron microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 147, 3896–3903 (2025).
Lv, J., Zhang, H., Zhang, D., Liu, L. & Han, Y. Low-dose electron microscopy imaging of electron beam-sensitive crystalline materials. Acc. Mater. Res. 3, 552–564 (2022).
Mastronarde, D. N. Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J. Struct. Biol. 152, 36–51 (2005).
Levin, B. D. A. Direct detectors and their applications in electron microscopy for materials science. J. Phys. Mater. 4, 042005 (2021).
Wang, X. et al. New insights on the structure of electrochemically deposited lithium metal and its solid electrolyte interphases via cryogenic TEM. Nano Lett. 17, 7606–7612 (2017).
Weng, S., Li, Y. & Wang, X. Cryo-EM for battery materials and interfaces: workflow, achievements, and perspectives. iScience 24, 103402 (2021).
Wang, X., Li, Y. & Meng, Y. S. Cryogenic electron microscopy for characterizing and diagnosing batteries. Joule 2, 2225–2234 (2018).
Quinn, J. et al. Tracking the oxidation of silicon anodes using cryo-EELS upon battery cycling. ACS Nano 16, 21063–21070 (2022).
Xu, Y. et al. Sweeping potential regulated structural and chemical evolution of solid-electrolyte interphase on Cu and Li as revealed by cryo-TEM. Nano Energy 76, 105040 (2020).
Dai, Q. et al. Cryo-EM studies of atomic-scale structures of interfaces in garnet-type electrolyte based solid-state batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2208682 (2022).
Guo, B. et al. Cryo-EM revealing the origin of excessive capacity of the Se cathode in sulfide-based all-solid-state Li–Se batteries. ACS Nano 16, 17414–17423 (2022).
Liu, Y. et al. Visualizing the sensitive lithium with atomic precision: cryogenic electron microscopy for batteries. Acc. Chem. Res. 54, 2088–2099 (2021).
Ju, Z. Cryo-electron microscopy for unveiling the sensitive battery materials. Small Sci. 1, 2100055 (2021).
Dou, W. et al. Review on the binders for sustainable high-energy-density lithium ion batteries: status, solutions, and prospects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2305161 (2023).
Yousaf, M. et al. Visualization of battery materials and their interfaces/interphases using cryogenic electron microscopy. Mater. Today 58, 238–274 (2022).
Zhang, J. et al. Construction of stable Li2O-rich solid electrolyte interphase for practical PEO-based Li-metal batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 14, 2302587 (2024).
Li, S. et al. Cation replacement method enables high-performance electrolytes for multivalent metal batteries. Nat. Energy 9, 285–297 (2024).
Sun, T. et al. Atomic-level characterization of dynamics of a 3D covalent organic framework by cryo-electron diffraction tomography. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 10962–10966 (2019).
Beyeh, N. K. et al. Crystalline cyclophane–protein cage frameworks. ACS Nano 12, 8029–8036 (2018).
Zhao, W. et al. Nanoscale covalent organic frameworks for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production. Nat. Commun. 15, 6482 (2024).
Chen, J. et al. Chiral inorganic nanomaterials characterized by advanced TEM: a qualitative and quantitative study. Adv. Mater. 36, 2410676 (2024).
Ogata, A. F. et al. Direct observation of amorphous precursor phases in the nucleation of protein-metal-organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 1433–1442 (2020).
Franco, C. et al. Biomimetic synthesis of sub-20 nm covalent organic frameworks in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 3540–3547 (2020).
Sun, B. et al. Homochiral porous nanosheets for enantiomer sieving. Nat. Mater. 17, 599–604 (2018).
Fan, Q. et al. Phase segregation dynamics in mixed-halide perovskites revealed by plunge-freeze cryogenic electron microscopy. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 6, 102653 (2025).
Huang, R. et al. Real-time direct observation of Li in LiCoO2 cathode material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 051913 (2011).
Fundenberger, J.-J., Morawiec, A., Bouzy, E. & Lecomte, J. S. Polycrystal orientation maps from TEM. Ultramicroscopy 96, 127–137 (2003).
Kobler, A., Kashiwar, A., Hahn, H. & Kü bel, C. Combination of in situ straining and ACOM TEM: a novel method for analysis of plastic deformation of nanocrystalline metals. Ultramicroscopy 128, 68–81 (2013).
Usuda, K. et al. Strain relaxation of strained-Si layers on SiGe-on-insulator (SGOI) structures after mesa isolation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 224, 113–116 (2004).
Béché, A., Rouviè re, J. L., Clément, L. & Hartmann, J. M. Improved precision in strain measurement using nanobeam electron diffraction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 123114 (2009).
Caswell, T. A. et al. A high-speed area detector for novel imaging techniques in a scanning transmission electron microscope. Ultramicroscopy 109, 304–311 (2009).
Savitzky, B. H. et al. Py4DSTEM: a software package for four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy data analysis. Microsc. Microanal. 27, 712–743 (2021).
Wakonig, K. et al. PtychoShelves, a versatile high-level framework for high-performance analysis of ptychographic data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 53, 574–586 (2020).
Jiang, Y. Fold_slice. GitHub https://github.com/yijiang1/fold_slice (2020).
Panova, O. et al. Diffraction imaging of nanocrystalline structures in organic semiconductor molecular thin films. Nat. Mater. 18, 860 (2019).
Bustillo, K. C. et al. 4D-STEM of beam-sensitive materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 54, 2543–2551 (2021).
Tsarfati, Y. et al. The hierarchical structure of organic mixed ionic−electronic conductors and its evolution in water. Nat. Mater. 24, 101–108 (2025).
Gallagher-Jones, M. et al. Nanoscale mosaicity revealed in peptide microcrystals by scanning electron nanodiffraction. Commun. Biol. 2, 26 (2019).
Mu, X., Mazilkin, A., Sprau, C., Colsmann, A. & Kübel, C. Mapping structure and morphology of amorphous organic thin films by 4D-STEM pair distribution function analysis. Microscopy 68, 301–309 (2019).
Donohue, J. et al. Cryogenic 4D-STEM analysis of an amorphous-crystalline polymer blend: combined nanocrystalline and amorphous phase mapping. iScience 25, 103882 (2022).
Markovich, D. et al. Revealing the crystalline architecture of semicrystalline ion exchange membranes for the design of conductive and durable alkaline anion exchange membranes. ACS Nano 19, 20871–20880 (2025).
Koh, H., Das, S., Zhang, Y., Detsi, E. & Stach, E. Electron beam-induced artifacts in SEI characterization: evidence from controlled-dose diffraction studies. ACS Energy Lett. 10, 534–540 (2025).
Jiang, Y. et al. Electron ptychography of 2D materials to deep sub-ångström resolution. Nature 559, 343–349 (2018).
Zhang, H. et al. Three-dimensional inhomogeneity of zeolite structure and composition revealed by electron ptychography. Science 380, 633–638 (2023).
Zhou, L. et al. Low-dose phase retrieval of biological specimens using cryo-electron ptychography. Nat. Commun. 11, 2773 (2020).
Pei, X. et al. Cryogenic electron ptychographic single particle analysis with wide bandwidth information transfer. Nat. Commun. 14, 3027 (2023).
Küçükoğlu, B. et al. Low-dose cryo-electron ptychography of proteins at sub-nanometer resolution. Nat. Commun. 15, 8062 (2024).
García de Arquer, F. P. et al. CO2 electrolysis to multicarbon products at activities greater than 1 A cm−2. Science 367, 661–666 (2020).
Dandey, V. P. et al. Time-resolved cryo-EM using Spotiton. Nat. Methods 17, 897–900 (2020).
Hovden, R. et al. Atomic lattice disorder in charge-density-wave phases of exfoliated dichalcogenides (1T-TaS2). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, 11420 (2016).
Savitzky, B. H. et al. Image registration of low signal-to-noise cryo-STEM data. Ultramicroscopy 191, 56–65 (2018).
El Baggari, I. et al. Nature and evolution of incommensurate charge order in manganites visualized with cryogenic scanning transmission electron microscopy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115, 1445 (2018).
El Baggari, I. et al. Charge order textures induced by non-linear couplings in a half-doped manganite. Nat. Commun. 12, 3747 (2021).
Keimer, B. & Moore, J. E. The physics of quantum materials. Nat. Phys. 13, 1045–1055 (2017).
Han, M. et al. Topological magnetic-spin textures in two-dimensional van der Waals Cr2Ge2Te6. Nano Lett. 19, 7859–7865 (2019).
Midgley, P. A. & Dunin-Borkowski, R. E. Electron tomography and holography in materials science. Nat. Mater. 8, 271–280 (2009).
Hagen, W. J., Wan, W. & Briggs, J. A. Implementation of a cryo-electron tomography tilt-scheme optimized for high resolution subtomogram averaging. J. Struct. Biol. 197, 191–198 (2017).
Hoppe, W., Langer, R., Knesch, G. & Poppe, C. Protein-Kristallstrukturanalyse mit Elektronenstrahlen. Naturwissenschaften 55, 333–336 (1968).
Hart, R. G. Electron microscopy of unstained biological material: the polytropic montage. Science 159, 1464–1467 (1968).
Cheng, Y. Single-particle cryo-EM — how did it get here and where will it go. Science 361, 876–880 (2018).
Turk, M. & Baumeister, W. The promise and the challenges of cryo-electron tomography. FEBS Lett. 594, 3243–3261 (2020).
Danev, R., Yanagisawa, H. & Kikkawa, M. Cryo-electron microscopy methodology: current aspects and future directions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 44, 837–848 (2019).
Beck, M. & Baumeister, W. Cryo-electron tomography: can it reveal the molecular sociology of cells in atomic detail? Trends Cell Biol. 26, 825–837 (2016).
Vos, M. R. et al. Insights in the organization of DNA−surfactant monolayers using cryo-electron tomography. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 11894–11895 (2007).
Parry, A., Bomans, P. H., Holder, S. J., Sommerdijk, N. A. & Biagini, S. C. Cryo electron tomography reveals confined complex morphologies of tripeptide-containing amphiphilic double-comb diblock copolymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 8859–8862 (2008).
Pouget, E. M. et al. The initial stages of template-controlled CaCO3 formation revealed by cryo-TEM. Science 323, 1455–1458 (2009).
Allen, F. I. et al. Morphology of hydrated as-cast nafion revealed through cryo electron tomography. ACS Macro Lett. 4, 1–5 (2015).
Wolf, S. G., Houben, L. & Elbaum, M. Cryo-scanning transmission electron tomography of vitrified cells. Nat. Methods 11, 423–428 (2014).
Han, B. et al. Cryo-electron tomography of highly deformable and adherent solid-electrolyte interphase exoskeleton in Li-metal batteries with ether-based electrolyte. Adv. Mater. 34, 2108252 (2022).
He, Y. et al. Progressive growth of the solid–electrolyte interphase towards the Si anode interior causes capacity fading. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1113–1120 (2021).
Radon, J. On the determination of functions from their integral values along certain manifolds. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 5, 170–176 (1986).
Bracewell, R. N. Strip integration in radio astronomy. Aust. J. Phys. 9, 198–217 (1956).
Bepler, T. et al. Topaz-Denoise: general deep denoising models for cryoEM and cryoET. Nat. Commun. 11, 5208 (2020).
Ding, G., Liu, Y., Zhang, R. & Xin, H. L. A joint deep learning model to recover information and reduce artifacts in missing-wedge sinograms for electron tomography and beyond. Sci. Rep. 9, 12803 (2019).
Liu, J., He, J., Zhu, Q. & Xu, Z. TomoGAN: low-dose cryo-electron tomography with generative adversarial networks. Sci. Rep. 11, 664 (2021).
Susi, T., Meyer, J. C. & Kotakoski, J. Quantifying transmission electron microscopy irradiation effects using two-dimensional materials. Nat. Rev. Phys. 1, 397–405 (2019).
Faruqi, A. R. & McMullan, G. Direct imaging detectors for electron microscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 878, 180–190 (2018).
Mendez, J. H., Mehrani, A., Randolph, P. & Stagg, S. Throughput and resolution with a next-generation direct electron detector. IUCrJ 6, 1007–1013 (2019).
K3 direct detection cameras. Gatan https://www.sep.ae/storage/app/products/brochure/1712047444_K3DatasheetFL4.pdf.
McMullan, G., Faruqi, A. R., Clare, D. & Henderson, A. R. Comparison of optimal performance at 300 keV of three direct electron detectors for use in low dose electron microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 147, 156–163 (2014).
Electron microscope pixel array detector (EMPAD). ThermoFisher https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/MSD/Datasheets/EMPAD-Datasheet.pdf (2021).
User Manual Dectris Arina v1.8.1. Dectris https://media.dectris.com/filer_public/2f/0d/2f0d2d2d-320a-4190-96ed-d545b03fcc54/usermanual_arina_181.pdf (2024).
Chiu, W. et al. Electron radiation damage of a thin protein crystal at 4 K. Ultramicroscopy 6, 291–295 (1981).
Pfeil-Gardiner, O., Mills, D. J., Vonck, J. & Kuehlbrandt, W. A comparative study of single-particle cryo-EM with liquid-nitrogen and liquid-helium cooling. IUCrJ 6, 1099–1105 (2019).
Egerton, R. F., McLeod, R., Wang, F. & Malac, M. Basic questions related to electron-induced sputtering in the TEM. Ultramicroscopy 110, 991–997 (2010).
Wang, F. et al. Chemical distribution and bonding of lithium in intercalated graphite: identification with optimized electron energy loss spectroscopy. ACS Nano 5, 1190–1197 (2011).
Tzyy-Wen, J. & Chiu, W. Quantitative assessment of radiation damage in a thin protein crystal. J. Microsc. 136, 35–44 (1984).
Benjamin, B. E. et al. Radiation damage effects at four specimen temperatures from 4–100 K. J. Struct. Biol. 169, 331–341 (2010).
Mu, X. et al. Mapping structure and morphology of amorphous organic thin films by STEM pair distribution function analysis. Microscopy 68, 301–309 (2019).
Egerton, R. F. Control of radiation damage in the TEM. Ultramicroscopy 127, 100–108 (2013).
Hooley, R. W. M. et al. A quantitative evaluation of electron beam sensitivity in calcite nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 902, 012005 (2017).
Pan, M. & Crozier, P. A. Quantitative imaging and diffraction of zeolites using a slow-scan CCD camera. Ultramicroscopy 52, 487–498 (1993).
Drummy, L. F., Yang, J. & Martin, D. C. Low-voltage electron microscopy of polymer and organic molecular thin films. Ultramicroscopy 99, 247–256 (2004).
Glaeser, R. M. Limitations to significant information in biological electron microscopy as a result of radiation damage. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 36, 466–482 (1971).
Glaeser, R. M. Retrospective: radiation damage and its associated ‘information limitations’. J. Struct. Biol. 163, 271–276 (2008).
Siegel, G. Influence of very low temperature on radiation damage of organic crystals irradiated by 100-keV electrons. Z. Naturforsch. 27, 325–332 (1972).
Fryer, J. R., McConnell, C. H., Zelmin, F. & Dorset, D. K. Effect of temperature on radiation damage to aromatic organic molecules. Ultramicroscopy 40, 163–169 (1992).
Li, Y. et al. The cage effect of electron beam irradiation damage in cryo-electron microscopy. npj Comput. Mater. 10, 115 (2024).
Fryer, J. R. Radiation damage in organic crystalline films. Ultramicroscopy 14, 227–236 (1984).
Hobbs, L. W. Radiation damage in electron microscopy of inorganic solids. Ultramicroscopy 3, 381–386 (1978).
Shockley, W. Problems related to p–n junctions in silicon. Czech. J. Phys. 11, 81 (1961).
Arumainayagam, C. R. et al. Low-energy electron-induced reactions in condensed matter. Surf. Sci. Rep. 65, 1–44 (2010).
Neelisetty, K. K. et al. Electron beam effects on oxide thin films — structure and electrical property correlations. Microsc. Microanal. 25, 592–600 (2019).
Wu, B. & Neureuther, A. R. Energy deposition and transfer in electron-beam lithography. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 19, 2508–2511 (2001).
Regev, O. et al. A study of the microstructure of a four-component nonionic microemulsion by cryo-TEM, NMR, SAXS, and SANS. Langmuir 12, 668–674 (1996).
Nave, C. & Hill, M. A. Will reduced radiation damage occur with very small crystals? J. Synchrotron Radiat. 12, 299–303 (2005).
Egerton, R. F., Lazar, S. & Libera, M. Delocalized radiation damage in polymers. Micron 43, 2–7 (2012).
Egerton, R. F., Li, P. & Malac, M. Radiation damage in the TEM and SEM. Micron 35, 399–409 (2004).
Sansinena, M., Santos, M. V., Zaritzky, N. & Chirife, J. Comparison of heat transfer in liquid and slush nitrogen by numerical simulation of cooling rates for French straws used for sperm cryopreservation. Theriogenology 77, 1717–1721 (2012).
Shirota, M. et al. Dynamic Leidenfrost effect: relevant time and length scales. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 064501 (2016).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge cryo-EM FWP support from the Office of Basic Energy Sciences, US Department of Energy, Division of Materials Science and Engineering, DE-AC02-76SF00515.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to all aspects of this work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Physics thanks Yimo Han, Xuefeng Wang and Yu Han for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Y., Zhang, Z., Sinclair, R. et al. Cryogenic electron microscopy and tomography for beam-sensitive materials. Nat Rev Phys 8, 40–54 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42254-025-00896-4
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42254-025-00896-4