Abstract
In highly regulated domains such as finance and healthcare, where stringent data-sharing constraints pose substantial obstacles, federated learning (FL) has emerged as a transformative paradigm in distributed machine learning, facilitating collaborative model training, preserving data decentralization and upholding governance standards. Despite its advantages, FL is vulnerable to poisoning attacks during central model aggregation, prompting the development of Byzantine-robust FL systems that use robust aggregation rules to counter malicious attacks. However, neural network models in such systems are susceptible to unintentionally memorizing and revealing individual training instances, thereby introducing substantial information leakage risks, as adversaries may exploit this vulnerability to reconstruct sensitive data through model outputs transmitted over the air. Existing solutions fall short of providing a viable Byzantine-robust FL system that is completely secure against information leakage and is computationally efficient. To address these concerns, we propose Lancelot, an efficient and effective Byzantine-robust FL framework that uses fully homomorphic encryption to safeguard against malicious client activities. Lancelot introduces a mask-based encrypted sorting mechanism that overcomes the limitations of multiplication depth in ciphertext sorting with zero information leakage. It incorporates cryptographic enhancements like lazy relinearization, dynamic hoisting and GPU acceleration to ensure practical computational efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Lancelot surpasses existing approaches, achieving a 20-fold enhancement in processing speed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Machine learning (ML) has achieved remarkable success, largely driven by access to large, diverse datasets for researchers. However, in domains such as healthcare and finance, strict privacy regulations and legal constraints hinder data sharing, limiting the development of more accurate and generalizable models. Institutions in these sectors often cannot centralize or exchange data due to compliance with laws like HIPAA1 and GDPR2, which impose strict controls on the transfer of personal, even pseudonymized, data across jurisdictions, bringing substantial challenges for collaborative research and model advancement.
Federated learning (FL) is a paradigm that enables knowledge sharing without gathering personal data. For example, FL allows healthcare providers to jointly develop models by exchanging only aggregated results or updated models and maintain data governance. Therefore, FL provides opportunities to utilize large and diverse volumes of data distributed across multiple institutions, aiding in the development of accurate, unbiased and generalizable AI algorithms and accelerating discoveries3. This is especially vital for rare diseases or genomic data analysis4, where individual institutions often lack sufficient patient data to identify statistically meaningful patterns. Owing to its decentralized architecture, FL is inherently vulnerable to adversarial manipulations by malicious clients, either as fake entities introduced by attackers or compromised legitimate participants. These adversaries can undermine the integrity of the global model by injecting poisoned data5/models6 during local training. Such attacks can lead to widespread mispredictions, posing grave risks in sensitive domains. To counter these threats, Byzantine-robust FL (BRFL)7 aims to construct a reliable global model even in the presence of malicious clients by using Byzantine-robust aggregation rules. It is capable of identifying and excluding statistical outliers in local model updates, for example, by comparing weight distances, before updating the global model. For example, BRFL has been applied to diagnose thorax diseases using X-rays and identify pigmented skin lesions, mitigating malicious attacks and preserving privacy by avoiding raw data sharing8.
However, BRFL cannot fully meet the compliance standards required by institutions under strict regulations. Specifically, BRFL relies on clients sharing gradient updates with a central server, which poses risks since deep neural networks can memorize individual training instances, potentially leading to information leakage breaches. For example, DLG9 and IDLG10 showed the possibility of stealing private training data from the shared gradients of other clients. To mitigate such information leakage, more advanced solutions for FL have been explored. For example, differential privacy11,12 seeks to safeguard sensitive information by injecting carefully calibrated noise into the data or model updates. However, achieving strong privacy guarantees often necessitates a substantial amount of noise, which can severely impair model accuracy. Although recent techniques can relieve such accuracy dropping to some extent13,14, the parameters of the model still appear in plaintext. Unlike differential privacy that can directly protect data privacy15,16, cryptographic frameworks such as multi-party computation17, partially homomorphic encryption (HE)18 and fully homomorphic encryption (FHE)19 have been developed to enable secure computations and prevent unauthorized access. These methods preserve data confidentiality throughout the processing pipeline, though they exhibit differing trade-offs in terms of computational efficiency and communication overhead. For example, multi-party computation incurs higher network communication overhead as the number of data providers grows. Partially HE, such as BatchCrypt20, is efficient for standard aggregation tasks in conventional FL. However, partially HE falls short when it comes to supporting the more advanced operations required in BRFL. Specifically, BRFL demands not only addition operation (for example, for model aggregation) but also more complex operations, such as multiplication and encrypted sorting (for example, for robust client selection), which are within the capabilities of FHE. Furthermore, FHE offers stronger post-quantum protection guarantees21, making it a promising approach to ensuring data confidentiality.
There are mainly two critical challenges to building an FHE-based BRFL system. The first challenge arises from performing sorting operations on ciphertexts for implementing the BRFL aggregation rules, which is constrained by the limited multiplication depth. For instance, many typical BRFL aggregation rules necessitate sorting distances computed from model weights, which entails a substantial number of ciphertext comparisons throughout the training process. Second, ciphertext operations like addition or multiplication are computationally intensive, greatly prolonging training. For example, training time typically increases thousands of times after adopting FHE20. Recently, several open-source platforms, such as FedScale22, Flower23, NVFLARE24, IBM-FL25 and FedML26, have been developed to simplify access to FL algorithms. It allows users to federate any workload, any ML framework and any programming language. However, none of the existing platforms effectively addresses the issue of indirect information leakage in BRFL. It remains uncertain whether these solutions can meaningfully streamline FHE-based BRFL systems compared with traditional centralized workflows, particularly when local model updates may still be regarded as personally identifiable information. Thus, our goal is to design an FHE-based BRFL system that addresses these challenges.
Therefore, to comply with data protection regulations such as HIPAA1 and GDPR2, this paper aims to investigate a problem under the combination of BRFL and FHE in which data remain in plaintext on local devices (clients) and are aggregated in ciphertext on the cloud (server). In particular, to address the two challenges, we propose an efficient and effective system, called Lancelot, which uses an interactive FL paradigm for decentralized collaboration between institutions, enabling the training of high-performance, robust models without information leakage and greatly reducing computation overhead. The paradigm includes a mask-based encrypted sorting method that alleviates ciphertext multiplication depth constraints through an interactive mode. Additionally, Lancelot incorporates algorithmic optimizations and hardware acceleration, including enhanced pairwise ciphertext multiplication strategies, polynomial matrix multiplication and complex operation additions, all of which are critical to its efficiency. Furthermore, the framework is designed to integrate seamlessly with differential privacy techniques (Supplementary Section 2.4.2). Our contributions are as follows: (1) we propose an efficient and effective FHE-based BRFL system for multi-institutional collaborations with heterogeneous data sources; (2) we incorporate FHE into BRFL to protect data confidentiality; and (3) we effectively reduce the computation overhead required to collaborate.
Results
System model and overview
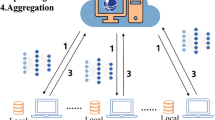
As shown in Fig. 1, Lancelot involves three entities: clients, server and key generation centre. The key generation centre, a trusted institution, generates public/private key pairs and distributes public keys to clients. Training data are stored in the clients entity, which only holds public keys, and its goal is to benefit from a well-trained global model. The server receives encrypted models from clients and performs computations directly on the ciphertext.
The key generation centre generates cryptographic keys: a secret key (sk) for decrypting ciphertexts, a public key (pk) for encrypting data and an evaluation key (evk) for homomorphic operations (for example, ciphertext multiplication or rotation). pk is securely shared with clients, and evk, with the server. The key generation centre handles key generation, robust aggregation rule processing and decryption of the aggregated model. The clients entity encrypts its models and sends them to the server, which processes the models in encrypted form using evk.
We provide an overview of Lancelot, which consists of the following nine stages. (1) Clients encrypt their trained models and (2) send them to the server. (3) The server then calculates the distance between models from different clients based on the aggregation rules with ciphertext. (4) The resulting encrypted distance list is then (5) sent to the key generation centre for decryption and sorting. (6) The sorted distance list is later encrypted into an intermediate mask and (7) sent back to the server for aggregation. The mask encodes the index of selected clients, enabling the server to apply aggregation rules directly on the encrypted data. (8) The server then combines the selected models based on the aggregation rules and sends the aggregated model to the key generation centre. (9) The key generation centre finally decrypts the model using the secret key and distributes it to all clients. In the final step, the model is decrypted and shared with all clients without exposing individual client data, ensuring data confidentiality. To address computational delays, we propose two acceleration strategies: cryptographic optimizations and hardware acceleration, which are detailed in the Methods.
Baseline and datasets
To evaluate the effectiveness of Lancelot, we conduct experiments on a public image classification benchmark with four datasets. We compare three BRFL algorithms: Krum27, Multi-Krum27 and Median28. Krum selects a single model among n local models that aligns most with others. Multi-Krum extends this by selecting multiple local model updates. Median sorts each parameter’s values across local updates and uses the median value. We modify the conventional Median approach to select median clients based on distance. We also compare vanilla BRFL and OpenFHE implementations of Krum, Multi-Krum and Median. Vanilla BRFL performs these algorithms in plaintext, whereas OpenFHE29, a state-of-the-art FHE library, offers efficient implementations of FHE schemes. Experiments are conducted on LeNet-5, ResNet-18, ResNet-34 and ResNet-50 models. For accuracy validation, we also present results comparing FedAvg under targeted attacks30 and untargeted attacks, like MPAF31.
We conduct experiments on Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology (MNIST), Fashion Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology (FMNIST), CIFAR-10 and Street View House Numbers (SVHN) datasets. MNIST and FMNIST each contain 60,000 training images of 28 × 28 pixels, whereas CIFAR-10 includes 50,000 RGB training images of 32 × 32 pixels. All three datasets have 10,000 test images for performance evaluation. SVHN, used for large-scale benchmarking, is a digit classification dataset of 32 × 32 pixels with 73,000 training images and 26,000 testing images of digits (0–9) cropped from house number plates. Moreover, we apply quantity skew32 across 10, 50 and 100 clients to simulate non-independent and identically distributed FL settings. Due to page limits, we use 10 clients for Krum, 50 for Multi-Krum and 100 for the Median algorithms, as the combination of aggregation algorithms and client numbers yields similar results.
Evaluation metrics and implementation details
To evaluate Lancelot, we compare its classification accuracy with the plaintext to validate the correctness of Lancelot. Additionally, we measure the total execution time per round, including both computation and communication time, to assess system performance. We design and implement Lancelot using NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 GPU and 4 × A100 GPUs on Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTS. Specifically, we allocate one process to manage server tasks, including compromised client selection and model aggregation. For each client, we establish a separate process responsible for local model updates and manage the data migration between CPUs and GPUs. Interprocess communication, executed in Python 3, facilitates the interaction between the server and nodes. The deep learning components of our system are implemented using PyTorch. In all experiments, we use stochastic gradient descent as the optimizer for local updates with a learning rate of 0.001. The local batch size is 32, and the default local epoch is 1. Each round of local training takes several gradient steps equivalent to one epoch over the private data. We limit the maximum global learning round to 200 for the FL methods. The model’s performance on the validation set is monitored using accuracy, and the training process is stopped early if the validation accuracy does not improve for eight consecutive epochs. We implement the FHE operation based on a well-designed HE GPU libraries33. We use the multiplication depth of 3 for the cryptographic parameters, the scaling factor bit digit of 40, an HE packing batch size of 4,096 and a security level of 128 bits as our default HE cryptographic parameters during the evaluation.
Performance of image classification benchmark
Accuracy and system performance of image classification datasets
We compare the total execution time per round for Lancelot, OpenFHE and plaintext on the MNIST, FMNIST, CIFAR-10 and SVHN datasets using LeNet-5, ResNet-18, ResNet-34 and ResNet-50 models. For simplicity and due to space constraints, we show results for 10 clients in Krum, 50 clients in Multi-Krum and 100 clients in Median, as other configurations (for example, 50 and 100 clients for Krum) yield similar results. First, we evaluate the accuracy of Krum, Multi-Krum and Median under targeted and untargeted attacks. Moreover, as shown in Fig. 2a, these methods outperform FedAvg. Additionally, Fig. 2b demonstrates that Lancelot drastically reduces the computation time and maintains data privacy. For instance, in the Krum algorithm with the ResNet-34 model on CIFAR-10, plaintext takes 30.13 s per round, whereas OpenFHE incurs 11,559.84 s, an impractical time cost. By using Lancelot, the time is reduced to 548.20 s on the CIFAR-10 dataset, achieving an ~21× speed-up, lowering complexity from hours to minutes. Across all datasets and models, Lancelot consistently reduces latency compared with other methods, achieving stable acceleration with constant multiplicity. We also observe that the time growth depends only on the model’s parameter size and the number of clients.
a, Accuracy comparison of Lancelot under targeted and untarget attacks across the MNIST, FMNIST, CIFAR-10 and SVHN datasets. b, Execution time per round of Lancelot, including both computation and communication time, among three methods across three datasets. Speed-up refers to the acceleration ratio between Lancelot and OpenFHE. MK, Multi-Krum.
Ablation study
We ablate Lancelot to analyse how various factors influence its system performance, that is, the total execution time, on the aforementioned datasets. Unless stated otherwise, we use the same settings as the leading results across all models. Specifically, we categorize our approaches into two types: cryptographic optimization and hardware acceleration. To enhance performance, we integrate hardware acceleration with algorithmic approaches, such as lazy relinearization and dynamic hoisting, for comparison. A detailed illustration of lazy relinearization and dynamic hoisting is shown in Fig. 3. Note that the speed-up achieved through cryptographic optimizations is a result of the hardware acceleration we have already adopted. As shown in Fig. 4, cryptographic optimizations like lazy relinearization and dynamic hoisting notably reduce the computation time across datasets and models. For instance, in the FMNIST dataset with the Krum method, lazy relinearization achieves a 3.76× speed-up, reducing the computation time from 8.57 s to 2.28 s. Similarly, dynamic hoisting provides a 40% speed-up, decreasing the computation time from 0.44 s to 0.32 s. Regarding hardware acceleration (Fig. 4), it delivers substantial speed-ups, particularly for GPU-friendly operations like polynomial multiplications, which are data-independent. For example, in the FMNIST dataset using Krum, hardware acceleration achieves a performance boost. Overall, implementing hardware acceleration in Lancelot results in over a 20-fold speed increase. Further details on lazy relinearization, dynamic hoisting and hardware acceleration are provided in the Methods.
Ablation study of Lancelot for cryptographic optimizations and hardware acceleration (HA) among three methods across three different datasets. LR, lazy relinearization; DH, dynamic hoisting.
Analysis of hardware performance
To further evaluate the system performance of Lancelot, we provide a practical hardware performance analysis. In particular, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of GPU processing time and other relevant hardware metrics for each user, both with and without the proposed hardware-level optimizations across MNIST, FMNIST, CIFAR-10 and SVHN. In this experiment, we measure several key metrics: GPU execution time, load efficiency (LoadEff), throughput (Elem/s) and global memory bandwidth (GlobalMem BW). As demonstrated in Table 1, the introduction of lazy relinearization and dynamic hoisting remarkably improves all the measured metrics. For example, lazy relinearization reduces GPU execution time by approximately eight times, increases load efficiency from about 59% to 93%, and enhances global memory bandwidth by more than eightfold. Similarly, dynamic hoisting results in a fourfold reduction in GPU time and a quadrupling of data throughput. These results clearly show the effectiveness of our optimization strategies in improving the overall GPU performance, demonstrating both efficiency gains and trade-offs introduced by our approach.
Analysis of cryptographic hyperparameter
We analyse the impact of FHE packing size N, representing the number of slots in a single ciphertext, typically ranging from 213 to 217. As shown in Fig. 5, we examine how N affects the execution time across the MNIST, FMNIST, CIFAR-10 and SVHN datasets for different models. We observe a clear trend in which the execution time decreases for deeper models, such as ResNet-18, ResNet-34 and ResNet-50, as the packing size increases, although the rate of reduction varies across models and datasets. For example, in the SVHN dataset with ResNet-50, the execution time decreases moderately from 609.20 s to 443.78 s as N increases from 213 to 217. Conversely, the LeNet-5 model on MNIST shows an unusual pattern, with the execution time initially dropping to 3.65 s at 213 but rising to 8.53 s at 217. These variations stem from model complexity, dataset characteristics and FHE packing efficiency. For instance, a potential reason is that the computation time per round for deeper models, such as ResNet-34, benefits from increased packing size, as a single ciphertext can hold more parameters. With fewer ciphertexts needed and constant parameter sizes, our hardware acceleration approach processes ciphertexts more efficiently, reducing the overall computation time.
We deploy the LeNet-5, ResNet-18, ResNet-34 and ResNet-50 models on the MNIST, FMNIST, CIFAR-10 and SVHN datasets, respectively. From left to right, the results correspond to experiments conducted on 10, 50 and 100 clients.
Analysis of large-scale real-world benchmarks, testbed and attacks
We present extensive experiments evaluating Lancelot on large-scale real-world benchmarks, including a medical dataset comprising diverse biomedical tasks, for example, colorectal cancer detection, peripheral blood analysis and thoracic disease diagnosis using X-rays, and two higher-resolution and dimension datasets, such as ImageNet34 and MosMedData35. The results on MedMNIST show that Lancelot delivers a 20-fold speed-up over OpenFHE and maintain data confidentiality. Comprehensive details are provided in Supplementary Section 1.1. To further evaluate communication overhead at various stages and compare it with computational overhead, we implemented a prototype of Lancelot on a real-world edge device within a practical network environment (for example, a local area network). Our evaluation shows that Lancelot substantially reduces server-side computation time and introduces only negligible additional communication latency. Supplementary Section 1.2 provides further details. To analyse the potential information leakage, we evaluate the robustness of Lancelot against various both external and internal attacks, including DLG9, IDLG10, inverting gradients attacks36, prior-aware inverting gradient attacks14, epoch-wise attacks37, backdoor attacks38 and label-flipping attacks30. As detailed in Supplementary Section 1.3, the results demonstrate that Lancelot effectively defends against both external and internal threats. Furthermore, to avoid the key-recovery attack39, we adopt the noise-flooding technique40 in Lancelot. The key idea is to introduce independent noise to decryption operations, disrupting the attacker’s ability to infer key-related information (Supplementary Section 1.4.1).
Discussion
In this paper, we demonstrate Lancelot, an efficient and effective BRFL framework for several complex tasks, including image recognition and biomedical diagnosis. Lancelot combines the strengths of both conventional BRFL approaches and cryptographic frameworks for secure computation, showing highly promising results for enhancing BRFL services in a computation-effective and reliable manner. In BRFL, hyperparameters can be uniform across clients or vary between them. In Lancelot, we use the same hyperparameters for all clients, distributed by a key generation centre to ensure synchronization and consistency. However, clients may also use different hyperparameters, which can affect convergence speed but not the accuracy of the HE process. To relieve this phenomenon, there are two main research directions to alleviate such situations. On one hand, algorithmic approaches use asynchronous aggregation such as weighted aggregation41, model splitting42 or clustered FL43. On the other hand, systematic approaches such as Oort44, PyramidFL45 and ArtFL32 use dynamic client selection and dropping strategies to address the challenges posed by such variations.
To the best of our knowledge, Lancelot is the first work to combine BRFL and FHE. There are limited works available for direct comparison with Lancelot. To broaden the scope of this work, we compare Lancelot with two categories of related works: heterogeneous-platform HE libraries and accelerators, and conventional FHE-based FL frameworks. In particular, heterogeneous-platform HE libraries and accelerators are typically designed for specific hardware platforms. For instance, BTS46 targets application-specific integrated circuits, whereas Flagger47 is optimized for field-programmable gate arrays. Other libraries, such as TenSEAL48, HElib49 and HEAAN50, support a wider range of platforms but are generally slower than Lancelot due to its high degree of parallelism enabled by GPU acceleration. In particular, OpenFHE29, which we select as the baseline, is the fastest among these libraries since it supports multi-process execution on CPUs. Furthermore, conventional FHE-based FL frameworks, such as MQFL-FHE51, EfficientHE-FL52, MASKCRYPT53 and FedML-HE54, cannot support BRFL. This limitation arises because these frameworks do not address the depth constraints in ciphertexts that are intrinsic to solving the sorting problem under Byzantine-robust aggregation rules. Detailed comparisons could be referred to in Supplementary Section 1.4.3.
Lancelot has scalable potential in assisting diagnosis and various other applications, such as stroke rehabilitation and Alzheimer’s disease monitoring55. Our study was enabled by the synergistic combination of ML technologies and cryptographic development. Similar to multi-server FL setups56,57,58, in Lancelot, the key generation centre functions as a secure server without high requirement for computational capabilities, making it particularly valuable for scenarios with limited computational resources, such as small- and medium-sized enterprises that lack extensive infrastructure for secure BRFL. Although substantial progress in the theory and practice of FHE has been made towards improving efficiency in recent years, FHE-based approaches are believed to have a crucial bottleneck to achieve practical performance, and the cryptographic protocol is still regarded as theoretical. Recently, multi-party and multi-key FHE-based approaches, such as the threshold or multi-key variant of Cheon–Kim–Kim–Song (CKKS) combined with FL59,60,61, have demonstrated feasibility and scalability for medical and genomic data analysis62. Although these approaches offer enhanced protection against information leakage and exhibit similar computational overhead on the server side compared with Lancelot, they face inevitable challenges in communication costs, making them impractical for BRFL involving multiple clients. We provide an analysis of adopting the threshold and multi-key CKKS in Supplementary Section 1.4.5.
Our work could be extended in several future directions to facilitate the adoption of Lancelot. The first direction is that the large-scale deployment of Lancelot would be a challenging yet important milestone for this endeavour, especially in cross-device FL scenarios. Our work demonstrates Lancelot’s applicability on a reliable baseline. It constitutes an essential step towards building trust in our technology and fostering its adoption, thereby enabling its use to discover scientific insights. Next, we will extend the capabilities of Lancelot by developing additional protocols for a broader range of standard analysis tools and ML algorithms in biomedical research. A key step in this direction is to make our implementation of Lancelot easily configurable by practitioners for their applications. Specifically, integrating Lancelot to existing user-friendly platforms such as NVFLARE24 or FedML26 to make it widely available would help empower increasing efforts to scientific discoveries. Last, by leveraging the FHE, the ciphertexts expand and cost more memory, but it can further optimize the communication cost from the cryptographic perspective. Therefore, Lancelot provides an initial foundation to establish a secure ecosystem between algorithm developers and data owners.
Methods
Lancelot aims to address the two aforementioned challenges in the FHE-based BRFL system. First, to mitigate the constraints imposed by the limited multiplication depth in FHE, we introduce a mask-based encrypted sorting method, which leverages interactive protocols to perform sorting operations efficiently and securely rather than relying on direct encrypted sorting. Second, to reduce computational overhead, we use a combination of two cryptographic optimizations alongside hardware acceleration, both of which synergize to expedite the entire training process. The organization of this section is shown as follows. We first outline the preliminaries of Lancelot. Next, we illustrate the implementation of mask-based encrypted sorting. Finally, we introduce the proposed cryptographic optimizations and hardware acceleration techniques in our system.
Problem formulation and threat model
In this work, we consider an FL scenario that considers the condition in which c out of n total clients are malicious. The malicious clients may keep their toxic data, but cannot access the local data of other honest clients. Both honest and malicious clients can get the decrypted global model, yet local model updates uploaded by a single honest client cannot be observed. Note that malicious clients can launch either targeted attacks or untargeted attacks. Malicious clients can redirect the global model in the wrong direction, impairing the efforts of honest clients. In addition, due to the inefficient computation of HE-based for the training phase, the goal of Lancelot is to minimize the training cost, that is, training time, and maintain the same accuracy performance as the original model, which can be formulated as follows:
where Ttotal is the overall training time, W* denotes the final model using the CKKS scheme for protection, W is the final aggregated model using plaintexts, TE is the training time for each round and Emax is the maximum epoch in training.
The threat model of this work is listed as follows. The key generation centre acts as a trusted third party. The server is defined as an honest but curious entity with high computational capability. This characterization implies that although the server faithfully executes the established protocols, it may be interested in extracting sensitive information. Our analysis further bifurcates clients into two distinct categories. The first category comprises honest clients who endeavour to enhance the global model. They do so by uploading genuine gradients, which have been trained on their local datasets. Conversely, the second category encapsulates malicious clients. These entities deliberately upload gradients designed to degrade the accuracy of the global model. They intend to sabotage the effectiveness of the model, thereby posing a major challenge to maintain model integrity. The potential threats caused by the above entities are shown as follows.
The following two threats are from the semi-honest server, that is, data leakage and inference attacks. The gradient essentially acts as a map of the client’s local data. Suppose that a client directly uploads these plaintext gradients; the client inadvertently exposes pathways for attackers to infer or extract the original data of honest clients, which leads to substantial data leakage, posing a considerable risk to client privacy. Meanwhile, in Lancelot, the server and the key generation centre exchange certain intermediate results to facilitate the aggregation of local updates. Although essential for operation, this process could potentially be exploited to infer sensitive information from these intermediate results, posing a risk in FL. In addition, the malicious clients bring threats, that is, poisoning attacks. Malicious clients aim to manipulate the global model’s performance without detection. They can execute poisoning attacks in numerous ways. In particular, through a label-flipping attack, a malicious client can alter data labels and subsequently upload gradients trained on these manipulated data. These tactics pose critical threats to the integrity and reliability of the learning process in FL.
Preliminaries
Private distance evaluation
Our solution requires protecting two transmissions to ensure data confidentiality: from the clients to the server and from the server to the key generation centre. Since the server follows a semi-honest model and the key generation centre is trusted, we designed specific approaches for each to ensure both efficiency and security. In particular, during distance computation, the ith client sends its model \(W_i\) to the server, which calculates the distance as \(d_{i,j}\) ≔ ∣∣ \(W_i-W_j\) ∣∣2. To protect model information, the weight matrix is encrypted using the FHE scheme, enabling private distance evaluation on the server.
We use CKKS, a ring-based HE scheme that supports batching, to efficiently process multiple computations in a single-instruction–multiple-data manner. The ciphertext space is defined as the ring \(R:={\mathbb{Z}}[X]/({X}^{N}+1)\), where N is a power of 2. The modulus \({Q}=\mathop{\prod }\nolimits_{i = 0}^{L}{q}_{i}\) represents the maximum level L, and the level-ℓ modulus is \({Q}_{\ell }=\mathop{\prod }\nolimits_{i = 0}^{\ell }{q}_{i}\), where qi are primes. The corresponding residue ring modulo q is denoted as Rq = R/qR. Ciphertexts are represented using the residue number system (RNS) decomposition for efficient computation. With (pk, sk) as the public and secret key pair, ⟦⋅⟧ as the encryption and Decsk as decryption under sk, the following plaintext properties are used in HE schemes:
-
Homomorphic addition/subtraction (HAdd/HSub, ⊕/⊖): Decsk(⟦A⟧ ⊕ ⟦B⟧) = A + B, Decsk(⟦A⟧ ⊖ ⟦B⟧) = A − B.
-
Homomorphic multiplication/square (HMult/HSquare, ⊗): Decsk(⟦A⟧ ⊗ ⟦B⟧) = A × B, Decsk(HSquare (⟦A⟧)) ≔ A2.
-
Homomorphic rotation (HRotk): Decsk(HRotk(⟦A⟧)) = A ≫ k.
With this scheme, the computational pattern become ⟦\(d_{i,j}\)⟧ ≔ HSquare(HSub(⟦\(W_i\)⟧, ⟦\(W_j\)⟧)). The evaluation is performed on ciphertext, and only the entities with the knowledge of sk can obtain the results.
CKKS scheme description
The CKKS scheme allows batched computation by pre-splitting the input into different slots and is efficient for some time-consuming operations. Let λ be the security parameter, \(s\) be a random element in Rq and \({\mathcal{X}}={\mathcal{X}}(\lambda )\) be a distribution over Rq. The security of CKKS is based on the hardness of the ring learning with errors problem. This problem is defined to distinguish the samples (\(a_i\), \(b_i\)) from the uniform distribution on \({R}_{q}^{2}\), where \(b_i\) = \(a_i\) + \(e_i\), \(a_i\) ←$Rq and \({{{e}}}_{i}\leftarrow {\mathcal{X}}\). The security assumption of ring learning with errors states that there is no efficient algorithm that can distinguish the samples with non-negligible probability, forming a security assurance of the entire encryption system. Let p be a special modulus that can be used to control error growth in ciphertexts. Denote [a]Q as amodQ. The main components of the CKKS scheme are defined as follows.
-
Key generation. Given the system parameter params = (λ, N, Q) and distributions \({{\mathcal{X}}}_{{\rm{key}}}\) and \({{\mathcal{X}}}_{{\rm{err}}}\), we define the secret key, public key and evaluation key as sk ≔ (1, s), pk ≔ ([−a ⋅ s+e ]Q, a), \({\bf{evk}}:=({[-{{{a}}}^{{\prime} }\cdot {{s}}+{{{e}}}^{{\prime} }+p{{{s}}}^{{\prime} }]}_{p\cdot Q},{{a}}^{{\prime} })\), where \(s \leftarrow {{\mathcal{X}}}_{{\rm{key}}}\), a ← $RQ, \(a^{{\prime} }{\leftarrow }^{\$}{R}_{p\cdot Q}\), \(e,e^{{\prime} }\leftarrow {{\mathcal{X}}}_{{\rm{err}}}\) and \(s^{{\prime} }=[{s}^{2}]_{Q}\).
-
Encryption. Given a public key pk \(=({{u}}_{0},{{u}}_{1}) \in {R}_{Q}^{2}\) and a message m ∈ R, sample \(r\leftarrow {{\mathcal{X}}}_{{\rm{key}}}\) and \(e_0,e_1 \leftarrow {{\mathcal{X}}}_{{\rm{err}}}\). The resulting ciphertext of CKKS encryption is described as
$${{\mathtt{CKKS}}.{\mathtt{Enc}}}({\bf{pk}},m)=([m+{r} \cdot {{u}}_{0}+{{e}}_{0}]_{Q},{[{r}\cdot {{u}}_{1}+{{e}}_{1}]}_{Q}).$$ -
Decryption. Given a secret key sk = (1, s) and a ciphertext \({\bf{ct}}=({{{c}}}_{0},{{{c}}}_{1})\in {R}_{{Q}_{\ell }}^{2}\), sample z ← DR,σ, where DR,σ is a discrete Gaussian over the polynomial ring with σ as the standard deviation. The randomized decryption algorithm for sharing can be formalized as
$${\mathtt{CKKS.Dec}}({\bf{sk}},{\bf{ct}})={[{{{c}}}_{0}+{{{c}}}_{1}\cdot {{s}}+{{z}}]}_{{Q}_{\ell }}.$$ -
Evaluation. HE provides a way to perform operations on ciphertext without decryption. Common homomorphic evaluations include homomorphic addition and multiplication. For the three schemes, we give their detailed evaluation procedures below.
-
CKKS addition. Given two CKKS ciphertexts ct and ct′ in \({R}_{{Q}_{\ell }}^{2}\), their sum is defined as the follows:
$${\mathtt{CKKS.Add}}({\bf{ct}},{{\bf{ct}}}^{{\prime} })={[{\bf{ct}}+{{\bf{ct}}}^{{\prime} }]}_{{Q}_{\ell }}.$$ -
CKKS multiplication. Given two CKKS ciphertexts ct = (c0, c1) and \({{\bf{ct}}}^{{\prime} }=({{{c}}}_{0}^{{\prime} },{{{c}}}_{1}^{{\prime} })\) in \({R}_{{Q}_{\ell }}^{2}\), the product yields a triple defined as follows:
$${\mathtt{CKKS.Mult}}({\bf{ct}},{{\bf{ct}}}^{{\prime} })=({\tilde{{{c}}}}_{0},{\tilde{{{c}}}}_{1},{\tilde{{{c}}}}_{2})={[({{{c}}}_{0}\cdot {{{c}}}_{0}^{{\prime} },{{{c}}}_{0}\cdot {{{c}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }+{{{c}}}_{1}\cdot {{{c}}}_{0}^{{\prime} },{{{c}}}_{1}\cdot {{{c}}}_{1}^{{\prime} })]}_{{Q}_{\ell }}.$$
-
Batch encoding and decoding
In CKKS, a scaling factor Δ ≥ 1 is introduced to manage approximate arithmetic on floating-point data. The encoding and decoding procedures map between polynomials in R and length − N/2 vectors of complex numbers by leveraging the canonical embedding σ and projection π*. Concretely, decoding starts from a polynomial m ∈ R, rescales it by Δ−1, and applies the embedding σ that sends m into a subset of \({{\mathbb{C}}}^{N}\). Projection π* then extracts the relevant N/2 complex values, producing the final vector. Encoding essentially reverses this process. A complex vector \(\bf{z} \in {{\mathbb{C}}}^{N/2}\) is lifted back into \({{\mathbb{C}}}^{N}\) via π*−1, and then mapped into R by the inverse embedding σ−1. This result is multiplied by Δ to fix numerical precision, and the coefficients are rounded to obtain an integer polynomial in R. Since σ and π are isometric ring isomorphisms (up to dimension reduction), these transformations preserve both additive and multiplicative structures required for homomorphic operations. The scale Δ determines the trade-off between the precision of the approximated values and the size of the polynomial coefficients.
Mask-based encrypted sorting
To execute the Byzantine-robust aggregation rules, the server needs to sort the clients according to the corresponding distance. However, given the constraints imposed by the multiplication depth, relying on direct sorting is impractical, especially in large FL systems with lots of clients. This is primarily because sorting algorithms operating in the ciphertext space generally depend on pairwise ciphertext comparisons, which consume multiple levels of multiplication depth. To address this, we propose mask-based encrypted sorting, and its core concept is to utilize an interactive protocol between the server and the key generation centre that securely conveys the index information, ensuring both efficiency and privacy.
In particular, the server sends the distance list to the key generation centre. However, since the server is not allowed to know the specific index of selected clients, the key generation centre needs to encrypt the index information and send it to the server, where the server can execute the aggregation rules. Let the encrypted distance matrix be L; each element l ∈ L is the encrypted distance data. The key generation centre obtains the encrypted distance list, then it decrypts the encrypted distance list and obtains the sorting permutation π of n elements, which is defined as
The sorting permutation π can be represented in a two-line form as
Therefore, the n × n permutation matrix Pπ = pij obtained by permuting the columns of the identity matrix In, that is, for each i, pij = 1 if j = π(i) and pij = 0 otherwise. Since the entries in row i are all 0 except that a 1 appears in column π(i), we have
where ej is a standard basis vector that denotes a row vector of length n with 1 in the jth position and 0 in every other position. Note that the key generation centre knows the aggregation rules of the whole FL system. Therefore, Pπ only uses the ej value for the selected position whereas the other position is o—a zero vector. For example, if there are five clients in the whole FL system, and we only use the top three clients, for example, clients 1, 3 and 5 for aggregation in one round, then \({P}_{\pi }=\left[\begin{array}{c}{{\bf{e}}}_{\pi (1)},{{\bf{e}}}_{\pi (3)},{{\bf{e}}}_{\pi (5)},{\bf{o}},{\bf{o}}\end{array}\right]\).
To protect the index information, it is also necessary to encode the permutation matrix Pπ and then send it back to the server. Let Φ be the encoding mapping that encodes the sorting index from the plaintext into an encrypted mask ⟦M⟧, which can be formulated as follows:
When the server receives the encrypted mask ⟦Z⟧, the server uses the multiplication results of the encrypted weights ⟦W⟧ and ⟦M⟧ to obtain the aggregated model based on the aggregation rules. The reason is that after adopting the mask, ⟦W⟧ only transmits the information without any information leakage.
Lazy relinearization
The computation of homomorphic matrix multiplication evaluation traverses the elements in the matrix recursively to perform element-by-element homomorphic multiplication and sums the relevant results. Here in the ith iteration, we take two CKKS ciphertexts \({{\bf{ct}}}_{A}^{(i)}:=({{{c}}}_{A,0}^{(i)},{{{c}}}_{A,1}^{(i)}),{{\bf{ct}}}_{B}^{(i)}:=({{{c}}}_{B,0}^{(i)},{{{c}}}_{B,1}^{(i)})\), where each consists of a pair of ring elements, performs homomorphic multiplication and obtains a ring element triple \({{\bf{ct}}}^{(i)* }:=({{{c}}}_{0}^{(i)* },{{{c}}}_{1}^{(i)* },{{{c}}}_{2}^{(i)* })\), and then returns the ring element pair \({{\bf{ct}}}^{(i)}:=({{{c}}}_{0}^{(i)},{{{c}}}_{1}^{(i)})\) through relinearization; finally, we add all \({{\bf{ct}}}^{(i)}\) values. The relinearization bottlenecks this computation, whereas the homomorphic addition is much cheaper as it only performs coefficient-wise addition. Due to this consideration, we devise a lazy relinearization technique. Here m is the number of iterations. Different from the original method that computes \(\mathop{\sum }\nolimits_{i = 0}^{m-1}{{\bf{ct}}}^{(i)}\), we keep the multiplication result in ternary form ct(i)*, and perform the sum of all ternaries directly, that is, \(\mathop{\sum }\nolimits_{i = 0}^{m-1}{{\bf{ct}}}^{(i)* }\). Thus, we only need to linearize the summation result, thereby reducing the number of relinearization operations to one. This technique increases the number of additions, which is far less than the overhead of relinearization, resulting in a performance boost. For example, as illustrated in Fig. 3a, we initially have three ciphertext multiplication and addition operations. In conventional multiplication, these three ciphertexts undergo multiplication and relinearization three times, followed by an addition operation. However, with lazy relinearization, the relinearization step is deferred until after the addition operation. Compared with conventional multiplication, lazy relinearization eliminates two relinearization operations, resulting in noticeable computation time savings.
Dynamic hoisting
During the computation of the square of the matrix W, we take a row and column of W and multiply them element wise, and sum up all the multiplication results to obtain one element of the result vector. The dimension of W is denoted as n × n, where n is a power of 2. We need to perform homomorphic rotations to obtain the addition result. In detail, to compute ⟦y⟧ ≔ ⟦Wt⟧ ⊗ ⟦\({{\mathit{W}}}_{m}^{T}\)⟧, where \(t,m \in \left[0,n\right)\), we perform ⟦\({\bf{y}}_{i}^{(0)}\)⟧ ≔ HMult(⟦Wt⟧, ⟦Wm⟧), and then iteratively compute ⟦\({\bf{y}}_{i}^{(j+1)}\)⟧ ≔ HAdd(⟦\({\bf{y}}_{i}^{(j)}\)⟧, HRotj(⟦\({\bf{y}}_{i}^{(j)}\)⟧)); we finally obtain ⟦y⟧ ≔ ⟦\({\bf{y}}_{i}^{(\log [n])}\)⟧. Here the sequence of successive homomorphic rotations and addition processes involves a series of automorphisms and key-switching operations. For each \({\bf{y}}_{i}^{(j)}=({{{c}}}_{i,0}^{(j)},{{{c}}}_{i,1}^{(j)})\), the original processing is as follows:
-
Automorphism: the current automorphism is denoted as ϕk; we first apply the automorphism to each part of \({{\bf{y}}}_{i}^{(j)}\) and compute \({{\bf{y}}}_{i}^{{(j)}^{{\prime} }}=({{{c}}}_{i,0}^{{(j)}^{{\prime} }},{{{c}}}_{i,1}^{{(j)}^{{\prime} }}):=({\phi }_{k}({{{c}}}_{i,0}^{(j)}),{\phi }_{k}({{{c}}}_{i,1}^{(j)}))\).
-
Key switching: because this process implicitly changes the key, we need to perform a key-switching operation. This contains the following process:
-
RNS decomposition: dnum is the RNS decomposition number, and dnum = ⌈(L + 1)/α⌉, padding zero and then splitting \({{{c}}}_{i,1}^{{(j)}^{{\prime} }}\) into β = ⌈(ℓ + 1)/α⌉ parts, and multiplying with \({[{Q}^{{\prime} }: = {\Pi }_{i = \ell +1}^{\alpha \beta -1}]}_{{q}_{y\alpha +x}}\), where 0 ≤ x < α, 0 ≤ y < β.
-
ModUp: raise the modulus of each part to the modulus base of the key-switching operation.
-
Switch Key: perform an inner product with the key-switching keys.
-
ModDown: converse the modulus of the results to the original Qℓ.
-
One shortcoming of this computation is that the homomorphic addition and rotation are performed in an iterative pattern, which makes the entire parallelism equal to the polynomial dimension N. Additionally, during each interaction, we need to perform the fixed computational flow, including automorphism, raising the modulus, switching the underlying key, and then bringing the modulus back, which has high computational consumption.
To solve this issue, we unfold this iterative computation and get ⟦yi⟧ ≔ ⟦\({{\bf{y}}}_{i}^{(0)}\)⟧ \(\oplus \mathop{\sum }\nolimits_{k = 0}^{n-1}{{\mathsf{H}}_{{\mathsf{Rot}}}}_{k}\) (⟦\({{\bf{y}}}_{i}^{(0)}\)⟧); thus, log[n] times homomorphic rotation can be performed simultaneously, bringing a log[n]-fold increase in parallelism. Meanwhile, since this unfolding approach introduces more computation, we utilize the hoisting technique63 and reverse the order of automorphism and modulus raising to reduce computation. The key observation of this technique is that we can reverse the order of the first three steps above without affecting the correctness of the procedure. In particular, this key changed computational flow is as follows:
-
RNS decomposition and ModUp: padding zero and splitting \({{{c}}}_{i,1}^{(j)}\) into β parts and multiplying with \({[{Q}^{{\prime} }]}_{{q}_{y\alpha +x}}\), raising the modulus of each part to the modulus base of key-switching operation.
-
Automorphism: denote the current automorphism as ϕk, applying the automorphism to each part of the above step.
Afterwards, we perform the original inner product with the key-switching keys corresponding to each ϕk and finally convert the ciphertext modulus to Qℓ. After all computations of rotations are computed, which can be performed in parallel, we sum up all results to obtain ⟦yi⟧.
As the automorphism distributes over addition and multiplication and will not profoundly change the norm of an element, the correctness is ensured. Through this, the time-consuming operations of modulus raising up and down are required only once. For instance, we present an illustrative example in Fig. 3b. The computation of the time-consuming components is parallelized (light-blue box), which drastically reduces the computational overhead. By contrast, traditional methods (orange box) necessitate sequentially repeating the same computational procedures multiple times.
However, when n is large, this unfolding approach in the hoisting technique exponentially increases the number of rotations, substantially expanding the cipher space due to the generation of several ciphertexts simultaneously. It is not practical in real applications due to the memory limitation in heterogeneous devices. Therefore, we have devised a dynamic adjusting approach to the unfoldings to balance computation and parallelism better. In this case, instead of unfolding all the iterations, we only grow some of them, which optimizes the overall performance. We formulate this problem as follows:
where k represents the unfolding parameters, whereas TH and TD denote the hoisting and decomposition times, respectively, which are dictated by hardware characteristics. Additionally, Mc refers to the memory required by a ciphertext, and MB signifies the memory budget limit. Due to the problem being a linear convex optimization problem, we use the simplex method64 to solve it. Note that k can be determined in advance before the FL training, based on the memory of the device, and k is dynamically adjusted if other processes consume memory via recalculating the aforementioned optimizing problem.
Hardware acceleration
In Lancelot, the primary computational bottleneck lies in the server-side homomorphic evaluation of distance matrices, an inherently resource-intensive task. This overhead primarily stems from the CKKS-based homomorphic operations, which, although computationally demanding, offer immense potential for parallel execution. The computation of matrix elements is independent, allowing for the concurrent execution of many operations without synchronization. Thus, since servers are typically equipped with superior computational capabilities, we utilize GPU acceleration for the server-side homomorphic evaluations. Each thread is assigned one coefficient of the ring elements for every HE operation executed and then carries out the corresponding computation, ensuring that multiple coefficients are processed simultaneously. Furthermore, we develop a comprehensive GPU-based implementation to host the entire distance computation on the GPU. This approach necessitates just one data interaction between the CPU and GPU, with all subsequent operations retaining their data in the GPU’s global memory, remarkably curtailing input/output latency and boosting overall performance. The details of hardware acceleration are presented in Supplementary Section 2.2. Additionally, a pseudo-code of Lancelot is provided in Supplementary Section 3.
Data availability
The MNIST dataset is available at https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/hojjatk/mnist-dataset. The FMNIST dataset is available via GitHub at https://github.com/zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist. The CIFAR-10 dataset is available at https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html. The SVHN dataset is available at http://ufldl.stanford.edu/housenumbers/. The MedMNIST dataset is available at https://medmnist.com/. The MosMedData dataset is available at https://mosmed.ai/datasets/covid19_1110. The ImageNet dataset is available at https://www.image-net.org/. Source data are provided with this paper.
Code availability
All code necessary to run the public portion of the experiment is available via GitHub at https://github.com/siyang-jiang/Lancelot and via Zenodo at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.16022526 (ref. 65). The code is licensed using the MIT license.
References
Accountability Act Health insurance portability and accountability act of 1996. Public Law 104, 191 (1996).
European Parliament & Council. General data protection regulation. Off. J. Eur. Union L 119, 1–88 (2016).
Sav, S. et al. POSEIDON: privacy-preserving federated neural network learning. In 28th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS 2021) https://doi.org/10.14722/ndss.2021.24119 (The Internet Society, 2021).
Mendelsohn, S. et al. sfkit: a web-based toolkit for secure and federated genomic analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, W535–W541 (2023).
Biggio, B., Nelson, B. & Laskov, P. Poisoning attacks against support vector machines. In Proc. 29th International Conference on Machine Learning 1467–1474 (Omnipress, 2012).
Xie, C., Huang, K., Chen, P. & Li, B. DBA: distributed backdoor attacks against federated learning. In Proc. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations https://openreview.net/pdf?id=rkgyS0VFvr (ICLR, 2020).
Zhang, Y., Zeng, D., Luo, J., Xu, Z. & King, I. A survey of trustworthy federated learning with perspectives on security, robustness, and privacy. In Proc. ACM Web Conference 2023 Companion 1167–1176 (ACM, 2023).
Alkhunaizi, N., Kamzolov, D., Takáč, M. & Nandakumar, K. Suppressing poisoning attacks on federated learning for medical imaging. In Proc. 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention 673–683 (Springer, 2022).
Zhu, L., Liu, Z. & Han, S. Deep leakage from gradients. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32, 14747–14756 (2019).
Zhao, B., Mopuri, K. R. & Bilen, H. iDLG: improved deep leakage from gradients. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.02610 (2020).
Liu, J., Lou, J., Xiong, L., Liu, J. & Meng, X. Cross-silo federated learning with record-level personalized differential privacy. In Proc. 2024 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security 303–317 (ACM, 2024).
Liu, J., Lou, J., Xiong, L., Pei, J. & Sun, J. Dealer: an end-to-end model marketplace with differential privacy. Proc. VLDB Endow. 14, 957–969 (2021).
De, S., Berrada, L., Hayes, J., Smith, S. L. & Balle, B. Unlocking high-accuracy differentially private image classification through scale. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.13650 (2022).
Hayes, J., Balle, B. & Mahloujifar, S. Bounding training data reconstruction in DP-SGD. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 36, 78696–78722 (2023).
Dwork, C. Differential privacy: a survey of results. In Proc. 5th International Conference on Theory and Applications of Models of Computation 1–19 (Springer, 2008).
Dwork, C., Tankala, P. & Zhang, L. Differentially private learning beyond the classical dimensionality regime. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.13682 (2024).
Bonawitz, K. A. et al. Practical secure aggregation for privacy-preserving machine learning. In Proc. 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security 1175–1191 (ACM, 2017).
Mohammed, S. J. & Taha, D. B. Performance evaluation of RSA, ElGamal, and Paillier partial homomorphic encryption algorithms. In Proc. 2022 International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering 89–94 (IEEE, 2022).
Cheon, J. H., Kim, A., Kim, M. & Song, Y. Homomorphic encryption for arithmetic of approximate numbers. In Proc. 23rd International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security 409–437 (Springer, 2017).
Zhang, C. et al. BatchCrypt: efficient homomorphic encryption for cross-silo federated learning. In Proc. 2020 USENIX Annual Technical Conference 493–506 (USENIX Association, 2020).
Regev, O. On lattices, learning with errors, random linear codes, and cryptography. In Proc. 37th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing 84–93 (ACM, 2005).
Lai, F. et al. FedScale: benchmarking model and system performance of federated learning at scale. In Proc. 39th International Conference on Machine Learning 11814–11827 (PMLR, 2022).
Beutel, D. J. et al. Flower: a friendly federated learning research framework. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14390 (2020).
Roth, H. R. et al. NVIDIA FLARE: federated learning from simulation to real-world. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 46, 170–184 (2023).
Ludwig, H. et al. IBM federated learning: an enterprise framework white paper v0.1. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.10987 (2020).
He, C. et al. FedML: a research library and benchmark for federated machine learning. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.13518 (2020).
Blanchard, P., El Mhamdi, E. M., Guerraoui, R. & Stainer, J. Machine learning with adversaries: Byzantine tolerant gradient descent. In 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017) https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/file/f4b9ec30ad9f68f89b29639786cb62ef-Paper.pdf (2017).
Yin, D., Chen, Y., Kannan, R. & Bartlett, P. Byzantine-robust distributed learning: towards optimal statistical rates. In Proc. 35th International Conference on Machine Learning 5650–5659 (PMLR, 2018).
Al Badawi, A. et al. OpenFHE: open-source fully homomorphic encryption library. In Proc. 10th Workshop on Encrypted Computing & Applied Homomorphic Cryptography 53–63 (ACM, 2022).
Bhagoji, A. N., Chakraborty, S., Mittal, P. & Calo, S. Analyzing federated learning through an adversarial lens. In Proc. 36th International Conference on Machine Learning 634–643 (PMLR, 2019).
Cao, X. & Gong, N. Z. MPAF: model poisoning attacks to federated learning based on fake clients. In Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops 3396–3404 (IEEE, 2022).
Jiang, S., Shuai, X. & Xing, G. ArtFL: exploiting data resolution in federated learning for dynamic runtime inference via multi-scale training. In Proc. 23rd ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks 27–38 (IEEE, 2024).
Yang, H. et al. Implementing and benchmarking word-wise homomorphic encryption schemes on GPU. Preprint at Cryptology ePrint Archive https://eprint.iacr.org/2023/049 (2023).
Deng, J. et al. ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proc. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 248–255 (IEEE, 2009).
Morozov, S. P. et al. MosMedData: chest CT scans with COVID-19 related findings dataset. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.06465 (2020).
Geiping, J., Bauermeister, H., Dröge, H. & Moeller, M. Inverting gradients: how easy is it to break privacy in federated learning? In 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2020) https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2020/file/c4ede56bbd98819ae6112b20ac6bf145-Paper.pdf (2020).
Hatamizadeh, A. et al. Do gradient inversion attacks make federated learning unsafe?. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 42, 2044–2056 (2023).
Feng, S. & Tramèr, F. Privacy backdoors: stealing data with corrupted pretrained models. In Proc. 41st International Conference on Machine Learning 13326–13364 (2024).
Li, B. & Micciancio, D. On the security of homomorphic encryption on approximate numbers. In Proc. 40th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques 648–677 (Springer, 2021).
Cheon, J. H., Hong, S. & Kim, D. Remark on the security of CKKS scheme in practice. Preprint at Cryptology ePrint Archive https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/1581 (2020).
Hu, C., Chen, Z. & Larsson, E. G. Scheduling and aggregation design for asynchronous federated learning over wireless networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 41, 874–886 (2023).
Fan, B., Jiang, S., Su, X., Tarkoma, S. & Hui, P. A survey on model-heterogeneous federated learning: problems, methods, and prospects. In Proc. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Big Data 7725–7734 (IEEE, 2024).
Li, X. et al. ClassTer: mobile shift-robust personalized federated learning via class-wise clustering. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 24, 2014–2028 (2025).
Lai, F., Zhu, X., Madhyastha, H. V. & Chowdhury, M. Oort: efficient federated learning via guided participant selection. In Proc. 15th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation 19–35 (USENIX Association, 2021).
Li, C., Zeng, X., Zhang, M. & Cao, Z. PyramidFL: a fine-grained client selection framework for efficient federated learning. In Proc. 28th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking 158–171 (ACM, 2022).
Kim, S. et al. BTS: an accelerator for bootstrappable fully homomorphic encryption. In Proc. 49th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture 711–725 (ACM, 2022).
Pan, X. et al. Flagger: cooperative acceleration for large-scale cross-silo federated learning aggregation. In Proc. 51st ACM/IEEE Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture 915–930 (IEEE, 2024).
Benaissa, A., Retiat, B., Cebere, B. & Belfedhal, A. E. TenSEAL: a library for encrypted tensor operations using homomorphic encryption. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.03152 (2021).
Halevi, S. & Shoup, V. Design and implementation of HElib: a homomorphic encryption library. Preprint at Cryptology ePrint Archive https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/1481 (2020).
CryptoLab Inc. HEAAN software library. GitHub https://github.com/kimandrik/HEAAN (2018).
Dutta, S., Innan, N., Yahia, S. B., Shafique, M. & Neira, D. E. B. MQFL-FHE: multimodal quantum federated learning framework with fully homomorphic encryption. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.01858 (2025).
Guo, Y. et al. Efficient and privacy-preserving federated learning based on full homomorphic encryption. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.11519 (2024).
Hu, C. & Li, B. MaskCrypt: federated learning with selective homomorphic encryption. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 22, 221–233 (2025).
Jin, W. et al. FedML-HE: an efficient homomorphic-encryption-based privacy-preserving federated learning system. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.10837 (2024).
Ouyang, X. et al. ADMarker: a multi-modal federated learning system for monitoring digital biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. In Proc. 30th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking 404–419 (ACM, 2024).
Zhang, Z. et al. LSFL: a lightweight and secure federated learning scheme for edge computing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 18, 365–379 (2023).
Zhang, Z. & Li, Y. NSPFL: a novel secure and privacy-preserving federated learning with data integrity auditing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 19, 4494–4506 (2024).
Xu, G. et al. Privacy-preserving federated deep learning with irregular users. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secure Comput. 19, 1364–1381 (2022).
Kim, M., Song, Y., Li, B. & Micciancio, D. Semi-parallel logistic regression for GWAS on encrypted data. BMC Med. Genomics 13, 99 (2020).
Froelicher, D. et al. Truly privacy-preserving federated analytics for precision medicine with multiparty homomorphic encryption. Nat. Commun. 12, 5910 (2021).
Froelicher, D. et al. Scalable and privacy-preserving federated principal component analysis. In Proc. 2023 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy 1908–1925 (IEEE, 2023).
Cho, H. et al. Secure and federated genome-wide association studies for biobank-scale datasets. Nat. Genet. 57, 809–814 (2025).
Halevi, S. & Shoup, V. Faster homomorphic linear transformations in HElib. In Proc. 38th International Cryptology Conference 93–120 (Springer, 2018).
Nelder, J. A. & Mead, R. A simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 7, 308–313 (1965).
Jiang, S. et al. Lancelot-Dev codebase. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.16022526 (2025).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFB3103500), the Science and Technology Innovation Key R&D Program of Chongqing CSTB2025TIAD-STX0032, the fund which aims to improve scientific research capability of key construction disciplines in Guangdong province (2022ZDJS058), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62132008 and U22B2030), the Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC) grant C4072-21G and the RGC under General Research Fund (number 14212924). We would also like to thank S. Shen, L. Jiang, W. Dai, and M. Ding for their valuable suggestions and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.J., H.Y., Q.X. and C.M. contributed to the motivation and framework design. S.J. led the development of the mask-based encrypted sorting algorithm, implemented most of the work and wrote a majority of the manuscript. H.Y. contributed to the CKKS implementation and provided expertise in cryptography. S.J. and Q.X. conducted the experiments and analysed the results. C.M., Z.L., S.W., T.X. and G.X. contributed to partial drafts of this manuscript. All authors reviewed and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Machine Intelligence thanks Kim Miran, Yiyu Shi and Alexander Ziller for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Sections 1–4 and References.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, S., Yang, H., Xie, Q. et al. Towards compute-efficient Byzantine-robust federated learning with fully homomorphic encryption. Nat Mach Intell 7, 1657–1668 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-025-01107-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-025-01107-6
This article is cited by
-
Homomorphic encryption for secure healthcare artificial intelligence
Discover Artificial Intelligence (2026)