Abstract
In the Mediterranean Sea, the probability that a large earthquake-triggered tsunami will occur in the coming decades is high. Historical tsunami database informs us on their geographical occurrence but their sources, i.e., the faults that slipped during earthquakes and displaced the seafloor to generate tsunamis, are often unknown. Here we identify the submarine rupture of the Amorgos earthquake that on July 9, 1956, triggered the largest mediterranean tsunami in the past two centuries. Using submarines, we explored major normal faults in the epicentral area, and discovered a large surface rupture along the 75-km long Amorgos fault. The 9.8-16.8-m large seafloor offset is compatible with a Mw7.5 event. This finding prompts a reassessment of the largest (≥20 m) tsunami wave origin, previously attributed to earthquake-triggered submarine mass-wasting. It demonstrates that tsunami source can be determined several decades after an event, a key information to better assess future seismic and tsunami hazards.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Surface ruptures generated by large continental earthquakes, whether historical1,2 or recent3, are today systematically mapped through fieldwork, satellite data, and high-resolution topographic analyses. They provide key information that allows the seismic hazard of a region to be evaluated, in particular through the identification of the causative fault, the extent of the rupture, and the amount of slip generated by the earthquake. Such work was performed in only a few weeks following the 2023 Turkey–Syria earthquake4 for example. When the earthquake occurs offshore, similar analyses are challenging to perform, but they are of prime importance to understand the triggering of tsunamis and evaluate the seismic hazard along submarine faults5. The recent deployment of submarine vehicles (such as Remotely Operated Vehicles ROVs), however, offers new opportunities to image undersea fault scarps6,7,8,9, identify fault planes that have been recently exhumed by slip during an earthquake10, and map and quantify the related surface rupture11. With such a vehicle, we investigated the faults around the proposed epicenter of the 1956 Amorgos earthquake to identify seafloor ruptures and determine the fault responsible for this event.
The 1956 earthquake and tsunami
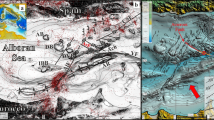
The Amorgos earthquake occurred on July 9, 1956, offshore Santorini and Amorgos (Cyclades, South Aegean Sea), along the Hellenic Volcanic Arc. It was recorded by a small number of seismometers, enabling seismologists to determine a magnitude of 7.2–7.812, depending on the authors. Several epicenters were obtained13 that located the earthquake between 5 and 20 km south of Amorgos island (Fig. 1). Its hypocentral depth, recognized to be poorly constrained14 and debated15, varies between 10 km and 45 km and was recently re-evaluated at ~25 km13, that is, at the Moho depth of the Hellenic arc16. The main shock was followed by a series of aftershocks. The first aftershock, called the twin earthquake, had a magnitude estimated between 6.0 and 7.2, and occurred only 13 min later, closer to Santorini (Fig. 1) and probably deeper (40–95 km), possibly along the subduction plate boundary13. The main shock caused severe damage to the surrounding islands, subsequently enhanced by the twin shock, especially in Santorini17. More than 3200 buildings were damaged, including ~500 that were completely destroyed; in addition, 54 people were killed in Santorini, and 100 people were injured.
Several epicenters for the main shock (star) and twin shock (dot) are represented, as summarized in Brüstle et al.13, with two proposed focal mechanism13,14 calculated for the epicenter marked with a star and an asterisk. Main faults are represented by black lines, with thicker traces for longer and taller faults, and are modified from previous works19,29,33. S.-A. fault: Santorini-Amorgos fault. Portions of faults explored with the ROVs during the AMORGOS-23 cruise are localized by yellow and white rectangles. Submarine landslides identified25 are in dashed red, while the observation19 of a probable fault mirror associated with the 1956 event along the Amorgos fault is a red dot. Measured run-ups14 of the 1956 tsunami are represented as blue bars. In the inset, other tsunami observations of the 1956 event are located by blue14 and white20 dots. Light purple areas are onshore and offshore volcanoes. The purple arrows on Astypalaea and Santorini show their relative displacements southeastward and southwestward, respectively, at a rate of ~4 mm/yr, with respect to central Aegean (Naxos)31. Mount Kroukelos on Amorgos is denoted by a black triangle. The two archeological sites that demonstrate long-term subsidence of the northern coast of Amorgos18 are located in Katapola (K.) and Aegiali (A.).
Several focal mechanisms were obtained to characterize the faults that are likely to have broken. The best-constrained ones point to a NE-SW striking normal fault plane13,14, in agreement with the local tectonic context and secondary faults visible along the southern coast of the island17,18,19 (Fig. 1). The coseismic slip probably occurred on a SE-dipping plane, calculated to be either a low-dipping plane (25°)14 or a steeper dipping plane (~65°)13 (both shown in Fig. 1), the latter being more typical of a normal fault. However, our knowledge of the fault that broke and produced this earthquake has until now been incomplete, due to our inability to identify and map the undersea fault.
In addition, the main shock triggered a large tsunami that reached the coastlines of Crete, Peloponnesus, western Turkey14,20,21, and that was recorded by one tide gauge in Israël22. Amorgians today still recall that after the earthquake, the sea retreated, allowing pedestrians to cross the Katapola Bay, before it inundated the land, with waves of 2–3 m high (Fig. 1). Along the southern coast of Amorgos island, run-ups of up to 20 m were reported14,20 while the northern coastline of Astypalaea island was also flooded with a run-up of up to 10 m14,20,23 (Fig. 1). These values are the highest reported in the Mediterranean basin in the twentieth and twenty-first centuries24. Despite a re-assessment of the testimonies of this tsunami14, the details of the arrival time of the wave remain vague14 across the archipelago. The polarity of the first wave is not well established21, while tide gauges installed in Crete and in Leros were damaged by the earthquake, so the tsunami arrival was not recorded21 in the near-field.
To explain the variation and local tsunami run-up heights along the coasts, a second source of sudden submarine seafloor motion was proposed, in addition, to slip on a low-angle normal fault14. Waves were probably enhanced by submarine landsliding20, later observed at the seafloor25 in the archipelago (Fig. 1). Such a scenario was tested with tsunami modeling14,22 so as to reproduce tsunami data (run-ups only14), using pre-determined source geometries. The geometry of the basins and the coastal bathymetry that greatly influence the run-up values at the coasts26 were, and are mostly still, unknown and thus unused in tsunami modeling14. All in all, the primary source of the earthquake and tsunami remains debated27, as epicentral solutions, tsunami data, and coastal bathymetry data are not sufficiently constrained.
On-land investigations were conducted to gain new insights into the origin of the events. Historical aerial images of Amorgos shorelines, acquired before and after the 1956 earthquake, suggest a coseismic uplift of the southern coast, while archeological masonries nowadays lying below sea level indicate long-term subsidence of the island’s northern coast18 (Fig. 1). These vertical motions are compatible with the break of a steep normal fault located within 5 km of the Amorgos’ southern coast18. Conversely, far-field subsidence of Holocene shorelines28 are compatible with the co- and post-seismic motion generated by a deep and low-angle normal fault. Using the different markers visible on land and in coastal areas is clearly insufficient to understand this earthquake and tsunami, as they do not converge towards a common source.
The submarine faults offshore Amorgos
In the past 10 years, marine geophysical data were acquired19,25,29,30 with sufficient resolution to identify, map, and characterize the faults in the area (Fig. 1). A 750-m deep, NE-SW striking trough, measuring 35 km in width, exists between the islands of Ios, Amorgos and Kinairos to the north, and Anafi and Astypalaea to the south. This trough is bordered to the north by a set of NE-SW to E–W striking normal faults, dipping to the south–southeast.
The main fault is the Amorgos fault, which constitutes the southern cliff of Amorgos island, whose summit reaches 821 m (Mt Kroukelos, Fig. 1). The main segment of the fault measures 45 km (Fig. 1, thick dark line), and up to 75 km if we consider secondary structures that connect or align with the main fault at its tips (Fig. 1, thin dark lines). Its activity induces the subsidence of its hanging wall, marked by the depth of Amorgos basin, reaching ~750 m below sea level19,29. Seismic reflection profiles acquired in the basin reveal that 700 m of sediments, tilted to the north, i.e., toward the fault, cover the alpine basement19, indicating about 2.2 km of vertical offset by the Amorgos fault.
The southern border of the trough is structured by the NE–SW striking, NW-dipping Anafi-Astypalaea fault system that extends from NW of Anafi to NW of Astypalaea island (Fig. 1). This fault is segmented, and in its central part it presents several sub-parallel smaller faults offsetting its hanging wall29. Its cumulative offset is lower than that of the Amorgos fault, about 1 km in its western part30, and it measures about 65 km in length.
In between the two main antithetic faults, several other faults offset the seafloor, creating horsts and grabens, including the Santorini–Amorgos (S–A) fault, located at ~8 km from the southern coasts of Amorgos. This structure is an NE–SW striking, SE-dipping normal fault, offsetting the basement by about 1.1 km19. In total, the Santorini–Amorgos fault measures about 55 km.
The orientation of this fault system is compatible with the two nodal planes of the focal mechanisms of the 1956 earthquake (Fig. 1). At the scale of the trough, these faults thus seem to accommodate mainly an NW–SE extension, in line with recent GPS data showing an NW–SE-oriented velocity gradient of 4 mm/yr between Naxos and Astypalaea31 (Fig. 1). On a larger scale, this fault system might accommodate some lateral motion of the southern Aegean domain with respect to the central Aegean domain, but this is still debated29,31,32,33.
Considering the uncertainty of the earthquake location and the incompleteness of the tsunami data, the three main faults of this system, that is, the Amorgos, Santorini–Amorgos, and Anafi faults, are all good candidates as sources for the 1956 main shock (Fig. 1). Moreover, as the surface (and thus length) of a fault is proportional to the magnitude of the largest earthquake it can generate34,35, the three faults are all long enough to host an M ≥ 7 earthquake such as the Amorgos 1956 main shock. However, recently acquired seismic reflection profiles19 imaged a particularly steep 8–10 m high scarp at the base of the Amorgos fault (Fig. 1). This suggests that a recently exhumed fault mirror may be preserved here, and thus that this fault could be the source of the 1956 earthquake.
We surveyed the three faults for the first time using an autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) and a hybrid remotely operated vehicle (HROV) onboard the R/V Europe36,37, in order to characterize the faults’ morphologies with bathymetric data (resolutions of 1 and 10 m), and image its surface to identify potential ruptures using 4 K video imagery (Fig. 1). The strategy carried out to survey optically each of the three faults was the same: HROV dived at fault sites showing the steepest cumulative scarp (identified in the bathymetry), and the simplest geometry (deformation is accommodated along one fault scarp only, observations were made far from fault relays). Dives were performed close to the epicentral area, away from large mass-wasting scars and associated deposits that could degrade or cover the markers of surface rupture on the seafloor. With this strategy, we identified that the Amorgos fault is the only one to exhibit a freshly exhumed fault mirror at the base of its cumulated scarp (Figs. 2 and 3).
a A 500 m long portion of the fault (located in Fig. 1) is represented in 3D with no vertical exaggeration. The HROV investigated the base of the fault scarp (navigation in pink and black). Gullies (yellow arrows) incise the fault mirror. At their outlets, cones of sediments (dashed white lines) are visible, they are affected by slope failures (white arrows) that deposit in the deep basin. b Bathymetric profile across one slope failure allows determining that it is at most 2 m deep (purple area).
Results: a fault mirror with fresh exhumation traces
Offshore of the south-eastern coast of Amorgos island, the new high-resolution bathymetric data reveals that the Amorgos fault exhibits a >600 m high submarine scarp visible all along its strike. At the HROV dive site presented below, this scarp is particularly steep (50–60°) and linear (Fig. 2a, Supplementary Fig. S1). It shows neither segmentation nor synthetic or antithetic parallel splays, inducing that the deformation localizes here along a single fault plane.
In the 1-m resolution digital elevation model (DEM), the base of the cumulative scarp is smooth, showing only a few narrow gullies parallel to the slope that incises it (Fig. 2a). At the gullies’ outlet, small cones are visible, and cover the fault scarp locally. The base of the fault scarp dips between 40° and 60° (Fig. 2a, Supplementary Fig. S2), a range comparable to the dips determined at depth with geophysical19 and seismological27 observations (38°–66°). A colluvial wedge covers its foot and dips toward the basin, with slopes up to 30° close to the scarp, and only 2° at 300 m far from the scarp (Figs. 2a and S2). Close to the scarp, the colluvial wedge has been locally eroded by failures and gravity collapses and shows local depressions that are up to three meters deep (Figs. 2a, b and S1).
Using the 4 K camera of the HROV Ariane, we imaged both the fault scarp and the colluvial wedge (Fig. 3, Supplementary Movie 1). The surface of the colluvial wedge is covered by unconsolidated fine sediments that are easily mobilized by fishes, currents, and the HROV propellers. Below the surface, the colluvial wedge exhibits stratified sediments exposed at the edges of the depressions that dissect the wedge (Fig. S1). As the edges of these failures are vertical, sediments forming the first few meters of the wedge are thus cohesive and probably indurated. Strata are ~1 m thick, composed of fine light-colored sediments, and dipping toward the basin (away from the fault).
a 3D textured Digital Outcrop Model and b–e raw pictures of the submarine fault mirror observed at the base of the Amorgos fault (location shown on Fig. 2), and associated with the 1956 Amorgos event. It shows striae (d), gouge coatings (e), and is topped by the remnants of the paleo-wedge portion/section that has been uplifted (a–c). We interpret this uplifted paleo-wedge material as a marker of the paleo-contact between the fault and the seafloor prior to the earthquake that exhumed the fault mirror. In addition, the fresh fault mirror is distinguished from the older fault plane that is darker (due to Mn coating, a–c). At this location, the fresh fault mirror is 14.6–16.8 m high (corresponding to the on-fault offset). Supplementary Movie 1, recorded by the HROV, was used to produce this model. The evolution of the fault plane morphology before and after the earthquake is represented by diagrams in (f) and (g), respectively.
The fault scarp is made of indurated rocks whose nature and geometry could not be determined during the dives. We speculate that they are similar to the metamorphic rocks outcropping on land, and forming the Alpine basement offset by the fault19. We identified that the base of the cumulative fault scarp displays a smooth and well-preserved surface (Fig. 3, Supplementary Fig. S3, Supplementary Movie 1), that is continuous over at least a length of ~500 m. This surface exhibits numerous striae that are in the dip direction of the fault plane. Some of them are continuous over the colluvial wedge indicating that they are rills linked to sedimentary and erosion processes (Figs. 3a and S3f). Other striae are covered at their lower end by the colluvial wedge (Fig. S3b and Supplementary Movie 1), suggesting that they are not linked to such current processes. We also identified that some parts of the scarp are coated by a brown material, that is fine-grained but contains cm-large clasts (Fig. 3e). This brown coating is indurated and fills the irregularities of the bedrock that lies beneath (visible in holes through the coating, Fig. 3e, Supplementary Movie 1). The striae unrelated to sedimentary processes are probably tectoglyphs created by dip-slip fault motion, while the coating resembles fault gouge (or fault breccias) made of rocks crushed during fault slip. We thus interpret the base of the cumulative scarp as a fault mirror, i.e., a surface that has been polished by slip, and with a displacement generally down-dip, with limited lateral motion.
This fault mirror is heterogeneous. It exhibits a light brown color surface over the first ~10 m or more, while above, the scarp is often covered by a dark coating (visible on raw images and 3D models, Fig. 3a–c and S3a, b, c, f), or has a rougher aspect (Fig. S3a, f) and can be incised by small gullies (Fig. S3d, e). Such color and roughness changes are often observed at seismically active faults on land38,39, and are an indicator of surface aging due to weathering of different portions of the fault that have been exhumed at different periods due to seismic displacement. The color changes we observe on the Amorgos fault are also characteristic of active submarine faults10,11, with coatings of Fe–Mn oxide, depositing at very slow rates (1 μm/yr to 0.125 mm/yr40) but efficiently darkening surfaces exposed to seawater. Lighter and smoother fault sections have thus been recently exposed.
Locally, the fault mirror is also topped by a thick stripe of fine white sediment (Fig. 3a–c and S3). It is indistinguishable in appearance from the hemipelagic sediment of the wedge below, seen within failure scars (Fig. S1), and can present remnants of stratified sediments from the wedge (Fig. S3d, f). We interpret this deposit as the top of the sediment wedge abutting the fault scarp prior to the earthquake, that has been detached from the hanging wall (i.e., the sediment wedge, Fig. 3f, g) by relative down-dip displacement with respect to the footwall (i.e., the fault scarp). Similar tectonically uplifted remnants of soil41 or colluvial wedge42 are exhumed and uplifted by coseismic fault slip on land.
Georeferenced and scaled digital outcrop models (DOMs) of seven vertical transects have been generated from the HROV 4 K videos (Figs. 3 and S3). DOMs allow quantifying the offset of the seafloor by measuring the distance between the present contact of the scarp and colluvial wedge, and the paleo-contact that is now uplifted. This paleo-contact is identified by the top of the paleo-wedge, often associated with a color or a texture change (Figs. 3 and S3). We measured the distance in the direction of the sub-vertical striae, along the fault plane (along-dip). In the seven sites, these on-fault distances range between 9.8 and 16.8 m (Fig. 4 and Supplementary Table S4). We attribute this variability over the ROV path to local differences in erosion and sedimentation processes (in the form of small failure depressions and small cones, Fig. 3a) that affect the current colluvial wedge since the fault slip. Small-scale variations in the strike, dip, and rake of the fault certainly generate variability in the measured vertical offset43, but not to the extent observed along this ~500 m of fault. Overall, the Amorgos fault exhibits a fresh fault mirror, with a mean height of 12.7 m along-dip, at the location presented here. Similar markers of recent deformation are visible at other places over ~30 km along the fault (Fig. 1), but they are distributed along several fault branches, hindering offset estimation.
On-fault offsets of the seafloor (1) measured on digital outcrop models (DOMs) of the fault mirror, acquired along several vertical transects, are shown by dots linked by a solid line. The upper bound of the gray surface associated with the line corresponds to the maximum on-fault offsets measured on the DOMs, while the lower bound corresponds with the minimum. The DOM presented in Fig. 3 is located. The fault mirror dip (in red) and its variations (red surface bounded by minimum and maximum dips) were measured in the 1 m AUV DEM, allowing us to calculate the corresponding vertical offsets (2) and horizontal extensions (3) (and their uncertainties shown as gray surfaces). The origin of the x-axis is plotted in Fig. 1a by a black circle on the black HROV path, and DOMs are located on a map in Supplementary Fig. S1.
Discussion and implications
The preserved remnants of the paleo-wedge and the color difference on the fault scarp argue that the fault exhumation is recent. As no method exists yet that would allow sampling and dating this fault scarp, we must seek seismic events reported in instrumental and historical catalogs44,45,46,47,48 in order to discuss its age. Since 1956, no large earthquake has occurred near the Amorgos fault27. Before 1956, a few historical earthquakes, not linked to volcanic activity, struck the island of Amorgos on December 23rd, 1733 and on April 7th, 1891, and were felt with large intensities within the archipelago. Although their locations are not well constrained, the distributions of the macroseismic intensities suggest epicentral areas closer to Sifnos and Chios respectively44,45. Prior to these two events, there are no testimonies indicating that a significant earthquake occurred in the vicinity of Amorgos Island during the past millennium44,45,47, nor before44,48.
Therefore, the recently exposed fault mirror is most plausibly linked to the 1956 event. Tectoglyphs visible on the exhumed fault plane are compatible with focal mechanisms calculated of the mainshock13, although they might have formed earlier and deeper. This fault mirror recorded either solely coseismic displacement, or both coseismic and post-seismic slip, with no data available to distinguish one from the other.
Scaling laws provide empirical correlations between earthquake magnitude and rupture parameters, including coseismic displacement, and can be used to evaluate if the displacement observed at Amorgos fault is consistent with the magnitudes of the 1956 event, or exclude it as a possible source. Even though coseismic slip is heterogeneous along a seismic rupture49, we can tentatively calculate the seismic moment M0 and the moment magnitude Mw of an earthquake able to generate the on-fault displacement that is observed, in order to discuss our observations. Different scaling laws link the seismic moment magnitude of an earthquake either to the rupture area A and the mean displacement on the fault50, or to the maximum slip at the surface51.
To use the first formulation50, we considered that the earthquake broke the crust and reached the Moho (in agreement with the recently determined seismogenic depth of the Hellenic arc52), along a fault dipping at 60°, with an associated rupture length ranging from 45 km (the main segment) to 75 km (the entire fault system), that the shear modulus is 3.2 × 1010 N/m2, and that our observations correspond to the mean coseismic displacement on the fault during the earthquake. These assumptions yield a moment magnitude, Mw, ranging from 7.7 to 8.0 and somewhat greater than the magnitude calculated from seismological data12. If we assume instead that the on-fault offset we observed is representative of the maximum surface displacement along the fault, the second formulation linking magnitude and maximum displacement at the surface51 yields a moment magnitude Mw of 7.5 (±0.1), a value in line with the moment magnitude calculated with seismological data12, which is between 7.2 and 7.8.
Seismic and tsunami hazard implications
The Amorgos tsunamigenic earthquake remains one of the largest normal faulting earthquakes recorded globally and generated the largest tsunami in the Mediterranean Sea for the past two centuries24. Our data provides the first geological evidence that the Amorgos fault was the host of this event. The Amorgos rupture identified and described in this paper shows a vertical offset that varies from 6.4 up to 13.4 m, with a mean of about 9 m at the seafloor (Fig. 4 and Supplementary Table S4, S5). This large vertical displacement, occurring only 1 km from the Amorgos coastline, suggests that the tsunami could plausibly have been triggered solely by the rupture and sudden vertical displacement of the seafloor. This justifies a revision of the role of mass wastings in generating the highest tsunami waves, in this event, at least close to the epicentral area. While mass-wasting seafloor structures are identified in the vicinity (Fig. 1), they are undated, and their link to the 1956 earthquake remains to be established.
Considering the local fault dips, and the on-fault offset, the 1956 earthquake accommodated 9 m of horizontal extension on average (varying between 5 and 11.6 m, Fig. 4, Table S4). A recent study based on GNSS data31 quantifies that the fault system between Naxos and Astypalaea must accommodate 4 mm/yr of horizontal extension. This rate implies that about 2250 years of loading is necessary to produce an earthquake similar to the 1956 main shock. If this duration represents the recurrence time for a large earthquake on the Amorgos fault, it may explain the scarcity of events in the 20th century45,47 and in historical records44,45, assuming the latter is complete. This possibility should be investigated by future paleoseismological studies in the area, in order to better constrain the seismic and tsunami hazards of the Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean.
The other fault systems in the vicinity of the 1956 epicentral area, namely the Santorini-Amorgos fault, the Anafi-Astypalaea fault system, the Ios fault system, and the Kinairos fault, remain unbroken today (Fig. 1). Although the seismicity of the Santorini–Amorgos region is among the most sustained of the Hellenic Volcanic arc, it is largely triggered by magmatic phenomena28 that are intense around Santorini and other submarine volcanoes (Fig. 1). In historical chronicles, the closest and largest earthquake to have occurred in the vicinity of the fault system was the 42 AD event, located between Santorini and Amorgos, and was probably linked to the volcanic activity of the Santorini volcano, which erupted in 46 AD53. In recent times, only two Mw 6 earthquakes have occurred, in 1911 and 1919, between the Anafi-Astypalaea and Santorini-Amorgos faults54, which are both long enough to host earthquakes of Mw ≥ 7. With the exception of the Santorini–Amorgos fault, the other faults left unbroken show very little microseismicity27. This may suggest that they are either locked and accumulating stress, or that aseismic slip is occurring27. The seismic coupling coefficient (SCC) calculated in this part of the Aegean Sea establishes that the region is strongly coupled (SCC ~ 80%)52, except in the vicinity of Santorini (SCC ~ 40%). This indicates that stress is mainly released in the form of large earthquakes in this region and that the Anafi-Astypalaea fault system, the Ios fault system, and the Kinairos fault could break in the future.
Conclusion
Sixty-seven years after the 1956 Amorgos earthquake, we have used submarine vehicles to observe well-preserved and clearly visible traces of a large seafloor rupture along the Amorgos fault, allowing us to identify this as the likely source of the earthquake. This result, together with previous studies of the Les Saintes earthquake10,11, opens the door to submarine explorations looking for the—still debated—fault sources of major historical earthquakes and tsunamis elsewhere, such as the 1783 and 1908 Messina strait events, the 1755 Lisbon earthquake and the 1833 Showa-Sanriku and 1977 Sumba outer-rise events. Comprehensive and detailed submarine geological observations will also lead to a better understanding of the mechanisms behind tsunami triggering55. Data from submarine exploration will be particularly important to better predict future sources of underwater earthquakes and tsunamis and to assess how our communities can adapt to these natural hazards, especially where tourism can have a major impact on a region’s vulnerability.
Methods
Bathymetry data
During the AMORGOS-2236 and AMORGOS-2337 cruises, we acquired shallow and deep bathymetry using the multibeam echosounder Kongsberg ME70 onboard R/V Europe. Bathymetry was acquired at low speed (2-5 kt) to densify the beams and thus increase the resolution along the steep fault scarp. During the AMORGOS-2236 cruise, we also collected near-bottom, high-resolution bathymetry data using the AUV Idefx (IFREMER, France), equipped with a Kongsberg Reson SMF EM2040. The AUV surveyed ~70 m above the seafloor, parallel to the faults. All bathymetric data were processed using GLOBE (IFREMER) and gridded to produce digital elevation models (DEMs) with a 1 m cell size for the AUV and a 10 m cell size for the ship bathymetry (Fig. 2a).
ROV 3D digital outcrop models from video imagery
During the AMORGOS-2337 cruise, we deployed the HROV Ariane (IFREMER) in order to collect video imagery at multiple locations along the fault scarps (Figs. 3 and S3). It is equipped with a 4 K camera (DeepSea Apex SeaCam) mounted on a pan-and-tilt platform at the front of the vehicle, and a second HD camera mounted on the lower-right corner of the vehicle. We surveyed the fault scarp horizontally and vertically, using overlapping tracks at speeds of <0.5 m/s and at distances of ~2–5 m from outcrops. Extracted video frames (every 2 s) were corrected for illumination attenuation prior to processing, using the MATISSE 3D Preprocessing tool56 (IFREMER). A structure-from-motion technique was then applied with MATISSE 3D software (v.1.4)56 to obtain three-dimensional digital outcrop models that correspond to vertical transects (method A). The HROV navigation data were used as a priori constraints to build the sparse point cloud, and bundle adjustment was performed before densifying the point cloud, meshing, and texturing the models. Terrain models are thus georeferenced and scaled to allow geological interpretations and provide proper scaling for quantitative studies with model resolutions of ~1 cm or better.
To verify the obtained displacements with method A, we used different processing pipelines with two additional methods and algorithms. Method B used the 3DF ZEPHYR software using the HROV navigation data as a priori constraints but without the bundle adjustment. Method C57 used the navigation data as a posteriori constraint to scale the model. In total, 21 DOMs were obtained that model the seven vertical transects. We used 3DF ZEPHYR’s drawing and measuring tools to map the striae, the base, and the top of the fresh fault mirror on each model. We measured the minimum and maximum distances on the model that separate the top and bottom of the fault mirror, in the direction of the striae (i.e., along-dip). Figure S3 presents the seven vertical transects modeled with method A. Table S5 presents the measurements for each of the seven sites, measured with the three methods (A–C). Overall, the on-fault offset measurements show the same trend. Half of the measurements done with method B and C agree with measurements performed with method A within 4.8% and 6.4%, respectively (i.e., median). A few measurements performed with method C depart by up to 26.5% from method A. The DOM of the vertical transect presented in Fig. 3a is very well constrained, as the three methods give similar results (mean on-fault offset of 15.8 ± 0.1). This site displays the largest offset we observed during the dive.
For consistency in the main text and main figures, all on-fault offsets measured and discussed are obtained with MATISSE 3D (method A). Therefore, all vertical offsets and horizontal extensions are derived from method A measurements. Despite this modeling effort, DOMs were misoriented due to inaccurate recording of the pan and tilt of the cameras during acquisition. While this does not impact the on-fault distance measurements, we could not use the DOMs to measure the scarp dip and calculate the vertical offset and horizontal extension discussed in the main text. To overcome this limitation, the 1 m DEM derived from AUV surveys allowed us to measure scarp dip, presented in Supplementary Table S4.
Data availability
The 1 m DEM58 from the AMORGOS-22 cruise and the 10 m DEM59 from the AMORGOS-23 cruise, presented in Fig. 2, are available at https://doi.org/10.17882/99212 and https://doi.org/10.17882/90284 respectively. The HROV-navigation file of dive 1 from the AMORGOS-2337 cruise is available at https://campagnes.flotteoceanographique.fr/campagnes/18003211/. Video-derived 3D Digital Outcrop Models60 are available at https://doi.org/10.17882/99228.
Change history
25 July 2025
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-025-02580-y
References
Johnson, K. L., Nissen, E. & Lajoie, L. Surface rupture morphology and vertical slip distribution of the 1959 M w 7.2 Hebgen Lake (Montana) earthquake from airborne lidar topography. J. Geophys. Res. 123, 8229–8248 (2018).
Haddon, E. K., Amos, C. B., Zielke, O., Jayko, A. S. & Bürgmann, R. Surface slip during large Owens Valley earthquakes. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 17, 2239–2269 (2016).
Civico, R. et al. Surface ruptures following the 30 October 2016 M w 6.5 Norcia earthquake, central Italy. J. Maps 14, 151–160 (2018).
Guo, Y. et al. 2023. Preliminary report of coseismic surface rupture (part) of Turkey’s Mw7. 8 earthquake by remote sensing interpretation. Earthq. Res. Adv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eqrea.2023.100219 (2023).
Grezio, A. et al. Probabilistic tsunami hazard analysis: multiple sources and global applications. Rev. Geophys. 55, 1158–1198 (2017).
Armijo, R. et al. Submarine fault scarps in the Sea of Marmara pull‐apart (North Anatolian Fault): implications for seismic hazard in Istanbul. Geochem. Geophys, Geosyst. 6 (2005).
Elias, A. et al. Active thrusting offshore Mount Lebanon: source of the tsunamigenic AD 551 Beirut-Tripoli earthquake. Geology 35, 755–758 (2007).
Ueda, H., Kitazato, H. & Jamieson, A. The submarine fault scarp of the 2011 Tohoku-oki Earthquake in the Japan Trench. Commun. Earth Environ. 4, 476 (2023).
ten Brink, U. et al. Seafloor observations eliminate a landslide as the source of the 1918 Puerto Rico Tsunami. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 113, 268–280 (2023).
Escartín, J. et al. First direct observation of coseismic slip and seafloor rupture along a submarine normal fault and implications for fault slip history. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 450, 96–107 (2016).
Hughes, A. et al. Seafloor earthquake ruptures and mass wasting from the 2004 Mw 6.3 Les Saintes submarine earthquake. Commun. Earth Environ. 4, 270 (2023).
Lee, W. H. K. & Engdahl, E. R. Bibliographical search for reliable seismic moments of large earthquakes during 1900-1979 to compute MW in the ISC-GEM Global Instrumental Reference Earthquake Catalogue (1900-2009). Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 239, 25–32 (2015).
Brüstle, A., Friederich, W., Meier, T. & Gross, C. Focal mechanism and depth of the 1956 Amorgos twin earthquakes from waveform matching of analogue seismograms. Solid Earth 5, 1027–1044 (2014).
Okal, E. A., Synolakis, C. E., Uslu, B., Kalligeris, N. & Voukouvalas, E. The 1956 earthquake and tsunami in Amorgos, Greece. Geophys. J. Int. 178, 1533–1554 (2009).
Konstantinou, K. I. Crustal rheology of the Santorini–Amorgos zone: implications for the nucleation depth and rupture extent of the 9 July 1956 Amorgos earthquake, southern Aegean. J. Geodyn. 50, 400–409 (2010).
Grigoriadis, V. N., Tziavos, I. N., Tsokas, G. N. & Stampolidis, A. Gravity data inversion for Moho depth modeling in the Hellenic area. Pure Appl. Geophys. 173, 1223–1241 (2016).
Papadopoulos, G. A. & Pavlides, S. B. The large 1956 earthquake in the South Aegean: macroseismic field configuration, faulting, and neotectonics of Amorgos Island. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 113, 383–396 (1992).
Stiros, S. C., Marangou, L. & Arnold, M. Quaternary uplift and tilting of Amorgos Island (southern Aegean) and the 1956 earthquake. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 128, 65–76 (1994).
Nomikou, P. et al. Expanding extension, subsidence and lateral segmentation within the Santorini-Amorgos basins during Quaternary: implications for the 1956 Amorgos events, central-south Aegean Sea, Greece. Tectonophysics 722, 138–153 (2018).
Galanopoulos, A. G. The seismic sea wave of 9 July 1956. Prakt. Akad. Athens 32, 90–101 (1957). in Greek.
Ambraseys, N. The seismic sea wave of July 1956 in the Greek Archipelago. J. Geophys. Res. 65, 1257–1265 (1960).
Beisel, S. et al. The 1956 Greek tsunami recorded at Yafo, Israel, and its numerical modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 114, 1–18 (2009).
Dominey-Howes, D., Cundy, A. & Croudace, I. High energy marine flood deposits on Astypalaea Island, Greece: possible evidence for the AD 1956 southern Aegean tsunami. Mar. Geol. 163, 303–315 (2000).
Maramai, A., Brizuela, B. & Graziani, L. The Euro-mediterranean tsunami catalogue. Ann. Geophys. 57, S0435 (2014).
Hooft, E. E. et al. Backarc tectonism, volcanism, and mass wasting shape seafloor morphology in the Santorini-Christiana-Amorgos region of the Hellenic Volcanic Arc. Tectonophysics 712, 396–414 (2017).
Rabinovich, A. B. Spectral analysis of tsunami waves: separation of source and topography effects. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 12663–12676 (1997). C6.
Andinisari, R., Konstantinou, K. I. & Ranjan, P. Seismicity along the Santorini-Amorgos zone and its relationship with active tectonics and fluid distribution. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 312, 106660 (2021).
Evelpidou, N., Melini, D., Pirazzoli, P. & Vassilopoulos, A. Evidence of a recent rapid subsidence in the S–E Cyclades (Greece): an effect of the 1956 Amorgos earthquake? Continental Shelf Res. 39, 27–40 (2012).
Tsampouraki-Kraounaki, K. et al. The Santorini-Amorgos Shear Zone: evidence for dextral transtension in the South Aegean Back-Arc Region, Greece. Geosciences 11, 216 (2021).
Preine, J., Hübscher, C., Karstens, J. & Nomikou, P. Volcano‐tectonic evolution of the Christiana‐Santorini‐Kolumbo Rift Zone. Tectonics 41, e2022TC007524 (2022).
Briole, P., Ganas, A., Elias, P. & Dimitrov, D. The GPS velocity field of the Aegean. New observations, contribution of the earthquakes, crustal blocks model. Geophys. J. Int. 226, 468–492 (2021).
Piper, D. J. W. & Perissoratis, C. Quaternary neotectonics of the South Aegean arc. Mar. Geol. 198, 259–288 (2003).
Feuillet, N. The 2011–2012 unrest at Santorini rift: stress interaction between active faulting and volcanism. Geophys. Res. Lett. 40, 3532–3537 (2013).
Kanamori, H. & Anderson, D. L. Theoretical basis of some empirical relations in seismology. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 65, 1073–1095 (1975).
Geller, R. J. Scaling relations for earthquake source parameters and magnitudes. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 66, 1501–1523 (1976).
Leclerc, F. & Escartin J. AMORGOS-22 cruise, RV L’Europe. https://doi.org/10.17600/18001479 (2022).
Leclerc F. & Escartin J. AMORGOS-23 cruise, RV L’Europe. https://doi.org/10.17600/18003211 (2023).
Benedetti, L. et al. Motion on the Kaparelli fault (Greece) prior to the 1981 earthquake sequence determined from 36Cl cosmogenic dating. Terra Nova 15, 118–124 (2003).
Lyon‐Caen, H. E. A. et al. The 1986 Kalamata (South Peloponnesus) earthquake: detailed study of a normal fault, evidences for east‐west extension in the Hellenic Arc. J. Geophys. Res. 93, 14967–15000 (1988). B12.
Koschinsky, A. & Hein, J. R. Marine ferromanganese encrustations: archives of changing oceans. Elements 13, 177–182 (2017).
Villani, F. et al. A database of the coseismic effects following the 30 October 2016 Norcia earthquake in Central Italy. Sci. Data 5, 1–11 (2018).
Armijo, R., Lyon-Caen, H. & Papanastassiou, D. A possible normal-fault rupture for the 464 BC Sparta earthquake. Nature 351, 137–139 (1991).
Iezzi, F. et al. Coseismic throw variation across along‐strike bends on active normal faults: Implications for displacement versus length scaling of earthquake ruptures. J. Geophys. Res. 123, 9817–9841 (2018).
Ambraseys, N. Earthquakes in the Mediterranean and Middle East: A Multidisciplinary Study of Seismicity Up to 1900. (Cambridge University Press, 2009).
Papazachos, B. C. & Papazachou, C. B. The Earthquakes of Greece 3rd Edition. (Ziti Publ. Thessaloniki, Greece, 2003) 286 pp. (in Greek).
Albini, P., Locati, M., Rovida, A. & Stucchi, M. European Archive of Historical EArthquake Data (AHEAD). Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV). https://doi.org/10.6092/ingv.it-ahead (2013).
Makropoulos, K., Kaviris, G. & Kouskouna, V. An updated and extended earthquake catalogue for Greece and adjacent areas since 1900. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 12, 1425–1430 (2012).
- http://www.geophysics.geol.uoa.gr/frame_en/catal/menucatal_en.html
Perrin, C., Manighetti, I., Ampuero, J. P., Cappa, F. & Gaudemer, Y. Location of largest earthquake slip and fast rupture controlled by along‐strike change in fault structural maturity due to fault growth. J. Geophys. Res.h 121, 3666–3685 (2016).
Hanks, T. C. & Kanamori, H. A moment magnitude scale. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 2348–2350 (1979). B5.
Wells, D. L. & Coppersmith, K. J. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 84, 974–1002 (1994).
Sparacino, F., Galuzzi, B. G., Palano, M., Segou, M. & Chiarabba, C. Seismic coupling for the Aegean-Anatolian region. Earth Sci. Rev. 228, 103993 (2022).
Georgalas, G. C. Catalogue of the Active Volcanoes of the World including Solfatara Fields. 12, 40, Napoli, Greece (1962).
Di Giacomo, D., Engdahl, E. R. & Storchak, D. A. The ISC-GEM Earthquake Catalogue (1904–2014): status after the Extension Project. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 10, 1877–1899 (2018).
Cordrie, L., Gailler, A., Escartin, J., Feuillet, N. & Heinrich, P. Simulation of the 2004 tsunami of Les Saintes in Guadeloupe (Lesser Antilles) using new source constraints. Nat. Hazards 103, 2103–2129 (2020).
Arnaubec, A. et al. Underwater 3D reconstruction from video or still imagery: matisse and 3DMetrics processing and exploitation software. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 11, 985 (2023).
Istenič, K., Gracias, N., Arnaubec, A., Escartín, J. & Garcia, R. Scale accuracy evaluation of image-based 3D reconstruction strategies using laser photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 11, 2093 (2019).
Leclerc, F. et al. Near-bottom bathymetry and back-scatter data acquired with AUV IDEFX during the AMORGOS-22 cruise. SEANOE https://doi.org/10.17882/99212 (2022).
Leclerc, F. et al. AMORGOS-23 ME70 bathymetry and back-scatter data. SEANOE https://doi.org/10.17882/90284 (2023).
Leclerc, F., Palagonia, S., Nomikou, P., Feuillet, N. & Escartin, J. 3D textured Digital Outcrop Models along the Amorgos Fault scarp (Aegean Sea, Greece)—Dive 244-01—AMORGOS-23 cruise. SEANOE https://doi.org/10.17882/99228 (2023).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the captains and crews of the R/V Europe during the AMORGOS-22 and AMORGOS-23 oceanographic cruises, the AUV and HROV teams of Genavir, and the Flotte Océanographique Française that funded ship time and related expenses. This work has been supported by the French government, through the UCAJEDI Investments in the Future project managed by the National Research Agency (ANR) with the reference number ANR-15-IDEX-01. This work was also supported by the Tellus Program of CNRS-INSU, and by the Observatoire de la Côte d’Azur. We thank the Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs for the cruise permissions. We thank Christophe Larroque and four anonymous reviewers for their comments on the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F. Leclerc designed the study, supervised the ship, AUV and ROV data acquisition and processing, processed the 3D models with Matisse 3D and 3DF Zephyr, interpreted the data and wrote the original paper. S. Palagonia took part in the ship and ROV data acquisition and bathymetric data processing, interpreted the data and revised the paper. N. Feuillet and P. Nomikou took part in the ship, AUV and ROV data acquisition, interpreted the data and revised the paper. D. Lampridou took part in the ship and AUV data acquisition, processed the ship bathymetric data. P. Barrière processed the AUV bathymetric data. A. Dano supervised and processed the AUV and ship bathymetric data. E. Ochoa processed the 3D models with method C and revised the paper. N. Gracias supervised the 3D model processing and revised the paper. J. Escartin designed the study, interpreted the data and revised the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Earth & Environment thanks Hayto Ueda, Mélody Philippon and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editors: Derya Gürer and Joe Aslin. A peer review file is available
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Leclerc, F., Palagonia, S., Feuillet, N. et al. Large seafloor rupture caused by the 1956 Amorgos tsunamigenic earthquake, Greece. Commun Earth Environ 5, 663 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-024-01839-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-024-01839-0
This article is cited by
-
Sedimentological characteristics of Mass Transport Deposits (MTDs) triggered by the Amorgos 1956 earthquake: sediment provenance and geochemical elements
Geo-Marine Letters (2025)
-
Focal mechanisms and bouguer-gravity anomalies of the 2025 earthquake cluster in the Santorini-Amorgos region (Southern Aegean Sea, Greece): evidence for shallow extensional magmatism
Journal of Seismology (2025)
-
Volcanic crisis reveals coupled magma system at Santorini and Kolumbo
Nature (2025)