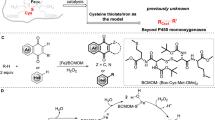
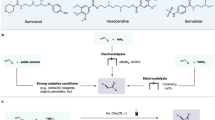
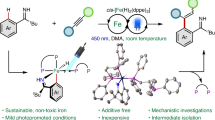
Abstract
Transition metal-catalysed difunctionalization of alkenes enables the rapid construction of complex molecules by converting a flat C(sp2)–C(sp2) π-fragment to form a three-dimensional structure with neighbouring sp3-hybridized carbons and two new C(sp3)–G bonds (G = carbon, heteroatom, halogen and so on) in a single step. Iron catalysis is attractive because of its lower cost, higher Earth abundance, lower mining carbon footprint and lower toxicity in comparison to traditional transition metal catalysts, but lags behind nickel and palladium in terms of synthetic applications and mechanistic understanding. Here we present an overview of recent reaction development progress and unmet challenges in iron-catalysed difunctionalization reactions, with a focus on three-component radical cross-coupling processes that use commercially available iron salts in combination with readily available ligands. For each case, we highlight the mechanistic insights gained from (in)organic synthesis, computational modelling and spectroscopic techniques that advance our understanding and guide the development of new transformations.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lovering, F., Bikker, J. & Humblet, C. Escape from Flatland: increasing saturation as an approach to improving clinical success. J. Med. Chem. 52, 6752–6756 (2009).
Lovering, F. Escape from Flatland 2: complexity and promiscuity. Med. Chem. Commun. 4, 515–519 (2013).
Cox, B. et al. Escaping from Flatland: substituted bridged pyrrolidine fragments with inherent three-dimensional character. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 11, 1185–1190 (2020).
Dhungana, R. K., KC, S., Basnet, P. & Giri, R. Transition metal-catalyzed dicarbofunctionalization of unactivated olefins. Chem. Rec. 18, 1314–1340 (2018).
Yin, G., Mu, X. & Liu, G. Palladium(II)-catalyzed oxidative difunctionalization of alkenes: bond forming at a high-valent palladium center. Acc. Chem. Res. 49, 2413–2423 (2016).
Zhang, J.-S., Liu, L., Chen, T. & Han, L.-B. Transition-metal-catalyzed three-component difunctionalizations of alkenes. Chem. Asian J. 13, 2277–2291 (2018).
Gao, P., Niu, Y.-J., Yang, F., Guo, L.-N. & Duan, X.-H. Three-component 1,2-dicarbofunctionalization of alkenes involving alkyl radicals. Chem. Commun. 58, 730–746 (2022).
Ciesielski, J., Dequirez, G., Retailleau, P., Gandon, V. & Dauban, P. Rhodium-catalyzed alkene difunctionalization with nitrenes. Chem. Eur. J. 22, 9338–9347 (2016).
Zhang, Z., Su, B., Gong, J., Tao, H. & Mai, S. Rhodium-catalyzed difunctionalization of alkenes using cyclic 1,3-dicarbonyl-derived iodonium ylides. Org. Lett. 26, 1886–1890 (2024).
Wagner-Carlberg, N., Dorsheimer, J. R. & Rovis, T. Rh(III)-catalyzed alkene anti nucleoamidation to access diverse heterocycles. ACS Catal. 14, 17033–17038 (2024).
Wickham, L. M. & Giri, R. Transition metal (Ni, Cu, Pd)-catalyzed alkene dicarbofunctionalization reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 54, 3415–3437 (2021).
Qi, X. & Diao, T. Nickel-catalyzed dicarbofunctionalization of alkenes. ACS Catal. 10, 8542–8556 (2020).
Egorova, K. S. & Ananikov, V. P. Which metals are green for catalysis? Comparison of the toxicities of Ni, Cu, Fe, Pd, Pt, Rh and Au salts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 12150–12162 (2016).
Rana, S., Biswas, J. P., Paul, S., Paik, A. & Maiti, D. Organic synthesis with the most abundant transition metal-iron: from rust to multitasking catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 243–472 (2021).
Nuss, P. & Eckelman, M. J. Life cycle assessment of metals: a scientific synthesis. PLoS ONE 9, e101298 (2014).
Bauer, I. & Knölker, H.-J. Iron catalysis in organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 115, 3170–3387 (2015).
Fürstner, A. Iron catalysis in organic synthesis: a critical assessment of what it takes to make this base metal a multitasking champion. ACS Cent. Sci. 2, 778–789 (2016).
Casnati, A., Lanzi, M. & Cera, G. Recent advances in asymmetric iron catalysis. Molecules 25, 3889 (2020).
Mondal, S., Das, K. K. & Panda, S. Iron catalysis: a new horizon towards organoboron-mediated C–C cross-coupling. Chem. Asian J. 17, e202200847 (2022).
Plietker, B. & Beller, M. Iron Catalysis: Fundamentals and Applications. Topics in Organometallic Chemistry Vol. 33 (Springer, 2011).
Kharasch, M. S. & Fields, E. K. Factors determining the course and mechanisms of Grignard reactions. IV. The effect of metallic halides on the reaction of aryl Grignard reagents and organic halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 63, 2316–2320 (1941).
Tamura, M. & Kochi, J. K. Vinylation of Grignard reagents. Catalysis by iron. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 93, 1487–1489 (1971).
Fabre, J.-L., Julia, M. & Verpeaux, J.-N. Couplage mixte entre sulfones vinyliques et réactifs de Grignard en présence de sels de métal de transition: synthèse stéréosélective d’oléfines trisubstituées. Tetrahedron Lett. 23, 2469–2472 (1982).
Molander, G. A., Rahn, B. J., Shubert, D. C. & Bonde, S. E. Iron catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. Synthesis of arylethenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 24, 5449–5452 (1983).
Cahiez, G. & Marquais, S. Highly chemo- and stereoselective Fe-catalyzed alkenylation of organomanganese reagents. Tetrahedron Lett. 37, 1773–1776 (1996).
Cahiez, G. & Avedissian, H. Highly stereo- and chemoselective iron-catalyzed alkenylation of organomagnesium compounds. Synthesis 1998, 1199–1205 (1998).
Fürstner, A. & Leitner, A. Iron-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of alkyl-Grignard reagents with aryl chlorides, tosylates and triflates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41, 609–612 (2002).
Fürstner, A., Leitner, A., Méndez, M. & Krause, H. Iron-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 13856–13863 (2002).
Martin, R. & Fürstner, A. Cross-coupling of alkyl halides with aryl Grignard reagents catalyzed by a low-valent iron complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 3955–3957 (2004).
Nagano, T. & Hayashi, T. Iron-catalyzed Grignard cross-coupling with alkyl halides possessing β-hydrogens. Org. Lett. 6, 1297–1299 (2004).
Nakamura, M., Matsuo, K., Ito, S. & Nakamura, E. Iron-catalyzed cross-coupling of primary and secondary alkyl halides with aryl Grignard reagents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 3686–3687 (2004).
Scheiper, B., Bonnekessel, M., Krause, H. & Fürstner, A. Selective iron-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of Grignard reagents with enol triflates, acid chlorides and dichloroarenes. J. Org. Chem. 69, 3943–3949 (2004).
Nakamura, M., Ito, S., Matsuo, K. & Nakamura, E. Iron-catalyzed chemoselective cross-coupling of primary and secondary alkyl halides with arylzinc reagents. Synlett 2005, 1794–1798 (2005).
Hatakeyama, T. et al. Iron-catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura coupling of alkyl halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 10674–10676 (2010).
Jin, M., Adak, L. & Nakamura, M. Iron-catalyzed enantioselective cross-coupling reactions of α-chloroesters with aryl Grignard reagents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 7128–7134 (2015).
Muñoz, S. B. III, Daifuku, S. L., Brennessel, W. W. & Neidig, M. L. Isolation, characterization and reactivity of Fe8Me12−: Kochi’s S = 1/2 species in iron-catalyzed cross-couplings with MeMgBr and ferric salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 7492–7495 (2016).
Liu, L. et al. Intra- and intermolecular Fe-catalyzed dicarbofunctionalization of vinyl cyclopropanes. Chem. Sci. 11, 3146–3151 (2020).
Youshaw, C. R. et al. Iron-catalyzed enantioselective multicomponent cross-couplings of α-boryl radicals. Org. Lett. 25, 8320–8325 (2023).
Wu, X. et al. Enantioselective 1,2-difunctionalization of dienes enabled by chiral palladium complex-catalyzed cascade arylation/allylic alkylation reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 13476–13479 (2015).
Shu, W. et al. Ni-catalyzed reductive dicarbofunctionalization of nonactivated alkenes: scope and mechanistic insights. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 13812–13821 (2019).
Ouyang, X.-H., Song, R.-J., Hu, M., Yang, Y. & Li, J.-H. Silver-mediated intermolecular 1,2-alkylarylation of styrenes with α-carbonyl alkyl bromides and indoles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 3187–3191 (2016).
Wang, F., Wang, D., Mu, X., Chen, P. & Liu, G. Copper-catalyzed intermolecular trifluoromethylarylation of alkenes: mutual activation of arylboronic acid and CF3+ reagent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 10202–10205 (2014).
Wu, L. et al. Asymmetric Cu-catalyzed intermolecular trifluoromethylarylation of styrenes: enantioselective arylation of benzylic radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 2904–2907 (2017).
Dongol, K. G., Koh, H., Sau, M. & Chai, C. L. L. Iron-catalysed sp3–sp3 cross-coupling reactions of unactivated alkyl halides with alkyl Grignard reagents. Adv. Synth. Catal. 349, 1015–1018 (2007).
Muñoz, S. B. et al. The N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) effect in iron-catalyzed cross-coupling with simple ferric salts and MeMgBr. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 6496–6500 (2018).
Sears, J. D., Neate, P. G. N. & Neidig, M. L. Intermediates and mechanism in iron-catalyzed cross-coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 11872–11883 (2018).
Neidig, M. L. et al. Development and evolution of mechanistic understanding in iron-catalyzed cross-coupling. Acc. Chem. Res. 52, 140–150 (2019).
Bakas, N. J. & Neidig, M. L. Additive and counterion effects in iron-catalyzed reactions relevant to C–C bond formation. ACS Catal. 11, 8493–8503 (2021).
Aguilera, M. C. et al. Insight into radical initiation, solvent effects, and biphenyl production in iron-bisphosphine cross-couplings. ACS Catal. 13, 8987–8996 (2023).
Liu, L. et al. Fe-catalyzed three-component dicarbofunctionalization of unactivated alkenes with alkyl halides and Grignard reagents. Chem. Sci. 11, 8301–8305 (2020).
Chierchia, M., Xu, P., Lovinger, G. J. & Morken, J. P. Enantioselective radical addition/cross-coupling of organozinc reagents, alkyl iodides, and alkenyl boron reagents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 14245–14249 (2019).
Sun, S.-Z., Duan, Y., Mega, R. S., Somerville, R. J. & Martin, R. Site-selective 1,2-dicarbofunctionalization of vinyl boronates through dual catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 4370–4374 (2020).
Wang, X.-X., Lu, X., He, S.-J. & Fu, Y. Nickel-catalyzed three-component olefin reductive dicarbofunctionalization to access alkylborates. Chem. Sci. 11, 7950–7956 (2020).
Campbell, M. W., Compton, J. S., Kelly, C. B. & Molander, G. A. Three-component olefin dicarbofunctionalization enabled by nickel/photoredox dual catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 20069–20078 (2019).
García-Domínguez, A., Mondal, R. & Nevado, C. Dual photoredox/nickel-catalyzed three-component carbofunctionalization of alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 12286–12290 (2019).
Mega, R. S., Duong, V. K., Noble, A. & Aggarwal, V. K. Decarboxylative conjunctive cross-coupling of vinyl boronic esters using metallaphotoredox catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 4375–4379 (2020).
Liu, L. et al. General method for iron-catalyzed multicomponent radical cascades–cross-couplings. Science 374, 432–439 (2021).
Giese, B. Formation of C-C bonds by addition of free radicals to alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 22, 753–764 (1983).
Fleming, I. in Molecular Orbitals and Organic Chemical Reactions 275–297 (Wiley, 2009).
Parsaee, F. et al. Radical philicity and its role in selective organic transformations. Nat. Rev. Chem. 5, 486–499 (2021).
Rotella, M. E., Sar, D., Liu, L. & Gutierrez, O. Fe-catalyzed dicarbofunctionalization of electron-rich alkenes with Grignard reagents and (fluoro)alkyl halides. Chem. Commun. 57, 12508–12511 (2021).
Sar, D. et al. Expanding the chemical space of enol silyl ethers: catalytic dicarbofunctionalization enabled by iron catalysis. Chem. Sci. 14, 13007–13013 (2023).
Rentería-Gómez, Á., Guerrero, M., Ramirez-Lopez, M. & Gutierrez, O. Regioselective fluoroalkylarylation of enamides enabled by an iron-catalyzed multicomponent radical cross-coupling strategy. Org. Lett. 25, 7440–7445 (2023).
Guerrero, M., Rentería-Gómez, Á., Das, D. & Gutierrez, O. Fe-catalyzed fluoroalkyl(hetero)arylation of vinyl azaarenes: rapid and modular synthesis of unsymmetrical 1,1-bis(hetero)arylalkanes. Org. Lett. 26, 7015–7020 (2024).
Maity, T., Rentería-Gómez, Á. & Gutierrez, O. Stereoselective Fe-catalyzed decoupled cross-couplings: chiral vinyl oxazolidinones as effective radical lynchpins for diastereoselective C(sp2)-C(sp3) bond formation. ACS Catal. 14, 13049–13054 (2024).
Newcomb, M. in Encyclopedia of Radicals in Chemistry, Biology and Materials (eds Chatgilialoglu, C. & Studer, A.) Ch. 5, 107–124 (Wiley, 2012).
Gutierrez, O., Tellis, J. C., Primer, D. N., Molander, G. A. & Kozlowski, M. C. Nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling of photoredox-generated radicals: uncovering a general manifold for stereoconvergence in nickel-catalyzed cross-couplings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 4896–4899 (2015).
Evans, D. J., Henderson, R. A., Hills, A., Hughes, D. L. & Oglieve, K. E. Involvement of iron alkyl complexes and alkyl radicals in the Kharasch reactions: probing the catalysis using iron phosphine complexes. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1992, 1259–1265 (1992).
Geist, E., Kirschning, A. & Schmidt, T. sp3–sp3 coupling reactions in the synthesis of natural products and biologically active molecules. Nat. Prod. Rep. 31, 441–448 (2014).
Choi, J. & Fu, G. C. Transition metal-catalyzed alkyl-alkyl bond formation: another dimension in cross-coupling chemistry. Science 356, eaaf7230 (2017).
Tan, T.-D. et al. Congested C(sp3)-rich architectures enabled by iron-catalysed conjunctive alkylation. Nat. Catal. 7, 321–329 (2024).
Tan, T.-D. et al. Kinetically controlled Z-alkene synthesis using iron-catalysed allene dialkylation. Nat. Synth. 4, 116–123 (2025).
Xu, W. et al. Fe-catalyzed dicarbofunctionalization of vinylarenes with alkylsilyl peroxides and β-keto carbonyl substrates. Org. Lett. 24, 2641–2645 (2022).
Lux, D. M., Lee, D. J., Sapkota, R. R. & Giri, R. Iron-mediated dialkylation of alkenylarenes with benzyl bromides. J. Org. Chem. 89, 16292–16299 (2024).
Jian, W., Ge, L., Jiao, Y., Qian, B. & Bao, H. Iron-catalyzed decarboxylative alkyl etherification of vinylarenes with aliphatic acids as the alkyl source. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 3650–3654 (2017).
Qian, B., Chen, S., Wang, T., Zhang, X. & Bao, H. Iron-catalyzed carboamination of olefins: synthesis of amines and disubstituted β-amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 13076–13082 (2017).
Xu, R. & Cai, C. Iron-catalyzed three-component intermolecular trifluoromethyl-acyloxylation of styrenes with NaSO2CF3 and benzoic acids. Org. Chem. Front. 7, 318–323 (2020).
Li, W.-Y., Wang, Q.-Q. & Yang, L. Fe-catalyzed radical-type difunctionalization of styrenes with aliphatic aldehydes and trimethylsilyl azide via a decarbonylative alkylation-azidation cascade. Org. Biomol. Chem. 15, 9987–9991 (2017).
Wu, C.-S., Li, R., Wang, Q.-Q. & Yang, L. Fe-catalyzed decarbonylative alkylation-peroxidation of alkenes with aliphatic aldehydes and hydroperoxide under mild conditions. Green Chem. 21, 269–274 (2019).
Zhu, C.-L. et al. Iron(II)-catalyzed azidotrifluoromethylation of olefins and N-heterocycles for expedient vicinal trifluoromethyl amine synthesis. ACS Catal. 8, 5032–5037 (2018).
Ge, L., Li, Y. & Bao, H. Iron-catalyzed radical acyl-azidation of alkenes with aldehydes: synthesis of unsymmetrical β-azido ketones. Org. Lett. 21, 256–260 (2019).
Xiong, H. et al. Iron-catalyzed carboazidation of alkenes and alkynes. Nat. Commun. 10, 122 (2019).
Wei, R. et al. Iron-catalyzed alkylazidation of 1,1-disubstituted alkenes with diacylperoxides and TMSN3. Org. Lett. 22, 3195–3199 (2020).
Ge, L. et al. Iron-catalysed asymmetric carboazidation of styrenes. Nat. Catal. 4, 28–35 (2021).
Liu, S. et al. Fe-catalyzed alkylazidation of α-trifluoromethylalkenes: an access to quaternary stereocenters containing CF3 and N3 groups. Org. Lett. 25, 1336–1341 (2023).
Zhu, F., Xue, J. & Wu, X.-F. Iron-catalyzed intermolecular 1,2-difunctionalization of alkenes with nucleophiles and using di-tert-butyl peroxide as the methylation reagent. Tetrahedron 149, 133735 (2023).
Pozhydaiev, V., Vayer, M., Fave, C., Moran, J. & Lebœuf, D. Synthesis of unprotected β-arylethylamines by iron(II)-catalyzed 1,2-aminoarylation of alkenes in hexafluoroisopropanol. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202305108 (2023).
Kambe, N., Iwasaki, T. & Terao, J. Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of alkyl halides. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 4937–4947 (2011).
Du, W. et al. Iron-catalyzed radical oxidative coupling reaction of aryl olefins with 1,3-dithiane. Org. Lett. 16, 2470–2473 (2014).
Liu, T. et al. Alcohol-mediated direct dithioacetalization of alkynes with 2-chloro-1,3-dithiane for the synthesis of Markovnikov dithianes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 15, 4068–4071 (2017).
Xu, T., Cheung, C. W. & Hu, X. Iron-catalyzed 1,2-addition of perfluoroalkyl iodides to alkynes and alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 4910–4914 (2014).
Deng, W., Li, Y., Li, Y.-G. & Bao, H. Iron-catalyzed carboiodination of alkynes. Synth 50, 2974–2980 (2018).
Xu, C., He, Z., Yang, H., Chen, H. & Zeng, Q. FeCl3-catalyzed three-component aryl-selenylation of alkenes. Tetrahedron 91, 132239 (2021).
Yu, X., Zheng, H., Zhao, H., Lee, B. C. & Koh, M. J. Iron-catalyzed regioselective alkenylboration of olefins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 2104–2109 (2021).
Brunner, H. A new hydrosilylation mechanism—new preparative opportunities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 2749–2750 (2004).
Bart, S. C., Lobkovsky, E. & Chirik, P. J. Preparation and molecular and electronic structures of iron(0) dinitrogen and silane complexes and their application to catalytic hydrogenation and hydrosilation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 13794–13807 (2004).
Tondreau, A. M. et al. Iron catalysts for selective anti-Markovnikov alkene hydrosilylation using tertiary silanes. Science 335, 567–570 (2012).
Greenhalgh, M. D., Frank, D. J. & Thomas, S. P. Iron-catalysed chemo-, regio- and stereoselective hydrosilylation of alkenes and alkynes using a bench-stable iron(II) pre-catalyst. Adv. Synth. Catal. 356, 584–590 (2014).
Peng, D. et al. Phosphinite-iminopyridine iron catalysts for chemoselective alkene hydrosilylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 19154–19166 (2013).
Chen, J., Cheng, B., Cao, M. & Lu, Z. Iron-catalyzed asymmetric hydrosilylation of 1,1-disubstituted alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 4661–4664 (2015).
Cheng, B., Liu, W. & Lu, Z. Iron-catalyzed highly enantioselective hydrosilylation of unactivated terminal alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 5014–5017 (2018).
Hu, M.-Y. et al. Ligands with 1,10-phenanthroline scaffold for highly regioselective iron-catalyzed alkene hydrosilylation. Nat. Commun. 9, 221 (2018).
Sun, W. et al. Phenanthroline-imine ligands for iron-catalyzed alkene hydrosilylation. Chem. Sci. 13, 2721–2728 (2022).
Docherty, J. H., Peng, J., Dominey, A. P. & Thomas, S. P. Activation and discovery of earth-abundant metal catalysts using sodium tert-butoxide. Nat. Chem. 9, 595–600 (2017).
Zhang, L., Peng, D., Leng, X. & Huang, Z. Iron-catalyzed, atom-economical, chemo- and regioselective alkene hydroboration with pinacolborane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 3676–3680 (2013).
Chen, J., Xi, T. & Lu, Z. Iminopyridine oxazoline iron catalyst for asymmetric hydroboration of 1,1-disubstituted aryl alkenes. Org. Lett. 16, 6452–6455 (2014).
Zhang, H. & Lu, Z. Dual-stereocontrol asymmetric cobalt-catalyzed hydroboration of sterically hindered styrenes. ACS Catal. 6, 6596–6600 (2016).
Su, W. et al. Ligand-free iron-catalyzed regioselectivity-controlled hydroboration of aliphatic terminal alkenes. ACS Catal. 10, 11963–11970 (2020).
Lu, D.-F., Zhu, C.-L., Jia, Z.-X. & Xu, H. Iron(II)-catalyzed intermolecular amino-oxygenation of olefins through the N-O bond cleavage of functionalized hydroxylamines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 13186–13189 (2014).
Lu, D.-F., Zhu, C.-L., Sears, J. D. & Xu, H. Iron(II)-catalyzed intermolecular aminofluorination of unfunctionalized olefins using fluoride ion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 11360–11367 (2016).
Radović, A. et al. Mechanistic studies of iron-PyBOX-catalyzed olefin amino-oxygenation with functionalized hydroxylamines. Organometallics 42, 1810–1817 (2023).
Legnani, L. & Morandi, B. Direct catalytic synthesis of unprotected 2-amino-1-phenylethanols from alkenes using iron(II) phthalocyanine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 2248–2251 (2016).
Legnani, L., Prina-Cerai, G., Delcaillau, T., Willems, S. & Morandi, B. Efficient access to unprotected primary amines by iron-catalyzed aminochlorination of alkenes. Science 362, 434–439 (2018).
Falk, E., Makai, S., Delcaillau, T., Gürtler, L. & Morandi, B. Design and scalable synthesis of N-alkylhydroxylamine reagents for the direct iron-catalyzed installation of medicinally relevant amines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 21064–21071 (2020).
Makai, S., Falk, E. & Morandi, B. Direct synthesis of unprotected 2-azidoamines from alkenes via an iron-catalyzed difunctionalization reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 21548–21555 (2020).
Wei, W. et al. Iron-catalyzed direct difunctionalization of alkenes with dioxygen and sulfinic acids: a highly efficient and green approach to β-ketosulfones. Org. Biomol. Chem. 12, 7678–7681 (2014).
Zhang, J. et al. An iron-catalyzed multicomponent reaction of cycloketone oxime esters, alkenes, DABCO·(SO2)2 and trimethylsilyl azide. Org. Chem. Front. 9, 917–922 (2022).
Huang, B., Li, Y., Yang, C. & Xia, W. Three-component aminoselenation of alkenes via visible-light enabled Fe-catalysis. Green Chem. 22, 2804–2809 (2020).
Yang, Y. et al. Iron-catalyzed intermolecular 1,2-difunctionalization of styrenes and conjugated alkenes with silanes and nucleophiles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 7916–7919 (2017).
Lei, B., Wang, X., Ma, L., Li, Y. & Li, Z. NFSI-participated intermolecular aminoazidation of alkene through iron catalysis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 16, 3109–3113 (2018).
Wang, Y. et al. Iron(III)-catalyzed radical α,β-aminophosphinoylation of styrenes with diphenylphosphine oxides and anilines. Org. Biomol. Chem. 16, 7782–7786 (2018).
Ma, X. et al. Iron phthalocyanine-catalyzed radical phosphinoylazidation of alkenes: a facile synthesis of β-azido-phosphine oxide with a fast azido transfer step. Chin. J. Catal. 42, 1634–1640 (2021).
Xuan, J. & Xiao, W.-J. Visible-light photoredox catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 6828–6838 (2012).
Prier, C. K., Rankic, D. A. & MacMillan, D. W. C. Visible light photoredox catalysis with transition metal complexes: applications in organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 113, 5322–5363 (2013).
Schultz, D. M. & Yoon, T. P. Solar synthesis: prospects in visible light photocatalysis. Science 343, 1239176 (2014).
Ouyang, X.-H. et al. Intermolecular dialkylation of alkenes with two distinct C(sp3)-H bonds enabled by synergistic photoredox catalysis and iron catalysis. Sci. Adv. 5, eaav1291 (2019).
Ye, J.-H. et al. Visible-light-driven iron-promoted thiocarboxylation of styrenes and acrylates with CO2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 15416–15420 (2017).
Xu, R. & Cai, C. Three-component difluoroalkylation-thiolation of alkenes by iron-facilitated visible-light photoredox catalysis. Chem. Commun. 55, 4383–4386 (2019).
Yuan, L. et al. Visible-light-driven iron-catalyzed 1,2-difluoroalkylthiolation of alkenes. Org. Lett. 26, 7066–7071 (2024).
Ilic, A. et al. Photoredox catalysis via consecutive 2LMCT- and 3MLCT-excitation of an Fe(III/II)-N-heterocyclic carbene complex. Chem. Sci. 13, 9165–9175 (2022).
Zhang, W. et al. Modular and practical 1,2-aryl(alkenyl) heteroatom functionalization of alkenes through iron/photoredox dual catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202310978 (2023).
Jiang, X. et al. Iron photocatalysis via Brønsted acid-unlocked ligand-to-metal charge transfer. Nat. Commun. 15, 6115 (2024).
Feng, G., Wang, X. & Jin, J. Decarboxylative C–C and C–N bond formation by ligand-accelerated iron photocatalysis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 6728–6732 (2019).
Chinchole, A., Henriquez, M. A., Cortes-Arriagada, D., Cabrera, A. R. & Reiser, O. Iron(III)-light-induced homolysis: a dual photocatalytic approach for the hydroacylation of alkenes using acyl radicals via direct HAT from aldehydes. ACS Catal. 12, 13549–13554 (2022).
Yuan, X.-Y., Wang, C.-C. & Yu, B. Recent advances in FeCl3-photocatalyzed organic reactions via hydrogen-atom transfer. Chin. Chem. Lett. 35, 109517 (2024).
Kang, Y. C., Treacy, S. M. & Rovis, T. Iron-catalyzed photoinduced LMCT: a 1 °C-H abstraction enables skeletal rearrangements and C(sp3)–H alkylation. ACS Catal. 11, 7442–7449 (2021).
Wu, Q., Liu, W., Wang, M., Huang, Y. & Hu, P. Iron-catalyzed deconstructive alkylation through chlorine radical induced C-C single bond cleavage under visible light. Chem. Commun. 58, 9886–9889 (2022).
Jin, Y. et al. Convenient C(sp3)–H bond functionalisation of light alkanes and other compounds by iron photocatalysis. Green Chem. 23, 6984–6989 (2021).
Dai, Z.-Y., Zhang, S.-Q., Hong, X., Wang, P.-S. & Gong, L.-Z. A practical FeCl3/HCl photocatalyst for versatile aliphatic C-H functionalization. Chem. Catal. 2, 1211–1222 (2022).
Ding, L., Niu, K., Liu, Y. & Wang, Q. Visible light-induced hydrosilylation of electron-deficient alkenes by iron catalysis. ChemSusChem 15, e202200367 (2022).
Zhang, Q. et al. Iron-catalyzed photoredox functionalization of methane and heavier gaseous alkanes: scope, kinetics and computational studies. Org. Lett. 24, 1901–1906 (2022).
Klöpfer, V., Chinchole, A. & Reiser, O. Dual iron- and organophotocatalyzed hydroformylation, hydroacylation and hydrocarboxylation of Michael-acceptors utilizing 1,3,5-trioxanes as C1-synthone. Tetrahedron Chem 10, 100073 (2024).
Bian, K.-J. et al. Photocatalytic hydrofluoroalkylation of alkenes with carboxylic acids. Nat. Chem. 15, 1683–1692 (2023).
He, Y. et al. Remote functionalization of inert C(sp3)–H bonds via dual catalysis driven by alkene hydrofluoroalkylation using industrial feedstocks. Org. Lett. 26, 8278–8283 (2024).
Bian, K.-J., Kao, S.-C., Nemoto, D., Chen, X.-W. & West, J. G. Photochemical diazidation of alkenes enabled by ligand-to-metal charge transfer and radical ligand transfer. Nat. Commun. 13, 7881 (2022).
Bian, K.-J. et al. Photocatalytic, modular difunctionalization of alkenes enabled by ligand-to-metal charge transfer and radical ligand transfer. Chem. Sci. 15, 124–133 (2024).
Acknowledgements
O.G. acknowledges NIH NIGMS (R35GM137797) and NSF (2528517) for funding. M.J.K. acknowledges support from the SUSTech-NUS Joint Research Center Project Fund (A-8002271- 00-00, A-8002271-01-00 and A-8002271-02-00). We also thank all the Gutierrez group members for proofreading and providing valuable feedback to the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.R.G., A.R.-G., T.-D.T., J.W.N., M.J.K. and O.G. contributed equally to all aspects of the Article and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed substantially to discussion of the content. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Synthesis thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editor: Thomas West, in collaboration with the Nature Synthesis team.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gogoi, A.R., Rentería-Gómez, Á., Tan, TD. et al. Iron-catalysed radical difunctionalization of alkenes. Nat. Synth 4, 1036–1055 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-025-00860-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-025-00860-1