Abstract
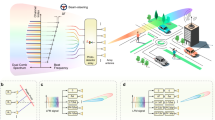
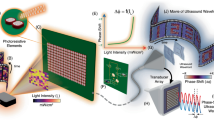
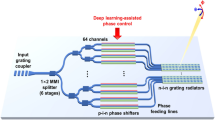
Targeted communication is made possible using beamforming. It is extensively employed in many disciplines involving electromagnetic waves, including arrayed ultrasonic, optical, and high-speed wireless communication. Conventional beam steering often requires the addition of separate active amplitude and phase control units after each radiating element. The high-power consumption and complexity of large-scale phased arrays can be overcome by reducing the number of active controllers, pushing beamforming into satellite communications and deep space exploration. To address this, we propose a phased array antenna design based on dimensionality-reduced cascaded angle offset phased array (DRCAO-PAA). By applying singular value decomposition (SVD) to compress the coefficient matrix of phase shifts, our method reduces the number of active controllers while maintaining beam-steering performance. Furthermore, the suggested DRCAO-PAA was sing the singular value deposition concept. For practical application the particle swarm optimization algorithm and deep neural network Transformer were adopted. Based on this theoretical framework, an experimental board was built to verify the theory. Finally, the 16/8/4 -array beam steering was demonstrated by using 4/3/2 active controllers, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the plots within this paper and the other finding of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
The code supporting the findings of this study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The custom scripts were developed using MATLAB/Python and are specific to the experiments described in this manuscript.
References
Wu, C. et al. A phased array based on large-area electronics that operates at gigahertz frequency. Nat. Electron. 4, Art. no. 10 (2021).
E. Aryafar, N. Anand, T. Salonidis, and E. W. Knightly, ‘Design and experimental evaluation of multi-user beamforming in wireless LANs’, in Proceedings of the sixteenth annual international conference on Mobile computing and networking, in MobiCom ’10. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2010. 197–208 https://doi.org/10.1145/1859995.1860019.
Cao, Z. et al. Advanced Integration Techniques on Broadband Millimeter-Wave Beam Steering for 5G Wireless Networks and Beyond. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 52, 1–20 (2016).
Koonen, T. et al. High-Capacity Optical Wireless Communication Using Two-Dimensional IR Beam Steering. J. Light. Technol. 36, 4486–4493 (2018).
Muñoz-Ferreras, J.-M. & Gómez-García, R. Beam-steering radars at low cost. Nat. Electron. 3, Art. no. 2 (2020).
Smith, B., Hellman, B., Gin, A., Espinoza, A. & Takashima, Y. Single chip lidar with discrete beam steering by digital micromirror device. Opt. Express 25, 14732–14745 (2017).
Pernot, M., Aubry, J.-F., Tanter, M., Thomas, J.-L. & Fink, M. High power transcranial beam steering for ultrasonic brain therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 48, 2577–2589 (2003).
Cook, D. A., Christoff, J. T. & Fernandez, J. E. Broadbeam multi-aspect synthetic aperture sonar. in MTS/IEEE Oceans 2001. An Ocean Odyssey. Conference Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No.01CH37295) 1, 188–192 (2001).
Van Veen, B. D. & Buckley, K. M. ‘Beamforming: a versatile approach to spatial filtering. IEEE ASSP Mag 5, 4–24 (1988).
C. Fischer, M. Goppelt, H.-L. Blöcher, and J. Dickmann, ‘Minimizing interference in automotive radar using digital beamforming’, in Advances in Radio Science, Copernicus GmbH, Jul. 2011. 45–48 https://doi.org/10.5194/ars-9-45-2011.
Oh, C. W., Cao, Z., Tangdiongga, E. & Koonen, T. Free-space transmission with passive 2D beam steering for multi-gigabit-per-second per-beam indoor optical wireless networks. Opt. Express 24, 19211–19227 (2016).
Cao, Z., Zhao, X., Soares, F. M., Tessema, N. & Koonen, A. M. J. 38-GHz Millimeter Wave Beam Steered Fiber Wireless Systems for 5G Indoor Coverage: Architectures, Devices, and Links. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 53, 1–9 (2017).
Zhi, K., Pan, C., Ren, H. & Wang, K. Power Scaling Law Analysis and Phase Shift Optimization of RIS-Aided Massive MIMO Systems With Statistical CSI. IEEE Trans. Commun. 70, 3558–3574 (2022).
Fu, Z., Hornbostel, A., Hammesfahr, J. & Konovaltsev, A. Suppression of multipath and jamming signals by digital beamforming for GPS/Galileo applications. GPS Solut 6, 257–264 (2003).
R. J. Mailloux, Phased Array Antenna Handbook, Third Edition. Artech House, 2017.
Mumcu, G., Kacar, M. & Mendoza, J. Mm-Wave Beam Steering Antenna With Reduced Hardware Complexity Using Lens Antenna Subarrays’, IEEE. Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 17, 1603–1607 (2018).
Reese, R. et al. A Millimeter-Wave Beam-Steering Lens Antenna With Reconfigurable Aperture Using Liquid Crystal. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67, 5313–5324 (2019).
Das, P., Mandal, K. & Lalbakhsh, A. Beam-steering of microstrip antenna using single-layer FSS based phase-shifting surface’. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 32, e23033 (2022).
Nishio, T., Xin, H., Wang, Y. & Itoh, T. ‘A frequency-controlled active phased array. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 14, 115–117 (2004).
J. Nemit, ‘Network approach for reducing the number of phase shifters in a limited scan phased array’, US3803625A, Apr. 09, 1974 Accessed: Aug. 22, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://patents.google.com/patent/US3803625A/en.
Li, Y., Iskander, M. F., Zhang, Z. & Feng, Z. ‘A New Low Cost Leaky Wave Coplanar Waveguide Continuous Transverse Stub Antenna Array Using Metamaterial-Based Phase Shifters for Beam Steering. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 61, 3511–3518 (2013).
Avser, B., Pierro, J. & Rebeiz, G. M. Random Feeding Networks for Reducing the Number of Phase Shifters in Limited-Scan Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 64, 4648–4658 (2016).
Avser, B., Frazita, R. F. & Rebeiz, G. M. Interwoven Feeding Networks With Aperture Sinc-Distribution for Limited-Scan Phased Arrays and Reduced Number of Phase Shifters. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66, 2401–2413 (2018).
Rupakula, B., Aljuhani, A. H. & Rebeiz, G. M. Limited Scan-Angle Phased Arrays Using Randomly Grouped Subarrays and Reduced Number of Phase Shifters. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68, 70–80 (2020).
Juárez, E. et al. An Innovative Way of Using Coherently Radiating Periodic Structures for Phased Arrays With Reduced Number of Phase Shifters. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 70, 307–316 (2022).
Juarez, E., Panduro, M. A., Covarrubias, D. H. & Reyna, A. Simplification of Linear Beam-Forming Networks by Applying a Novel Phase Interpolation Technique. in IEEE Open Journal of Antennas and Propagation 5, 1714–1723 (2024).
Verho, S. & Chung, J.-Y. Design of a Compact and Minimalistic Intermediate Phase Shifting Feed Network for Ka-Band Electrical Beam Steering. Sensors 24, 1235 (2024).
Ehyaie, D. & Mortazawi, A. ‘A new approach to design low cost, low complexity phased arrays’, in 2010 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, 2010. 1270–1273 https://doi.org/10.1109/MWSYM.2010.5517956.
Topak, E., Hasch, J., Wagner, C. & Zwick, T. ‘A Novel Millimeter-Wave Dual-Fed Phased Array for Beam Steering. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61, 3140–3147 (2013).
Akbar, F. & Mortazawi, A. Scalable Phased Array Architectures With a Reduced Number of Tunable Phase Shifters. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 65, 3428–3434 (2017).
Akbar, F. & Mortazawi, A. ‘A K-Band Low-Complexity Modular Scalable Wide-Scan Phased Array’, in 2020 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), 2020. 1227–1230 https://doi.org/10.1109/IMS30576.2020.9224071.
Akbar, F. & Mortazawi, A. ‘Design of a scalable phased array antenna with a simplified architecture’, in 2015 European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Sep. 2015. 1427–1430 https://doi.org/10.1109/EuMC.2015.7346041.
W. Liu and S. Weiss, Wideband Beamforming: Concepts and Techniques. John Wiley & Sons, 2010.
Juarez, E., Panduro, M. A., Covarrubias, D. H. & Reyna, A. Simplification of Linear Beam-Forming Networks by Applying a Novel Phase Interpolation Technique. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 5, 1714–1723 (2024).
Golub, G. H. & Reinsch, C. ‘Singular Value Decomposition and Least Squares Solutions’, in Linear Algebra, J. H. Wilkinson, C. Reinsch, and F. L. Bauer, Eds., in Handbook for Automatic Computation., Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1971. 134–151 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-39778-7_10.
Vaswani, A. et al. ‘Attention is All you Need’, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Curran Associates, Inc., 2017. Accessed: Aug. 24, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2017/hash/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Abstract.html.
Tan, M. & Le, Q. ‘EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks’, in Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, May 2019. 6105–6114. Accessed: Aug. 24, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v97/tan19a.html.
Graves, A. ‘Generating Sequences With Recurrent Neural Networks’, Jun. 05, 2014, arXiv: arXiv:1308.0850. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1308.0850.
Dosovitskiy, A. et al. ‘An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale’, Jun. 03, 2021, arXiv: arXiv:2010.11929. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2010.11929.
Kennedy, J. & Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. in Proceedings of ICNN’95 - International Conference on Neural Networks 4, 1942–1948 (1995).
Loshchilov, I. & Hutter, F., ‘Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam’, Feb. 2022, Accessed: Aug. 24, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://openreview.net/forum?id=rk6qdGgCZ.
Loshchilov, I. & Hutter, F. “Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam,” (arXiv:1711.05101) — later version: “Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization,” ICLR 2019.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (No.2025ZD1302100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z. Cao conceived the idea of DRCAO-PAA, the use of AI to empower the LIVG search process and led the theoretical analysis and the numerical simulation. S. Xia led the experimental research, designed the AI algorithm, and performed the numerical simulation. M. Zhao contributes to the theoretical analysis, numerical simulation, and design of the antenna array. Q. Ma led and performed the design and realization of the phase shifter board. X. Zhang and L. Yang led and performed the research on the antenna array. H. Chung contributed to the design of the phase shifter board. F. Li and Yazhi Pi supervised the research on the compatibility in communication system. Ad Reniers led the far-field pattern measurement of DRCAO-PAA. A.M.J. Koonen led the whole research and guided the paper writing. All authors contributed to the data discussion and wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Engineering thanks Hong Soo Park and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editors: [Miranda Vinay, Anastasiia Vasylchenkova, Rosamund Daw]. [A peer review file is available].
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, S., Zhao, M., Ma, Q. et al. Dimensionality reduced antenna array for beamforming/steering. Commun Eng (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44172-026-00588-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44172-026-00588-6