Abstract
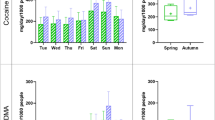
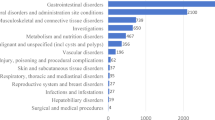
Steroidal androgens, non-steroidal androgens and other non-steroidal performance- and image-enhancing drugs that are Schedule III substances under the US Controlled Substances Act as well as Schedule 4 and 10 substances under the Australian Poisons Standard are being used by athletes and non-athletes. Recent data suggest that they are growing in popularity among those communities. However, more information is necessary to understand the extent of their use by the general population. This study provides more information by assessing the emergence and occurrence (temporal and spatial trends) of performance- and image-enhancing drug use within the general community through wastewater analysis. For this, archived wastewater collected from 2009 to 2021 from one treatment plant and wastewater collected in August 2021 from 51 treatment plants covering 11.6 million Australian people (45% of the national population) was extracted and analysed for 52 performance- and image-enhancing drugs. These included steroidal and non-steroidal androgens, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta agonist metabolites, ReV-ErbA agonists, β2-agonists, myostatin inhibitors and growth hormone secretagogues. Analysis of the samples from 2009 to 2021 showed the earliest detection of a non-steroidal androgen, enobosarm, in 2011, followed by cardarine metabolites, ibutamoren and ligandrol and testolone in 2014, 2016 and 2017, respectively. The concentrations of all identified substances increased until 2021 following their first detection. Steroidal androgens and non-steroidal performance-enhancing drugs were detected in samples from 49 of the 51 investigated wastewater treatment plants. A higher number of different analytes were detected in samples representing catchments with larger populations. Our study demonstrates that wastewater analysis can be a useful tool for providing information on performance-enhancing drug use in the general population.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data obtained during this study are provided in the Supplementary Information. To ensure anonymity of the WWTPs, population and flow data are not made available, but instead, mass loads are provided on a per capita basis or as raw concentrations.
References
Sjöqvist, F., Garle, M. & Rane, A. Use of doping agents, particularly anabolic steroids, in sports and society. Lancet 371, 1872–1882 (2008).
Brennan, B. P., Kanayama, G. & Pope, H. G. Jr. Performance-enhancing drugs on the web: a growing public-health issue. Am. J. Addict. 22, 158–161 (2013).
Kanayama, G., Kaufman, M. J. & Pope, H. G. Jr. Public health impact of androgens. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 25, 218–223 (2018).
Shimko, K. M. et al. Performance- and image-enhancing drug use in the community: use prevalence, user demographics and the potential role of wastewater-based epidemiology. J. Hazard. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126340 (2021).
World Anti-Doping Code World Anti-Doping Agency https://www.wada-ama.org/en/resources/world-anti-doping-program/world-anti-doping-code (2021).
Thevis, M. & Schanzer, W. Detection of SARMs in doping control analysis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 464, 34–45 (2018).
Kintz, P., Ameline, A., Gheddar, L. & Raul, J.-S. LGD-4033, S-4 and MK-2866—testing for SARMs in hair: about 2 doping cases. Toxicol. Anal. Clin. 31, 56–63 (2019).
Kintz, P. et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta agonist (PPAR-δ) and selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) abuse: clinical, analytical and biological data in a case involving a poisonous combination of GW1516 (cardarine) and MK2866 (ostarine). Toxics https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9100251 (2021).
Efimenko, I. V., Chertman, W., Masterson, T. A., Dubin, J. M. & Ramasamy, R. Analysis of the growing public interest in selective androgen receptor modulators. Andrologia, 53, e14238 (2021).
Van Wagoner, R. M., Eichner, A., Bhasin, S., Deuster, P. A. & Eichner, D. Chemical composition and labeling of substances marketed as selective androgen receptor modulators and sold via the internet. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 318, 2004–2010 (2017).
Chakrabarty, R., Grainger, J., Goebel, C., Brooker, L. & George, A. ‘For research use only’: a comprehensive analysis of SARMs and related IPEDs purchased on local Australian websites between 2017 and 2018. Perform. Enhanc. Health https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peh.2021.100201 (2021).
Temerdashev, A. Z. et al. Application of chromatography–mass spectrometry methods to the control of sport nutrition and medicines marketed via internet. J. Anal. Chem. 72, 1184–1192 (2017).
Leaney, A. E. et al. Analysis of supplements available to UK consumers purporting to contain selective androgen receptor modulators. Drug Test. Anal. 13, 122–127 (2021).
Ahmed, W. et al. First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: a proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci. Total Environ. 728, 138764 (2020).
Nattino, G. et al. Association between SARS-CoV-2 viral load in wastewater and reported cases, hospitalizations, and vaccinations in Milan, March 2020 to November 2021. J. Am. Med. Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.4908 (2022).
Sherchan, S. P. et al. First detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater in North America: a study in Louisiana, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 743, 140621 (2020).
Karthikeyan, S. et al. Wastewater sequencing reveals early cryptic SARS-CoV-2 variant transmission. Nature 609, 101–108 (2022).
Ort, C. et al. Spatial differences and temporal changes in illicit drug use in Europe quantified by wastewater analysis. Addiction 109, 1338–1352 (2014).
Thomas, K. V. et al. Comparing illicit drug use in 19 European cities through sewage analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 432, 432–439 (2012).
O’Brien, J. W. et al. A wastewater-based assessment of the impact of a minimum unit price (MUP) on population alcohol consumption in the Northern Territory, Australia. Addiction 117, 243–249 (2022).
Gonzalez-Marino, I. et al. Spatio-temporal assessment of illicit drug use at large scale: evidence from 7 years of international wastewater monitoring. Addiction 115, 109–120 (2020).
Choi, P. M. et al. Social, demographic, and economic correlates of food and chemical consumption measured by wastewater-based epidemiology. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116, 21864–21873 (2019).
Sobolevsky, T. & Ahrens, B. High-throughput liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assay as initial testing procedure for analysis of total urinary fraction. Drug Test. Anal. 13, 283–298 (2021).
Backe, W. J., Ort, C., Brewer, A. J. & Field, J. A. Analysis of androgenic steroids in environmental waters by large-volume injection liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 83, 2622–2630 (2011).
Shimko, K. M., O’Brien, J. W., Lin, X., Tscharke, B. J. & Thomas, K. V. In-sample stability of 52 performance- and image-enhancing drug biomarkers in wastewater. ACS ES T Water 3, 669–678 (2023).
Anti-Doping Testing Figures Report (World Anti-Doping Agency); https://www.wada-ama.org/en/resources/laboratories/anti-doping-testing-figures-report
Hahamyan, H. A., Vasireddi, N., Voos, J. E. & Calcei, J. G. Social media’s impact on widespread SARMs abuse. Phys. Sportsmed. https://doi.org/10.1080/00913847.2022.2078679 (2022).
Efimenko, I. V., Valancy, D., Dubin, J. M. & Ramasamy, R. Adverse effects and potential benefits among selective androgen receptor modulators users: a cross-sectional survey. Int. J. Impot. Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-021-00465-0 (2021).
Skarberg, K., Nyberg, F. & Engstrom, I. Multisubstance use as a feature of addiction to anabolic-androgenic steroids. Eur. Addict. Res. 15, 99–106 (2009).
Pope, H. G. Jr, Khalsa, J. H. & Bhasin, S. Body image disorders and abuse of anabolic-androgenic steroids among men. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 317, 23–24 (2017).
Pope, H. G. Jr. et al. Adverse health consequences of performance-enhancing drugs: an endocrine society scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 35, 341–375 (2014).
Shimko, K. M. et al. In-sewer stability assessment of anabolic steroids and selective androgen receptor modulators. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 1627–1638 (2022).
Lin, X. et al. Systematic evaluation of the in-sample stability of selected pharmaceuticals, Illicit drugs, and their metabolites in wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 7418–7429 (2021).
ICH Expert Working Group. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline. Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2(R1) (ICH, 2005); https://www.ich.org/page/quality-guidelines
Tscharke, B. J. et al. Harnessing the power of the census: characterizing wastewater treatment plant catchment populations for wastewater-based epidemiology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 10303–10311 (2019).
O’Brien, J. W. et al. A national wastewater monitoring program for a better understanding of public health: a case study using the Australian Census. Environ. Int. 122, 400–411 (2019).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by, and received funding from, Sport Integrity Australia. K.M.S. was the recipient of a University of Queensland Research Higher Degree Scholarship. J.W.O’B. is the recipient of an NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellowship (EL1 2009209). SCIEX provided access to the 7500 system mass spectrometer. Sample collection was funded in part by the Australian Research Council (LP150100364 and LP190101124). Pooling of the temporal samples was funded by the Commonwealth Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment (DAWE). We thank E. Knight who managed the DAWE project, from which the pooled temporal samples used in this study originated, and played a fundamental role in the planning and execution of the pooling strategy. The Queensland Alliance for Environmental Health Sciences, The University of Queensland receives financial support from Queensland Health, Australia. We acknowledge the WWTP personnel who collected the samples and provided flow data, catchment maps and additional metadata.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.M.S., J.W.O’B., B.J.T., N.S., J.F.M. and K.V.T. designed the research; K.M.S. and J.W.O’B. performed the research; K.M.S., B.J.T. and R.S. analysed the data; K.M.S. and J.W.O’B. drafted the manuscript; K.M.S., J.W.O’B., B.J.T., L.B., C.G., R.S., N.S., J.F.M. and K.V.T. contributed to the interpretation of data, provided critical revisions to the draft manuscript and approved the final draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interest.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Water thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary materials and methods, Fig. 1 and Tables 1–7.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shimko, K.M., O’Brien, J.W., Tscharke, B.J. et al. Emergence and occurrence of performance-enhancing substance use in Australia determined by wastewater analysis. Nat Water 1, 879–886 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-023-00136-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-023-00136-y
This article is cited by
-
Method validation for the detection of the anabolic–androgenic steroids methenolone and 19-norandrosterone in wastewater and application to real wastewater samples
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (2025)
-
When performance-enhancing substances are on the rise
Nature Water (2023)