Abstract
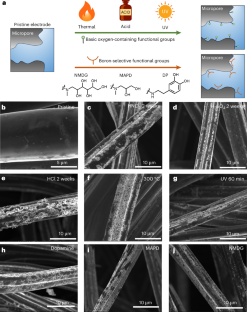
Selective removal of trace contaminants from water remains a crucial challenge in water treatment. Boron is a trace contaminant that is ubiquitous in seawater and has been widely detected in groundwater. Current boron removal methods, such as multi-stage reverse osmosis and ion-exchange adsorption, are chemical and energy intensive, necessitating the development of more sustainable technologies. Here we address this challenge by developing surface functionalized microporous electrodes that enable boron-selective bipolar membrane-assisted electrosorption. Our study demonstrates that micropore functionalization with oxygen-containing (hydroxyl, lactone and carboxyl) and boron-selective (dopamine, 3-methylamino-1,2-propanediol and N-methyl-d-glucamine) functional groups substantially improves electrode performance for boron removal and selectivity. The functionalized electrodes exhibit a boron removal selectivity that is an order of magnitude higher than that of the pristine electrode, facilitating energy efficient boron electrosorption. We identify hydroxyl groups as the key factor in enhancing boron removal performance and selectivity during electrosorption. Molecular dynamics simulations demonstrate the underlying mechanisms of boron selectivity, highlighting the role of hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl groups and boron in governing the boron-selective electrosorption process.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information. All data files in .xlsx format are available as Supplementary Data 1–3. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Mekonnen, M. M. & Hoekstra, A. Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2, e1500323 (2016).
Rodell, M. et al. Emerging trends in global freshwater availability. Nature 557, 651–659 (2018).
Mauter, M. S. et al. The role of nanotechnology in tackling global water challenges. Nat. Sustain. 1, 166–175 (2018).
Kurwadkar, S. et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and wastewater: a critical review of their global occurrence and distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 809, 151003 (2022).
Elimelech, M. & Phillip, W. A. The future of seawater desalination: energy, technology, and the environment. Science 333, 712–717 (2011).
Gin, D. L. & Noble, R. D. Designing the next generation of chemical separation membranes. Science 332, 674–676 (2011).
Wang, L. et al. Water transport in reverse osmosis membranes is governed by pore flow, not a solution-diffusion mechanism. Sci. Adv. 9, eadf8488 (2023).
Patel, S. K., Biesheuvel, P. M. & Elimelech, M. Energy consumption of brackish water desalination: identifying the sweet spots for electrodialysis and reverse osmosis. ACS ES&T Eng. 1, 851–864 (2021).
Wang, L., Violet, C., DuChanois, R. M. & Elimelech, M. Derivation of the theoretical minimum energy of separation of desalination processes. J. Chem. Edu. 97, 4361–4369 (2020).
Greenlee, L. F., Lawler, D. F., Freeman, B. D., Marrot, B. & Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 43, 2317–2348 (2009).
Patel, S. K., Pan, W., Shin, Y.-U., Kamcev, J. & Elimelech, M. Electrosorption integrated with bipolar membrane water dissociation: a coupled approach to chemical-free boron removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 4578–4590 (2023).
Boron in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality (World Health Organization, 2009).
Weinthal, E., Parag, Y., Vengosh, A., Muti, A. & Kloppmann, W. The EU drinking water directive: the boron standard and scientific uncertainty. Eur. Environ. 15, 1–12 (2005).
DeLeo, P. C., Stuard, S. B., Kinsky, O., Thiffault, C. & Baisch, B. Assessment of consumer exposure to boron in cleaning products: a case study of Canada. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 51, 359–371 (2021).
Drinking Water Health Advisory for Boron (US EPA, 2008); https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2014-09/documents/drinking_water_health_advisory_for_boron.pdf
Hilal, N., Kim, G. J. & Somerfield, C. Boron removal from saline water: a comprehensive review. Desalination 273, 23–35 (2011).
Lokiec, F. & Kronenberg, G. South Israel 100 million m3/y seawater desalination facility: build, operate and transfer (BOT) project. Desalination 156, 29–37 (2003).
Rybar, S., Boda, R. & Bartels, C. Split partial second pass design for SWRO plants. Desalin. Water Treat. 13, 186–194 (2010).
Chillón Arias, M. F., Valero i Bru, L., Prats Rico, D. & Varó Galvañ, P. Approximate cost of the elimination of boron in desalinated water by reverse osmosis and ion exchange resins. Desalination 273, 421–427 (2011).
Güler, E., Kaya, C., Kabay, N. & Arda, M. Boron removal from seawater: state-of-the-art review. Desalination 356, 85–93 (2015).
Suss, M. E. et al. Water desalination via capacitive deionization: what is it and what can we expect from it? Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 2296–2319 (2015).
Alkhadra, M. A. et al. Electrochemical methods for water purification, ion separations, and energy conversion. Chem. Rev. 122, 13547–13635 (2022).
Oren, Y. Capacitive deionization (CDI) for desalination and water treatment—past, present and future (a review). Desalination 228, 10–29 (2008).
Qin, M. et al. Comparison of energy consumption in desalination by capacitive deionization and reverse osmosis. Desalination 455, 100–114 (2019).
Patel, S. K., Qin, M., Walker, W. S. & Elimelech, M. Energy efficiency of electro-driven brackish water desalination: electrodialysis significantly outperforms membrane capacitive deionization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 3663–3677 (2020).
Shocron, A. N. et al. Electrochemical removal of amphoteric ions. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 118, e2108240118 (2021).
Shocron, A. N., Uwayid, R., Guyes, E. N., Dykstra, J. E. & Suss, M. E. Order-of-magnitude enhancement in boron removal by membrane-free capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 466, 142722 (2023).
Sun, J., Zhang, C., Song, Z. & Waite, T. D. Boron removal from reverse osmosis permeate using an electrosorption process: feasibility, kinetics, and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 10391–10401 (2022).
Gamaethiralalage, J. G. et al. Recent advances in ion selectivity with capacitive deionization. Energy Environ. Sci. 14, 1095–1120 (2021).
DeFrancesco H., Dudley J. & Coca A. in Boron Reagents in Synthesis Ch. 1 (ed. Coca, A.) (American Chemical Society, 2016).
Guan, Z., Lv, J., Bai, P. & Guo, X. Boron removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption—a review. Desalination 383, 29–37 (2016).
Kamcev, J. et al. Functionalized porous aromatic frameworks as high-performance adsorbents for the rapid removal of boric acid from water. Adv. Mater. 31, 1808027 (2019).
Uliana, A. A. et al. Ion-capture electrodialysis using multifunctional adsorptive membranes. Science 372, 296–299 (2021).
Polovina, M., Babić, B., Kaluderović, B. & Dekanski, A. Surface characterization of oxidized activated carbon cloth. Carbon 35, 1047–1052 (1997).
Cheng, N. et al. Acidically oxidized carbon cloth: a novel metal-free oxygen evolution electrode with high catalytic activity. Chem. Commun. 51, 1616–1619 (2015).
Bard A. J., Faulkner L. R. & White H. S. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications (Wiley, 2022).
Trasatti, S. & Petrii, O. Real surface area measurements in electrochemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 63, 711–734 (1991).
Zhang, Z. & Flaherty, D. W. Modified potentiometric titration method to distinguish and quantify oxygenated functional groups on carbon materials by pKa and chemical reactivity. Carbon 166, 436–445 (2020).
Petrovic, B., Gorbounov, M. & Masoudi Soltani, S. Impact of surface functional groups and their introduction methods on the mechanisms of CO2 adsorption on porous carbonaceous adsorbents. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 3, 100045 (2022).
Boehm, H. P. Some aspects of the surface chemistry of carbon blacks and other carbons. Carbon 32, 759–769 (1994).
Bhagyaraj, S., Al-Ghouti, M. A., Kasak, P. & Krupa, I. An updated review on boron removal from water through adsorption processes. Emergent Mater. 4, 1167–1186 (2021).
Soga, T. & Ross, G. A. Simultaneous determination of inorganic anions, organic acids, amino acids and carbohydrates by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 837, 231–239 (1999).
Lin, J.-Y., Mahasti, N. N. N. & Huang, Y.-H. Recent advances in adsorption and coagulation for boron removal from wastewater: a comprehensive review. J. Hazard. Mater. 407, 124401 (2021).
Yoshimura, K., Miyazaki, Y., Ota, F., Matsuoka, S. & Sakashita, H. Complexation of boric acid with the N-methyl-D-glucamine group in solution and in crosslinked polymer. J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 94, 683–689 (1998).
Manjunatha Reddy, G., Gerbec, J. A., Shimizu, F. & Chmelka, B. F. Nanoscale surface compositions and structures influence boron adsorption properties of anion exchange resins. Langmuir 35, 15661–15673 (2019).
Kang, J. S. et al. Surface electrochemistry of carbon electrodes and Faradaic reactions in capacitive deionization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 12602–12612 (2022).
Kotz, S., Balakrishnan, N., Read, C. B., Vidakovic, B. & Johnson, N. L. Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences Vol. 1 (Wiley, 2005).
Wang, Y., Huang, C. & Xu, T. Which is more competitive for production of organic acids, ion-exchange or electrodialysis with bipolar membranes? J. Membr. Sci. 374, 150–156 (2011).
Xing, Y., Dementev, N. & Borguet, E. Chemical labeling for quantitative characterization of surface chemistry. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 11, 86–91 (2007).
Goertzen, S. L., Thériault, K. D., Oickle, A. M., Tarasuk, A. C. & Andreas, H. A. Standardization of the Boehm titration. Part I. CO2 expulsion and endpoint determination. Carbon 48, 1252–1261 (2010).
Sneh, O. & George, S. M. Thermal stability of hydroxyl groups on a well-defined silica surface. J. Phys. Chem. 99, 4639–4647 (1995).
Lim, Y. J., Goh, K., Kurihara, M. & Wang, R. Seawater desalination by reverse osmosis: current development and future challenges in membrane fabrication–a review. J. Membr. Sci. 629, 119292 (2021).
Spencer, R. R. & Erdmann, D. E. Azomethine H colorimetric method for determining dissolved boron in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 954–956 (1979).
López, F., Giménez, E. & Hernández, F. Analytical study on the determination of boron in environmental water samples. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 346, 984–987 (1993).
Siepmann, J. I. & Sprik, M. Influence of surface topology and electrostatic potential on water/electrode systems. J. Chem. Phys. 102, 511–524 (1995).
Price, D. J. & Brooks, C. L. III A modified TIP3P water potential for simulation with Ewald summation. J. Chem. Phys. 121, 10096–10103 (2004).
Malde, A. K. et al. An automated force field topology builder (ATB) and repository: version 1.0. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 7, 4026–4037 (2011).
Cole, M. W. & Klein, J. R. The interaction between noble gases and the basal plane surface of graphite. Surf. Sci. 124, 547–554 (1983).
Kaminski, G. A., Friesner, R. A., Tirado-Rives, J. & Jorgensen, W. L. Evaluation and reparametrization of the OPLS-AA force field for proteins via comparison with accurate quantum chemical calculations on peptides. J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 6474–6487 (2001).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Alliance for Water Innovation (NAWI), funded by the US Department of Energy, Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), Advanced Manufacturing Office, under Funding Opportunity Announcement Number DE-FOA-0001905, and by the US National Science Foundation (NSF) and US-Israel Binational Science Foundation (BSF) under award number CBET-2001219. We thank Y. Duan from the Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering at Yale University for technical assistance with conducting the electrochemically active surface area measurement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.P., D.R., J.K. and M.E. conceptualized and designed the study. W.P., D.R. and E.A., conducted experimental research. B.U. and A.H.-A. performed computational research. W.P., D.R., B.U., S.K.P. and A.I. performed data analysis and visualization. J.K. and M.E. supervised the study. W.P., D.R., B.U., J.K. and M.E. wrote the manuscript, with all authors contributing to manuscript editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Water thanks Chia-Hung Hou and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Texts 1–6, Tables 1–3 and Figs. 1–18.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 2
Statistical source data for Fig. 2a–l.
Source Data Fig. 3
Numerical data for Fig. 3b–e.
Source Data Fig. 4
Numerical data for Fig. 4c–g.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, W., Roy, D., Uralcan, B. et al. A highly selective and energy efficient approach to boron removal overcomes the Achilles heel of seawater desalination. Nat Water 3, 99–109 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-024-00362-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-024-00362-y
This article is cited by
-
Flow-synchronized ring-shaped electrochemical ion pumping for redox-free desalination without terminal electrodes
Nature Chemical Engineering (2025)
-
Boron-selective electrosorption with functionalized electrodes
Nature Water (2025)
-
Concentrations, Sources and Health Risk of Boron in Surface Water of Huaihe River Basin, China
Water, Air, & Soil Pollution (2025)