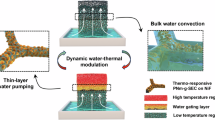
Abstract
Solar-driven steam generation (SSG) combines solar energy and water, two of Earth’s most abundant yet essential resources, and has garnered widespread attention. Over the past decade, substantial advancements have been made in improving both solar-to-steam conversion efficiency and long-term stability. However, relying solely on solar conversion efficiency as a performance benchmark is no longer sufficient, given the widespread achievement of high efficiency levels. Exciting progress has recently been made in the functionalization of SSG, suggesting a new and pivotal role for SSG in addressing broader application scenarios related to water and energy sustainability. In this Review we first trace milestones in the development of SSG and explore its conceptual functionalization, which is driving recent innovative strides in water and energy sustainability. Insights are provided to further exploit this promising potential. Finally, we discuss the challenges and future prospects of SSG, highlighting a pathway for future development and practical applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, C. et al. China’s energy transitions for carbon neutrality: challenges and opportunities. Carb. Neutral. 1, 7 (2022).
Staffell, I. et al. The role of hydrogen and fuel cells in the global energy system. Energy Environ. Sci. 12, 463–491 (2019).
Hauch, A. et al. Recent advances in solid oxide cell technology for electrolysis. Science 370, eaba6118 (2020).
Chen, C. et al. Challenges and perspectives for solar fuel production from water/carbon dioxide with thermochemical cycles. Carb. Neutral. 2, 9–27 (2023).
Montoya, J. H. et al. Materials for solar fuels and chemicals. Nat. Mater. 16, 70–81 (2017).
Chu, S. & Majumdar, A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future. Nature 488, 294–303 (2012).
Tao, P. et al. Solar-driven interfacial evaporation. Nat. Energy 3, 1031–1041 (2018).
Wu, S. et al. Solar-driven evaporators for water treatment: challenges and opportunities. Environ. Sci. Wat. Res. Technol. 7, 24–39 (2021).
Yang, H. C. et al. Membranes in solar‐driven evaporation: design principles and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2304580 (2023).
Li, X., Xie, W. & Zhu, J. Interfacial solar steam/vapor generation for heating and cooling. Adv. Sci. 9, 2104181 (2022).
Xu, N. et al. Going beyond efficiency for solar evaporation. Nat. Water. 1, 494–501 (2023).
Wang, W., Aleid, S. & Wang, P. Decentralized co‐generation of fresh water and electricity at point of consumption. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 4, 2000005 (2020).
Shi, P., Li, J., Song, Y., Xu, N. & Zhu, J. Cogeneration of clean water and valuable energy/resources via interfacial solar evaporation. Nano Lett. 24, 5673–5682 (2024).
Zhang, L. et al. Passive, high-efficiency thermally-localized solar desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 14, 1771–1793 (2021).
Yu, Z. et al. Interfacial solar evaporator for clean water production and beyond: from design to application. Appl. Energy 299, 117317 (2021).
Han, X., Ding, S., Hu, H. & Wang, S. Recent advances in structural regulation and optimization of high-performance solar-driven interfacial evaporation systems. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 1859–18541 (2022).
Wang, Z. et al. Pathways and challenges for efficient solar-thermal desalination. Sci. Adv. 5, eaax0763 (2019).
Onggowarsito, C. et al. Updated perspective on solar steam generation application. Energy Environ. Sci. 17, 2088–2099 (2024).
Finnerty, C. T. K. et al. Demand for off-grid desalination technology in small-island communities—can interfacial solar vapor generation be the answer? Desalination 553, 116454 (2023).
Yang, H. C. et al. Chinese ink: a powerful photothermal material for solar steam generation. Adv. Mater. Interf. 6, 1801252 (2019).
Kim, H. T. et al. Recent advances in high‐rate solar‐driven interfacial evaporation. Adv. Sci. 11, 2401322 (2024).
Zhang, Y., Xiong, T., Nandakumar, D. K. & Tan, S. C. Structure architecting for salt‐rejecting solar interfacial desalination to achieve high‐performance evaporation with in situ energy generation. Adv. Sci. 7, 1903478 (2020).
Li, X. et al. Enhancement of interfacial solar vapor generation by environmental energy. Joule 2, 1331–1338 (2018).
Gao, T., Wu, X., Wang, Y., Owens, G. & Xu, H. A hollow and compressible 3D photothermal evaporator for highly efficient solar steam generation without energy loss. Sol. RRL 5, 2100053 (2021).
Xu, W. et al. Flexible and salt resistant Janus absorbers by electrospinning for stable and efficient solar desalination. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1702884 (2018).
Ni, G. et al. A salt-rejecting floating solar still for low-cost desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 1510–1519 (2018).
Zhao, F. et al. Highly efficient solar vapour generation via hierarchically nanostructured gels. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 489–495 (2018).
Chiavazzo, E., Morciano, M., Viglino, F., Fasano, M. & Asinari, P. Passive solar high-yield seawater desalination by modular and low-cost distillation. Nat. Sustain. 1, 763–772 (2018).
Zhang, L. et al. Highly efficient and salt rejecting solar evaporation via a wick-free confined water layer. Nat. Commun. 13, 849 (2022).
Xu, Z. et al. Ultrahigh-efficiency desalination via a thermally-localized multistage solar still. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 830–839 (2020).
Yu, Z. et al. Enhanced interfacial solar evaporation through formation of micro‐meniscuses and microdroplets to reduce evaporation enthalpy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2108586 (2022).
Xia, Q. et al. Solar-driven abnormal evaporation of nanoconfined water. Sci. Adv. 10, eadj3760 (2024).
Ghasemi, H. et al. Solar steam generation by heat localization. Nat. Commun. 5, 4449 (2014).
Wu, X. et al. Interfacial solar evaporation: from fundamental research to applications. Adv. Mater. 36, 2313090 (2024).
Zhu, M. et al. Plasmonic wood for high-efficiency solar steam generation. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1701028 (2018).
Zhou, L. et al. 3D self-assembly of aluminium nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced solar desalination. Nat. Photon. 10, 393–398 (2016).
Zhou, L. et al. Self-assembly of highly efficient, broadband plasmonic absorbers for solar steam generation. Sci. Adv. 2, e1501227 (2016).
Liu, H. et al. Narrow bandgap semiconductor decorated wood membrane for high-efficiency solar-assisted water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 18839–18846 (2018).
Wang, J. et al. High-performance photothermal conversion of narrow-bandgap Ti2O3 nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 29, 1603730 (2017).
Cui, L. et al. High rate production of clean water based on the combined photo-electro-thermal effect of graphene architecture. Adv. Mater. 30, 1706805 (2018).
Shi, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, L. & Wang, P. Rational design of a bi-layered reduced graphene oxide film on polystyrene foam for solar-driven interfacial water evaporation. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 16212–16219 (2017).
Xu, N. et al. Mushrooms as efficient solar steam‐generation devices. Adv. Mater. 29, 1606762 (2017).
Chen, G. et al. Biradical‐featured stable organic‐small‐molecule photothermal materials for highly efficient solar‐driven water evaporation. Adv. Mater. 32, 1908537 (2020).
Li, X. et al. Graphene oxide-based efficient and scalable solar desalination under one sun with a confined 2D water path. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113, 13953–13958 (2016).
Chiavazzo, E. Critical aspects to enable viable solar-driven evaporative technologies for water treatment. Nat. Commun. 13, 5813 (2022).
Zhang, Y. & Tan, S. C. Best practices for solar water production technologies. Nat. Sustain. 5, 554–556 (2022).
Wang, F. et al. A high-performing single-stage invert-structured solar water purifier through enhanced absorption and condensation. Joule 5, 1602–1612 (2021).
Yao, H. et al. Janus-interface engineering boosting solar steam towards high-efficiency water collection. Energy Environ. Sci. 14, 5330–5338 (2021).
Kuang, Y. et al. A high-performance self-regenerating solar evaporator for continuous water desalination. Adv. Mater. 31, 1900498 (2019).
Zhang, Y. et al. Guaranteeing complete salt rejection by channeling saline water through fluidic photothermal structure toward synergistic zero energy clean water production and in situ energy generation. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 3397–3404 (2020).
Zhang, Y. et al. Manipulating unidirectional fluid transportation to drive sustainable solar water extraction and brine-drenching induced energy generation. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 4891–4902 (2020).
Yu, Z. et al. High-flux flowing interfacial water evaporation under multiple heating sources enabled by a biohybrid hydrogel. Nano Energy 98, 107287 (2022).
Morciano, M., Fasano, M., Boriskina, S. V., Chiavazzo, E. & Asinari, P. Solar passive distiller with high productivity and Marangoni effect-driven salt rejection. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 3646–3655 (2020).
Fecko, C. J., Eaves, J. D., Loparo, J. J., Tokmakoff, A. & Geissler, P. L. Ultrafast hydrogen-bond dynamics in the infrared spectroscopy of water. Science 301, 1698–1702 (2003).
Ducker, W. A. Decreasing the energy of evaporation using interfacial water: is this useful for solar evaporation efficiency? ACS Omega 8, 19705–19707 (2023).
Yang, B. et al. Flatband λ-Ti3O5 towards extraordinary solar steam generation. Nature 622, 499–506 (2023).
Tu, Y. et al. Plausible photomolecular effect leading to water evaporation exceeding the thermal limit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 120, e2312751120 (2023).
Lv, G., Tu, Y., Zhang, J. H. & Chen, G. Photomolecular effect: visible light interaction with air–water interface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 121, e2320844121 (2024).
Wang, W. et al. Simultaneous production of fresh water and electricity via multistage solar photovoltaic membrane distillation. Nat. Commun. 10, 3012 (2019).
Cheng, S., Li, Y., Jin, B., Yu, Z. & Gu, R. Designing salt transmission channel of solar-driven multistage desalination device for efficient and stable freshwater production from seawater. Desalination 531, 115688 (2022).
Gao, J. et al. Extreme salt-resisting multistage solar distillation with thermohaline convection. Joule 7, 2274–2290 (2023).
Song, H. et al. Cold vapor generation beyond the input solar energy limit. Adv. Sci. 5, 1800222 (2018).
Shi, Y. et al. A 3D photothermal structure toward improved energy efficiency in solar steam generation. Joule 2, 1171–1186 (2018).
Wu, S. et al. Suspended membrane evaporators integrating environmental and solar evaporation for oily wastewater purification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 13, 39513–39522 (2021).
Zhang, C. et al. Designing a next generation solar crystallizer for real seawater brine treatment with zero liquid discharge. Nat. Commun. 12, 998 (2021).
Finnerty, C. T. K. et al. Interfacial solar evaporation by a 3D graphene oxide stalk for highly concentrated brine treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 15435–15445 (2021).
Niu, R. et al. Bio‐inspired sandwich‐structured all‐day‐round solar evaporator for synergistic clean water and electricity generation. Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 2302451 (2023).
Zhu, L., Ding, T., Gao, M., Peh, C. K. N. & Ho, G. W. Shape conformal and thermal insulative organic solar absorber sponge for photothermal water evaporation and thermoelectric power generation. Adv. Energy Mater. 9, 1900250 (2019).
Chen, X. et al. Scaling up nanoscale water-driven energy conversion into evaporation-driven engines and generators. Nat. Commun. 6, 7346 (2015).
Cavusoglu, A., Chen, X., Gentine, P. & Sahin, O. Potential for natural evaporation as a reliable renewable energy resource. Nat. Commun. 8, 617 (2017).
Yang, P. et al. Solar-driven simultaneous steam production and electricity generation from salinity. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 1923–1927 (2017).
Wang, H. et al. Simultaneous solar steam and electricity generation from synergistic salinity‐temperature gradient. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2100481 (2021).
Xue, G. et al. Water-evaporation-induced electricity with nanostructured carbon materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12, 317–321 (2017).
Tan, J. et al. Self-sustained electricity generator driven by the compatible integration of ambient moisture adsorption and evaporation. Nat. Commun. 13, 3643 (2022).
Shen, Q. et al. An open thermo-electrochemical cell enabled by interfacial evaporation. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 6514–6521 (2019).
Li, X. et al. Storage and recycling of interfacial solar steam enthalpy. Joule 2, 2477–2484 (2018).
Li, J. et al. Interfacial solar steam generation enables fast-responsive, energy-efficient, and low-cost off-grid sterilization. Adv. Mater. 30, 1805159 (2018).
Chang, C. et al. High-efficiency superheated steam generation for portable sterilization under ambient pressure and low solar flux. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 11, 18466–18474 (2019).
Cooper, T. A. et al. Contactless steam generation and superheating under one sun illumination. Nat. Commun. 9, 5086 (2018).
Zhao, L. et al. A passive high-temperature high-pressure solar steam generator for medical sterilization. Joule 4, 2733–2745 (2020).
Yao, P. et al. Greener and higher conversion of esterification via interfacial photothermal catalysis. Nat. Sustain. 5, 348–356 (2022).
Li, D. et al. Mutual reinforcement of evaporation and catalysis for efficient freshwater–salt–chemical production. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2300353 (2023).
Lu, Z., Strobach, E., Chen, N., Ferralis, N. & Grossman, J. C. Passive sub-ambient cooling from a transparent evaporation-insulation bilayer. Joule 4, 2693–2701 (2020).
Xu, N. et al. Synergistic tandem solar electricity-water generators. Joule 4, 347–358 (2020).
Li, R., Shi, Y., Wu, M., Hong, S. & Wang, P. Photovoltaic panel cooling by atmospheric water sorption–evaporation cycle. Nat. Sustain. 3, 636–643 (2020).
Wang, W. et al. Integrated solar-driven PV cooling and seawater desalination with zero liquid discharge. Joule 5, 1873–1887 (2021).
Mao, Z. et al. Passive interfacial cooling-induced sustainable electricity–water cogeneration. Nat. Water 2, 93–100 (2024).
Xu, J. et al. Near-zero-energy smart battery thermal management enabled by sorption energy harvesting from air. ACS Cent. Sci. 6, 1542–1554 (2020).
Wang, C. et al. A thermal management strategy for electronic devices based on moisture sorption-desorption processes. Joule 4, 435–447 (2020).
Zhou, S. et al. Self-regulating solar steam generators enable volatile organic compound removal through in situ H2O2 generation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 10474–10482 (2022).
Qi, D. et al. Polymeric membranes with selective solution‐diffusion for intercepting volatile organic compounds during solar‐driven water remediation. Adv. Mater. 32, 2004401 (2020).
Ma, J. et al. A light-permeable solar evaporator with three-dimensional photocatalytic sites to boost volatile-organic-compound rejection for water purification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 9797–9805 (2022).
Guo, Y. et al. Biomass‐derived hybrid hydrogel evaporators for cost‐effective solar water purification. Adv. Mater. 32, 1907061 (2020).
Yu, Z. et al. Microplastic detection and remediation through efficient interfacial solar evaporation for immaculate water production. Nat. Commun. 15, 6081 (2024).
Wu, P., Wu, X., Wang, Y., Xu, H. & Owens, G. A biomimetic interfacial solar evaporator for heavy metal soil remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 435, 134793 (2022).
Zou, H. et al. Solar-driven scalable hygroscopic gel for recycling water from passive plant transpiration and soil evaporation. Nat. Water 2, 663–673 (2024).
Chen, W., Wang, T., Dou, Z. & Xie, X. Microalgae harvesting by self-driven 3D microfiltration with rationally designed porous superabsorbent polymer (PSAP) beads. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 15446–15455 (2021).
Wang, B., Zhao, S., Wang, S., Fu, Y. & Liu, M. Coupling photothermal evaporation into photocatalysis for enhanced hydrogen production from water. Innov. Energy 1, 100018 (2024).
Lee, W. H. et al. Floatable photocatalytic hydrogel nanocomposites for large-scale solar hydrogen production. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 754–762 (2023).
Pornrungroj, C. et al. Hybrid photothermal–photocatalyst sheets for solar-driven overall water splitting coupled to water purification. Nat. Water 1, 952–960 (2023).
Ren, L. et al. Nanostructuring of Mg-based hydrogen storage materials: recent advances for promoting key applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 15, 93 (2023).
Neumann, O. et al. Combining solar steam processing and solar distillation for fully off-grid production of cellulosic bioethanol. ACS Energy Lett. 2, 8–13 (2017).
Bian, Y. et al. Farming on the ocean via desalination (FOOD). Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 21104–21112 (2023).
Wang, M. et al. An integrated system with functions of solar desalination, power generation and crop irrigation. Nat. Water 1, 716–724 (2023).
Guo, S. et al. Repurposing face mask waste to construct floating photothermal evaporator for autonomous solar ocean farming. EcoMat 4, e12179 (2022).
Kazi, O. A. et al. Material design strategies for recovery of critical resources from water. Adv. Mater. 35, 2300913 (2023).
Chen, X. et al. Spatially separated crystallization for selective lithium extraction from saline water. Nat. Water 1, 808–817 (2023).
Li, H. et al. Design of photothermal ‘ion pumps’ for achieving energy-efficient, augmented, and durable lithium extraction from seawater. ACS Nano 18, 2434–2445 (2024).
Zhong, Y. et al. Bridging materials innovations to sorption-based atmospheric water harvesting devices. Nat. Rev. Mater. 9, 681–698 (2024).
Li, T. et al. Scalable and efficient solar-driven atmospheric water harvesting enabled by bidirectionally aligned and hierarchically structured nanocomposites. Nat. Water 1, 971–981 (2023).
Zhao, F., Guo, Y., Zhou, X., Shi, W. & Yu, G. Materials for solar-powered water evaporation. Nat. Rev. Mater. 5, 388–401 (2020).
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (grant number 2023YFB4005403) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 52306106). Y.Z. acknowledges financial support from Shanghai Jiao Tong University (grant number WH220428005) and S.C.T acknowledges financial support from Singapore Ministry of Education (grant number A-0009304-00-00).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Z. and S.C.T. conceptualized the manuscript. K.M., Y.Z. and S.C.T. researched data and performed analyses. K.M. and Y.Z. designed and produced Figs. 1–7. All authors contributed to discussions, writing and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Water thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, K., Zhang, Y. & Tan, S.C. Functionalizing solar-driven steam generation towards water and energy sustainability. Nat Water 3, 144–156 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-024-00363-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-024-00363-x
This article is cited by
-
Interfacial evaporation-induced localized multi-field coupling enables efficient co-recovery of freshwater and nitrates
Nature Communications (2026)
-
Nature-Inspired Upward Hanging Evaporator with Photothermal 3D Spacer Fabric for Zero-Liquid-Discharge Desalination
Nano-Micro Letters (2026)
-
Janus-interface engineering enhances hydrogel integrated with ZIF-8@Co9S8 composite featuring concave pyramid patterns for efficient solar-driven water purification
Science China Materials (2026)
-
Experimental performance enhancements of a stepped solar still using bio-inspired leaf shaped copper fins
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Effect of porous material and black coating on solar desalination for sustainable water harvesting: A thermo-exergo-economic and environmental analysis
Scientific Reports (2025)