Abstract
Interleukin 7 (IL-7) is an immunostimulatory cytokine essential for T cell development, proliferation, and maintenance. While IL-7 generates antitumor immunity, systemic IL-7 has not consistently produced strong anticancer effects. Achieving therapeutic cytokine concentrations in tumors often requires high systemic doses, leading to toxicity. To address this, localized cytokine expression within the tumor microenvironment (TME) has gained interest. One such approach involves cytokine expression by oncolytic viruses (OVs) that selectively replicate in cancerous cells while sparing ‘normal’ cells. Additionally, non-replicative viral vectors have become valuable tools for sustaining cytokine expression in the TME, inducing antitumor effects through non-lytic mechanisms. To effectively harness IL-7’s antitumor potential, both oncolytic and non-lytic viruses have been engineered to express IL-7, either alone or in combination with other immunomodulators, such as IL-12, IL-15, B7-1, or CCL19. Despite promising advancements, no comprehensive review exists on IL-7 expression in virus-based immunotherapy for cancer. Therefore, this manuscript aims to (i) summarize studies on viral IL-7 expression alone or with other immunomodulators, (ii) discuss the associated immune mechanisms of action, and (iii) explore opportunities for co-expressing IL-7 with other key cytokines to optimize immunovirotherapy strategies for cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Interleukin 7 (IL-7), a common gamma (γ) chain cytokine family, is an immunomodulatory cytokine naturally produced by stromal cells in the bone marrow and epithelial cells in the thymus [1, 2]. IL-7 binds to a heterodimeric receptor, which is formed by the IL-7 receptor alpha chain (IL-7Rα) and the common γ chain [3]. Furthermore, IL-7Rα pairs with the thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor (TSLPR) and forms another heterodimeric receptor for TSLP [1]. IL-7 interaction with the IL-7Rα subunit is essential for the activation of downstream signaling processes, such as phosphorylation- and redox-dependent signaling pathways, that impact cellular function in diverse ways [4]. For instance, IL-7Rα activation promotes phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on its intracellular domain, leading to the activation of kinases, such as Janus-associated kinase 1 (JAK1) or JAK3, that trigger additional signaling pathways involving Src, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5a/b (STAT5a/b), NADPH oxidase (NOX), and the phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin complex (mTORc)/Akt signaling axis [5]. In this way, IL-7 contributes to: (i) the development of T cells centrally in the thymus [6]; (ii) the long-term survival and homeostasis of natural killer (NK) cells and naïve, memory, and tumor-infiltrating T cells (TILs) in peripheral tissues [7]; (iii) B cell development, maturation, and homeostasis [7]; (iv) the proliferation of T cells, including cytotoxic T cells, and their infiltration into the tumor microenvironment (TME) [6]; (v) the prevention of immune exhaustion by reducing the expression of immune checkpoint molecules (e.g., PD-1) on TILs [8]; and (vi) the organogenesis of vital immune organs, such as lymph nodes [9] (Fig. 1). Due to these diverse properties, particularly its role in T-cell proliferation and homeostasis, IL-7 is considered a promising proinflammatory antitumor cytokine [5, 6]. However, IL-7 can be pro-tumorigenic, as it promotes cancer cell invasiveness by enhancing epithelial-mesenchymal transition [10]. Despite this duality, IL-7 is widely considered a beneficial T-cell immunomodulator [5, 6].
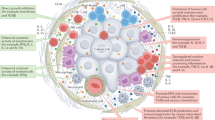
IL-7 helps in organogenesis (e.g., lymph nodes), T-cell development centrally in thymus, survival and homeostasis of natural killer (NK) and tumor-infiltrating T cells (TILs), and development, maturation, and homeostasis of B lymphocytes. IL-7 also enhances infiltration and proliferation of cytotoxic T cells into the tumor microenvironment and prevents T-cell exhaustion by reducing programmed death 1 (PD-1) expression on TILs.
The antitumor efficacy of IL-7 as a native macromolecule has been extensively evaluated in preclinical models, demonstrating antitumor immunity [5]. Importantly, recombinant IL-7 has undergone clinical testing alone or alongside other immunotherapies to stimulate the antitumor activity of T cells in refractory cancers (NCT05075603, NCT04588038, NCT04710043) [11]. Additionally, IL-7 has been used as an ‘immune reconstitution’ agent to replenish T cells in immune-depleted cancer patients [11, 12]. However, systemic cytokine therapy as a native macromolecule, including high doses of IL-7, can cause adverse effects and toxicities [11, 13]. Thus, alternative approaches are required to harness the antitumor potential of IL-7.
Oncolytic viruses (OVs) are first-in-class immunotherapy agents that selectively replicate in cancerous cells, sparing ‘normal’ cells and inducing antitumor immunity (i.e., in situ vaccine effect) [14,15,16,17]. The effect of OV-induced anticancer vaccines can be further enhanced by engineering viruses to express immunostimulatory cytokines locally within the TME [18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Among OVs, oncolytic herpes simplex virus (oHSV) is the most clinically advanced and the only OV approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for cancer treatment [25]. Non-replicative viral vectors have also emerged as promising tools in cancer immunotherapy [26]. Although they lack the oncolytic potential of OVs, they offer the advantage of sustained expression of immunostimulatory cytokines in the TME, thereby inducing antitumor effects through non-oncolytic (i.e., non-lytic) mechanisms [14, 26].
To safely utilize the antitumor potential of IL-7, lytic and non-lytic viral vectors have been engineered to express IL-7 locally within the TME [27,28,29]. Multiple studies have also explored the co-expression of IL-7 with other cytokines to achieve superior antitumor immunity. Examples include non-lytic Newcastle disease viruses (NDV) and oncolytic adenovirus, vaccinia, and herpes simplex viruses engineered to co-express IL-7 with IL-12 [30], IL-15 [31], B7-1 (CD86) [32], or CCL19 [33]. However, to date, no comprehensive review has compiled evidence related to IL-7 expression in the context of cancer immunovirotherapy. Thus, in this review, we aim to summarize studies involving viral expression of IL-7, either alone or in conjunction with other immunomodulators, and the associated immune responses and mechanisms of action.
Viral expression of IL-7 as a single cytokine
Viral expression of IL-7 induces tumor regression via T-cell activation
To date, three cytokines, IL-2, interferon alpha (IFNα), and an IL-15 receptor agonist, have been approved for cancer treatment [34, 35]. However, systemic cytokine therapy faces significant limitations, primarily due to poor cytokine accumulation in tumors following systemic delivery [13]. Achieving therapeutic concentrations in tumors often requires high-dose systemic cytokine therapy, which is associated with severe adverse effects before an optimal therapeutic concentration can be achieved [13]. To address these challenges, Kudling et al. engineered an oncolytic adenovirus (oAd) expressing human IL-7, designated Ad5/3-E2F-d24-hIL7 (TILT-517), for localized delivery of IL-7 directly into tumors [27]. Intratumoral administration of TILT-517 in an immunocompetent subcutaneous HapT1 pancreatic cancer model in Syrian hamsters significantly controlled tumor burden compared to the Ad5/3-E2F-d24 control lacking IL-7 expression [27].
Human IL-7 expression (by the TILT-517) shows cross-reactivity in hamsters, leading to antitumor activity by the TILT-517 in a Syrian hamster model [27]. This was associated with significant upregulation of T cell activation markers, such as CD25 and CD137, within tumors, increased tumoral infiltration of CD8+ T cells and Mac-2+ monocytes/macrophages, and elevated levels of CD4+, CD8+ T, and MHCII+ cells in the blood (Fig. 2; Table 1). Similarly, in patient-derived xenograft models of ovarian cancer receiving an intraperitoneal infusion of peripheral blood mononuclear cells, intratumoral TILT-517 resulted in significant tumor inhibition compared to a non-IL7-expressing oAd [27].
In ex vivo patient-derived ovarian cancer samples, TILT-517 infection significantly increased the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines while reducing anti-inflammatory cytokines, resulting in a higher pro-inflammatory/anti-inflammatory cytokine ratio than Ad5/3-E2F-d24 or mock. These findings suggest that the viral expression of IL-7 creates a pro-inflammatory TME. This concept was further validated when TILT-517-infected ovarian cancer samples showed significantly higher levels of chemoattractant (e.g., C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10)) compared to controls, leading to a substantial increase in ex vivo recruitment of cytotoxic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in TILT-517-treated samples [27] (Fig. 2; Table 1).
Overall, IL-7 expression within tumors creates a pro-inflammatory TME, a key characteristic for successful immunotherapy involving an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) [36]. Thus, further studies should explore the in-depth therapeutic potential of TILT-517 in combination with ICIs.
Viral expression of IL-7 induces tumor-specific immunity and improves the efficacy of autologous vaccine
Zhao et al. developed a non-replicative IL-7-expressing NDV by inserting the IL-7 transgene into the genome of the LX strain, a non-lytic NDV. The modified virus was designated as LX/IL-7 [28]. Subsequently, they developed an LX/IL-7-based autologous tumor vaccine by loading irradiated B16-F10 murine melanoma or EL-4 murine lymphoma cells with LX/IL-7 (i.e., B16-LX/IL-7 or EL4-LX/IL7) and tested its antitumor efficacy, prophylactically and therapeutically [28].
Prophylactically, subcutaneous immunization with B16-LX/IL-7 significantly inhibited homologous B16-F10 tumor growth compared to vaccination with irradiated B16-F10 cells loaded with LX strain expressing a red fluorescent protein (RFP) (i.e., B16-LX/RFP), highlighting the antitumor role of IL-7 expression. This finding was also similarly reproduced in the EL-4 model. The co-culture of splenocytes with B16 cell lysate demonstrated significantly more IFN-γ-expressing CD8+, not CD4+, T cells in the B16-LX/IL-7 group compared to controls [28]. This IFN-γ response was tumor-specific, as splenocytes harvested from B16-LX/IL-7-treated mice efficiently killed B16-F10 cells but not antigenically unrelated EL-4 cells. The tumor specificity of the B16-LX/IL-7 vaccine was further confirmed in vivo, where the B16-LX/IL-7 vaccine controlled B16-F10 tumor growth but failed to inhibit EL-4 lymphoma tumors [28] (Fig. 3; Table 1).
Therapeutically, the B16-LX/IL-7 vaccine significantly inhibits homologous B16-F10 tumor growth compared to the non-IL-7-expressing B16-LX/RFP vaccine. This was also reproduced in the EL-4 model using the autologous EL4-LX/IL-7 vaccine. The IL-7-expressing vaccine led to significantly increased infiltration of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells into tumors (vs. controls), and the therapeutic efficacy of the B16-LX/IL-7 vaccine was CD8+ T cell-dependent [28]. The vaccine efficacy was also tumor-specific in the therapeutic settings since the EL4-LX/IL-7 vaccine did not work against antigenically unrelated B16-F10 tumors (Table 1). Furthermore, the B16-LX/IL-7 vaccine induced a tumor-specific IFN-γ response, as splenocytes or TILs from B16-LX/IL-7-treated mice failed to produce IFN-γ when stimulated with EL-4 tumor cell lysate [28] (Fig. 3).
In summary, an autologous tumor cell vaccine loaded with a non-lytic NDV expressing IL-7 (i.e., LX/IL-7) provides significant prophylactic and therapeutic benefits by activating tumor-specific cytotoxic T-cell responses. Autologous tumor cell vaccine loaded with NDV without IL-7 expression has shown promising results in clinical studies [37], but the superior antitumor efficacy of autologous vaccine loaded with IL-7-expressing NDV in preclinical studies suggests that IL-7 expression offers substantial therapeutic advantages. However, before this vaccine can be brought into clinical translation, further in vivo characterization is necessary to evaluate the kinetics of IL-7 and the potential toxicities associated with IL-7 release. While IL-7 expression alone does not achieve complete tumor eradication, it significantly enhances vaccine efficacy associated with cytotoxic T cell responses [28]. This suggests that T cell-based immunotherapies, such as ICIs, chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T), or bi-specific T cell engagers, may produce synergistic effects when combined with an autologous tumor cell vaccine loaded with IL-7-expressing NDV. However, as the LX strain of NDV is non-lytic and does not induce oncolysis for at least 24 h post-infection [28], the release of tumor antigens and/or IL-7 may be limited. Future studies should explore the use of a lytic NDV strain expressing IL-7 and evaluate its efficacy in parallel with the non-lytic NDV strain expressing IL-7, with or without being loaded into autologous tumor cells.
Viral expression of IL-7 stimulates the proliferation of CAR-T cells and improves antitumor efficacy
B7-H3 (CD276) is an immune checkpoint molecule overexpressed in many cancer types, including 76% of glioblastoma (GBM) tumors [38], the most common primary malignant brain tumor in adults [39, 40]. B7-H3 is linked to tumor progression, therapy resistance, and cellular invasion [41]. Huang et al. constructed CAR-T cells targeting B7-H3 (referred to as B7H3-CAR-T) along with an oAd-expressing human IL-7 (oAd-IL7) and evaluated their combinatorial effect in orthotopic GBM models [29].
B7H3-CAR-T cells exposed to oAd-IL7-infected GBM cells demonstrated significantly greater proliferation and survival compared to B7H3-CAR-T cells exposed to control oAd-infected GBM cells [29]. This study underscores the beneficial role of IL-7 in enhancing T-cell survival and expansion. In vivo, in an orthotopic GBM xenograft model, the combination of oAd-IL7 and B7H3-CAR-T resulted in a significant proportion of long-term survivors (i.e., 80%), while the monotherapy using either oAd-IL7 or B7H3-CAR-T alone did not yield any survivors. The enhanced efficacy of the combinatorial therapy was associated with (i) increased tumoral infiltration of B7H3-CAR-T cells and (ii) significantly higher levels of Ki67 (a marker for proliferating cells) in the infiltrated B7H3-CAR-T cells. These effects were also accompanied by increased expression of T-cell exhaustion markers, such as LAG-3 and PD-1 [29] (Fig. 2; Table 1).
In summary, the IL-7 expression enhances the survival and expansion of CAR-T cells, resulting in promising antitumor efficacy and long-term survival. This combination strategy primarily targets B7-H3-expressing GBMs [38] but can also be applied to other B7-H3-expressing tumors, ensuring broader applicability. The safety of this compelling combination therapy needs to be assessed before clinical translation.
Viral co-expression of IL-7 with IL-12
While the expression of single cytokines has provided important data on their contribution to therapeutic antitumor responses, in general, the narrow therapeutic window for many cytokines has precluded meaningful efficacy against cancers [20, 23, 42,43,44,45,46]. Similarly, the viral expression of IL-7 alone does not consistently eradicate cancers or achieve durable efficacy [27,28,29]. One strategy to improve efficacy is to consider the expression of more than one immunomodulator [14, 21, 22, 47, 48]. To enhance the antitumor immunity of localized IL-7 expression, several viruses have been engineered to co-express IL-7 alongside other immunostimulatory cytokines [30,31,32,33]. This section and the following sections will summarize studies involving viruses that co-express IL-7 with another cytokine, highlighting their antitumor potential and mechanisms of action.
Viral co-expression of IL-7 plus IL-12 induces cytotoxic T cell-driven antitumor immunity
IL-12 activates dendritic cells (DCs) [49], stimulates macrophages and NK cells [18, 49], promotes T cell proliferation, and skews CD8+ T cells toward a cytotoxic phenotype [50, 51]. These diverse immunostimulatory properties make it a master proinflammatory cytokine, which has been tested clinically to treat cancer [52,53,54,55]. However, systemic IL-12 therapy causes severe toxicities, necessitating localized expression within the TME [56, 57]. Clinical studies with controlled release of IL-12 within the TME are ongoing [58].
Nakao et al. generated an oncolytic vaccinia virus co-expressing human IL-7 plus murine IL-12 (hIL7/mIL12-VV) and compared its efficacy with single cytokine-expressing (hIL7-VV, mIL12-VV) or non-cytokine-expressing (cont-VV) viruses in murine models [30]. Since human IL-7 is biologically active in mice [59], but human IL-12 is not [60], the study used murine IL-12. In the LLC lung carcinoma model, intratumoral injections of hIL7-VV had no significant antitumor effects, while IL-12 expression (mIL12-VV) inhibited tumor growth, achieving a complete response in 1/7 (14.3%) animals. The combinatorial use of hIL7-VV plus mIL12-VV further improved outcomes, with a 57.1% (4/7) complete response rate [30] (Fig. 2; Table 1). This enhanced efficacy correlated with increased intratumoral infiltration of CD4+ and CD8+ T, NK, and natural killer T (NKT) cells, with a significant effect observed on CD4+ T and NKT cells. Increased IFN-γ production in TME likely contributed to this effect (Fig. 2). Importantly, mice receiving the combinatorial treatment experienced no weight loss, suggesting that viral co-expression of dual cytokines within the tumor is well tolerated [30].
In the B16-F10 melanoma model, viral co-expression of IL-7 plus IL-12 (hIL7/mIL12-VV), instead of using two separate viruses (hIL7-VV plus mIL12-VV), resulted in a complete response in 75% (6/8) animals compared to 25% (2/8) in the cont-VV control group [30]. Dual cytokine expression by hIL7/mIL12-VV was also efficacious against poorly immunogenic TRAMP-C2 prostate tumors and advanced-stage (>160 mm3) CT26.WT tumors [30]. The antitumor activity of hIL7/mIL12-VV in the CT26.WT model was completely abrogated in the absence of CD8+ (not CD4+) T cells, suggesting a CD8+ T-cell-dependent mechanism [30]. However, due to the lack of relevant control viruses (i.e., hIL7-VV or mIL12-VV), it was unclear whether the observed efficacy was driven by the expression of one or both cytokines.
The antitumor role of the viral expression of IL-7 and/or IL-12 was further supported by another study [61]. For example, intratumoral injections of sindbis virus (SINV) expressing IL-7 or IL-12 (SINV-IL7 or SINV-IL12) in a subcutaneous U-87MG GBM model demonstrated superior efficacy compared to control SINV. A SINV co-expressing IL-7 plus IL-12 (SINV-IL7/IL12) further enhanced tumor suppression compared to SINV-IL7 or SINV-IL12, with SINV-IL7/IL12 achieved 80% long-term survivors in an intracranial U-87MG GBM model (Table 1). However, this study did not define the antitumor immune mechanisms of IL-7 and/or IL-12 expression [61].
Viral co-expression of IL-7 plus IL-12 induces abscopal tumor-specific immunity and immunologic memory
A key aspect of successful immunovirotherapy is assessing whether virus-induced immunostimulation generates systemic antitumor immunity (i.e., abscopal response) [62]. The dual cytokine-expressing hIL7/mIL12-VV effectively controlled distant tumor growth in bilateral CT26.WT and LLC models [30]. In the CT26.WT model, intratumoral injection of hIL7/mIL12-VV into one tumor resulted in 100% (6/6) eradication of injected tumors and 50% (3/6) of non-injected contralateral tumors, whereas cont-VV failed in both (Table 1). The inhibition of distant tumor growth by hIL7/mIL12-VV suggests its potential to manage metastatic diseases [30]. Although hIL7/mIL12-VV controlled non-injected tumors, viral DNA was detected only in injected tumors [30], indicating virus-induced systemic immunity rather than a direct oncolytic effect [62]. This correlated with enhanced MHC-II expression on antitumoral M1-like macrophages in non-injected tumors and spleens and elevated CD11b+ DCs in spleens [30] (Fig. 2). This suggests that hIL7/mIL12-VV treatment facilitated robust antigen presentation in distant lymphoid organs (e.g., spleens), critical for antitumor immunity [14].
Consistently, compared to cont-VV, hIL7/mIL12-VV significantly increased intratumoral infiltration of conventional T (CD4+FoxP3-), CD8+ T, NKT, NK, and regulatory T cells (CD4+FoxP3+) in both injected and distant tumors. Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) levels were significantly elevated following hIL7/mIL12-VV treatment, likely contributing to increased PD-L1 expression [45, 63] in both injected and non-injected CT26.WT tumors [30]. Furthermore, hIL7/mIL12-VV generated gp70 tumor antigen-specific (gp70+CD8+) T cells in both injected and distant CT26.WT tumors (Fig. 2; Table 1), reinforcing its systemic antitumor immune effect [30].
In the bilateral LLC model, hIL7/mIL12-VV reduced tumor growth by 43.1% in both injected and non-injected tumors [30]. Antitumor effects in non-injected tumors indicate virus-induced abscopal immunity [62]. Unlike CT26.WT model, viral DNA was present in both tumors. Mice cured of CT26.WT tumors rejected tumor rechallenge and remained tumor-free, suggesting the development of immune memory (Table 1). This immune memory was tumor-specific, as IFN-γ secretion (by splenocytes harvested from mice cured of CT26.WT tumors) was significantly higher against CT26.WT cells than antigenically unrelated cancer cells [30] (Fig. 2).
Viral co-expression of IL-7 plus IL-12 increases CD8+ T cell clonal diversity
The antitumor efficacy of hIL7/mIL12-VV was also evaluated in humanized tumor models. To achieve this, a new vaccinia virus co-expressing human IL-7 and human IL-12 (hIL7/hIL12-VV) was engineered, and its efficacy was assessed in immunocompromised mice bearing human HCT 116 colon tumors, U87 glioblastoma, or Detroit 562 head and neck tumors [30]. In all three models, hIL7/hIL12-VV led to significant tumor regression compared to mock treatment. Similarly, in humanized mice bearing subcutaneous NCI-H1373 tumors, hIL7/hIL12-VV was significantly more effective than cont-VV in reducing tumor burden. The superior efficacy of hIL7/hIL12-VV was associated with enhanced intratumoral infiltration of CD4+, CD8+ T, NKT, and NK cells compared to cont-VV or PBS [30] (Fig. 2; Table 1).
In a follow-up study, mechanisms of the hIL7/hIL12-VV virus were investigated and compared with corresponding controls, specifically involving viruses with or without IL-7 or IL-12 expression [64]. Interestingly, IL-7 expression alone did not promote the clonality of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. In contrast, IL-12 expression significantly enhanced CD8+ T cell clonality compared to IL-7 expression alone. The viral expression of IL-7 plus IL-12 within tumors increased the clonal diversity of CD8+ T cells compared to IL-7 expression; however, this combinatorial effect was not statistically different from IL-12 expression [64]. In another study, the same group demonstrated that viral co-expression of IL-7 and IL-12 by hIL7/mIL12-VV, compared to cont-VV treatment, significantly enhanced the percentage of ICOS+PD-1-CD8+ effector T cells within tumors in both CT26.WT and LLC models [65] (Fig. 2). Since inducible costimulatory (ICOS) is a marker for CD4+ helper T cells contributing to humoral immunity [66], this suggests that hIL7/mIL12-VV elicits humoral immunity in this context.
Viral co-expression of IL-7 plus IL-12 synergizes with ICIs
Virotherapy can be combined with systemic treatment to achieve better therapeutic outcomes [67]. In the bilateral CT26.WT model, the antitumor efficacy of hIL7/mIL12-VV was evaluated in combination with anti-PD-1 or anti-CTLA-4. Virotherapy (i.e., hIL7/mIL12-VV) alone eradicated only 10% of non-injected contralateral tumors (which mimic metastasis), while neither anti-PD-1 nor anti-CTLA-4 monotherapy showed efficacy. Importantly, combining hIL7/mIL12-VV with anti-PD-1 or anti-CTLA-4 eradicated 60% and 40% of non-injected contralateral tumors, respectively, showing the combinatorial effect [30] (Fig. 2; Table 1).
Overall, although IL-7 expression alone was not significantly beneficial in the models discussed above, it did appear to enhance the immune response elicited by IL-12 expression, as demonstrated in the LLC model. The above studies indicate that the viral co-expression of IL-7 and IL-12 within tumors effectively modifies the immune status of the TME both locally and systemically, enabling previously non-responsive tumors (such as CT26.WT and LLC) to become responsive to ICI without compromising safety [30]. Further, the local induction of IFN-γ may drive PD-L1 expression, which can also sensitize tumors to ICI [45]. Thus, the use of oncolytic cytokine-encoded viruses represents an increasingly popular strategy for combination immunovirotherapy, exploiting cytokine-expressing viruses to convert tumors from an immunologically ‘cold’ state to an immunologically ‘hot’ one, thereby sensitizing them to ICI [45, 67, 68].
The viral co-expression of IL-7 and IL-12 in one tumor alters the immune status of non-injected tumors and significantly regresses non-injected tumors [30], suggesting a strong induction of whole-body antitumor immunity, essential for targeting metastatic diseases [69]. Importantly, all cured mice treated with the dual cytokine-expressing vaccinia virus developed long-term immune memory responses, crucial for preventing recurrence [70]. Likewise, a combinatorial study using tumor matrix (collagen)-binding IL-7 and IL-12 showed synergistic antitumor effects associated with the induction of immunologic memory [71]. However, a limitation of most of the studies discussed in this section was the lack of single cytokine-encoding viruses as controls, making it challenging to delineate the specific role of each cytokine. Nevertheless, the strong antitumor effects observed with the virus co-expressing IL-7 and IL-12 underscore its clinical translatability once the antitumor role of each individual cytokine (IL-7 or IL-12) is defined preclinically.
Viral co-expression of IL-7 with IL-15
IL-7, a member of the common γ-chain cytokine family, maintains memory CD8+ T cell responses [6, 7, 72]. Like IL-7, IL-15 is another γ-chain cytokine maintaining memory CD8+ T cell responses [73]. Additionally, like IL-7, IL-15 promotes proliferation and activation of T and NK cells [74]. Because both IL-7 and IL-15 produce similar immunostimulatory effects on the host immune cells, especially T cells [75], it is believed that their co-expression by a virus can lead to superior antitumor immunity compared to single cytokine expression.
Viral co-expression of IL-7 plus IL-15 induces tumor-specific prophylactic antitumor immunity
As described above, irradiated B16-F10 cells loaded with non-lytic NDV LX strain expressing IL-7 (i.e., B16-LX/IL-7) were utilized as an autologous tumor cell vaccine [28]. Xu et al. further modified the LX strain to co-express IL-7 and IL-15, separated by a 2A peptide derived from the foot-and-mouth disease virus, creating LX/IL(15 + 7) [31]. As an improvement on the B16-LX/IL-7 vaccine [28], irradiated B16-F10 cells (treated with 200 Gy of radiation) were loaded with LX/IL(15 + 7), here referred to as the B16-LX/IL(15 + 7) vaccine [31].
Subcutaneous prophylactic immunization of C57BL/6 mice with LX/IL(15 + 7)-modified B16-F10 cells (B16-LX/IL(15 + 7)) or LX/RFP-modified B16-F10 cells (i.e., B16-LX/RFP) significantly inhibited B16-F10 tumor growth compared to immunization with irradiated B16-F10 cells without virus loading. Importantly, the B16-LX/IL(15 + 7) vaccine demonstrated a significantly superior prophylactic antitumor effect than the control B16-LX/RFP vaccine [31], indicating the antitumor role of dual cytokine expression. Both B16-LX/IL(15 + 7) and B16-LX/RFP vaccines similarly enhanced infiltration of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells into the TME compared to control irradiated B16-F10 cells. The antitumor response of the B16-LX/IL(15 + 7) vaccine was tumor-specific, as it did not inhibit the growth of antigenically distinct EL-4 lymphomas [31] (Fig. 3; Table 1).
Viral co-expression of IL-7 plus IL-15 induces tumor-specific and CD8-dependent therapeutic immunity
Like the prophylactic efficacy, the therapeutic B16-LX/IL(15 + 7) vaccine significantly inhibited B16-F10 tumor growth compared to the B16-LX/RFP vaccine, demonstrating the antitumor role of dual cytokines. The antitumor effect of the B16-LX/IL(15 + 7) vaccine was tumor-specific, as the EL4-LX/IL(15 + 7) vaccine (i.e., irradiated EL-4 tumor cells loaded with LX/IL(15 + 7)) did not inhibit antigenically unrelated B16-F10 tumor growth [31]. Mechanistically, although the B16-LX/IL(15 + 7) vaccine significantly increased intratumoral infiltration of CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells (vs. B16-LX/RFP), its efficacy was abrogated in the absence of CD8+ T cells, indicating CD8-dependent efficacy (Fig. 3; Table 1). However, no distinct contributions of IL-7 and IL-15 expression were clearly defined in this study due to the lack of appropriate controls, such as irradiated B16-F10 cells loaded with LX/IL-7 or LX/IL-15 [31]. Thus, future research is necessary to clarify this issue.
Viral co-expression of IL-7 plus B7.1
B7.1 (CD80) is a glycoprotein receptor recognized as a DC maturation marker [76]. CD80 binds to the CD28 co-stimulatory receptor, activating T cells, or to the CTLA-4 co-inhibitory receptor, downregulating T cell activity [77]. Since IL-7 is involved in T cell activation and maintenance [6, 7, 72] while the CD80-CD28 interaction contributes to T cell activation [77], the viral co-expression of IL-7 and CD80 will likely induce superior antitumor T cell activity. In this context, a replication-defective adenovirus co-expressing IL-7 and B7.1 (Ad.IL-7/B7.1) was developed, and its efficacy was evaluated against transplanted and chemically induced non-transplanted tumors [32], as outlined below.
Viral co-expression of IL-7 plus B7.1 produces T cell-dependent efficacy against transplanted tumors
Intratumoral injection of a control adenovirus expressing beta-galactosidase (Ad.βgal) inhibited the growth of subcutaneous TS/A adenocarcinoma in BALB/c mice compared to PBS injection. Tumor growth inhibition was more pronounced with intratumoral Ad.IL-7/B7.1 treatment compared to Ad.βgal, leading to 70% (7/10) tumor-free long-term survivors in the Ad.IL-7/B7.1 group, but there were no survivors in the Ad.βgal group (Table 1). This result highlights the antitumor role of IL-7 plus B7.1. However, Ad.IL-7/B7.1 did not show efficacy against established TS/A tumors in BALB/c nu/nu mice which lack T cells, indicating the efficacy of Ad.IL-7/B7.1 is T cell-dependent [32].
Meanwhile, intratumoral Ad.IL-7/B7.1 treatment enhanced the infiltration of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells into tumors compared to the control. However, it was unclear which T cell subtype (CD4+ or CD8+ T cells) was primarily responsible for the antitumor efficacy against transplanted tumors. 100% of the tumor-free mice due to Ad.IL-7/B7.1 treatment rejected TS/A tumor rechallenge [32], likely due to the treatment-induced immunological memory (Fig. 2; Table 1).
Viral co-expression of IL-7 plus B7.1 does not show efficacy against non-transplanted tumors
Although Ad.IL-7/B7.1 was effective against transplanted subcutaneous TS/A adenocarcinoma, intratumoral co-expression of IL-7 plus B7.1 did not show efficacy against 3-methylcholanthrene (3MC)-induced non-transplanted tumors. These non-transplanted tumors were generated by intramuscular injection of the 3MC carcinogen, which typically causes fibrosarcoma-like tumors, or by subcutaneous injection, which generates papilloma-like tumors. The lack of efficacy in this model was likely due to the absence of significant tumor immune infiltrates (CD4+ and CD8+ T cells) in the Ad.IL-7/B7.1 treatment group compared to the control group [32] (Fig. 2).
Interestingly, in a transplanted fibrosarcoma model derived from 3MC-induced MC51-9 fibrosarcoma cells, intratumoral Ad.IL-7/B7.1 was efficacious, leading to 87.5% (7/8) tumor-free long-term survivors [32] (Fig. 2). The reason for the contrasting efficacy of Ad.IL-7/B7.1 between the two models, i.e., no efficacy against non-transplanted tumors (generated by intramuscular or subcutaneous 3MC injection) versus 87.5% efficacy against transplanted tumors (derived from 3MC-treated MC51-9 fibrosarcoma cells), remains unclear. The authors concluded that the lack of efficacy against non-transplanted tumors was not due to the type or location of the tumor or limited adenoviral gene (IL-7/B7.1) transduction efficiency [32]. Unfortunately, no further studies were reported to understand these differences.
Viral co-expression of IL-7 and CCL19
While considerable investigations of OVs armed with anticancer cytokines with or without ICIs have been reported [18, 21, 22], another strategy is to encode chemokines that can help attract target immune cells to the tumor site. Indeed, the FDA-approved talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC) encodes granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), which was designed, in part, to attract local DCs to initiate tumor-associated antigen presentation [25]. Like IL-7, GM-CSF helps in T cell recruitment to the tumors [78]. CCL19, a cytokine that binds to CCR7 (a chemokine receptor), plays a vital role in T cell trafficking [79]. Therefore, CCL19 expression is expected to work synergistically with IL-7 or GM-CSF expression. The positive effects of cytokine expression and immune cell infiltration into tumors may be counterbalanced by the expression of immune checkpoints, such as PD-1 [80]. Consistent with this notion, viral expression of an antibody against PD-1 can reverse PD-1-related T cell exhaustion [81].
A type 2 oHSV was generated to co-express IL-7 and CCL19 (oHSV2-IL7×CCL19) and was then tested with additional type 2 oHSV vectors expressing GM-CSF (oHSV2-GMCSF), IL-12 (oHSV2-IL12), anti-PD-1 (oHSV2-PD1v), and IL-15 (oHSV2-IL15) [82]. The five oHSV constructs demonstrated superior antitumor efficacy, resulting in 100% long-term survivors in two murine tumor models (CT26 and 4T1). The oHSV2-IL7×CCL19 (or oHSV2-GMCSF) treatment showed better efficacy (but statistically insignificant) than the other three viruses (oHSV2-IL12, oHSV2-PD1v, or oHSV2-IL15) in the CT26 model (Table 1) [82]. The specific contribution of IL-7 to the antitumor efficacy, induced either by oHSV2-IL7×CCL19 or a cocktail of five oHSV2s, remains unclear. Further research, including testing the antitumor efficacy of the combination (i.e., oHSV2-IL7×CCL19) versus controls (e.g., oHSV2-IL7, oHSV2-CCL19, oHSV2-IL12, oHSV2-PD1v, or oHSV2-IL15), is needed to define the antitumor role of IL-7 (or other cytokines) expression.
Conclusions
IL-7 has immunomodulatory properties that can facilitate T cell activation and promote cancer immunotherapy. A major obstacle in driving therapeutic responses by systemic IL-7 cytokine therapy is the narrow therapeutic window exhibited by IL-7. Here, we describe the use of oncolytic and non-oncolytic virus vectors as novel strategies for locally delivering high doses of IL-7 with less systemic toxicity. Various viruses engineered to express IL-7 have now been tested in several preclinical cancer models [27,28,29], demonstrating superior antitumor immunity via activation of TILs—a hallmark of “immunologically hot” tumors [67]—compared to non-IL7-expressing viruses. The local expression of IL-7 alone, and in combination with other cytokines and chemokines, remodels the TME and enables tumor susceptibility to immunotherapy [29, 67]. In some cases where viral expression of a single cytokine is insufficient to eradicate tumors [27], combination approaches were able to mediate tumor eradication, long-term survival, and the development of tumor-specific immunological memory [45]. Furthermore, viral expression of IL-7 alone, and especially with other cytokines, within tumors improves the antitumor efficacy of CAR-T cell immunotherapy [29], autologous tumor cell vaccines [28], and ICI treatment [30].
While there is strong preclinical evidence that multiple cytokine vectors (e.g., IL-7 plus IL-12, IL-7 plus IL-15, IL-7 plus B7.1, or IL-7 plus CCL19) have superior therapeutic activity in vivo, the absence of appropriate controls in those preclinical reports has been a limitation in understanding the contribution of individual cytokines. Nonetheless, there is intriguing data suggesting that certain IL-7 combinations may be especially interesting. For example, given that IL-12 is a key pro-inflammatory cytokine that promotes T cell proliferation and cytotoxicity [50, 51], while IL-7 supports T cell proliferation, maintenance, and survival [6, 7, 72], the viral co-expression of IL-7 and IL-12 may represent a promising strategy for dual cytokine-expressing viruses in cancer immunotherapy. Recent studies involving an oncolytic vaccinia virus co-expressing IL-7 and IL-12 demonstrated potent antitumor efficacy across melanoma, colon, and lung cancer models [30].
While IL-12 appears to be promising for viral co-expression with IL-7, another cytokine that has not been as well evaluated is IL-2. Like IL-12, IL-2 is another potent proinflammatory cytokine that can also be expressed by viruses [20]. IL-7 synergizes with IL-2, creating an immune-active TME and sensitizing tumors to ICIs [83]. This combination (i.e., IL-7 plus IL-2) could be expressed using replicative oHSVs to induce immune responses with oncolysis [84] or non-replicative oHSVs for sustained cytokine expression and antitumor immunity via a non-lytic mechanism [26]. Tumor models are important, so testing constructs in “immunologically cold” cancer types (e.g., GBM) that are minimally responsive or not responsive to ICIs [85] can be informative. Additionally, it would be worthwhile to virally co-express IL-7 in conjunction with T cell co-stimulatory ligands, such as 4-1BBL [86], OX40L [87], ICOSL [66, 88], or similar ligands [89], which are known to generate potent antitumor immunity. Several oncolytic viruses that have been approved or are under clinical development for cancer treatment express cytokines, including GM-CSF, IFNα, and IL-15 receptor agonists. Further studies of virally encoded IL-7 expression alone and in combination merit further investigation as a strategy for realizing the potential therapeutic value of IL-7 for cancer treatment.
References
Winer H, Rodrigues GOL, Hixon JA, Aiello FB, Hsu TC, Wachter BT, et al. IL-7: Comprehensive review. Cytokine. 2022;160:156049.
Sprent J, Surh CD. Interleukin 7, maestro of the immune system. Semin Immunol. 2012;24:149–50.
Leonard WJ, Lin JX, O’Shea JJ. The γ(c) family of cytokines: basic biology to therapeutic ramifications. Immunity. 2019;50:832–50.
Kesarwani P, Murali AK, Al-Khami AA, Mehrotra S. Redox regulation of T-cell function: from molecular mechanisms to significance in human health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18:1497–534.
Lin J, Zhu Z, Xiao H, Wakefield MR, Ding VA, Bai Q, et al. The role of IL-7 in immunity and cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017;37:963–7.
Park JH, Lee SW, Choi D, Lee C, Sung YC. Harnessing the power of IL-7 to boost T cell immunity in experimental and clinical immunotherapies. Immune Netw. 2024;24:e9.
Chen D, Tang TX, Deng H, Yang XP, Tang ZH. Interleukin-7 biology and its effects on immune cells: mediator of generation, differentiation, survival, and homeostasis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:747324.
Pellegrini M, Calzascia T, Elford AR, Shahinian A, Lin AE, Dissanayake D, et al. Adjuvant IL-7 antagonizes multiple cellular and molecular inhibitory networks to enhance immunotherapies. Nat Med. 2009;15:528–36.
Onder L, Narang P, Scandella E, Chai Q, Iolyeva M, Hoorweg K, et al. IL-7-producing stromal cells are critical for lymph node remodeling. Blood. 2012;120:4675–83.
Seol MA, Kim JH, Oh K, Kim G, Seo MW, Shin YK, et al. Interleukin-7 contributes to the invasiveness of prostate cancer cells by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Sci Rep. 2019;9:6917.
Sportès C, Babb RR, Krumlauf MC, Hakim FT, Steinberg SM, Chow CK, et al. Phase I study of recombinant human interleukin-7 administration in subjects with refractory malignancy. Clinical Cancer Res. 2010;16:727–35.
Morre M, Beq S. Interleukin-7 and immune reconstitution in cancer patients: a new paradigm for dramatically increasing overall survival. Target Oncol. 2012;7:55–68.
Abdul-Rahman T, Ghosh S, Badar SM, Nazir A, Bamigbade GB, Aji N, et al. The paradoxical role of cytokines and chemokines at the tumor microenvironment: a comprehensive review. Eur J Med Res. 2024;29:124.
Ayele K, Wakimoto H, Nauwynck HJ, Kaufman HL, Rabkin SD, Saha D. Understanding the interplay between oHSV and the host immune system: Implications for therapeutic oncolytic virus development. Mol Ther.2024;33:1327–43.
Bommareddy PK, Peters C, Saha D, Rabkin SD, Kaufman HL. Oncolytic herpes simplex viruses as a paradigm for the treatment of cancer. Annual Rev Cancer Biol. 2018;2:155–73.
Saha D, Wakimoto H, Rabkin SD. Oncolytic herpes simplex virus interactions with the host immune system. Curr Opin Virol. 2016;21:26–34.
Saha D, Ahmed SS, Rabkin SD. Exploring the antitumor effect of virus in malignant glioma. Drugs Fut. 2015;40:739–49.
Wang H, Borlongan M, Kaufman HL, Le U, Nauwynck HJ, Rabkin SD, et al. Cytokine-armed oncolytic herpes simplex viruses: a game-changer in cancer immunotherapy? J Immunother Cancer. 2024;12:e008025.
Wang H, Borlongan M, Hemminki A, Basnet S, Sah N, Kaufman HL, et al. Viral vectors expressing interleukin 2 for cancer immunotherapy. Hum Gene Ther. 2023;34:878–95.
Bommareddy PK, Wakimoto H, Martuza RL, Kaufman HL, Rabkin SD, Saha D. Oncolytic herpes simplex virus expressing IL-2 controls glioblastoma growth and improves survival. J Immunother Cancer. 2024;12:e008880.
Ayele K, Wakimoto H, Saha D. An oncolytic adenovirus co-expressing a bi-specific T cell engager and IL-2 for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Mol Ther. 2024;32:2810–3.
Ayele K, Feng X, Saha D. A novel oncolytic HSV co-expressing IL-12 and anti-PD-1 for glioblastoma. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024;32:200810.
Ghouse SM, Nguyen HM, Bommareddy PK, Guz-Montgomery K, Saha D. Oncolytic herpes simplex virus encoding IL12 controls triple-negative breast cancer growth and metastasis. Front Oncol. 2020;10:384.
Nguyen HM, Guz-Montgomery K, Saha D. Oncolytic virus encoding a master pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin 12 in cancer immunotherapy. Cells. 2020;9:400.
Andtbacka RH, Kaufman HL, Collichio F, Amatruda T, Senzer N, Chesney J, et al. Talimogene laherparepvec improves durable response rate in patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:2780–8.
Epstein AL, Rabkin SD. Safety of non-replicative and oncolytic replication-selective HSV vectors. Trends Mol Med. 2024;30:781–94.
Kudling TV, Clubb JHA, Quixabeira DCA, Santos JM, Havunen R, Kononov A, et al. Local delivery of interleukin 7 with an oncolytic adenovirus activates tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and causes tumor regression. Oncoimmunology. 2022;11:2096572.
Zhao L, Mei Y, Sun Q, Guo L, Wu Y, Yu X, et al. Autologous tumor vaccine modified with recombinant new castle disease virus expressing IL-7 promotes antitumor immune response. J Immunol. 2014;193:735–45.
Huang J, Zheng M, Zhang Z, Tang X, Chen Y, Peng A, et al. Interleukin-7-loaded oncolytic adenovirus improves CAR-T cell therapy for glioblastoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021;70:2453–65.
Nakao S, Arai Y, Tasaki M, Yamashita M, Murakami R, Kawase T, et al. Intratumoral expression of IL-7 and IL-12 using an oncolytic virus increases systemic sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12:eaax7992.
Xu X, Sun Q, Mei Y, Liu Y, Zhao L. Newcastle disease virus co-expressing interleukin 7 and interleukin 15 modified tumor cells as a vaccine for cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:279–88.
Willimsky G, Blankenstein T. Interleukin-7/B7.1-encoding adenoviruses induce rejection of transplanted but not nontransplanted tumors. Cancer Res. 2000;60:685–92.
Hu H, Zhang S, Cai L, Duan H, Li Y, Yang J, et al. A novel cocktail therapy based on quintuplet combination of oncolytic herpes simplex virus-2 vectors armed with interleukin-12, interleukin-15, GM-CSF, PD1v, and IL-7 × CCL19 results in enhanced antitumor efficacy. Virol J. 2022;19:74.
Floros T, Tarhini AA. Anticancer cytokines: biology and clinical effects of interferon-α2, interleukin (IL)-2, IL-15, IL-21, and IL-12. Semin Oncol. 2015;42:539–48.
Mullard A. First-in-class IL-15 receptor agonist nabs FDA approval for bladder cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024;23:410.
Li JY, Chen YP, Li YQ, Liu N, Ma J. Chemotherapeutic and targeted agents can modulate the tumor microenvironment and increase the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockades. Mol Cancer. 2021;20:27.
Schirrmacher V. Clinical trials of antitumor vaccination with an autologous tumor cell vaccine modified by virus infection: improvement of patient survival based on improved antitumor immune memory. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005;54:587–98.
Nehama D, Di Ianni N, Musio S, Du H, Patané M, Pollo B, et al. B7-H3-redirected chimeric antigen receptor T cells target glioblastoma and neurospheres. EBioMedicine. 2019;47:33–43.
Nguyen HM, Guz-Montgomery K, Lowe DB, Saha D. Pathogenetic features and current management of glioblastoma. Cancers. 2021;13:856.
Nguyen HM, Saha D. The current state of oncolytic herpes simplex virus for glioblastoma treatment. Oncolytic Virother. 2021;10:1–27.
Getu AA, Tigabu A, Zhou M, Lu J, Fodstad Ø, Tan M. New frontiers in immune checkpoint B7-H3 (CD276) research and drug development. Mol Cancer. 2023;22:43.
Saha D, Rabkin SD, Martuza RL. Temozolomide antagonizes oncolytic immunovirotherapy in glioblastoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e000345.
Saha D, Wakimoto H, Peters CW, Antoszczyk SJ, Rabkin SD, Martuza RL. Combinatorial effects of VEGFR kinase inhibitor axitinib and oncolytic virotherapy in mouse and human glioblastoma stem-like cell models. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:3409–22.
Saha D, Martuza RL, Rabkin SD. Oncolytic herpes simplex virus immunovirotherapy in combination with immune checkpoint blockade to treat glioblastoma. Immunotherapy. 2018;10:779–86.
Saha D, Martuza RL, Rabkin SD. Macrophage polarization contributes to glioblastoma eradication by combination immunovirotherapy and immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:253–67.e5.
Saha D, Martuza RL, Rabkin SD. Curing glioblastoma: oncolytic HSV-IL12 and checkpoint blockade. Oncoscience. 2017;4:67–9.
Siurala M, Havunen R, Saha D, Lumen D, Airaksinen AJ, Tähtinen S, et al. Adenoviral delivery of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-2 enables successful adoptive cell therapy of immunosuppressive melanoma. Mol Ther. 2016;24:1435–43.
Tähtinen S, Blattner C, Vähä-Koskela M, Saha D, Siurala M, Parviainen S, et al. T-cell therapy enabling adenoviruses coding for IL2 and TNFα induce systemic immunomodulation in mice with spontaneous melanoma. J Immunother. 2016;39:343–54.
Kaka AS, Foster AE, Weiss HL, Rooney CM, Leen AM. Using dendritic cell maturation and IL-12 producing capacity as markers of function: a cautionary tale. J Immunother. 2008;31:359–69.
Mehrotra PT, Wu D, Crim JA, Mostowski HS, Siegel JP. Effects of IL-12 on the generation of cytotoxic activity in human CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993;151:2444–52.
Veinalde R, Grossardt C, Hartmann L, Bourgeois-Daigneault MC, Bell JC, Jager D, et al. Oncolytic measles virus encoding interleukin-12 mediates potent antitumor effects through T cell activation. Oncoimmunology. 2017;6:e1285992.
Daud AI, DeConti RC, Andrews S, Urbas P, Riker AI, Sondak VK, et al. Phase I trial of interleukin-12 plasmid electroporation in patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5896–903.
Leonard JP, Sherman ML, Fisher GL, Buchanan LJ, Larsen G, Atkins MB, et al. Effects of single-dose interleukin-12 exposure on interleukin-12-associated toxicity and interferon-gamma production. Blood. 1997;90:2541–8.
Atkins MB, Robertson MJ, Gordon M, Lotze MT, DeCoste M, DuBois JS, et al. Phase I evaluation of intravenous recombinant human interleukin 12 in patients with advanced malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:409–17.
Gollob JA, Mier JW, Veenstra K, McDermott DF, Clancy D, Clancy M, et al. Phase I trial of twice-weekly intravenous interleukin 12 in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer or malignant melanoma: ability to maintain IFN-gamma induction is associated with clinical response. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:1678–92.
Nguyen KG, Vrabel MR, Mantooth SM, Hopkins JJ, Wagner ES, Gabaldon TA, et al. Localized interleukin-12 for cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2020;11:575597.
Berraondo P, Etxeberria I, Ponz-Sarvise M, Melero I. Revisiting interleukin-12 as a cancer immunotherapy agent. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:2716–8.
Barrett JA, Cai H, Miao J, Khare PD, Gonzalez P, Dalsing-Hernandez J, et al. Regulated intratumoral expression of IL-12 using a RheoSwitch Therapeutic System(®) (RTS(®)) gene switch as gene therapy for the treatment of glioma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2018;25:106–16.
Faltynek CR, Wang S, Miller D, Young E, Tiberio L, Kross K, et al. Administration of human recombinant IL-7 to normal and irradiated mice increases the numbers of lymphocytes and some immature cells of the myeloid lineage. J Immunol. 1992;149:1276–82.
Zou JJ, Schoenhaut DS, Carvajal DM, Warrier RR, Presky DH, Gately MK, et al. Structure-function analysis of the p35 subunit of mouse interleukin 12. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:5864–71.
Sun K, Shi X, Li L, Nie X, Xu L, Jia F, et al. Oncolytic viral therapy for glioma by recombinant sindbis virus. Cancers. 2023;15:4738.
Jahan N, Ghouse SM, Martuza RL, Rabkin SD. In situ cancer vaccination and immunovirotherapy using oncolytic HSV. Viruses. 2021;13:1740.
Abiko K, Matsumura N, Hamanishi J, Horikawa N, Murakami R, Yamaguchi K, et al. IFN-γ from lymphocytes induces PD-L1 expression and promotes progression of ovarian cancer. Brit J Cancer. 2015;112:1501–9.
Tasaki M, Yamashita M, Arai Y, Nakamura T, Nakao S. IL-7 coupled with IL-12 increases intratumoral T cell clonality, leading to complete regression of non-immunogenic tumors. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021;70:3557–71.
Yamashita M, Tasaki M, Murakami R, Arai Y, Nakamura T, Nakao S. Oncolytic vaccinia virus induces a novel phenotype of CD8(+) effector T cells characterized by high ICOS expression. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021;20:422–32.
Solinas C, Gu-Trantien C, Willard-Gallo K. The rationale behind targeting the ICOS-ICOS ligand costimulatory pathway in cancer immunotherapy. ESMO Open. 2020;5:e000544.
Ribas A, Dummer R, Puzanov I, VanderWalde A, Andtbacka RHI, Michielin O, et al. Oncolytic virotherapy promotes intratumoral T cell infiltration and improves anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Cell. 2017;170:1109–19.e10.
Nguyen HM, Bommareddy PK, Silk AW, Saha D. Optimal timing of PD-1 blockade in combination with oncolytic virus therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;86:971–80.
Link B, Torres Crigna A, Hölzel M, Giordano FA, Golubnitschaja O. Abscopal effects in metastatic cancer: is a predictive approach possible to improve individual outcomes? J Clin Med. 2021;10:5124.
Alvero AB, Fox A, Madina BR, Krady MM, Gogoi R, Chehade H, et al. Immune modulation of innate and adaptive responses restores immune surveillance and establishes antitumor immunologic memory. Cancer Immunol Res. 2024;12:261–74.
Kang S, Mansurov A, Kurtanich T, Chun HR, Slezak AJ, Volpatti LR, et al. Engineered IL-7 synergizes with IL-12 immunotherapy to prevent T cell exhaustion and promote memory without exacerbating toxicity. Sci Adv. 2023;9:eadh9879.
Colombetti S, Lévy F, Chapatte L. IL-7 adjuvant treatment enhances long-term tumor-antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell responses after immunization with recombinant lentivector. Blood. 2009;113:6629–37.
Sandau MM, Kohlmeier JE, Woodland DL, Jameson SC. IL-15 regulates both quantitative and qualitative features of the memory CD8 T cell pool. J Immunol. 2010;184:35–44.
Lee H, Park SH, Shin EC. IL-15 in T-Cell Responses and Immunopathogenesis. Immune Netw. 2024;24:e11.
Wallace DL, Bérard M, Soares MV, Oldham J, Cook JE, Akbar AN, et al. Prolonged exposure of naïve CD8+ T cells to interleukin-7 or interleukin-15 stimulates proliferation without differentiation or loss of telomere length. Immunology. 2006;119:243–53.
Dalod M, Chelbi R, Malissen B, Lawrence T. Dendritic cell maturation: functional specialization through signaling specificity and transcriptional programming. Embo j. 2014;33:1104–16.
Hossen MM, Ma Y, Yin Z, Xia Y, Du J, Huang JY, et al. Current understanding of CTLA-4: from mechanism to autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1198365.
Kumar A, Taghi Khani A, Sanchez Ortiz A, Swaminathan S. GM-CSF: a double-edged sword in cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2022;13:901277.
Yan Y, Chen R, Wang X, Hu K, Huang L, Lu M, et al. CCL19 and CCR7 expression, signaling pathways, and adjuvant functions in viral infection and prevention. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:212.
Murciano-Goroff YR, Warner AB, Wolchok JD. The future of cancer immunotherapy: microenvironment-targeting combinations. Cell Res. 2020;30:507–19.
Xu-Monette ZY, Zhang M, Li J, Young KH. PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: have we found the key to unleash the antitumor immune response?. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1597.
Hu H, Zhang S, Cai L, Duan H, Li Y, Yang J, et al. A novel cocktail therapy based on quintuplet combination of oncolytic herpes simplex virus-2 vectors armed with interleukin-12, interleukin-15, GM-CSF, PD1v, and IL-7 x CCL19 results in enhanced antitumor efficacy. Virol J. 2022;19:74.
Lee M, Im SK, Baek S, Ji M, Kim M, Lee EJ, et al. rhIL-7-hyFc and hIL-2/TCB2c combination promotes an immune-stimulatory tumor microenvironment that improves antitumor efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. 2024;12:e008001.
Peters C, Paget M, Tshilenge KT, Saha D, Antoszczyk S, Baars A, et al. Restriction of replication of oncolytic herpes simplex virus with a deletion of γ34.5 in glioblastoma stem-like cells. J Virol. 2018;92:e00246-18.
Reardon DA, Brandes AA, Omuro A, Mulholland P, Lim M, Wick A, et al. Effect of nivolumab vs bevacizumab in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: the checkmate 143 phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6:1003–10.
Gao W, Zhao Z, Bi Y, Li J, Tian N, Zhang C, et al. 4-1BBL-armed oncolytic herpes simplex virus exerts antitumor effects in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Vaccines. 2024;12:1309.
Yang N, Wang Y, Liu S, Tariq SB, Luna JM, Mazo G. et al. OX40L-expressing recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara induces potent antitumor immunity via reprogramming Tregs. J Exp Med. 2023;220:e20221166.
Saffarzadeh N, Foord E, O’Leary E, Mahmoun R, Birkballe Hansen T, Levitsky V, et al. Inducing expression of ICOS-L by oncolytic adenovirus to enhance tumor-specific bi-specific antibody efficacy. J Transl Med. 2024;22:250.
Kober J, Leitner J, Klauser C, Woitek R, Majdic O, Stöckl J, et al. The capacity of the TNF family members 4-1BBL, OX40L, CD70, GITRL, CD30L and LIGHT to costimulate human T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38:2678–88.
Acknowledgements
DS was supported in part by a fund from the Division of Academic Affairs at North Carolina A&T State University, while RHN was supported in part by a grant from the NIH (1R35GM153737). Likewise, SDR was supported in part by a grant from the NIH (R01 CA160762) and the Thomas A. Pappas chair in Neurosciences. All illustrations were generated with BioRender.com.
Funding
Open access funding provided by the Carolinas Consortium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MH: Edited the manuscript and was involved in the manuscript preparation process; RHN, CJR, BLH, HLK, SDR, and JGJ: Edited the manuscript and provided relevant expertise and critical inputs; DS: Conceptualization, wrote the manuscript, prepared figures, and funding. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
SDR is a co-inventor on patents relating to oncolytic herpes simplex viruses, owned, and managed by Georgetown University and Massachusetts General Hospital, which have received royalties from Amgen and Acti\Vec Inc., and acted as a consultant and received honoraria from Replimune, Cellinta, and Greenfire Bio, and honoraria and equity from EG 427. HLK is an employee of Ankyra Therapeutics and has received honoraria for participating on advisory boards for Castle Biosciences, Midatech Pharma, Marengo Therapeutics, and Virogin. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hudson, M., Newman, R.H., Rorie, C.J. et al. Promoting the therapeutic potential of interleukin-7 (IL-7) by expression in viral vectors. Cancer Gene Ther 32, 1166–1176 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-025-00960-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-025-00960-2