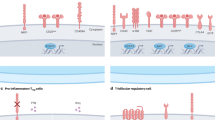
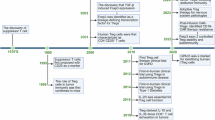
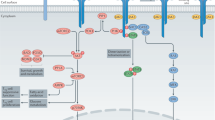
Abstract
Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a suppressive subset of CD4+ T cells that maintain immune homeostasis and restrain inflammation. Three decades after their discovery, the promise of strategies to harness Treg cells for therapy has never been stronger. Multiple clinical trials seeking to enhance endogenous Treg cells or deliver them as a cell-based therapy have been performed and hint at signs of success, as well as to important limitations and unanswered questions. Strategies to deplete Treg cells in cancer are also in active clinical testing. Furthermore, multi-dimensional methods to interrogate the biology of Treg cells are leading to a refined understanding of Treg cell biology and new approaches to harness tissue-specific functions for therapy. A new generation of Treg cell clinical trials is now being fuelled by advances in nanomedicine and synthetic biology, seeking more precise ways to tailor Treg cell function. This Review will discuss recent advances in our understanding of human Treg cell biology, with a focus on mechanisms of action and strategies to assess outcomes of Treg cell-targeted therapies. It highlights results from recent clinical trials aiming to enhance or inhibit Treg cell activity in a variety of diseases, including allergy, transplantation, autoimmunity and cancer, and discusses ongoing strategies to refine these approaches.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thome, J. J. et al. Early-life compartmentalization of human T cell differentiation and regulatory function in mucosal and lymphoid tissues. Nat. Med. 22, 72–77 (2016).
Wildin, R. S. et al. X-linked neonatal diabetes mellitus, enteropathy and endocrinopathy syndrome is the human equivalent of mouse scurfy. Nat. Genet. 27, 18–20 (2001).
Bennett, C. L. et al. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat. Genet. 27, 20–21 (2001).
Hernandez, R., Poder, J., LaPorte, K. M. & Malek, T. R. Engineering IL-2 for immunotherapy of autoimmunity and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 22, 614–628 (2022).
Levings, M. K., Sangregorio, R. & Roncarolo, M. G. Human CD25+CD4+ T regulatory cells suppress naive and memory T cell proliferation and can be expanded in vitro without loss of function. J. Exp. Med. 193, 1295–1302 (2001).
Feinerman, O. et al. Single-cell quantification of IL-2 response by effector and regulatory T cells reveals critical plasticity in immune response. Mol. Syst. Biol. 6, 437 (2010).
Allan, S. E. et al. Generation of potent and stable human CD4+ T regulatory cells by activation-independent expression of FOXP3. Mol. Ther. 16, 194–202 (2008).
Wu, Y. et al. FOXP3 controls regulatory T cell function through cooperation with NFAT. Cell 126, 375–387 (2006).
Freeborn, R. A., Strubbe, S. & Roncarolo, M. G. Type 1 regulatory T cell-mediated tolerance in health and disease. Front. Immunol. 13, 1032575 (2022).
Flippe, L., Bezie, S., Anegon, I. & Guillonneau, C. Future prospects for CD8+ regulatory T cells in immune tolerance. Immunol. Rev. 292, 209–224 (2019).
Park, J. E. et al. A cell atlas of human thymic development defines T cell repertoire formation. Science 367, eaay3224 (2020).
Morgana, F. et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals discrete steps in regulatory T cell development in the human thymus. J. Immunol. 208, 384–395 (2022).
Lagattuta, K. A. et al. Repertoire analyses reveal T cell antigen receptor sequence features that influence T cell fate. Nat. Immunol. 23, 446–457 (2022).
Tai, X. et al. How autoreactive thymocytes differentiate into regulatory versus effector CD4+ T cells after avoiding clonal deletion. Nat. Immunol. 24, 637–651 (2023). Effector T and Treg cell differentiation are instructed via persistent or TGF-β-disrupted TCR signalling in the mouse thymus, respectively.
Hemmers, S. et al. IL-2 production by self-reactive CD4 thymocytes scales regulatory T cell generation in the thymus. J. Exp. Med. 216, 2466–2478 (2019).
Burton, O. T. et al. The tissue-resident regulatory T cell pool is shaped by transient multi-tissue migration and a conserved residency program. Immunity 57, 1586–1602.e10 (2024).
Lam, A. J. et al. Optimized CRISPR-mediated gene knockin reveals FOXP3-independent maintenance of human Treg identity. Cell Rep. 36, 109494 (2021). Knockout of FOXP3 in mature human Tregs has little effect on their phenotype or function.
van der Veeken, J. et al. The transcription factor Foxp3 shapes regulatory T cell identity by tuning the activity of trans-acting intermediaries. Immunity 53, 971–984.e5 (2020).
Hill, J. A. et al. Foxp3 transcription-factor-dependent and -independent regulation of the regulatory T cell transcriptional signature. Immunity 27, 786–800 (2007).
Trujillo-Ochoa, J. L., Kazemian, M. & Afzali, B. The role of transcription factors in shaping regulatory T cell identity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 23, 842–856 (2023).
Lyu, M. et al. ILC3s select microbiota-specific regulatory T cells to establish tolerance in the gut. Nature 610, 744–751 (2022).
Kedmi, R. et al. A RORγt+ cell instructs gut microbiota-specific Treg cell differentiation. Nature 610, 737–743 (2022).
Akagbosu, B. et al. Novel antigen-presenting cell imparts Treg-dependent tolerance to gut microbiota. Nature 610, 752–760 (2022).
van der Veeken, J. et al. Genetic tracing reveals transcription factor Foxp3-dependent and Foxp3-independent functionality of peripherally induced Treg cells. Immunity 55, 1173–1184.e7 (2022).
Cepika, A. M. et al. Tregopathies: monogenic diseases resulting in regulatory T-cell deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 142, 1679–1695 (2018).
Weiss, J. M. et al. Neuropilin 1 is expressed on thymus-derived natural regulatory T cells, but not mucosa-generated induced Foxp3+ T reg cells. J. Exp. Med. 209, 1723–1742 (2012).
Milpied, P. et al. Neuropilin-1 is not a marker of human Foxp3+ Treg. Eur. J. Immunol. 39, 1466–1471 (2009).
Lam, A. J., Uday, P., Gillies, J. K. & Levings, M. K. Helios is a marker, not a driver, of human Treg stability. Eur. J. Immunol. 52, 75–84 (2022).
Zheng, Y. et al. Role of conserved non-coding DNA elements in the Foxp3 gene in regulatory T-cell fate. Nature 463, 808–812 (2010).
Rubtsov, Y. P. et al. Stability of the regulatory T cell lineage in vivo. Science 329, 1667–1671 (2010).
Bailey-Bucktrout, S. L. et al. Self-antigen-driven activation induces instability of regulatory T cells during an inflammatory autoimmune response. Immunity 39, 949–962 (2013).
Komatsu, N. et al. Pathogenic conversion of Foxp3+ T cells into TH17 cells in autoimmune arthritis. Nat. Med. 20, 62–68 (2014).
Allan, S. E. et al. Activation-induced FOXP3 in human T effector cells does not suppress proliferation or cytokine production. Int. Immunol. 19, 345–354 (2007).
Joudi, A. M., Reyes Flores, C. P. & Singer, B. D. Epigenetic control of regulatory T cell stability and function: implications for translation. Front. Immunol. 13, 861607 (2022).
Borna, S. et al. Identification of unstable regulatory and autoreactive effector T cells that are expanded in patients with FOXP3 mutations. Sci. Transl. Med. 15, eadg6822 (2023). FOXP3 mutations drive Treg cell destabilization into effector T cells; this is prevented in the presence of wildtype-expressing FOXP3+ Treg cells.
Skartsis, N. et al. IL-6 and TNFα drive extensive proliferation of human tregs without compromising their lineage stability or function. Front. Immunol. 12, 783282 (2021). Human Treg cells cultured in pro-inflammatory cytokines have enhanced proliferation, while maintaining their stability and function.
Hoeppli, R. E. et al. Tailoring the homing capacity of human Tregs for directed migration to sites of Th1-inflammation or intestinal regions. Am. J. Transpl. 19, 62–76 (2019).
MacDonald, K. G. et al. Alloantigen-specific regulatory T cells generated with a chimeric antigen receptor. J. Clin. Invest. 126, 1413–1424 (2016).
Proics, E. et al. Preclinical assessment of antigen-specific chimeric antigen receptor regulatory T cells for use in solid organ transplantation. Gene Ther. 30, 309–322 (2023).
Ellis, G. I. et al. Trafficking and persistence of alloantigen-specific chimeric antigen receptor regulatory T cells in Cynomolgus macaque. Cell Rep. Med. 3, 100614 (2022).
Shahin, T. et al. Germline biallelic mutation affecting the transcription factor Helios causes pleiotropic defects of immunity. Sci. Immunol. 6, eabe3981 (2021).
Henry, Y. L. et al. A germline heterozygous dominant negative IKZF2 variant causing syndromic primary immune regulatory disorder and ICHAD. Preprint at medRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.09.09.23295301 (2023).
Chinen, T. et al. An essential role for the IL-2 receptor in Treg cell function. Nat. Immunol. 17, 1322–1333 (2016).
Wing, K. et al. CTLA-4 control over Foxp3+ regulatory T cell function. Science 322, 271–275 (2008).
Rubtsov, Y. P. et al. Regulatory T cell-derived interleukin-10 limits inflammation at environmental interfaces. Immunity 28, 546–558 (2008).
Marie, J. C., Letterio, J. J., Gavin, M. & Rudensky, A. Y. TGF-β1 maintains suppressor function and Foxp3 expression in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 201, 1061–1067 (2005).
Dikiy, S. & Rudensky, A. Y. Principles of regulatory T cell function. Immunity 56, 240–255 (2023).
Tay, C., Tanaka, A. & Sakaguchi, S. Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells as targets of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 41, 450–465 (2023).
Akkaya, B. et al. Regulatory T cells mediate specific suppression by depleting peptide-MHC class II from dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 20, 218–231 (2019).
Waters, E., Williams, C., Kennedy, A. & Sansom, D. M. In vitro analysis of CTLA-4-mediated transendocytosis by regulatory T cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2559, 171–187 (2023).
Tekguc, M., Wing, J. B., Osaki, M., Long, J. & Sakaguchi, S. Treg-expressed CTLA-4 depletes CD80/CD86 by trogocytosis, releasing free PD-L1 on antigen-presenting cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118, e2023739118 (2021).
Schubert, D. et al. Autosomal dominant immune dysregulation syndrome in humans with CTLA4 mutations. Nat. Med. 20, 1410–1416 (2014).
Zaitsu, M., Issa, F., Hester, J., Vanhove, B. & Wood, K. J. Selective blockade of CD28 on human T cells facilitates regulation of alloimmune responses.JCI Insight 2, e89381 (2017).
Stockis, J. et al. Blocking immunosuppression by human Tregs in vivo with antibodies targeting integrin αVβ8. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, E10161–E10168 (2017).
Cuende, J. et al. Monoclonal antibodies against GARP/TGF-β1 complexes inhibit the immunosuppressive activity of human regulatory T cells in vivo. Sci. Transl. Med. 7, 284ra256 (2015).
Glocker, E. O. et al. Inflammatory bowel disease and mutations affecting the interleukin-10 receptor. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 2033–2045 (2009).
Ye, C., Yano, H., Workman, C. J. & Vignali, D. A. A. Interleukin-35: structure, function and its impact on immune-related diseases. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 41, 391–406 (2021).
Perrot, I. et al. Blocking antibodies targeting the CD39/CD73 immunosuppressive pathway unleash immune responses in combination cancer therapies. Cell Rep. 27, 2411–2425.e9 (2019).
Jarvis, L. B. et al. Therapeutically expanded human regulatory T-cells are super-suppressive due to HIF1A induced expression of CD73. Commun. Biol. 4, 1186 (2021).
Wang, X., Rickert, M. & Garcia, K. C. Structure of the quaternary complex of interleukin-2 with its α, β, and γc receptors. Science 310, 1159–1163 (2005).
Wong, H. S. et al. A local regulatory T cell feedback circuit maintains immune homeostasis by pruning self-activated T cells. Cell 184, 3981–3997.e22 (2021).
Dong, S. et al. The effect of low-dose IL-2 and Treg adoptive cell therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes. JCI Insight 6, e147474 (2021).
Kendal, A. R. & Waldmann, H. Infectious tolerance: therapeutic potential. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 22, 560–565 (2010).
Andersson, J. et al. CD4+ FoxP3+ regulatory T cells confer infectious tolerance in a TGF-β-dependent manner. J. Exp. Med. 205, 1975–1981 (2008).
Jonuleit, H. et al. Infectious tolerance: human CD25+ regulatory T cells convey suppressor activity to conventional CD4+ T helper cells. J. Exp. Med. 196, 255–260 (2002).
Mikami, N. et al. Epigenetic conversion of conventional T cells into regulatory T cells by CD28 signal deprivation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 12258–12268 (2020).
Wardell, C. M. et al. Short report: CAR Tregs mediate linked suppression and infectious tolerance in islet transplantation. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.04.06.588414 (2024).
Waldmann, H., Adams, E., Fairchild, P. & Cobbold, S. Infectious tolerance and the long-term acceptance of transplanted tissue. Immunol. Rev. 212, 301–313 (2006).
Qin, S. et al. “Infectious” transplantation tolerance. Science 259, 974–977 (1993).
Cossarizza, A. et al. Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies (third edition). Eur. J. Immunol. 51, 2708–3145 (2021).
Miyara, M. et al. Functional delineation and differentiation dynamics of human CD4+ T cells expressing the FoxP3 transcription factor. Immunity 30, 899–911 (2009).
Pesenacker, A. M. et al. Treg gene signatures predict and measure type 1 diabetes trajectory. JCI Insight 4, e123879 (2019).
Kim, J. V. et al. Regulatory T cell biomarkers identify patients at risk of developing acute cellular rejection in the first year following heart transplantation. Transplantation 107, 1810–1819 (2023).
Wen, X. et al. Increased islet antigen-specific regulatory and effector CD4+ T cells in healthy individuals with the type 1 diabetes-protective haplotype. Sci. Immunol. 5, eaax8767 (2020).
Sharma, S. et al. Measuring anti-islet autoimmunity in mouse and human by profiling peripheral blood antigen-specific CD4 T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 15, eade3614 (2023).
Poloni, C. et al. T-cell activation-induced marker assays in health and disease. Immunol. Cell Biol. 101, 491–503 (2023).
Bacher, P. et al. Regulatory T cell specificity directs tolerance versus allergy against aeroantigens in humans. Cell 167, 1067–1078.e16 (2016).
Saggau, C., Scheffold, A. & Bacher, P. Flow cytometric characterization of human antigen-reactive T-helper cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2285, 141–152 (2021).
Lemieux, A. et al. Enhanced detection of antigen-specific T cells by a multiplexed AIM assay. Cell Rep. Methods 4, 100690 (2024).
Thornton, A. M. & Shevach, E. M. CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production. J. Exp. Med. 188, 287–296 (1998).
McMurchy, A. N. & Levings, M. K. Suppression assays with human T regulatory cells: a technical guide. Eur. J. Immunol. 42, 27–34 (2012).
Dawson, N. A. J. et al. Functional effects of chimeric antigen receptor co-receptor signaling domains in human regulatory T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 12, eaaz3866 (2020). The function of different types of CAR-engineered human Treg cells is correlated with their ability to suppress antigen presenting cells rather than T cells.
Papp, D., Korcsmaros, T. & Hautefort, I. Revolutionising immune research with organoid-based co-culture and chip systems. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 218, 40–54 (2024).
Cohrs, C. M., Chen, C., Atkinson, M. A., Drotar, D. M. & Speier, S. Bridging the gap: pancreas tissue slices from organ and tissue donors for the study of diabetes pathogenesis. Diabetes 73, 11–22 (2024).
Bertolini, T. B. et al. Role of orally induced regulatory T cells in immunotherapy and tolerance. Cell. Immunol. 359, 104251 (2021).
Bacher, P. & Scheffold, A. The effect of regulatory T cells on tolerance to airborne allergens and allergen immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 142, 1697–1709 (2018).
Bajzik, V. et al. Oral desensitization therapy for peanut allergy induces dynamic changes in peanut-specific immune responses. Allergy 77, 2534–2548 (2022). The PALISADE trial showed that oral peanut immunotherapy was very effective at inducing tolerance of peanuts in previously allergic patients and reduced the abundance of circulating peanut-reactive effector T cells, but did not influence peanut-reactive Treg cells.
Syed, A. et al. Peanut oral immunotherapy results in increased antigen-induced regulatory T-cell function and hypomethylation of forkhead box protein 3 (FOXP3). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 133, 500–510, (2014).
Abdel-Gadir, A. et al. Oral immunotherapy with omalizumab reverses the Th2 cell-like programme of regulatory T cells and restores their function. Clin. Exp. Allergy 48, 825–836 (2018).
Sharif, H. et al. Immunologic mechanisms of a short-course of Lolium perenne peptide immunotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 144, 738–749 (2019).
Sirvent, S. et al. Novel vaccines targeting dendritic cells by coupling allergoids to nonoxidized mannan enhance allergen uptake and induce functional regulatory T cells through programmed death ligand 1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 138, 558–567.e511 (2016).
Nieto, A. et al. First-in-human phase 2 trial with mite allergoids coupled to mannan in subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy. Allergy 77, 3096–3107 (2022).
Abdel-Gadir, A. et al. Microbiota therapy acts via a regulatory T cell MyD88/RORγt pathway to suppress food allergy. Nat. Med. 25, 1164–1174 (2019).
Tchitchek, N. et al. Low-dose IL-2 shapes a tolerogenic gut microbiota that improves autoimmunity and gut inflammation. JCI Insight 7, e159406 (2022).
Lamikanra, A. A. et al. The migratory properties and numbers of T regulatory cell subsets in circulation are differentially influenced by season and are associated with vitamin D status. Front. Immunol. 11, 685 (2020).
Fisher, S. A. et al. The role of vitamin D in increasing circulating T regulatory cell numbers and modulating T regulatory cell phenotypes in patients with inflammatory disease or in healthy volunteers: a systematic review. PLoS One 14, e0222313 (2019).
Hahn, J. et al. Vitamin D and marine omega 3 fatty acid supplementation and incident autoimmune disease: VITAL randomized controlled trial. BMJ 376, e066452 (2022).
Corte-Real, B. F. et al. Sodium perturbs mitochondrial respiration and induces dysfunctional Tregs. Cell Metab. 35, 299–315.e298 (2023).
Feuerer, M. et al. Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat. Med. 15, 930–939 (2009).
Bradley, D. et al. Interferon gamma mediates the reduction of adipose tissue regulatory T cells in human obesity. Nat. Commun. 13, 5606 (2022).
Wu, D. et al. Characterization of regulatory T cells in obese omental adipose tissue in humans. Eur. J. Immunol. 49, 336–347 (2019).
Cignarella, F. et al. Intermittent fasting confers protection in CNS autoimmunity by altering the gut microbiota. Cell Metab. 27, 1222–1235.e6 (2018).
Langston, P. K. et al. Regulatory T cells shield muscle mitochondria from interferon-γ-mediated damage to promote the beneficial effects of exercise. Sci. Immunol. 8, eadi5377 (2023).
Becker, M. et al. Regulatory T cells require IL6 receptor alpha signaling to control skeletal muscle function and regeneration. Cell Metab. 35, 1736–1751.e7 (2023). Mouse Treg cells require IL-6 signalling to mediate muscle repair.
Burzyn, D. et al. A special population of regulatory T cells potentiates muscle repair. Cell 155, 1282–1295 (2013).
Harris, F., Arroyo Berdugo, Y. & Tree, T. IL-2-based approaches to Treg enhancement. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 211, 149–163 (2022).
Koreth, J. et al. Interleukin-2 and regulatory T cells in graft-versus-host disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 2055–2066 (2011).
Saadoun, D. et al. Regulatory T-cell responses to low-dose interleukin-2 in HCV-induced vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 2067–2077 (2011).
Rosenzwajg, M. et al. Immunological and clinical effects of low-dose interleukin-2 across 11 autoimmune diseases in a single, open clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 78, 209–217 (2019).
Zhang, S. X. et al. Low-dose IL-2 therapy limits the reduction in absolute numbers of circulating regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 13, 1759720X211011370 (2021).
He, J. et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose IL-2 in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 79, 141–149 (2020).
Humrich, J. Y. et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 therapy in active systemic lupus erythematosus (LUPIL-2): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised and placebo-controlled phase II trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 81, 1685–1694 (2022).
Rosenzwajg, M. et al. Low-dose IL-2 in children with recently diagnosed type 1 diabetes: a phase I/II randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-finding study. Diabetologia 63, 1808–1821 (2020).
Murakami, N. et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 promotes immune regulation in face transplantation: a pilot study. Am. J. Transpl. 23, 549–558 (2023).
Lim, T. Y. et al. Low dose interleukin-2 selectively expands circulating regulatory T cells but fails to promote liver allograft tolerance in humans. J. Hepatol. 78, 153–164 (2023).
Todd, J. A. et al. Regulatory T cell responses in participants with type 1 diabetes after a single dose of interleukin-2: a non-randomised, open label, adaptive dose-finding trial. PLoS Med. 13, e1002139 (2016).
McQuaid, S. L. et al. Low-dose IL-2 induces CD56bright NK regulation of T cells via NKp44 and NKp46. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 200, 228–241 (2020).
Tchao, N. et al. Ab0432 efavaleukin alfa, a novel Il-2 mutein, selectively expands regulatory T cells in patients with sle: final results of a phase 1b multiple ascending dose study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 81, 1343–1344 (2022).
Fanton, C. et al. Selective expansion of regulatory T cells by NKTR-358 in healthy volunteers and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 5, 100152 (2022).
Nektar announces promising new and corrected rezpegaldesleukin efficacy data which were previously reported in 2022 and incorrectly calculated by former collaborator Eli Lilly & Company. PR Newswire (7 August 2023); https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/nektar-announces-promising-new-and-corrected-rezpegaldesleukin-efficacy-data-which-were-previously-reported-in-2022-and-incorrectly-calculated-by-former-collaborator-eli-lilly--company-301894443.html.
VanDyke, D. et al. Engineered human cytokine/antibody fusion proteins expand regulatory T cells and confer autoimmune disease protection. Cell Rep. 41, 111478 (2022). An anti-IL-2 antibody complexed with IL-2 selectively expands Treg cells to protect against multiple preclinical autoimmune diseases.
Stremska, M. E. et al. IL233, a novel IL-2 and IL-33 hybrid cytokine, ameliorates renal injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 28, 2681–2693 (2017).
Venkatadri, R. et al. Hybrid cytokine IL233 renders protection in murine acute graft vs host disease (aGVHD). Cell. Immunol. 364, 104345 (2021).
Benne, N., Ter Braake, D., Stoppelenburg, A. J. & Broere, F. Nanoparticles for inducing antigen-specific T cell tolerance in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 13, 864403 (2022).
Krienke, C. et al. A noninflammatory mRNA vaccine for treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Science 371, 145–153 (2021). A nanoparticle loaded with autoantigen-encoding m1Ψ mRNA expands Treg cells to treat a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.
Prasad, S. et al. Tolerogenic Ag-PLG nanoparticles induce tregs to suppress activated diabetogenic CD4 and CD8 T cells. J. Autoimmun. 89, 112–124 (2018).
Liu, Q. et al. Use of polymeric nanoparticle platform targeting the liver to induce treg-mediated antigen-specific immune tolerance in a pulmonary allergen sensitization model. ACS Nano 13, 4778–4794 (2019).
Maldonado, R. A. et al. Polymeric synthetic nanoparticles for the induction of antigen-specific immunological tolerance. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, E156–E165 (2015).
Casey, L. M. et al. Conjugation of transforming growth factor beta to antigen-loaded poly(lactide- co-glycolide) nanoparticles enhances efficiency of antigen-specific tolerance. Bioconjug. Chem. 29, 813–823 (2018).
Rhodes, K. R. et al. Bioengineered particles expand myelin-specific regulatory T cells and reverse autoreactivity in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Sci. Adv. 9, eadd8693 (2023).
Kivitz, A. et al. Phase 2 dose-finding study in patients with gout using SEL-212, a novel PEGylated uricase (SEL-037) combined with tolerogenic nanoparticles (SEL-110). Rheumatol. Ther. 10, 825–847 (2023).
Kishimoto, T. K. et al. Rapamycin nanoparticles increase the therapeutic window of engineered interleukin-2 and drive expansion of antigen-specific regulatory T cells for protection against autoimmune disease. J. Autoimmun. 140, 103125 (2023).
Fraser, H. et al. A rapamycin-based GMP-compatible process for the isolation and expansion of regulatory T cells for clinical trials. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 8, 198–209 (2018).
Hoffmann, P. et al. Only the CD45RA+ subpopulation of CD4+CD25high T cells gives rise to homogeneous regulatory T-cell lines upon in vitro expansion. Blood 108, 4260–4267 (2006).
Hoffmann, P. et al. Loss of FOXP3 expression in natural human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells upon repetitive in vitro stimulation. Eur. J. Immunol. 39, 1088–1097 (2009).
Brown, M. E. et al. Human CD4+CD25+CD226- Tregs demonstrate increased purity, lineage stability, and suppressive capacity versus CD4+CD25+CD127lo/- Tregs for adoptive cell therapy. Front. Immunol. 13, 873560 (2022).
Opstelten, R. et al. GPA33: a marker to identify stable human regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 204, 3139–3148 (2020).
Seay, H. R. et al. Expansion of human Tregs from cryopreserved umbilical cord blood for GMP-compliant autologous adoptive cell transfer therapy. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 4, 178–191 (2017).
Motwani, K. et al. Human regulatory T cells from umbilical cord blood display increased repertoire diversity and lineage stability relative to adult peripheral blood. Front. Immunol. 11, 611 (2020).
Brunstein, C. G. et al. Infusion of ex vivo expanded T regulatory cells in adults transplanted with umbilical cord blood: safety profile and detection kinetics. Blood 117, 1061–1070 (2011).
Brunstein, C. G. et al. Umbilical cord blood-derived T regulatory cells to prevent GVHD: kinetics, toxicity profile, and clinical effect. Blood 127, 1044–1051 (2016).
Kellner, J. N. et al. Third party, umbilical cord blood derived regulatory T-cells for prevention of graft versus host disease in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: feasibility, safety and immune reconstitution. Oncotarget 9, 35611–35622 (2018).
Gladstone, D. E. et al. Randomized, double blinded, placebo controlled trial of allogeneic cord blood T-regulatory cell for treatment of COVID-19 ARDS. Blood Adv. 7, 3075–3079 (2023).
Caplan, H. W. et al. Human cord blood-derived regulatory T-cell therapy modulates the central and peripheral immune response after traumatic brain injury. Stem Cell Transl. Med. 9, 903–916 (2020).
Lyu, M. A. et al. Allogeneic cord blood regulatory T cells can resolve lung inflammation. Cytotherapy 25, 245–253 (2023).
Dijke, I. E. et al. Discarded human thymus is a novel source of stable and long-lived therapeutic regulatory T cells. Am. J. Transpl. 16, 58–71 (2016).
Romano, M. et al. Isolation and expansion of thymus-derived regulatory T cells for use in pediatric heart transplant patients. Eur. J. Immunol. 51, 2086–2092 (2021).
Bernaldo-de-Quiros, E. et al. A novel GMP protocol to produce high-quality Treg cells from the pediatric thymic tissue to be employed as cellular therapy. Front. Immunol. 13, 893576 (2022).
MacDonald, K. N. et al. Consequences of adjusting cell density and feed frequency on serum-free expansion of thymic regulatory T cells. Cytotherapy 24, 1121–1135 (2022).
Bernaldo-de-Quiros, E. et al. First-in-human therapy with Treg produced from thymic tissue (thyTreg) in a heart transplant infant. J. Exp. Med. 220, e20231045 (2023). Autologous thymic Treg cells administered to a patient receiving a heart transplant enabled Treg cell engraftment and was not associated with adverse effects.
MacMillan, M. L. et al. First-in-human phase 1 trial of induced regulatory T cells for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in HLA-matched siblings. Blood Adv. 5, 1425–1436 (2021).
Schmidt, A., Eriksson, M., Shang, M. M., Weyd, H. & Tegner, J. Comparative analysis of protocols to induce human CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by combinations of IL-2, TGF-beta, retinoic acid, rapamycin and butyrate. PLoS One 11, e0148474 (2016).
Cook, L. et al. Induction of stable human FOXP3+ Tregs by a parasite-derived TGF-β mimic. Immunol. Cell Biol. 99, 833–847 (2021).
Yano, H. et al. Human iPSC-derived CD4+ Treg-like cells engineered with chimeric antigen receptors control GvHD in a xenograft model. Cell Stem Cell 31, 795–802.e6 (2024). First published report of successful generation of human Treg cells from induced pluripotent stem cells.
Fong, H. et al. A serum- and feeder-free system to generate CD4 and regulatory T cells from human iPSCs. Preprint at BioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.01.547333 (2023).
Sato, Y. et al. Human-engineered Treg-like cells suppress FOXP3-deficient T cells but preserve adaptive immune responses in vivo. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 9, e1214 (2020).
Honaker, Y. et al. Gene editing to induce FOXP3 expression in human CD4+ T cells leads to a stable regulatory phenotype and function. Sci. Transl. Med 12, eaay6422 (2020).
Santoni de Sio, F. R. et al. Ectopic FOXP3 expression preserves primitive features of human hematopoietic stem cells while impairing functional T cell differentiation. Sci. Rep. 7, 15820 (2017).
Masiuk, K. E., Laborada, J., Roncarolo, M. G., Hollis, R. P. & Kohn, D. B. Lentiviral gene therapy in HSCs restores lineage-specific Foxp3 expression and suppresses autoimmunity in a mouse model of IPEX syndrome. Cell Stem Cell 24, 309–317.e7 (2019).
Seng, A. et al. Coexpression of FOXP3 and a Helios isoform enhances the effectiveness of human engineered regulatory T cells. Blood Adv. 4, 1325–1339 (2020).
Sato, Y. et al. A novel FOXP3 knockout-humanized mouse model for pre-clinical safety and efficacy evaluation of Treg-like cell products. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 31, 101150 (2023). Humanized mouse model to test effects of Treg cell therapies on intestinal inflammation; proof of concept that basiliximab can be used as a safety switch.
Bluestone, J. A., McKenzie, B. S., Beilke, J. & Ramsdell, F. Opportunities for Treg cell therapy for the treatment of human disease. Front. Immunol. 14, 1166135 (2023).
Sawitzki, B. et al. Regulatory cell therapy in kidney transplantation (The ONE Study): a harmonised design and analysis of seven non-randomised, single-arm, phase 1/2A trials. Lancet 395, 1627–1639 (2020). A multi-site, phase 1/2A trial reported that autologous polyclonal Treg cellular therapy is safe in kidney transplantation and reduces the expected incidence of viral complications.
Roemhild, A. et al. Regulatory T cells for minimising immune suppression in kidney transplantation: phase I/IIa clinical trial. BMJ 371, m3734 (2020).
Brook, M. O. et al. Transplantation Without Overimmunosuppression (TWO) study protocol: a phase 2b randomised controlled single-centre trial of regulatory T cell therapy to facilitate immunosuppression reduction in living donor kidney transplant recipients. BMJ Open 12, e061864 (2022).
Brook, M. O. et al. Late treatment with autologous expanded regulatory T-cell therapy after alemtuzumab induction is safe and facilitates immunosuppression minimization in living donor renal transplantation. Transplantation 108, 2278–2286 (2024).
Meyer, E. H. et al. Transplantation of donor grafts with defined ratio of conventional and regulatory T cells in HLA-matched recipients. JCI Insight 4, 127244 (2019).
Landwehr-Kenzel, S. et al. Adoptive transfer of ex vivo expanded regulatory T cells improves immune cell engraftment and therapy-refractory chronic GvHD. Mol. Ther. 30, 2298–2314 (2022).
Whangbo, J. et al. A phase 1 study of donor regulatory T-cell infusion plus low-dose interleukin-2 for steroid-refractory chronic graft-vs-host disease. Blood Adv. 6, 5786–5796 (2022).
Meyer, E. H. et al. Orca-T, a precision Treg-engineered donor product, prevents acute GVHD with less immunosuppression in an early multicenter experience with myeloablative HLA-matched transplants. Blood 136, 47–48 (2020). Orca Bio’s Orca-T cell product, consisting of a dose of Treg cells and CD34+ cells followed by conventional T cell administration, reduced the risk of GVHD in patients with haematologic malignancies.
Villar-Prados, A. et al. Phase 1 trial results for patients with advanced hematologic malignancies undergoing reduced intensity allogeneic HCT with orca-T donor cell therapy product and single agent tacrolimus. Blood 142, 3560 (2023).
Marek-Trzonkowska, N. et al. Therapy of type 1 diabetes with CD4+CD25highCD127− regulatory T cells prolongs survival of pancreatic islets — results of one year follow-up. Clin. Immunol. 153, 23–30 (2014).
Marek-Trzonkowska, N. et al. Administration of CD4+CD25highCD127− regulatory T cells preserves β-cell function in type 1 diabetes in children. Diabetes Care 35, 1817–1820 (2012).
Zielinski, M. et al. Combined therapy with CD4+ CD25highCD127− T regulatory cells and anti-CD20 antibody in recent-onset type 1 diabetes is superior to monotherapy: randomized phase I/II trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 24, 1534–1543 (2022). A combination of polyclonal Treg cells and rituximab significantly enhanced c-peptide preservation in patients with recent-onset T1D.
Bluestone, J. A. et al. Type 1 diabetes immunotherapy using polyclonal regulatory T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 7, 315ra189 (2015).
Bender, C. et al. A phase 2 randomized trial with autologous polyclonal expanded regulatory T cells in children with new-onset type 1 diabetes. Sci. Transl. Med. 16, eadn2404 (2024). A phase 2 autologous polyclonal Treg cell therapy trial showed no clinical benefit in children with recent onset type 1 diabetes.
Dall’Era, M. et al. Adoptive Treg cell therapy in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71, 431–440 (2019).
Voskens, C. et al. Autologous regulatory T-cell transfer in refractory ulcerative colitis with concomitant primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut 72, 49–53 (2022).
Boardman, D. A., Jacob, J., Smyth, L. A., Lombardi, G. & Lechler, R. I. What is direct allorecognition? Curr. Transpl. Rep. 3, 275–283 (2016).
Putnam, A. L. et al. Clinical grade manufacturing of human alloantigen-reactive regulatory T cells for use in transplantation. Am. J. Transpl. 13, 3010–3020 (2013).
Guinan, E. C. et al. Donor antigen-specific regulatory T cell administration to recipients of live donor kidneys: a ONE Study consortium pilot trial. Am. J. Transpl. 23, 1872–1881 (2023).
Tang, Q. et al. Selective decrease of donor-reactive Tregs after liver transplantation limits Treg therapy for promoting allograft tolerance in humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 14, eabo2628 (2022).
Ezzelarab, M. B. et al. Ex vivo expanded donor alloreactive regulatory T cells lose immunoregulatory, proliferation, and antiapoptotic markers after infusion into ATG-lymphodepleted, nonhuman primate heart allograft recipients. Transplantation 105, 1965–1979 (2021).
Tuomela, K., Salim, K. & Levings, M. K. Eras of designer Tregs: harnessing synthetic biology for immune suppression. Immunol. Rev. 320, 250–267 (2023).
Hull, C. M. et al. Generation of human islet-specific regulatory T cells by TCR gene transfer. J. Autoimmun. 79, 63–73 (2017).
Yang, S. J. et al. Pancreatic islet-specific engineered Tregs exhibit robust antigen-specific and bystander immune suppression in type 1 diabetes models. Sci. Transl. Med. 14, eabn1716 (2022). Generation of antigen-specific, therapeutic Treg cells by editing conventional T cells to over-express FOXP3 and diabetes relevant TCRs.
Cook, P. J. et al. A chemically inducible IL-2 receptor signaling complex allows for effective in vitro and in vivo selection of engineered CD4+ T cells. Mol. Ther. 31, 2472–2488 (2023).
Boardman, D. A. & Levings, M. K. Emerging strategies for treating autoimmune disorders with genetically modified Treg cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 149, 1–11 (2022).
Dawson, N. A. et al. Systematic testing and specificity mapping of alloantigen-specific chimeric antigen receptors in regulatory T cells. JCI Insight 4, e123672 (2019).
Muller, Y. D. et al. Precision engineering of an anti-HLA-A2 chimeric antigen receptor in regulatory T cells for transplant immune tolerance. Front. Immunol. 12, 686439 (2021).
Wagner, J. C., Ronin, E., Ho, P., Peng, Y. & Tang, Q. Anti-HLA-A2-CAR Tregs prolong vascularized mouse heterotopic heart allograft survival. Am. J. Transpl. 22, 2237–2245 (2022).
Boroughs, A. C. et al. Chimeric antigen receptor costimulation domains modulate human regulatory T cell function. JCI Insight 5, e126194 (2019).
Rosado-Sanchez, I. et al. Regulatory T cells integrate native and CAR-mediated co-stimulatory signals for control of allograft rejection. JCI Insight 8, e167215 (2023).
Imura, Y., Ando, M., Kondo, T., Ito, M. & Yoshimura, A. CD19-targeted CAR regulatory T cells suppress B cell pathology without GvHD. JCI Insight 5, e136185 (2020).
Bolivar-Wagers, S. et al. Murine CAR19 Tregs suppress acute graft-versus-host disease and maintain graft-versus-tumor responses. JCI Insight 7, e160674 (2022).
Shimabukuro-Vornhagen, A. et al. Cytokine release syndrome. J. Immunother. Cancer 6, 56 (2018).
Doglio, M. et al. Regulatory T cells expressing CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor restore homeostasis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Commun. 15, 2542 (2024). FOXP3-overexpressing CD19-CAR Treg cells restrict autoantibody production in a humanized mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus in the absence of toxicity.
Spanier, J. A. et al. Tregs with an MHC class II peptide-specific chimeric antigen receptor prevent autoimmune diabetes in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 133, e168601 (2023).
Obarorakpor, N. et al. Regulatory T cells targeting a pathogenic MHC class II: Insulin peptide epitope postpone spontaneous autoimmune diabetes. Front. Immunol. 14, 1207108 (2023).
Rana, J. et al. CAR- and TRuC-redirected regulatory T cells differ in capacity to control adaptive immunity to FVIII. Mol. Ther. 29, 2660–2676 (2021).
Yoon, J. et al. FVIII-specific human chimeric antigen receptor T-regulatory cells suppress T- and B-cell responses to FVIII. Blood 129, 238–245 (2017).
Boardman, D. A. et al. Flagellin-specific human CAR Tregs for immune regulation in IBD. J. Autoimmun. 134, 102961 (2023).
McGovern, J., Holler, A., Thomas, S. & Stauss, H. J. Forced Fox-P3 expression can improve the safety and antigen-specific function of engineered regulatory T cells. J. Autoimmun. 132, 102888 (2022).
Lamarche, C. et al. Tonic-signaling chimeric antigen receptors drive human regulatory T cell exhaustion. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 120, e2219086120 (2023).
Lamarthee, B. et al. Transient mTOR inhibition rescues 4-1BB CAR-Tregs from tonic signal-induced dysfunction. Nat. Commun. 12, 6446 (2021).
Ratnasothy, K. et al. IL-2 therapy preferentially expands adoptively transferred donor-specific Tregs improving skin allograft survival. Am. J. Transpl. 19, 2092–2100 (2019).
Cabello-Kindelan, C. et al. Immunomodulation followed by antigen-specific Treg infusion controls islet autoimmunity. Diabetes 69, 215–227 (2020).
Muckenhuber, M. et al. Optimum timing of antithymocyte globulin in relation to adoptive regulatory T cell therapy. Am. J. Transpl. 23, 84–92 (2023).
Camirand, G. & Riella, L. V. Treg-centric view of immunosuppressive drugs in transplantation: a balancing act. Am. J. Transpl. 17, 601–610 (2017).
Amini, L. et al. CRISPR-Cas9-edited tacrolimus-resistant antiviral T cells for advanced adoptive immunotherapy in transplant recipients. Mol. Ther. 29, 32–46 (2021).
Poirot, L. et al. Multiplex genome-edited T-cell manufacturing platform for “off-the-shelf” adoptive T-cell immunotherapies. Cancer Res. 75, 3853–3864 (2015).
Sockolosky, J. T. et al. Selective targeting of engineered T cells using orthogonal IL-2 cytokine-receptor complexes. Science 359, 1037–1042 (2018).
Zhang, Q. et al. A human orthogonal IL-2 and IL-2Rβ system enhances CAR T cell expansion and antitumor activity in a murine model of leukemia. Sci. Transl. Med. 13, eabg6986 (2021).
Ramos, T. L. et al. Prevention of acute GVHD using an orthogonal IL-2/IL-2Rβ system to selectively expand regulatory T cells in vivo. Blood 141, 1337–1352 (2023).
Hirai, T. et al. Selective expansion of regulatory T cells using an orthogonal IL-2/IL-2 receptor system facilitates transplantation tolerance. J. Clin. Invest. 131, e139991 (2021).
Bittner, S. et al. Biosensors for inflammation as a strategy to engineer regulatory T cells for cell therapy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2208436119 (2022). Expression of CARs with TNFR family cytokine receptors on the exterior portion allows Treg cells to be activated by generalized inflammation.
Sicard, A. et al. Donor-specific chimeric antigen receptor Tregs limit rejection in naive but not sensitized allograft recipients. Am. J. Transpl. 20, 1562–1573 (2020).
Mohseni, Y. R. et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified human regulatory T cells that constitutively express IL-10 maintain their phenotype and are potently suppressive. Eur. J. Immunol. 51, 2522–2530 (2021).
Cook, L. et al. Suppressive and gut-reparative functions of human type 1 T regulatory cells. Gastroenterology 157, 1584–1598 (2019).
Stadtmauer, E. A. et al. CRISPR-engineered T cells in patients with refractory cancer. Science 367, eaba7365 (2020).
Hu, Y. et al. Safety and efficacy of CRISPR-based non-viral PD1 locus specifically integrated anti-CD19 CAR-T cells in patients with relapsed or refractory Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a first-in-human phase I study. EClinicalMedicine 60, 102010 (2023).
McCallion, O. et al. Matching or genetic engineering of HLA Class I and II facilitates successful allogeneic ‘off-the-shelf’ regulatory T cell therapy. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.06.551956 (2023).
Gornalusse, G. G. et al. HLA-E-expressing pluripotent stem cells escape allogeneic responses and lysis by NK cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 35, 765–772 (2017).
Jo, S. et al. Endowing universal CAR T-cell with immune-evasive properties using TALEN-gene editing. Nat. Commun. 13, 3453 (2022).
Li, W. et al. Simultaneous editing of TCR, HLA-I/II and HLA-E resulted in enhanced universal CAR-T resistance to allo-rejection. Front. Immunol. 13, 1052717 (2022).
Jandus, C. et al. Interactions between Siglec-7/9 receptors and ligands influence NK cell-dependent tumor immunosurveillance. J. Clin. Invest. 124, 1810–1820 (2014).
Deuse, T. et al. Hypoimmunogenic derivatives of induced pluripotent stem cells evade immune rejection in fully immunocompetent allogeneic recipients. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 252–258 (2019).
Saleh, R. & Elkord, E. FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in cancer: prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cancer Lett. 490, 174–185 (2020).
Baur, A. S. et al. Denileukin diftitox (ONTAK) induces a tolerogenic phenotype in dendritic cells and stimulates survival of resting Treg. Blood 122, 2185–2194 (2013).
Kawai, H. et al. Phase II study of E7777 in Japanese patients with relapsed/refractory peripheral and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 112, 2426–2435 (2021).
Solomon, I. et al. CD25-Treg-depleting antibodies preserving IL-2 signaling on effector T cells enhance effector activation and antitumor immunity. Nat. Cancer 1, 1153–1166 (2020).
Revenko, A. et al. Direct targeting of FOXP3 in Tregs with AZD8701, a novel antisense oligonucleotide to relieve immunosuppression in cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 10, e003892 (2022).
Nagira, Y. et al. S-531011, a novel anti-human CCR8 antibody, induces potent antitumor responses through depletion of tumor-infiltrating CCR8-expressing regulatory T cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 22, 1063–1072 (2023). A human CCR8 antibody depletes intratumoral Treg cells in a preclinical cancer model without inducing autoimmunity.
Kidani, Y. et al. CCR8-targeted specific depletion of clonally expanded Treg cells in tumor tissues evokes potent tumor immunity with long-lasting memory. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2114282119 (2022).
Chuckran, C. A. et al. Prevalence of intratumoral regulatory T cells expressing neuropilin-1 is associated with poorer outcomes in patients with cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 13, eabf8495 (2021).
Zhao, J. et al. Selective depletion of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by low-dose cyclophosphamide is explained by reduced intracellular ATP levels. Cancer Res. 70, 4850–4858 (2010).
Herbst, R. S. et al. COAST: an open-label, phase II, multidrug platform study of durvalumab alone or in combination with oleclumab or monalizumab in patients with unresectable, stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 40, 3383–3393 (2022).
Long, G. V. et al. Epacadostat plus pembrolizumab versus placebo plus pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma (ECHO-301/KEYNOTE-252): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind study. Lancet Oncol. 20, 1083–1097 (2019).
Eynde, B. J. V. D., Baren, N. V. & Baurain, J.-F. Is there a clinical future for IDO1 inhibitors after the failure of epacadostat in melanoma? Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 4, 241–256 (2020).
Tang, K., Wu, Y. H., Song, Y. & Yu, B. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) inhibitors in clinical trials for cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 14, 68 (2021).
Holmgaard, R. B. et al. Targeting the TGFβ pathway with galunisertib, a TGFβRI small molecule inhibitor, promotes anti-tumor immunity leading to durable, complete responses, as monotherapy and in combination with checkpoint blockade. J. Immunother. Cancer 6, 47 (2018).
Hira, S. K. et al. Galunisertib drives Treg fragility and promotes dendritic cell-mediated immunity against experimental lymphoma. iScience 23, 101623 (2020).
Yamazaki, T. et al. Galunisertib plus neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer: a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 23, 1189–1200 (2022).
Tan, C. L. et al. PD-1 restraint of regulatory T cell suppressive activity is critical for immune tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 218, e20182232 (2021).
Kamada, T. et al. PD-1+ regulatory T cells amplified by PD-1 blockade promote hyperprogression of cancer. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116, 9999–10008 (2019).
Kumagai, S. et al. The PD-1 expression balance between effector and regulatory T cells predicts the clinical efficacy of PD-1 blockade therapies. Nat. Immunol. 21, 1346–1358 (2020). Tumours infiltrated with high numbers of Treg cells expressing PD-1 are at a higher risk of hyper-progressive disease post-PD-1 blockade.
Simpson, T. R. et al. Fc-dependent depletion of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells co-defines the efficacy of anti-CTLA-4 therapy against melanoma. J. Exp. Med. 210, 1695–1710 (2013).
Romano, E. et al. Ipilimumab-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of regulatory T cells ex vivo by nonclassical monocytes in melanoma patients. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 6140–6145 (2015).
van Pul, K. M. et al. Local delivery of low-dose anti-CTLA-4 to the melanoma lymphatic basin leads to systemic Treg reduction and effector T cell activation. Sci. Immunol. 7, eabn8097 (2022).
Sharma, A. et al. Anti-CTLA-4 immunotherapy does not deplete FOXP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) in human cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 25, 1233–1238 (2019).
Alissafi, T., Hatzioannou, A., Legaki, A. I., Varveri, A. & Verginis, P. Balancing cancer immunotherapy and immune-related adverse events: the emerging role of regulatory T cells. J. Autoimmun. 104, 102310 (2019).
Luoma, A. M. et al. Molecular pathways of colon inflammation induced by cancer immunotherapy. Cell 182, 655–671.e22 (2020).
Kartolo, A., Sattar, J., Sahai, V., Baetz, T. & Lakoff, J. M. Predictors of immunotherapy-induced immune-related adverse events. Curr. Oncol. 25, e403–e410 (2018).
Cortellini, A. et al. Correlations between the immune-related adverse events spectrum and efficacy of anti-PD1 immunotherapy In NSCLC patients. Clin. Lung Cancer 20, 237–247.e1 (2019).
Tombacz, I. et al. Highly efficient CD4+ T cell targeting and genetic recombination using engineered CD4+ cell-homing mRNA-LNPs. Mol. Ther. 29, 3293–3304 (2021).
Hou, X., Zaks, T., Langer, R. & Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 1078–1094 (2021).
Monian, B. et al. Peanut oral immunotherapy differentially suppresses clonally distinct subsets of T helper cells. J. Clin. Invest. 132, e150634 (2022).
Kulis, M. et al. High- and low-dose oral immunotherapy similarly suppress pro-allergic cytokines and basophil activation in young children. Clin. Exp. Allergy 49, 180–189 (2019).
Zhang, Y. et al. Successful milk oral immunotherapy promotes generation of casein-specific CD137+ FOXP3+ regulatory T cells detectable in peripheral blood. Front. Immunol. 12, 705615 (2021).
de Picciotto, S. et al. Selective activation and expansion of regulatory T cells using lipid encapsulated mRNA encoding a long-acting IL-2 mutein. Nat. Commun. 13, 3866 (2022). A nanoparticle carrying mRNA encoding an IL-2 mutein selectively expands Treg cells in mice and non-human primates.
Podojil, J. R. et al. Tolerogenic immune-modifying nanoparticles encapsulating multiple recombinant pancreatic β cell proteins prevent onset and progression of type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J. Immunol. 209, 465–475 (2022).
Arpaia, N. et al. A distinct function of regulatory T cells in tissue protection. Cell 162, 1078–1089 (2015).
Yang, H. et al. Adoptive therapy with amyloid-β specific regulatory T cells alleviates Alzheimer’s disease. Theranostics 12, 7668–7680 (2022).
Sheean, R. K. et al. Association of regulatory T-cell expansion with progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a study of humans and a transgenic mouse model. JAMA Neurol. 75, 681–689 (2018).
Zacchigna, S. et al. Paracrine effect of regulatory T cells promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation during pregnancy and after myocardial infarction. Nat. Commun. 9, 2432 (2018).
Leung, O. M. et al. Regulatory T cells promote apelin-mediated sprouting angiogenesis in type 2 diabetes. Cell Rep. 24, 1610–1626 (2018).
Ito, M. et al. Brain regulatory T cells suppress astrogliosis and potentiate neurological recovery. Nature 565, 246–250 (2019).
Yshii, L. et al. Astrocyte-targeted gene delivery of interleukin 2 specifically increases brain-resident regulatory T cell numbers and protects against pathological neuroinflammation. Nat. Immunol. 23, 878–891 (2022). Astrocyte-targeted IL-2 delivery expands brain Treg cells that protect against mouse models of traumatic brain injury, stroke and multiple sclerosis.
Park, T. Y. et al. Co-transplantation of autologous Treg cells in a cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Nature 619, 606–615 (2023).
Acknowledgements
The authors’ work in this area is funded by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR; FDN-154304), Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Canada (3-COE-2022-1103-M-B), U.S. Department of Defense/Reconstructive Transplant Research Program (HT94252310626), and the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust. C.M.W. is supported by a CIHR doctoral award. D.A.B. was supported by fellowships from the CIHR and Michael Smith Health Research BC. M.K.L. is Canada Research Chair in Immune Engineering and receives a Scientist Salary Award from the BC Children’s Hospital Research Institute. We thank K. Salim for providing sample flow plots displayed in Fig. 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.M.W. and M.K.L. conceived the article. All authors contributed to the research, writing and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
M.K.L. is a science advisory board member for Anokion, advises for and holds shares in Integrated Nanotherapeutics, and is an inventor on patent applications related to A2-chimaeric antigen receptor regulatory T cells with licensed technology to Sangamo Therapeutics. C.M.W. and D.A.B. declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery thanks Leonardo Ferreira and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Related links
ClinicalTrials.gov: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
EudraCT: https://eudract.ema.europa.eu/
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wardell, C.M., Boardman, D.A. & Levings, M.K. Harnessing the biology of regulatory T cells to treat disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 24, 93–111 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-024-01089-x
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-024-01089-x