Abstract
EGFR-TKIs are effective therapies for non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with EGFR-activating mutations. However, responses vary within individuals and resistant disease inevitably emerges. A prospective cohort of 130 patients with advanced EGFR mutation NSCLC were enrolled. Pre-and post-treatment plasma from subjects treated with EGFR-TKIs were obtained. The correlation between EGFR mutation abundance using the Idylla™ ctEGFR mutation assay, radiographic assessment, and clinical outcomes were analyzed. Eighty-nine patients with retrieved blood collection were analyzed. Undetectable ctEGFR (49.5%), detectable ctEGFR CqMut-high (23.5%), and detectable ctEGFR CqMut low (27%) using CqMut cutoff at 28.1, represented consecutive incremental tumor burden by radiographic assessment and outcome of treatment. Median PFS was 13.4 months [95% CI 12.0-14.8] in undetectable ctEGFR, 10.4 months [95% CI 9.9–10.9] in ctEGFR CqMut-high, and 5.9 months [95% CI 3.8–7.4] in ctEGFR CqMut-low. Number of metastasis sites > 3 was found in 22.7%, 23.8%, and 58.3% of the 3-tier ctEGFR tumor burden levels, respectively (p-value 0.01). Presence of liver metastasis was significantly correlated with number of metastasis sites > 3 and ctEGFR CqMut-low (45.8%). Liver metastasis was an independent factor of reduced PFS and OS by multivariate analysis with an HR = 2.41 [95% CI 1.27–4.60, p-value 0.007]) and HR = 2.96 [95% CI 1.35–6.51, p-value 0.007], respectively. The pretreatment ctEGFR detection using the Idylla™ ctEGFR mutation assay served as a surrogate marker for tumor abundance and tumor burden. Presence of liver metastasis was found to be a clinical predictor associated with high tumor abundance and worsening treatment outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are effective therapies for non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with EGFR-activating mutations. However, responses vary within individuals with progression-free survival (PFS) ranging from a few months to several years and resistant disease inevitably emerges. Recent studies have shown that EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC is highly heterogeneous at the cellular level, facilitating the clonal expansion of resistant tumors via multiple molecular mechanisms1,2. Intratumor heterogeneity was correlated with poor prognostic outcomes in stage I-III resectable lung cancer3. Intratumor heterogeneity was also a characteristic of genomic complexity in more advanced diseases4. High tumor burden is also correlated with high intratumor heterogeneity5,6. The detectable pretreatment ctEGFR7,8,9,10,11,12 and the presence of liver metastasis13,14,15 had been reported as prognostic values. The relative abundance of EGFR mutations and tumor burden was also reported16 .
As molecular genotyping has been traditionally performed using tissue biopsies that represent only a small sample from a single tumor site, it is thought not to reflect the actual intra-tumoral heterogeneity status of tumors. Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive method to identify somatic mutations from circulating tumors (ctDNA) for molecular profiling. Theoretically, it offers a real-time assessment of total-body molecular tumor genotypes, assuming all tumor deposits shed DNA into the bloodstream. Ease of sampling also allows frequent evaluation and monitoring of mutational load over time.
In this study, we will explore the association between tumor burden, semi-quantitative EGFR-mutant abundance using the Idylla™ ctEGFR mutation assay, and depth of response in patients with advanced NSCLC treated with EGFR-TKI. To fill the gap by exploring the EGFR abundance, the tumor burden and clinical factors might let the clinician define risk stratification and adopt precision medicine for individual patients.
Materials and methods
Study population
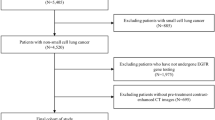
A prospective cohort of 130 patients who were diagnosed with recurrent or metastatic NSCLC and EGFR-activating mutation at The King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital (KCMH) over a period of 2 years (January 1, 2020, to December 31, 2021) was enrolled. All patient tumors harbored sensitizing EGFR-activating mutations. All patients had been treated with EGFR-TKIs (gefitinib, erlotinib, afatinib, and osimertinib). Pretreatment plasma from 89 patients were obtained (Figure S1). Clinicopathologic features including gender, age, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS) is assessed on a scale from 0 to 5, with higher scores indicating greater levels of disability (0 indicates the individual is fully active and able to perform all pre-disease activities without restriction, 1 reflects some limitation in strenuous activity but the ability to perform light or sedentary work, 2 signifies the ability to perform self-care but not work, 3 indicates limited ability to perform self-care and confinement to a bed or chair for more than half of the day, 4 represents complete disability, with an inability to perform self-care and confinement to a bed or chair, and 5 indicates death), histological type, smoking status, EGFR mutation status, and type of EGFR-TKIs were retrieved. Tumor response and follow-up were assessed every two to three months as the standard protocol for lung cancer treatment. Objective response rate (ORR) and PFS were determined according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.1 (RECIST v1.1) and classified as progressive disease (PD), complete response (CR), partial response (PR), or stable disease (SD) by our investigators (TT, WC, II) who were blinded to patient treatment outcomes. All patients provided written informed consent. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Faculty of Medicine at Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand (No. 894/63) and performed in accordance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act and the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in 2013).
Quantitative circulating DNA assays and semi-quantitative plasma EGFR mutation assay
Blood samples were collected in EDTA containers and centrifuged at 1600 g for 10 min. The plasma was stored at − 80 °C until used. Two milliliters of plasma were extracted using DNA blood Mini Kit (QIAGEN) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Quantitative circulating DNA measurement was performed with primer and Taqman probe specific to reference gene RPP30 using ABI PRISM® 7500 system (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and standard curve as previous published17. Total amount of circulating DNA, measured by amplified RPP30, was calculated per 1 ml of plasma.
For semi-quantitative plasma EGFR mutations, two milliliters of plasma were loaded into a fully-automated Idylla™ ctEGFR Mutation Assay cartridge (Biocartis NV, Mechelen, Belgium) as per protocol recommendation. The cycle of quantification (Cq) was analyzed by the Idylla console software. The Idylla™ ctEGFR Mutation Assay covered 49 mutations of the EGFR gene (including G719X in exon 18, 36 deletions in exon 19, T790M/S768I in exon 20, 5 insertions in exon 20, and L858R/L861Q in exon 21). The control signal corresponded to the amplification of the EGFR wild-type. The predefined range of the difference between the EGFR-mutant Cq (CqMut) and sample processing control (SPC) Cq signal is defined as “mutation detected” results. Out of this range, a “no mutation detected” result is reported. Higher CqMut values indicate a lower mutation abundance18.
Statistical analysis
Categorical variables were summarized by frequencies and percentages while continuous variables were reported by median and interquartile range (IQR). Variables include age, gender, ECOG PS, smoking status, histology, stage at diagnosis, presence of liver or brain metastasis, number of metastatic sites, EGFR mutation subtypes, EGFR TKI, and treatment outcome were analyzed using Chi-square or Fisher exact test for categorical data. The Mann-Whitney test was used for continuous data, as appropriate. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to determine the optimal cutoff value of CqMut to define high abundance vs. low abundance of plasma EGFR mutation. Progression-free survival (PFS) was calculated from the first day of treatment with EGFR TKI to disease progression or death from any cause, whichever occurred first. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from the date of diagnosis of recurrent or metastatic disease until the date of death or last follow-up. Patients who did not develop the event (progression or death) at the end of the study were censored at the date of June 30, 2022. Comparative PFS and OS were analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test. Multivariate analysis was performed by binary logistic regression or Cox’s proportional hazards regression model, as appropriate. The level of statistical significance was determined as a p-value less than 0.05. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 23.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, Illinois, USA) or GraphPad Prism 9.4 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
Results
Patient characteristics
Eighty-nine EGFR-mutated advanced-stage NSCLC patients were included in the analysis. At the data cut-off, the median follow-up time was 19.1 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 18.1–20.0). Sixty-two patients (70%) had disease progression, and 39 patients (44%) had died. The median PFS and OS of the overall study cohort were 10.4 months (95% CI 7.1–13.8) and 21.6 months (95% CI NE-NE), respectively. Patient baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The median age was 67 years (interquartile range [IQR] 59 to 74 years), with 65% women. Most patients were never smokers (74%) and had a 0–1 score of ECOG PS (85%). The majority had adenocarcinoma (93%), metastatic disease at presentation (87%), and 0–2 metastatic sites (66%). Baseline brain and liver metastases were present in 24.7% and 24.7% of the overall population, respectively. Our prospective cohort revealed a slightly higher prevalence of liver metastasis than the others, which revealed the prevalence of liver metastasis around 10–20%13,14,15. This might reflect the advancement at the time of diagnosis of Thai NSCLC patients. Regarding EGFR mutation status, 53 patients (60%) harbored exon 19 deletion, 30 patients (34%) harbored L858R, and six patients (6%) had uncommon mutations including G719X in exon 18 (N = 2), de novo T790M in exon 20 (N = 1), L861G or Q in exon 21 (N = 2) and one patient had complex mutations including L861Q with G719X.
A total of 85 patients (96%) received EGFR TKIs as first-line treatment, and the remaining four patients (4%) were treated subsequently with chemotherapy. Gefitinib, erlotinib, afatinib, and osimertinib were administered in 29 (33%), 54 (61%), 2 (2%), and four patients (4%), respectively. The objective response rate (ORR) of EGFR TKIs in our cohort was 69.7%. The remaining were SD 13% (n = 12), and PD 9% (n = 8). The response was not available in 7 patients. At the data cutoff, 26 (29%) patients were still receiving treatment. The median duration of EGFR TKI treatment was 10.5 months (IQR 6.6 to 14.1 months).
Impact of quantitative circulating DNA and semi-quantitative ctEGFR detection
The median total amount of pretreatment circulating DNA (cirDNA) was 12 [range 0.9–144] ngml− 1 of plasma. Using the Idylla™ ctEGFR mutation assay, 45 patients (50.5%) had detectable pretreatment plasma EGFR mutation (ctEGFR). Pretreatment cirDNA in detectable ctEGFR by the Idylla™ ctEGFR mutation assay was not significantly higher than undetectable ctEGFR (median 14.7 [range 1.7–85.9] and 9.7 [range 0.9–144.9] ngml− 1, respectively, p-value 0.16). There was a very modest correlation between cirDNA and the sum of target lesions (Spearman’s r = 0.25, p-value 0.04, Figure S2D). The total amount of cirDNA, which included tumor-derived and non-tumor-derived19 might not correctly reflect tumor-derived genomic abundance.
Baseline characteristics of patients with undetectable vs. detectable ctEGFR were reported. However, detectable ctEGFR was further classified into low vs. high abundance (next session) (Table 1). Patients with a high number of metastatic sites (≥ 3 sites) were significantly associated with detected ctEGFR (44.4% vs. 22.7%). Presence of liver metastasis was also correlated with detected ctEGFR (31.1% vs. 18.2%). Seventy-one patients (80%) had measurable lesions at baseline. The sum of target lesions was not different between detectable and non-detectable ctEGFR, with a median of 30 [IQR 16–43] and 23 [IQR 9.5–38], p-value 0.3, respectively. There were no differences in the objective response rate by ctEGFR status at baseline. The ORR between undetectable and detectable ctEGFR was 64% and 71%, respectively (p-value 0.12). The association between depth of response and pretreatment ctEGFR status was explored. A waterfall plot revealed that the maximum percent change from baseline in the sum of the longest diameters of target lesions among the undetectable and detectable ctEGFR was similar (− 33% [IQR-51.6, -21.7] and − 41.9% [IQR − 52.9, -30.4], respectively) (Figure S3A).
At the data cut-off, patients with pretreatment undetectable ctEGFR mutation had a significantly longer PFS and a higher though non-significant difference in OS than patients with detectable ctEGFR. Median PFS was 13.4 months [95% CI 12.0-14.8], and 8.7 months [95% CI 6.7–10.7], respectively; p-value 0.03; Fig. 1A. Uncommon EGFR mutations and the presence of liver metastasis were independent prognostic factors for PFS in multivariate analysis (HR 7.71 [95% CI 2.97–19.99], p-value < 0.001 and HR 2.41 [95% CI 1.27–4.60], p-value 0.007, respectively) (Table 2). Median OS was shorter in detectable than undetectable ctEGFR; 14.6 months vs. not reached (NR) respectively [95% CI 10.9–18.3, p-value 0.009; Fig. 1B). Presence of liver metastasis, poor performance status (ECOG ≥ 2), and detectable ctEGFR were significant independent prognostic factors for OS with HRs of 2.96 [95% CI 1.35–6.51, p-value 0.007], 2.21 [95%CI 1.03–4.73, p-value 0.04] and 1.99 [95% CI 1-3.98, p-value 0.05], respectively) (Table 3).
Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC according to detectable ctEGFR mutation status and Cq of mutant EGFR values at baseline. (A) PFS (13.4 months for undetectable ctEGFR mutation, and 8.7 months for detectable ctEGFR mutation; p = 0.03). (B) OS (not reached for undetectable ctEGFR mutation, and 14.6 months for detectable ctEGFR mutation; p = 0.009). (C) PFS (10.4 months for CqMut-high, and 5.9 months for CqMut-low; p = 0.09). (D) OS (not reached for CqMut-high, and 10.6 months for CqMut-low; p < 0.001). Statistical significance (*, p < 0.05).
Impact of semi-quantitative ctEGFR mutation and clinical outcomes to EGFR-TKIs
Based on a previous study demonstrating the concordance between the quantitative droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) KRAS mutation allele frequency (MAF) values and Idylla™ ctKRAS Mutation Assay CqMut values18, we completed a semi-quantitative analysis of EGFR mutation by using the Cq of mutant EGFR values (CqMut) to compare high vs. low abundance. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to identify the optimal cutoff value of CqMut. Using the cutoff value of 28.1, the sensitivity and specificity were 61.3% and 92.3%, respectively, with an AUC of 0.74 (95% CI 0.60–0.89).
Patients were divided into detectable ctEGFR CqMut-high (low abundance) and CqMut-low (high abundance) categories based on the cutoff value (≥ 28.1 or < 28.1). Baseline characteristics between the ctEGFR CqMut-high and ctEGFR CqMut-low are shown in Table 1. Patients with ctEGFR CqMut-high (low abundance) had a substantially lower number of metastatic sites (< 3 metastatic sites; 71.4%) and an absence of liver metastases (85.7%). There was no significant difference in age, gender, ECOG PS status, smoking status, histology, baseline brain metastasis, lines of treatment, and generation of EGFR TKI (1st, 2nd and 3rd ) between the high and low abundance groups. The association between the depth of response and pretreatment ctEGFR CqMut status was also analyzed. A waterfall plot demonstrated that the maximum percent change from baseline in the sum of the longest diameters of target lesions was similar between the ctEGFR CqMut-high and ctEGFR CqMut-low groups (-34.4% [IQR: -48.9, -30.8] and − 48.4% [IQR: -58.3, -31.5], respectively) (Figure S3B).
Patients with ctEGFR CqMut-high revealed a higher though non-significance PFS (Table S1) and a statistically significant better OS than patients who had ctEGFR CqMut-low with a median PFS of 10.4 months [95% CI 9.9–10.9] and 5.9 months [95% CI 3.8–7.4], respectively; p-value 0.09 (Fig. 1C). Median OS was not reached (NR) in ctEGFR CqMut-high and 10.6 months [95% CI 8.3–12.9] in ctEGFR CqMut-low, p-value < 0.001 (Fig. 1D). The multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model performed on the clinical prognostic factors revealed that ctEGFR CqMut values were significantly associated with OS (HR 3.20; 95% CI 1.22–8.39, p-value 0.02) (Table S2).
Association between detectable ctEGFR mutation and tumor burden
We investigated whether pretreatment of ctEGFR CqMut values was associated with tumor burden in terms of the number of metastatic sites and the presence of liver metastases at the time of diagnosis. The patients with liver metastases or a higher number of metastatic sites (more than three sites) had significantly lower ctEGFR CqMut values (median of 24.3[IQR 23.5–24.9] and 24.1 [IQR 22.9–28.6], respectively) than those without liver metastases or < 3 number of metastatic sites (median of 29.1 [IQR 26.1–30.4] and 29.2 [IQR 26.9–30.3], p-value 0.02 and 0.004, respectively) (Fig. 2A-B). Correlations were found between ctEGFR CqMut and the total amount of cirDNA with the number of metastatic sites (Spearman’s r = -0.38, p-value 0.01 and Spearman’s r 0.32, p-value 0.004) (Figure S2A & C). However, the sum of the longest diameters of all target lesions that were measurable was not significantly different in patients who had low ctEGFR CqMut-low as compared to high ctEGFR CqMut-patients (85.23 mm vs. 66.81 mm, p-value 0.24). Collectively, these results suggested that patients with low ctEGFR CqMut values, indicating high tumor abundance, were associated with a high tumor burden, which may contribute to worse clinical outcomes.
Dynamic change of ctEGFR status during EGFR-TKI treatment
Eight to 12-week post-treatment plasma samples were obtained from 65 patients. Of the 45 patients who had detectable ctEGFR at baseline, 37 patients (82%) completed a follow-up blood sample. Among this group, ctEGFR switched from detectable to undetectable during treatment in 28 patients, while nine patients continued to have detectable ctEGFR., 4 of which showed decreasing ctEGFR in plasma after EGFR TKI treatment. 81% of patients who showed a subsequent reduction or undetectable in ctEGFR during treatment (ctEGFR clearance) achieved a radiologic response by RECIST criteria. Among those with persistent detectable ctEGFR during treatment (ctEGFR non-clearance), 40% had radiologic progressive disease. The mean percentage change of tumor shrinkage was 41.4 ± 3.1 in the ctEGFR clearance group and 18.1 ± 9.8 in the ctEGFR non-clearance group (p-value 0.015).
Patients who achieved ctEGFR clearance during treatment exhibited a longer PFS. However, the difference was not statistically significant compared to patients with ctEGFR non-clearance (median PFS 10.4 months [95% CI: 6.9–13.9] vs. 7.3 months [95% CI: 5.8–8.8]; p-value 0.06) (Fig. 3A). However, ctEGFR clearance was associated with a significantly improved OS compared to ctEGFR non-clearance. The median OS was 19 months [95% CI: 13.1–24.9] for patients with ctEGFR clearance versus 9.7 months [95% CI: 6.7–12.8] for those without clearance (p-value < 0.001) (Fig. 3B).
Progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC according to dynamic change of ctDNA status during EGFR-TKI treatment. (A) PFS (10.4 months for patients who had switched from detectable to undetectable ctDNA, and 7.3 months for patients who continued to have detectable ctDNA; p = 0.06). (B) OS (19 months for patients who had changed from detectable to undetectable ctDNA, and 9.7 months for patients who continued to have detectable ctDNA; p < 0.001). Statistical significance (*, p < 0.05).
Discussion
Our study demonstrated that semi-quantitative pretreatment ctEGFR measured by Idylla™ ctEGFR mutation assay testing was correlated with radiographic assessment and clinical outcomes. Consistent with previous studies, pretreatment ctEGFR could predict clinical outcomes in patients with EGFR mutation NSCLC receiving EGFR-TKIs treatment. Patients with detectable pretreatment ctEGFR had a significantly shorter PFS and OS than those where ctEGFR could not be detected7,8. Furthermore, we demonstrated an association between semi-quantitative ctEGFR mutation and CqMut which serves as a surrogate marker for tumor burden. Patients with detectable ctEGFR CqMut-low indicating high tumor abundance were associated with poorer outcomes in terms of shorter PFS/OS, consistent with other studies6,20. Undetectable ctEGFR, detectable ctEGFR CqMut-high, and detectable ctEGFR CqMut-low all represented consecutive incremental tumor abundance/tumor burdens correlated with outcomes.
We demonstrated that the presence of liver metastasis was the sole clinical factor correlated with high tumor abundance and poor prognosis. Presence of liver metastasis was significantly correlated with > 3 distant metastasis sites (77% vs. 19%, p-value < 0.001). Our multivariate analysis also found liver metastasis indicating both shorter PFS and shorter OS [PFS HR = 2.41 [95% CI 1.27–4.60, p-value 0.007; OS HR = 2.96 [95% CI 1.35–6.51, p-value 0.007]. High tumor heterogeneity, correlated with high tumor abundance, might be an underlying mechanism for poorer outcomes. Liver metastasis is employed as a surrogate marker of adverse prognosis of EGFR TKI treatment.
The ctEGFR clearance at initial early treatment can predict the clinical efficacy of EGFR-TKIs. It showed a correlation with radiographic partial response in 81% of patients. This finding was consistent with previous studies7,8,21,22. Detection of ctEGFR is considered complementary to tissue-based testing. A review of several commercial ctEGFR mutation testing machines found the Idylla™ ctEGFR mutation assay testing, which can be performed easily and relatively quickly (approximately 3-hr hand-on), is convenient for application in clinical practice.
Lastly, we have to state some limitations of our study. First, our cohort received first-generation EGFR TKI, which is the standard treatment reimbursed by the Civil Servant Medical Benefit Scheme (CSMBS) and universal health coverage in Thailand. Some medical oncologists think that this treatment is not a current standard option. Second, our study was conducted by using a semi-quantitative ctEGFR assay. It is a commercial assay, which might limit the accessibility of testing. However, we meet our goal to demonstrate a correlation between consecutive incremental tumor abundance (ctEGFR) and define clinical risk factors and radiographic findings using radiologists blind to ctEGFR mutation assay results. This correlation was demonstrated both by the baseline tumor and by response evaluation. The Presence of liver metastasis remains the best clinical predictor supporting high tumor abundance. This information might guide risk-adaptive treatment in advanced stage EGFR-positive lung cancer receiving EGFR TKI treatment.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
References
Taniguchi, K. et al. Intratumor heterogeneity of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer and its correlation to the response to gefitinib. Cancer Sci. 99 (5), 929–935 (2008).
Blakely, C. M. et al. Evolution and clinical impact of co-occurring genetic alterations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Nat. Genet. 49 (12), 1693–1704 (2017).
Jamal-Hanjani, M. et al. Tracking the evolution of Non-small-cell Lung Cancer. N Engl. J. Med. 376 (22), 2109–2121 (2017).
Vinayanuwattikun, C. et al. Elucidating genomic characteristics of Lung Cancer Progression from in situ to invasive Adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 6, 31628 (2016).
Guo, L. et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity of EGFR-activating mutations in advanced NSCLC patients at the single-cell level. BMC Cancer. 19 (1), 369 (2019).
Pan, Y. et al. Larger tumors are associated with inferior progression-free survival of first-line EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and a lower abundance of EGFR mutation in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer. 10 (4), 686–694 (2019).
Ebert, E. B. F. et al. Clearing of circulating tumour DNA predicts clinical response to first line tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced epidermal growth factor receptor mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 141, 37–43 (2020).
Moiseyenko, F. V. et al. Changes in the concentration of EGFR-mutated plasma DNA in the first hours of targeted therapy allow the prediction of tumor response in patients with EGFR-driven lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 27 (5), 850–862 (2022).
Zhou, Q. et al. Relative abundance of EGFR mutations predicts benefit from gefitinib treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 29 (24), 3316–3321 (2011).
Zhao, Z. R. et al. Mutation abundance affects the efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor readministration in non-small-cell lung cancer with acquired resistance. Med. Oncol. 31 (1), 810 (2014).
Li, X. et al. Comprehensive Analysis of EGFR-Mutant abundance and its Effect on Efficacy of EGFR TKIs in Advanced NSCLC with EGFR mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 12 (9), 1388–1397 (2017).
Wang, H. et al. Mutation abundance affects the therapeutic efficacy of EGFR-TKI in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: a retrospective analysis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 19 (8), 687–694 (2018).
Yao, Z. H. et al. Real-World Data on prognostic factors for overall survival in EGFR mutation-positive Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer patients treated with First-Line Gefitinib. Oncologist 22 (9), 1075–1083 (2017).
Jiang, T. et al. Characterization of liver metastasis and its effect on targeted therapy in EGFR-mutant NSCLC: a Multicenter Study. Clin. Lung Cancer. 18 (6), 631–639 (2017). e2.
Taniguchi, Y. et al. Impact of metastatic status on the prognosis of EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with first-generation EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncol. Lett. 14 (6), 7589–7596 (2017).
Zhu, Y. J. et al. Quantitative cell-free circulating EGFR mutation concentration is correlated with tumor burden in advanced NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer. 109, 124–127 (2017).
Sitthideatphaiboon, P. et al. Paradoxical prognostic phenomenon of plasma T-cell-derived circulating DNA level in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl Oncol. 22 (7), 1117–1125 (2020).
Holm, M. et al. Detection of KRAS mutations in liquid biopsies from metastatic colorectal cancer patients using droplet digital PCR, Idylla, and next generation sequencing. PLoS One. 15 (11), e0239819 (2020).
Vinayanuwattikun, C. et al. The impact of non-tumor-derived circulating nucleic acids implicates the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 139 (1), 67–76 (2013).
Yanagita, M. et al. A prospective evaluation of circulating Tumor cells and cell-free DNA in EGFR-Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer patients treated with Erlotinib on a phase II trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 22 (24), 6010–6020 (2016).
Lee, J. Y. et al. Longitudinal monitoring of EGFR mutations in plasma predicts outcomes of NSCLC patients treated with EGFR TKIs: Korean Lung Cancer Consortium (KLCC-12-02). Oncotarget, 7(6): pp. 6984-93. (2016).
Taus, A. et al. Dynamics of EGFR Mutation load in plasma for prediction of treatment response and disease progression in patients with EGFR-Mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Lung Cancer. 19 (5), 387–394 (2018). e2.
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgment: This research was supported by the Health Systems Research Institute (Thailand) (Grant number 66-153) to PS, VS and CV. The biospecimen collection was supported by Biobank, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand. Idylla™ reagents have been provided free of charge by Biocartis which was not involved in the study design, specimen collection, analysis, interpretation of data, report writing, and the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Contributions: (I) Conception and design: P Sitthideatphaiboon, C Vinayanuwattikun; (II) Administrative support: S. Shuangshoti, V Sriuranpong; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: P Sitthideatphaiboon, C Vinayanuwattikun, V Sriuranpong; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: P Sitthideatphaiboon, P. Simseekeaw, C. Teerapakpinyo, T. Tongbai, N. Zungsontiporn; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: P Sitthideatphaiboon, T. Tongbai, C Vinayanuwattikun; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Sitthideatphaiboon, P., Simseekeaw, P., Teerapakpinyo, C. et al. Presence of liver metastasis correlated with high tumor abundance and indicated adverse prognostic feature in EGFR mutation non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Sci Rep 15, 165 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-83930-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-83930-2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dynamic liver dysfunction predicts poor survival in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer and liver metastases treated with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
BMC Cancer (2026)
-
Third-generation versus first-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in Asian patients with advanced EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Discover Oncology (2025)