Abstract
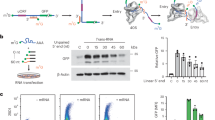
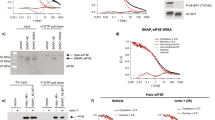
Protein synthesis is inhibited during apoptosis. However, the translation of many mRNAs still proceeds driven by internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs). Here we show that the 5′UTR of hid and grim mRNAs promote translation of uncapped-mRNA reporters in cell-free embryonic extracts and that hid and grim mRNA 5′UTRs drive IRES-mediated translation. The translation of capped-reporters proceeds in the presence of cap competitor and in extracts where cap-dependent translation is impaired. We show that the endogenous hid and grim mRNAs are present in polysomes of heat-shocked embryos, indicating that cap recognition is not required for translation. In contrast, sickle mRNA is translated in a cap-dependent manner in all these assays. Our results show that IRES-dependent initiation may play a role in the translation of Drosophila proapoptotic genes and suggest a variety of regulatory pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- cad :
-
caudal
- eIF:
-
eukaryotic initiation factor
- FLuc:
-
Firefly luciferase
- hid :
-
head involution defective
- hsp :
-
heat-shock protein
- IRES:
-
internal ribosome entry site
- PABP:
-
poly(A)-binding protein
- RLuc:
-
Renilla Luciferase
- rpr :
-
reaper
- skl :
-
sickle
- UTR:
-
untranslated region
References
Meier P, Finch A, Evan G. . Apoptosis in development. Nature 2000; 407 (6805): 796–801.
Abrams JM, White K, Fessler LI, Steller H . Programed cell death during Drosophila embryogenesis. Development 1993; 117: 29–43.
Abrams JM . An emerging blueprint for apoptosis in Drosophila. Trends Cell Biol 1999; 9 (11): 435–440.
White K, Grether ME, Abrams JM, Young LM, Farrell K, Steller H . Genetic control of programmed cell death in Drosophila. Science 1994; 264: 677–683.
Grether ME, Abrams JM, Agapite J, White K, Steller H . The head involution defective gene of Drosophila melanogaster functions in programmed cell death. Genes Dev 1995; 9 (14): 1694–1708.
Chen P, Nordstrom W, Gish B, Abrams JM . grim, a novel cell death gene in Drosophila. Genes Dev 1996; 10 (14): 1773–1782.
Christich A, Kauppila S, Chen P, Sogame N, Ho SI, Abrams JM . The damage-responsive Drosophila gene sickle encodes a novel IAP binding protein similar to but distinct from reaper, grim, and hid. Curr Biol 2002; 12 (2): 137–140.
Srinivasula SM, Datta P, Kobayashi M, Wu JW, Fujioka M, Hegde R et al. sickle, a novel Drosophila death gene in the reaper/hid/grim region, encodes an IAP-inhibitory protein. Curr Biol 2002; 12 (2): 125–130.
Wing JP, Karres JS, Ogdahl JL, Zhou L, Schwartz LM, Nambu JR . Drosophila sickle is a novel grim-reaper cell death activator. Curr Biol 2002; 12 (2): 131–135.
Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N . eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Ann Rev Biochem 1999; 68: 913–963.
Hellen CU, Sarnow P . Internal ribosome entry sites in eukaryotic mRNA molecules. Genes Dev 2001; 15 (13): 1593–1612.
Clemens MJ, Bushell M, Jeffrey IW, Pain VM, Morley SJ . Translation initiation factor modifications and the regulation of protein synthesis in apoptotic cells. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: 603–615.
Holcik M, Sonenberg N, Korneluk RG . Internal ribosome initiation of translation and the control of cell death. Trends Genet 2000; 16: 469–473.
Hernández G, Vazquez-Pianzola P, Sierra JM, Rivera-Pomar R . Internal ribosome entry site drives cap-independent translation of reaper and heat shock protein 70 mRNAs in Drosophila embryos. RNA 2004; 10 (11): 1783–1797.
Vazquez-Pianzola P, Urlaub H, Rivera-Pomar R . Proteomic analysis of reaper 5′ untranslated region-interacting factors isolated by tobramycin affinity-selection reveals a role for La antigen in reaper mRNA translation. Proteomics 2005; 5 (6): 1645–1655.
Maroto FG, Sierra JM . Purification and characterization of mRNA cap-binding protein from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Mol Cell Biol 1989; 9 (5): 2181–2190.
Gebauer F, Corona DFV, Preiss T, Becker PB, Hentze MW . Translational control of dosage compensation in Drosophila by sex-lethal: cooperative silencing via the 5′ and 3′ UTRs of msl-2 mRNA is independent of the poly(A) tail. EMBO J 1999; 18: 6146–6154.
Maroto FG, Sierra JM . Translational control in heat-shocked Drosophila embryos. J Biol Chem 1988; 263: 15720–15725.
Schneider RJ . Translational control during heat shock. In: Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB and Mathews MB (eds). Translational Control of Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, 2000, pp 615–635.
Lee CY, Clough EA, Yellon P, Teslovich TM, Stephan DA, Baehrecke EH . Genome-wide analyses of steroid- and radiation-triggered programmed cell death in Drosophila. Curr Biol 2003; 13 (4): 350–357.
Sogame N, Kim M, Abrams JM . Drosophila p53 preserves genomic stability by regulating cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100 (8): 4696–4701.
Brodsky MH, Nordstrom W, Tsang G, Kwan E, Rubin GM, Abrams JM . Drosophila p53 binds a damage response element at the reaper locus. Cell 2000; 101 (1): 103–113.
Brodsky MH, Weinert BT, Tsang G, Rong YS, McGinnis NM, Golic KC et al. Drosophila melanogaster MNK/Chk2 and p53 regulate multiple DNA repair and apoptotic pathways following DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24 (3): 1219–1231.
Horton LE, Bushell M, Barth-Baus D, Tilleray VJ, Clemens MJ, Hensold JO . p53 activation results in rapid dephosphorylation of the eIF4E-binding protein 4E-BP1, inhibition of ribosomal protein S6 kinase and inhibition of translation initiation. Oncogene 2002; 21 (34): 5325–5334.
Holcik M, Lefebvre C, Yeh C, Chow T, Korneluk RG . A new internal-ribosome-entry-site motif potentiates XIAP-mediated cytoprotection. Nat Cell Biol 1999; 1 (3): 190–192.
Van Eden ME, Byrd MP, Sherrill KW, Lloyd RE . Translation of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 (c-IAP1) mRNA is IRES mediated and regulated during cell stress. RNA 2004; 10 (3): 469–481.
Warnakulasuriyarachchi D, Cerquozzi S, Cheung HH, Holcik M . Translational induction of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein HIAP2 during endoplasmic reticulum stress attenuates cell death and is mediated via an inducible internal ribosome entry site element. J Biol Chem 2004; 279 (17): 17148–17157.
Sherrill KW, Byrd MP, Van Eden ME, Lloyd RE . BCL-2 translation is mediated via internal ribosome entry during cell stress. J Biol Chem 2004; 279 (28): 29066–29074.
Rubtsova MP, Sizova DV, Dmitriev SE, Ivanov DS, Prassolov VS, Shatsky IN . Distinctive properties of the 5′-untranslated region of human hsp70 mRNA. J Biol Chem 2003; 278 (25): 22350–22356.
Henis-Korenblit S, Strumpf NL, Goldstaub D, Kimchi A . A novel form of DAP5 protein accumulates in apoptotic cells as a result of caspase cleavage and internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20 (2): 496–506.
Coldwell MJ, Mitchell SA, Stoneley M, MacFarlane M, Willis AE . Initiation of Apaf-1 translation by internal ribosome entry. Oncogene 2000; 19 (7): 899–905.
Nanbru C, Lafon I, Audigier S, Gensac MC, Vagner S, Huez G et al. Alternative translation of the proto-oncogene c-myc by an internal ribosome entry site. J Biol Chem 1997; 272 (51): 32061–32066.
Ingolia TD, Craig EA . Primary sequence of the 5′ flanking regions of the Drosophila heat shock genes in chromosome subdivision 67B. Nucl Acids Res 1981; 9 (7): 1627–1642.
Hess MA, Duncan RF . Sequence and structure determinants of Drosophila Hsp70 mRNA translation: 5′UTR secondary structure specifically inhibits heat shock protein mRNA translation. Nucl Acids Res 1996; 24 (12): 2441–2449.
Stark A, Brennecke J, Russell RB, Cohen SM . Identification of Drosophila MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol 2003; 1 (3): E60.
Lai EC, Tomancak P, Williams RW, Rubin GM . Computational identification of Drosophila microRNA genes. Genome Biol 2003; 4 (7): R42.
Leaman D, Chen PY, Fak J, Yalcin A, Pearce M, Unnerstall U et al. Antisense-mediated depletion reveals essential and specific functions of microRNAs in Drosophila development. Cell 2005; 121 (7): 1097–1108.
Brennecke J, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM . Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol 2005; 3 (3): e85.
Colon-Ramos DA, Shenvi CL, Weitzel DH, Gan EC, Matts R, Cate J et al. Direct ribosomal binding by a cellular inhibitor of translation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2006; 13 (2): 103–111.
Klinger M, Gergen P . Regulation of runt transcription by Drosophila segmentation genes. Mech Dev 1993; 43: 3–19.
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Zechel for excellent technical assistance, R. Kühnlein for plasmid pRK27, J. M. Abrams for plasmid SK+II-Grim-short-cDNA, S. Höppner for proofreading the manuscript and M. Altmann for valuable comments on the manuscript. We also acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for constructive criticisms. This work was supported by the Max Planck Gesellschaft (MPG), the Deutsches Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (grant 031U215B to R.R.-P.) and the University of La Plata. R.R.-P. is recipient of an International Partner Laboratory Program of the MPG in CREG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by J Abrams
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vazquez-Pianzola, P., Hernández, G., Suter, B. et al. Different modes of translation for hid, grim and sickle mRNAs in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ 14, 286–295 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401990
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401990
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulation of Drosophila melanogaster pro-apoptotic gene hid
Apoptosis (2009)