Abstract
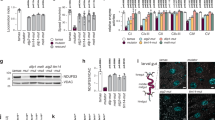
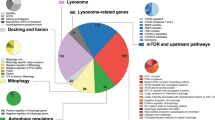
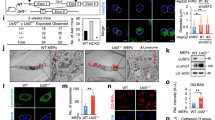
In Drosophila, the fat body undergoes a massive burst of autophagy at the end of larval development in preparation for the pupal transition. To identify genes involved in this process, we carried out a microarray analysis. We found that mRNA levels of the homologs of Atg8, the coat protein of early autophagic structures, and lysosomal hydrolases were upregulated, consistent with previous results. Genes encoding mitochondrial proteins and many chaperones were downregulated, including the inhibitor of eIF2alpha kinases and the peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase FK506-binding protein of 39 kDa (FKBP39). Genetic manipulation of FKBP39 expression had a significant effect on autophagy, potentially through modulation of the transcription factor Foxo. Accordingly, we found that Foxo mutants cannot properly undergo autophagy in response to starvation, and that overexpression of Foxo induces autophagy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- dIPK:
-
Drosophila inhibitor of protein kinases
- FKBP39:
-
FK506-binding protein of 39 kDa
- JNK:
-
Jun N-terminal kinase
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidyl-inositol 3-kinase
- Ppiase:
-
peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase
- QRT-PCR:
-
quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- Tor:
-
target of rapamycin
References
Klionsky DJ, Emr SD . Autophagy as a regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science 2000; 290: 1717–1721.
Klionsky DJ, Cregg JM, Dunn Jr WA, Emr SD, Sakai Y, Sandoval IV et al. A unified nomenclature for yeast autophagy-related genes. Dev Cell 2003; 5: 539–545.
Levine B, Klionsky DJ . Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell 2004 Apr; 6: 463–477.
Mizushima N . The pleiotropic role of autophagy: from protein metabolism to bactericide. Cell Death Differ 2005 Nov; 12 (Suppl 2): 1535–1541.
Sass M, Kovacs J . The effect of ecdysone on the fat body cells of the penultimate larvae of Mamestra brassicae. Cell Tissue Res 1977; 180: 403–409.
Butterworth FM, Forrest EC . Ultrastructure of the preparative phase of cell death in the larval fat body of Drosophila melanogaster. Tissue Cell 1984; 16: 237–250.
Butterworth FM, Emerson L, Rasch EM . Maturation and degeneration of the fat body in the Drosophila larva and pupa as revealed by morphometric analysis. Tissue Cell 1988; 20: 255–268.
Juhasz G, Csikos G, Sinka R, Erdelyi M, Sass M . The Drosophila homolog of Aut1 is essential for autophagy and development. FEBS Lett 2003; 543: 154–158.
Sass M, Kovacs J . Ecdysterone and an analogue of juvenile hormone on the autophagy in the cells of fat body of mamestra brassicae. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung 1975; 26: 189–196.
Rusten TE, Lindmo K, Juhasz G, Sass M, Seglen PO, Brech A et al. Programmed autophagy in the Drosophila fat body is induced by ecdysone through regulation of the PI3K pathway. Dev Cell 2004 Aug; 7: 179–192.
Noda T, Kim J, Huang WP, Baba M, Tokunaga C, Ohsumi Y et al. Apg9p/Cvt7p is an integral membrane protein required for transport vesicle formation in the Cvt and autophagy pathways. J Cell Biol 2000 Feb 7; 148: 465–480.
Blommaart EF, Luiken JJ, Blommaart PJ, van Woerkom GM, Meijer AJ . Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 is inhibitory for autophagy in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 2320–2326.
Scott RC, Schuldiner O, Neufeld TP . Role and regulation of starvation-induced autophagy in the Drosophila fat body. Dev Cell 2004 Aug; 7: 167–178.
Kamada Y, Funakoshi T, Shintani T, Nagano K, Ohsumi M, Ohsumi Y . Tor-mediated induction of autophagy via an Apg1 protein kinase complex. J Cell Biol 2000; 150: 1507–1513.
Kirisako T, Baba M, Ishihara N, Miyazawa K, Ohsumi M, Yoshimori T et al. Formation process of autophagosome is traced with Apg8/Aut7p in yeast. J Cell Biol 1999; 147: 435–446.
Zinke I, Schutz CS, Katzenberger JD, Bauer M, Pankratz MJ . Nutrient control of gene expression in Drosophila: microarray analysis of starvation and sugar-dependent response. EMBO J 2002; 21: 6162–6173.
Szuperak M, Zvara A, Erdelyi M . Identification of germ plasm-enriched mRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster by the cDNA microarray technique. Gene Exp Patterns 2005 Jun; 5: 717–723.
Tearle R . Tissue specific effects of ommochrome pathway mutations in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res 1991 Jun; 57: 257–266.
Theopold U, Dal Zotto L, Hultmark D . FKBP39, a Drosophila member of a family of proteins that bind the immunosuppressive drug FK506. Gene 1995 Apr 24; 156: 247–251.
Melville MW, Katze MG, Tan SL . P58IPK, a novel cochaperone containing tetratricopeptide repeats and a J-domain with oncogenic potential. Cell Mol Life Sci 2000 Feb; 57: 311–322.
Drysdale RA, Crosby MA . FlyBase: genes and gene models. Nucleic Acids Res 2005 Jan 1; 33: D390–D395.
Ryder E, Blows F, Ashburner M, Bautista-Llacer R, Coulson D, Drummond J et al. The DrosDel collection: a set of P-element insertions for generating custom chromosomal aberrations in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2004 Jun; 167: 797–813.
Harrar Y, Bellini C, Faure JD . FKBPs: at the crossroads of folding and transduction. Trends Plant Sci 2001 Sep; 6: 426–431.
Klettner A, Baumgrass R, Zhang Y, Fischer G, Burger E, Herdegen T et al. The neuroprotective actions of FK506 binding protein ligands: neuronal survival is triggered by de novo RNA synthesis, but is independent of inhibition of JNK and calcineurin. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2001 Dec 16; 97: 21–31.
Britton JS, Lockwood WK, Li L, Cohen SM, Edgar BA . Drosophila's insulin/PI3-kinase pathway coordinates cellular metabolism with nutritional conditions. Dev Cell 2002; 2: 239–249.
Hwangbo DS, Gersham B, Tu MP, Palmer M, Tatar M . Drosophila dFOXO controls lifespan and regulates insulin signalling in brain and fat body. Nature 2004 Jun 3; 429: 562–566.
Lee CY, Clough EA, Yellon P, Teslovich TM, Stephan DA, Baehrecke EH . Genome-wide analyses of steroid- and radiation-triggered programmed cell death in Drosophila. Curr Biol 2003 Feb 18; 13: 350–357.
Gorski SM, Chittaranjan S, Pleasance ED, Freeman JD, Anderson CL, Varhol RJ et al. A SAGE approach to discovery of genes involved in autophagic cell death. Curr Biol 2003 Feb 18; 13: 358–363.
Akdemir F, Farkas R, Chen P, Juhasz G, Medved'ova L, Sass M et al. Autophagy occurs upstream or parallel to the apoptosome during histolytic cell death. Development 2006 Apr; 133: 1457–1465.
Juhasz G, Sass M . Hid can induce, but is not required for autophagy in polyploid larval Drosophila tissues. Eur J Cell Biol 2005 Apr; 84: 491–502.
Yan W, Frank CL, Korth MJ, Sopher BL, Novoa I, Ron D et al. Control of PERK eIF2alpha kinase activity by the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced molecular chaperone P58IPK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002 Dec 10; 99: 15920–15925.
Tan SL, Gale Jr MJ, Katze MG . Double-stranded RNA-independent dimerization of interferon-induced protein kinase PKR and inhibition of dimerization by the cellular P58IPK inhibitor. Mol Cell Biol 1998 May; 18: 2431–2443.
Pain VM . Translational control during amino acid starvation. Biochimie 1994; 76: 718–728.
Williams BR . PKR; a sentinel kinase for cellular stress. Oncogene 1999 Nov 1; 18: 6112–6120.
Tang NM, Korth MJ, Gale Jr M, Wambach M, Der SD, Bandyopadhyay SK et al. Inhibition of double-stranded RNA- and tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated apoptosis by tetratricopeptide repeat protein and cochaperone P58(IPK). Mol Cell Biol 1999 Jul; 19: 4757–4765.
Talloczy Z, Jiang W, Virgin HWt, Leib DA, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ et al. Regulation of starvation- and virus-induced autophagy by the eIF2alpha kinase signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002 Jan 8; 99: 190–195.
Junger MA, Rintelen F, Stocker H, Wasserman JD, Vegh M, Radimerski T et al. The Drosophila Forkhead transcription factor FOXO mediates the reduction in cell number associated with reduced insulin signaling. J Biol 2003; 2: 20.
Wang MC, Bohmann D, Jasper H . JNK extends life span and limits growth by antagonizing cellular and organism-wide responses to insulin signaling. Cell 2005 Apr 8; 121: 115–125.
Puskas LG, Zvara A, Hackler Jr L, Micsik T, van Hummelen P . Production of bulk amounts of universal RNA for DNA microarrays. Biotechniques 2002 Oct; 33: 898–900, 902, 904..
Puskas LG, Zvara A, Hackler Jr L, Van Hummelen P . RNA amplification results in reproducible microarray data with slight ratio bias. Biotechniques 2002 Jun; 32: 1330–1334, 1336, 1338, 1340.
Acknowledgements
We thank Zsoltné Pálfia, Mariann Saródy and Emese Léder for the excellent technical assistance, our colleagues listed in the Materials and Methods section for providing reagents, and our anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments. This work was supported by NIH grant RO1 GM62509 provided to TPN and by the Hungarian Ministry of Education grant MEDICHEM 1/047 NKFP provided to MS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by E Baehrecke
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juhász, G., Puskás, L., Komonyi, O. et al. Gene expression profiling identifies FKBP39 as an inhibitor of autophagy in larval Drosophila fat body. Cell Death Differ 14, 1181–1190 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402123
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402123
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification, characterization and spatiotemporal expression analysis of the FKBP family genes in Locusta migratoria
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Early-adult methionine restriction reduces methionine sulfoxide and extends lifespan in Drosophila
Nature Communications (2023)
-
FKBP39 controls nutrient dependent Nprl3 expression and TORC1 activity in Drosophila
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Proteostasis-associated aging: lessons from a Drosophila model
Genes & Genomics (2021)
-
FOXO1 promotes HIV latency by suppressing ER stress in T cells
Nature Microbiology (2020)