Abstract
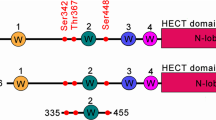
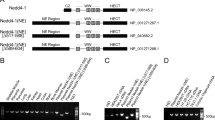
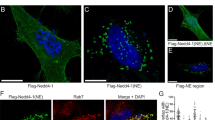
In the Drosophila wing, the Nedd4 ubiquitin ligases (E3s), dNedd4 and Su(dx), are important negative regulators of Notch signaling; they ubiquitinate Notch, promoting its endocytosis and turnover. Here, we show that Drosophila Nedd4 family interacting protein (dNdfip) interacts with the Drosophila Nedd4-like E3s. dNdfip expression dramatically enhances dNedd4 and Su(dx)-mediated wing phenotypes and further disrupts Notch signaling. dNdfip colocalizes with Notch in wing imaginal discs and with the late endosomal marker Rab7 in cultured cells. In addition, dNdfip expression in the wing leads to ectopic Notch signaling. Supporting this, expression of dNdfip suppressed Notch+/− wing phenotype and knockdown of dNdfip enhanced the Notch+/− wing phenotype. The increase in Notch activity by dNdfip is ligand independent as dNdfip expression also suppressed deltex RNAi and Serrate+/− wing phenotypes. The opposing effects of dNdfip expression on Notch signaling and its late endosomal localization support a model whereby dNdfip promotes localization of Notch to the limiting membrane of late endosomes allowing for activation, similar to the model previously shown with ectopic Deltex expression. When dNedd4 or Su(dx) are also present, dNdfip promotes their activity in Notch ubiquitination and internalization to the lysosomal lumen for degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- Dx:
-
deltex
- Ser:
-
Serrate
- Su(dx):
-
Suppressor of deltex
- Wg:
-
wingless
- Ndfip:
-
Nedd4 family interacting protein
- dNdfip:
-
Drosophila Ndfip
References
Strizzi L, Hardy KM, Seftor EA, Costa FF, Kirschmann DA, Seftor RE et al. Development and cancer: at the crossroads of Nodal and Notch signaling. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 7131–7134.
Talora C, Campese AF, Bellavia D, Felli MP, Vacca A, Gulino A et al. Notch signaling and diseases: an evolutionary journey from a simple beginning to complex outcomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008; 1782: 489–497.
Wang Z, Li Y, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH . Emerging role of Notch in stem cells and cancer. Cancer Lett 2009; 279: 8–12.
Windler SL, Bilder D . Endocytic internalization routes required for delta/notch signaling. Curr Biol 2010; 20: 538–543.
Wilkin M, Tongngok P, Gensch N, Clemence S, Motoki M, Yamada K et al. Drosophila HOPS and AP-3 complex genes are required for a Deltex-regulated activation of notch in the endosomal trafficking pathway. Dev Cell 2008; 15: 762–772.
Wilkin MB, Baron M . Endocytic regulation of Notch activation and down-regulation (review). Mol Membr Biol 2005; 22: 279–289.
Xu T, Artavanis-Tsakonas S . deltex, a Locus Interacting with the Neurogenic Genes, Notch, Delta and mastermind in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1990; 126: 665–677.
Hori K, Fostier M, Ito M, Fuwa TJ, Go MJ, Okano H et al. Drosophila deltex mediates suppressor of Hairless-independent and late-endosomal activation of Notch signaling. Development 2004; 131: 5527–5537.
Sakata T, Sakaguchi H, Tsuda L, Higashitani A, Aigaki T, Matsuno K et al. Drosophila Nedd4 regulates endocytosis of notch and suppresses its ligand-independent activation. Curr Biol 2004; 14: 2228–2236.
Wilkin MB, Carbery AM, Fostier M, Aslam H, Mazaleyrat SL, Higgs J et al. Regulation of notch endosomal sorting and signaling by Drosophila Nedd4 family proteins. Curr Biol 2004; 14: 2237–2244.
Rotin D, Kumar S . Physiological functions of the HECT family of ubiquitin ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10: 398–409.
Yang B, Kumar S . Nedd4 and Nedd4-2: closely related ubiquitin-protein ligases with distinct physiological functions. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 68–77.
Shearwin-Whyatt L, Dalton HE, Foot N, Kumar S . Regulation of functional diversity within the Nedd4 family by accessory and adaptor proteins. Bioessays 2006; 28: 617–628.
Jolliffe CN, Harvey KF, Haines BP, Parasivam G, Kumar S . Identification of multiple proteins expressed in murine embryos as binding partners for the WW domains of the ubiquitin-protein ligase Nedd4. Biochem J 2000; 351: 557–565.
Harvey KF, Shearwin-Whyatt LM, Fotia A, Parton RG, Kumar S . N4WBP5, a potential target for ubiquitination by the Nedd4 family of proteins, is a novel Golgi-associated protein. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 9307–9317.
Konstas AA, Shearwin-Whyatt LM, Fotia AB, Degger B, Riccardi D, Cook DI et al. Regulation of the epithelial sodium channel by N4WBP5A, a novel Nedd4/Nedd4-2-interacting protein. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 29406–29416.
Shearwin-Whyatt LM, Brown DL, Wylie FG, Stow JL, Kumar S . N4WBP5A (Ndfip2), a Nedd4-interacting protein, localizes to multivesicular bodies and the Golgi, and has a potential role in protein trafficking. J Cell Sci 2004; 117: 3679–3689.
Oliver PM, Cao X, Worthen GS, Shi P, Briones N, Macleod M et al. Ndfip1 protein promotes the function of itch ubiquitin ligase to prevent T cell activation and T helper 2 cell-mediated inflammation. Immunity 2006; 25: 929–940.
Mund T, Pelham HR . Control of the activity of WW-HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligases by NDFIP proteins. EMBO Reports 2009; 10: 501–507.
Foot NJ, Dalton HE, Shearwin-Whyatt LM, Dorstyn L, Tan S-S, Yang B et al. Regulation of the divalent metal ion transporter DMT1 and iron homeostasis by a ubiquitin-dependent mechanism involving Ndfips and WWP2. Blood 2008; 112: 4268–4275.
Howitt J, Putz U, Lackovic J, Doan A, Dorstyn L, Cheng H et al. Divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) regulation by Ndfip1 prevents metal toxicity in human neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 15489–15494.
Putz U, Howitt J, Lackovic J, Foot N, Kumar S, Silke J et al. Nedd4 family-interacting protein 1 (Ndfip1) is required for the exosomal secretion of Nedd4 family proteins. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 32621–32627.
de Celis JF, Garcia-Bellido A, Bray SJ . Activation and function of Notch at the dorsal-ventral boundary of the wing imaginal disc. Development 1996; 122: 359–369.
Micchelli CA, Rulifson EJ, Blair SS . The function and regulation of cut expression on the wing margin of Drosophila: notch, Wingless and a dominant negative role for Delta and Serrate. Development 1997; 124: 1485–1495.
Bray SJ . Notch signaling: a simple pathway becomes complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 678–689.
Jennings MD, Blankley RT, Baron M, Golovanov AP, Avis JM . Specificity and autoregulation of Notch binding by tandem WW domains in suppressor of Deltex. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 29032–29042.
McGill MA, Dho SE, Weinmaster G, McGlade CJ . Numb regulates post-endocytic trafficking and degradation of Notch1. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 26427–26438.
Chastagner P, Israel A, Brou C . AIP4/Itch regulates Notch receptor degradation in the absence of ligand. PLoS One 2008; 3: e2735.
Lieber T, Wesley CS, Alcamo E, Hassel B, Krane JF, Campos-Ortega JA et al. Single amino acid substitutions in EGF-like elements of Notch and Delta modify Drosophila development and affect cell adhesion in vitro. Neuron 1992; 9: 847–859.
Cellier M, Prive G, Belouchi A, Kwan T, Rodrigues V, Chia W et al. Nramp defines a family of membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 10089–10093.
Mund T, Pelham HR . Regulation of PTEN/Akt and MAP kinase signaling pathways by the ubiquitin ligase activators Ndfip1 and Ndfip2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 11429–11434.
Brand AH, Perrimon N . Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 1993; 118: 401–415.
Treier M, Staszewski LM, Bohmann D . Ubiquitin-dependent c-Jun degradation in vivo is mediated by the delta domain. Cell 1994; 78: 787–798.
Colussi PA, Quinn LM, Huang DC, Coombe M, Read SH, Richardson H et al. Debcl, a proapoptotic Bcl-2 homologue, is a component of the Drosophila melanogaster cell death machinery. J Cell Biol 2000; 148: 703–714.
Cornell M, Evans DA, Mann R, Fostier M, Flasza M, Monthatong M et al. The Drosophila melanogaster Suppressor of deltex gene, a regulator of the Notch receptor signaling pathway, is an E3 class ubiquitin ligase. Genetics 1999; 152: 567–576.
Dietzl G, Chen D, Schnorrer F, Su KC, Barinova Y, Fellner M et al. A genome-wide transgenic RNAi library for conditional gene inactivation in Drosophila. Nature 2007; 448: 151–156.
Acknowledgements
We thank S Hayashi, M Baron and T Shandala for the provision of fly stocks, C Wesley for the stably expressing Notch cell line S2N and A Paterson for performing some of the real-time PCR analysis. We also thank the Bloomington and VDRC Stock Centers, the Australian Drosophila Biomedical Research Support Facility (OzDros) for fly lines, and Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (University of Iowa) for antibodies. This work was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia project grant (508085) and fellowship (399300) to SK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by E Baehrecke
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalton, H., Denton, D., Foot, N. et al. Drosophila Ndfip is a novel regulator of Notch signaling. Cell Death Differ 18, 1150–1160 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.130
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.130
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Adaptors as the regulators of HECT ubiquitin ligases
Cell Death & Differentiation (2021)
-
Notch signalling in cancer progression and bone metastasis
British Journal of Cancer (2011)