Abstract
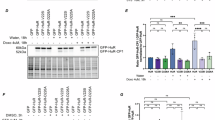
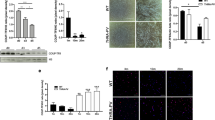
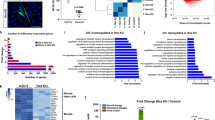
Although the function of posttranscriptional processes in regulating the expression of genes involved in muscle fiber formation (myogenesis) is well accepted, the mechanisms by which these effects are mediated remain elusive. Here, we uncover such a mechanism and show that during myogenesis, a fraction of the posttranscriptional regulator human antigen R (HuR) is cleaved in a caspase-dependent manner in both cell culture and animal models. Disruption of caspase activity in cultured myoblasts or knocking out the caspase-3 gene in mice significantly reduced HuR cleavage and the cytoplasmic accumulation of HuR in muscle fibers. The non-cleavable isoform of HuR, HuRD226A, failed to reestablish the myogenic potential of HuR-depleted myoblasts. HuR cleavage generates two fragments: HuR-cleavage product 1 (HuR-CP1) (24 kDa) and HuR-CP2 (8 kDa). Here, we show that one of these fragments (HuR-CP1) binds to the HuR import factor transportin-2 (TRN2) allowing HuR to accumulate in the cytoplasm. As this cytoplasmic accumulation is required for the promyogenic function of HuR, our data support a model, whereby during the transition phase from myoblasts to myotubes, a proportion of HuR is cleaved to generate HuR-CP1. By interfering with the TRN2-mediated import of HuR, this CP helps non-cleaved HuR accumulate in the cytoplasm thus promoting myogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- HuR:
-
human antigen R
- TRN2:
-
transportin-2
- MRFs:
-
myogenic regulatory factors
- AREs:
-
AU-rich elements
- HuR-CP:
-
HuR cleavage product
- caspase-CP:
-
caspase cleavage product
- AP:
-
antennapedia
- GFP:
-
green fluorescence protein
- Rec:
-
recombinant
- GST:
-
gluthation S-transferase
- RRM:
-
RNA recognition motif
- ActD:
-
actinomycin D
References
Charge SB, Rudnicki MA . Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev 2004; 84: 209–238.
Kaeser MD, Emerson BM . Remodeling plans for cellular specialization: unique styles for every room. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2006; 16: 508–512.
Sabourin LA, Rudnicki MA . The molecular regulation of myogenesis. Clin Genet 2000; 57: 16–25.
Lassar AB, Skapek SX, Novitch B . Regulatory mechanisms that coordinate skeletal muscle differentiation and cell cycle withdrawal. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1994; 6: 788–794.
Figueroa A, Cuadrado A, Fan J, Atasoy U, Muscat GE, Munoz-Canoves P et al. Role of HuR in skeletal myogenesis through coordinate regulation of muscle differentiation genes. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 4991–5004.
van der Giessen K, Di-Marco S, Clair E, Gallouzi IE . RNAi-mediated HuR depletion leads to the inhibition of muscle cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 47119–47128.
von Roretz C, Gallouzi IE . Decoding ARE-mediated decay: is microRNA part of the equation? J Cell Biol 2008; 181: 189–194.
Barreau C, Paillard L, Osborne HB . AU-rich elements and associated factors: are there unifying principles? Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: 7138–7150.
Deschenes-Furry J, Belanger G, Mwanjewe J, Lunde JA, Parks RJ, Perrone-Bizzozero N et al. The RNA-binding protein HuR binds to acetylcholinesterase transcripts and regulates their expression in differentiating skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 25361–25368.
van der Giessen K, Gallouzi IE . Involvement of transportin 2-mediated HuR import in muscle cell differentiation. Mol Biol Cell 2007; 18: 2619–2629.
Mazroui R, Di Marco S, Clair E, von Roretz C, Tenenbaum SA, Keene JD et al. Caspase-mediated cleavage of HuR in the cytoplasm contributes to pp32/PHAP-I regulation of apoptosis. J Cell Biol 2008; 180: 113–127.
Fernando P, Kelly JF, Balazsi K, Slack RS, Megeney LA . Caspase 3 activity is required for skeletal muscle differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 11025–11030.
Huh MS, Parker MH, Scime A, Parks R, Rudnicki MA . Rb is required for progression through myogenic differentiation but not maintenance of terminal differentiation. J Cell Biol 2004; 166: 865–876.
Porrello A, Cerone MA, Coen S, Gurtner A, Fontemaggi G, Cimino L et al. p53 regulates myogenesis by triggering the differentiation activity of pRb. J Cell Biol 2000; 151: 1295–1304.
Murray TV, McMahon JM, Howley BA, Stanley A, Ritter T, Mohr A et al. A non-apoptotic role for caspase-9 in muscle differentiation. J Cell Sci 2008; 121 (Pt 22): 3786–3793.
Yaffe D, Saxel O . Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature 1977; 270: 725–727.
Yaffe D, Saxel O . A myogenic cell line with altered serum requirements for differentiation. Differentiation 1977; 7: 159–166.
Huppertz B, Tews DS, Kaufmann P . Apoptosis and syncytial fusion in human placental trophoblast and skeletal muscle. Int Rev Cytol 2001; 205: 215–253.
Gallouzi IE, Brennan CM, Stenberg MG, Swanson MS, Eversole A, Maizels N et al. HuR binding to cytoplasmic mRNA is perturbed by heat shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 3073–3078.
Miura P, Thompson J, Chakkalakal JV, Holcik M, Jasmin BJ . The utrophin A 5′-untranslated region confers internal ribosome entry site-mediated translational control during regeneration of skeletal muscle fibers. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 32997–33005.
Yan Z, Choi S, Liu X, Zhang M, Schageman JJ, Lee SY et al. Highly coordinated gene regulation in mouse skeletal muscle regeneration. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 8826–8836.
Chipuk JE, Green DR . Cytoplasmic p53: bax and forward. Cell Cycle 2004; 3: 429–431.
Coletti D, Yang E, Marazzi G, Sassoon D . TNFalpha inhibits skeletal myogenesis through a PW1-dependent pathway by recruitment of caspase pathways. EMBO J 2002; 21: 631–642.
Rebane A, Aab A, Steitz JA . Transportins 1 and 2 are redundant nuclear import factors for hnRNP A1 and HuR. RNA 2004; 10: 590–599.
Abdelmohsen K, Kuwano Y, Kim HH, Gorospe M . Posttranscriptional gene regulation by RNA-binding proteins during oxidative stress: implications for cellular senescence. Biol Chem 2008; 389: 243–255.
Dormoy-Raclet V, Menard I, Clair E, Kurban G, Mazroui R, Di Marco S et al. The RNA-binding protein HuR promotes cell migration and cell invasion by stabilizing the beta-actin mRNA in a U-rich-element-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 5365–5380.
Fadeel B, Ottosson A, Pervaiz S . Big wheel keeps on turning: apoptosome regulation and its role in chemoresistance. Cell Death Differ 2008; 15: 443–452.
Yi CH, Yuan J . The Jekyll and Hyde functions of caspases. Dev Cell 2009; 16: 21–34.
Brennan CM, Gallouzi IE, Steitz JA . Protein ligands to HuR modulate its interaction with target mRNAs in vivo. J Cell Biol 2000; 151: 1–14.
Gramolini AO, Angus LM, Schaeffer L, Burton EA, Tinsley JM, Davies KE et al. Induction of utrophin gene expression by heregulin in skeletal muscle cells: role of the N-box motif and GA binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 3223–3227.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs S Di Marco and V Dormoy-Raclet for their helpful suggestions throughout the progress of this work. We also thank Ms C Clow for her technical help with the in vivo experiments, and Mr N Punjani for his assistance with the production of cleavable GST-plasmids and proteins. This work was supported by a Cole Foundation fellowship for PB, a FRSQ Master's fellowship for CN, a CIHR Doctoral Research Award for CvR, and a CIHR (MOP-89798) operating grant to IG. IG is a recipient of a Tier II Canada Research Chair.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by R De Maria
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beauchamp, P., Nassif, C., Hillock, S. et al. The cleavage of HuR interferes with its transportin-2-mediated nuclear import and promotes muscle fiber formation. Cell Death Differ 17, 1588–1599 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.34
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.34
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Repression of caspase-3 and RNA-binding protein HuR cleavage by cyclooxygenase-2 promotes drug resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Oncogene (2017)
-
The beneficial role of proteolysis in skeletal muscle growth and stress adaptation
Skeletal Muscle (2016)
-
Destabilization of nucleophosmin mRNA by the HuR/KSRP complex is required for muscle fibre formation
Nature Communications (2014)
-
Apoptotic-induced cleavage shifts HuR from being a promoter of survival to an activator of caspase-mediated apoptosis
Cell Death & Differentiation (2013)