Abstract
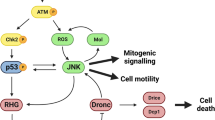
Programmed cell death (apoptosis) is a conserved process aimed to eliminate unwanted cells. The key molecules are a group of proteases called caspases that cleave vital proteins, which leads to the death of cells. In Drosophila, the apoptotic pathway is usually represented as a cascade of events in which an initial stimulus activates one or more of the proapoptotic genes (hid, rpr, grim), which in turn activate caspases. In stress-induced apoptosis, the dp53 (Drosophila p53) gene and the Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway function upstream in the activation of the proapoptotic genes. Here we demonstrate that dp53 and JNK also function downstream of proapoptotic genes and the initiator caspase Dronc (Drosophila NEDD2-like caspase) and that they establish a feedback loop that amplifies the initial apoptotic stimulus. This loop plays a critical role in the apoptotic response because in its absence there is a dramatic decrease in the amount of cell death after a pulse of the proapoptotic proteins Hid and Rpr. Thus, our results indicate that stress-induced apoptosis in Drosophila is dependant on an amplification loop mediated by dp53 and JNK. Furthermore, they also demonstrate a mechanism of mutual activation of proapoptotic genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- Diap1:
-
Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1
- dp53 :
-
Drosophila p53
- dp53-i :
-
dp53 RNA interference
- dpp :
-
decapenthaplegic
- Drice:
-
Drosophila interleukin converting enzyme
- Dronc:
-
Drosophila NEDD2-like caspase
- dronc-i:
-
dronc RNA-interference
- en :
-
engrailed
- gfp :
-
green fluorescent protein
- hep :
-
hemipterous
- hid :
-
head involution defective
- hs-hid :
-
heat shock-head involution defective
- hs-rpr :
-
heat shock-reaper
- IAP:
-
inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- JNK:
-
Jun N-terminal kinase
- puc :
-
puckered
- ROI:
-
region of interest
- rpr :
-
reaper
- sal :
-
spalt
- TUNEL:
-
TdT-mediated fluoroscein-dUTP nick end labelling
- UAS:
-
upstream activation sequence
- wg :
-
wingless
References
Jacobson MD, Weil M, Raff MC . Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell 1997; 88: 347–354.
Meier P, Finch A, Evan G . Apoptosis in development. Nature 2000; 407: 796–801.
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y . Caspases: enemies within. Science 1998; 281: 1312–1316.
Reed JC, Doctor KS, Godzik A . The domains of apoptosis: a genomics perspective. Sci STKE 2004; 2004: re9.
Shiozaki EN, Shi Y . Caspases, IAPs and Smac/DIABLO: mechanisms from structural biology. Trends Biochem Sci 2004; 29: 486–494.
Hay BA, Guo M . Caspase-dependent cell death in Drosophila. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2006; 22: 623–650.
Wilson R, Goyal L, Ditzel M, Zachariou A, Baker DA, Agapite J et al. The DIAP1 RING finger mediates ubiquitination of Dronc and is indispensable for regulating apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2002; 4: 445–450.
Steller H . Drosophila p53: meeting the Grim Reaper. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2: E100–E102.
Riley T, Sontag E, Chen P, Levine A . Transcriptional control of human p53-regulated genes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 402–412.
Zilfou JT, Lowe SW . Tumor suppressive functions of p53. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2009; 1: a001883.
Fan Y, Lee TV, Xu D, Chen Z, Lamblin AF, Steller H et al. Dual roles of Drosophila p53 in cell death and cell differentiation. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 912–921.
Brodsky MH, Nordstrom W, Tsang G, Kwan E, Rubin GM, Abrams JM . Drosophila p53 binds a damage response element at the reaper locus. Cell 2000; 101: 103–113.
Kanda H, Miura M . Regulatory roles of JNK in programmed cell death. J Biochem 2004; 136: 1–6.
Adachi-Yamada T, O’Connor MB . Morphogenetic apoptosis: a mechanism for correcting discontinuities in morphogen gradients. Dev Biol 2002; 251: 74–90.
Igaki T . Correcting developmental errors by apoptosis: lessons from Drosophila JNK signaling. Apoptosis 2009; 14: 1021–1028.
Hay BA, Wolff T, Rubin GM . Expression of baculovirus P35 prevents cell death in Drosophila. Development 1994; 120: 2121–2129.
Martin FA, Perez-Garijo A, Morata G . Apoptosis in Drosophila: compensatory proliferation and undead cells. Int J Dev Biol 2009; 53: 1341–1347.
Perez-Garijo A, Martin FA, Morata G . Caspase inhibition during apoptosis causes abnormal signalling and developmental aberrations in Drosophila. Development 2004; 131: 5591–5598.
Wells BS, Yoshida E, Johnston LA . Compensatory proliferation in Drosophila imaginal discs requires Dronc-dependent p53 activity. Curr Biol 2006; 16: 1606–1615.
McEwen DG, Peifer M . Puckered, a Drosophila MAPK phosphatase, ensures cell viability by antagonizing JNK-induced apoptosis. Development 2005; 132: 3935–3946.
Ryoo HD, Gorenc T, Steller H . Apoptotic cells can induce compensatory cell proliferation through the JNK and the Wingless signaling pathways. Dev Cell 2004; 7: 491–501.
Perez-Garijo A, Shlevkov E, Morata G . The role of Dpp and Wg in compensatory proliferation and in the formation of hyperplastic overgrowths caused by apoptotic cells in the Drosophila wing disc. Development 2009; 136: 1169–1177.
Brand AH, Perrimon N . Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 1993; 118: 401–415.
Cruz C, Glavic A, Casado M, de Celis JF . A gain-of-function screen identifying genes required for growth and pattern formation of the Drosophila melanogaster wing. Genetics 2009; 183: 1005–1026.
Luo X, Puig O, Hyun J, Bohmann D, Jasper H . Foxo and Fos regulate the decision between cell death and survival in response to UV irradiation. EMBO J 2007; 26: 380–390.
Adachi-Yamada T, Fujimura-Kamada K, Nishida Y, Matsumoto K . Distortion of proximodistal information causes JNK-dependent apoptosis in Drosophila wing. Nature 1999; 400: 166–169.
Martín-Blanco E, Gampel A, Ring J, Virdee K, Kirov N, Tolkovsky AM et al. puckered encodes a phosphatase that mediates a feedback loop regulating JNK activity during dorsal closure in Drosophila. Genes Dev 1998; 12: 557–570.
Grether ME, Abrams JM, Agapite J, White K, Steller H . The head involution defective gene of Drosophila melanogaster functions in programmed cell death. Genes Dev 1995; 9: 1694–1708.
Xu D, Li Y, Arcaro M, Lackey M, Bergmann A . The CARD-carrying caspase Dronc is essential for most, but not all, developmental cell death in Drosophila. Development 2005; 132: 2125–2134.
Shapiro PJ, Hsu HH, Jung H, Robbins ES, Ryoo HD . Regulation of the Drosophila apoptosome through feedback inhibition. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 1440–1446.
Kuranaga E, Kanuka H, Igaki T, Sawamoto K, Ichijo H, Okano H et al. Reaper-mediated inhibition of DIAP1-induced DTRAF1 degradation results in activation of JNK in Drosophila. Nat Cell Biol 2002; 4: 705–710.
Lohmann I, McGinnis N, Bodmer M, McGinnis W . The Drosophila Hox gene deformed sculpts head morphology via direct regulation of the apoptosis activator reaper. Cell 2002; 110: 457–466.
Manjon C, Sanchez-Herrero E, Suzanne M . Sharp boundaries of Dpp signalling trigger local cell death required for Drosophila leg morphogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 2007; 9: 57–63.
Menendez J, Perez-Garijo A, Calleja M, Morata G . A tumor-suppressing mechanism in Drosophila involving cell competition and the Hippo pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 14651–14656.
Brodsky MH, Weinert BT, Tsang G, Rong YS, McGinnis NM, Golic KG et al. Drosophila melanogaster MNK/Chk2 and p53 regulate multiple DNA repair and apoptotic pathways following DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 1219–1231.
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter Jr GA, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ et al. Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 2006; 311: 847–851.
Sayan BS, Sayan AE, Knight RA, Melino G, Cohen GM. p53 is cleaved by caspases generating fragments localizing to mitochondria. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 13566–13573.
Fuchs SY, Adler V, Pincus MR, Ronai Z . MEKK1/JNK signaling stabilizes and activates p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 10541–10546.
Adachi-Yamada T, Harumoto T, Sakurai K, Ueda R, Saigo K, O’Connor MB et al. Wing-to-Leg homeosis by spineless causes apoptosis regulated by Fish-lips, a novel leucine-rich repeat transmembrane protein. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 3140–3150.
White K, Tahaoglu E, Steller H . Cell killing by the Drosophila gene reaper. Science 1996; 271: 805–807.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ernesto Sanchez-Herrero for fruitful discussions, Francisco A Martín and Hermann Steller for critical reading of the manuscript and Ana Guarner for help with leg preparations. We also thank Andreas Bergmann for dronc mutants, Hermann Steller for the heat shock stocks, Jose F de Celis for the salEPv-Gal4 line, Don Ryoo for the anti-Hid antibody, Ingrid Lohmann for the rpr probe and the Confocal Microscopy Service at the CBMSO for help with acquisition and processing of images. We also thank Angelica Cantarero and Rosa Gonzalez for general help and the members of the lab for discussions. The experimental work has been funded by grants from the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (Consolider CSD 20700008-B and BFU 2008 03196/BMC) and by an institutional grant from the Fundación Ramón Areces. ES is supported by a FPU scholarship (AP2005-4875).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by S Kumar
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shlevkov, E., Morata, G. A dp53/JNK-dependant feedback amplification loop is essential for the apoptotic response to stress in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ 19, 451–460 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.113
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.113
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lack of apoptosis leads to cellular senescence and tumorigenesis in Drosophila epithelial cells
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
Coordination between cell proliferation and apoptosis after DNA damage in Drosophila
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)
-
Basement membrane damage by ROS- and JNK-mediated Mmp2 activation drives macrophage recruitment to overgrown tissue
Nature Communications (2020)
-
JNK-mediated Slit-Robo signaling facilitates epithelial wound repair by extruding dying cells
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Short-term activation of the Jun N-terminal kinase pathway in apoptosis-deficient cells of Drosophila induces tumorigenesis
Nature Communications (2018)