Abstract
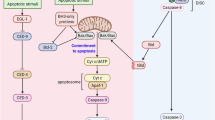
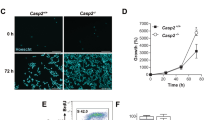
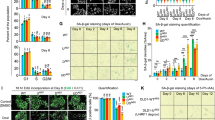
Caspase-2 is an initiator caspase, which has been implicated to function in apoptotic and non-apoptotic signalling pathways, including cell-cycle regulation, DNA-damage signalling and tumour suppression. We previously demonstrated that caspase-2 deficiency enhances E1A/Ras oncogene-induced cell transformation and augments lymphomagenesis in the EμMyc mouse model. Caspase-2−/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts (casp2−/− MEFs) show aberrant cell-cycle checkpoint regulation and a defective apoptotic response following DNA damage. Disruption of cell-cycle checkpoints often leads to genomic instability (GIN), which is a common phenotype of cancer cells and can contribute to cellular transformation. Here we show that caspase-2 deficiency results in increased DNA damage and GIN in proliferating cells. Casp2−/− MEFs readily escape senescence in culture and exhibit increased micronuclei formation and sustained DNA damage during cell culture and following γ-irradiation. Metaphase analyses demonstrated that a lack of caspase-2 is associated with increased aneuploidy in both MEFs and in EμMyc lymphoma cells. In addition, casp2−/− MEFs and lymphoma cells exhibit significantly decreased telomere length. We also noted that loss of caspase-2 leads to defective p53-mediated signalling and decreased trans-activation of p53 target genes upon DNA damage. Our findings suggest that loss of caspase-2 serves as a key function in maintaining genomic integrity, during cell proliferation and following DNA damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Change history
09 July 2012
This article has been corrected sinceAdvance OnlinePublication and aCorrigendumis also printed in this issue
Abbreviations
- ATM:
-
ataxia telangiectasia mutated
- ATR:
-
ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related
- CBMN:
-
cytokinesis block micronuclei
- CIN:
-
chromosome instability
- DDR:
-
DNA-damage response
- DSB:
-
double-strand breaks
- FISH:
-
fluorescence in situ hybridisation
- GIN:
-
genomic instability
- IR:
-
ionising radiation
- MEF:
-
murine embryonic fibroblasts
- MN:
-
micronuclei
- MOMP:
-
mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilisation
- Rb:
-
retinoblastoma
- iMEF:
-
immortalised MEF
- siRNA:
-
short interfering RNA
References
Kumar S, Kinoshita M, Noda M, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA . Induction of apoptosis by the mouse Nedd2 gene, which encodes a protein similar to the product of the Caenorhabditis elegans cell death gene ced-3 and the mammalian IL-1 beta-converting enzyme. Genes Dev 1994; 8: 1613–1626.
Lassus P, Opitz-Araya X, Lazebnik Y . Requirement for caspase-2 in stress-induced apoptosis before mitochondrial permeabilization. Science 2002; 297: 1352–1354.
Robertson JD, Enoksson M, Suomela M, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S . Caspase-2 acts upstream of mitochondria to promote cytochrome c release during etoposide-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 29803–29809.
Bonzon C, Bouchier-Hayes L, Pagliari LJ, Green DR, Newmeyer DD . Caspase-2-induced apoptosis requires bid cleavage: a physiological role for bid in heat shock-induced death. Mol Biol Cell 2006; 17: 2150–2157.
Shin S, Lee Y, Kim W, Ko H, Choi H, Kim K . Caspase-2 primes cancer cells for TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by processing procaspase-8. EMBO J 2005; 24: 3532–3542.
Ho LH, Read SH, Dorstyn L, Lambrusco L, Kumar S . Caspase-2 is required for cell death induced by cytoskeletal disruption. Oncogene 2008; 27: 3393–3404.
Bergeron L, Perez GI, Macdonald G, Shi L, Sun Y, Jurisicova A et al. Defects in regulation of apoptosis in caspase-2-deficient mice. Genes Dev 1998; 12: 1304–1314.
Nutt LK, Margolis SS, Jensen M, Herman CE, Dunphy WG, Rathmell JC et al. Metabolic regulation of oocyte cell death through the CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation of caspase-2. Cell 2005; 123: 89–103.
O’Reilly LA, Ekert P, Harvey N, Marsden V, Cullen L, Vaux DL et al. Caspase-2 is not required for thymocyte or neuronal apoptosis even though cleavage of caspase-2 is dependent on both Apaf-1 and caspase-9. Cell Death Differ 2002; 9: 832–841.
Marsden VS, Ekert PG, Van Delft M, Vaux DL, Adams JM, Strasser A . Bcl-2-regulated apoptosis and cytochrome c release can occur independently of both caspase-2 and caspase-9. J Cell Biol 2004; 165: 775–780.
Braga M, Sinha Hikim AP, Datta S, Ferrini MG, Brown D, Kovacheva EL et al. Involvement of oxidative stress and caspase 2-mediated intrinsic pathway signaling in age-related increase in muscle cell apoptosis in mice. Apoptosis 2008; 13: 822–832.
Zhang Y, Padalecki SS, Chaudhuri AR, De Waal E, Goins BA, Grubbs B et al. Caspase-2 deficiency enhances aging-related traits in mice. Mech Ageing Dev 2007; 128: 213–221.
Shalini S, Dorstyn L, Wilson C, Puccini J, Ho L, Kumar S . Impaired antioxidant defence and accumulation of oxidative stress in caspase-2-deficient mice. Cell Death Differ 2012 e-pub ahead of print 17 February 2012 doi:10.1038/cdd.2012.13.
Baliga BC, Colussi PA, Read SH, Dias MM, Jans DA, Kumar S . Role of prodomain in importin-mediated nuclear localization and activation of caspase-2. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 4899–4905.
Colussi PA, Harvey NL, Kumar S . Prodomain-dependent nuclear localization of the caspase-2 (Nedd2) precursor. A novel function for a caspase prodomain. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 24535–24542.
Kumar S . Caspase 2 in apoptosis, the DNA damage response and tumour suppression: enigma no more? Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 897–903.
Ho LH, Taylor R, Dorstyn L, Cakouros D, Bouillet P, Kumar S . A tumor suppressor function for caspase-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 5336–5341.
Sidi S, Sanda T, Kennedy RD, Hagen AT, Jette CA, Hoffmans R et al. Chk1 suppresses a caspase-2 apoptotic response to DNA damage that bypasses p53, Bcl-2, and caspase-3. Cell 2008; 133: 864–877.
Carnero A, Hudson JD, Price CM, Beach DH . p16INK4A and p19ARF act in overlapping pathways in cellular immortalization. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2: 148–155.
Harper JW, Elledge SJ . The DNA damage response: ten years after. Mol Cell 2007; 28: 739–745.
Tao W, Levine AJ . Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of oncoprotein Hdm2 is required for Hdm2-mediated degradation of p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 3077–3080.
Tao W, Levine AJ . P19(ARF) stabilizes p53 by blocking nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of Mdm2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 6937–6941.
Riley T, Sontag E, Chen P, Levine A . Transcriptional control of human p53-regulated genes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 402–412.
Lavin MF . Ataxia-telangiectasia: from a rare disorder to a paradigm for cell signalling and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 759–769.
Cimprich KA, Cortez D . ATR: an essential regulator of genome integrity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 616–627.
Caldecott KW . Single-strand break repair and genetic disease. Nat Rev Genet 2008; 9: 619–631.
Holland AJ, Cleveland DW . Boveri revisited: chromosomal instability, aneuploidy and tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10: 478–487.
Tomasini R, Mak TW, Melino G . The impact of p53 and p73 on aneuploidy and cancer. Trends Cell Biol 2008; 18: 244–252.
Li M, Fang X, Baker DJ, Guo L, Gao X, Wei Z et al. The ATM-p53 pathway suppresses aneuploidy-induced tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 14188–14193.
Parrinello S, Samper E, Krtolica A, Goldstein J, Melov S, Campisi J . Oxygen sensitivity severely limits the replicative lifespan of murine fibroblasts. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5: 741–747.
Bringold F, Serrano M . Tumor suppressors and oncogenes in cellular senescence. Exp Gerontol 2000; 35: 317–329.
Todaro GJ, Green H. . Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol 1963; 17: 299–313.
Sohn D, Budach W, Janicke RU . Caspase-2 is required for DNA damage-induced expression of the CDK inhibitor p21(WAF1/CIP1). Cell Death Differ 2011; 18: 1664–1674.
Taghiyev AF, Rokhlin OW, Glover RB . Caspase-2-based regulation of the androgen receptor and cell cycle in the prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Genes Cancer 2011; 2: 745–752.
Fenech M . Chromosomal biomarkers of genomic instability relevant to cancer. Drug Discov Today 2002; 7: 1128–1137.
Burma S, Chen BP, Murphy M, Kurimasa A, Chen DJ . ATM phosphorylates histone H2AX in response to DNA double-strand breaks. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 42462–42467.
Gartel AL, Radhakrishnan SK . Lost in transcription: p21 repression, mechanisms, and consequences. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 3980–3985.
Keogh MC, Kim JA, Downey M, Fillingham J, Chowdhury D, Harrison JC et al. A phosphatase complex that dephosphorylates gammaH2AX regulates DNA damage checkpoint recovery. Nature 2006; 439: 497–501.
Woo RA, Poon RY . Activated oncogenes promote and cooperate with chromosomal instability for neoplastic transformation. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 1317–1330.
Oliver TG, Meylan E, Chang GP, Xue W, Burke JR, Humpton TJ et al. Caspase-2-mediated cleavage of Mdm2 creates a p53-induced positive feedback loop. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 57–71.
Acknowledgements
We thank David Vaux, Ygal Haupt, Andreas Villunger and Paul Neilson for providing various reagents, and staff of the SA Pathology animal resource facility for help in maintaining the mouse strains. We thank members of our laboratory for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) of Australia project grant (626905), a South Australian Cancer Collaborative Fellowship to LD and a NHMRC Senior Principal Research Fellowship (1002863) to SK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by G Melino
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorstyn, L., Puccini, J., Wilson, C. et al. Caspase-2 deficiency promotes aberrant DNA-damage response and genetic instability. Cell Death Differ 19, 1288–1298 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.36
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.36
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The p53-caspase-2 axis in the cell cycle and DNA damage response
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
Effects of intravitreal injection of siRNA against caspase-2 on retinal and optic nerve degeneration in air blast induced ocular trauma
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Uncovering the PIDDosome and caspase-2 as regulators of organogenesis and cellular differentiation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2020)
-
Trisomy 21 is Associated with Caspase-2 Upregulation in Cytotrophoblasts at the Maternal-Fetal Interface
Reproductive Sciences (2020)
-
Transcriptome profiling of caspase-2 deficient EμMyc and Th-MYCN mouse tumors identifies distinct putative roles for caspase-2 in neuronal differentiation and immune signaling
Cell Death & Disease (2019)