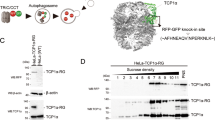
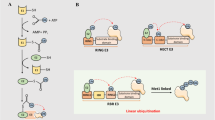
Abstract
The serine threonine kinase checkpoint kinase 2 (CHK2) is a DNA damage checkpoint protein important for the ATM-p53 signaling pathway. In addition to its phosphorylation, CHK2 is also ubiquitylated, and both post-translational modifications are important for its function. However, although the mechanisms that regulate CHK2 phosphorylation are well established, those that control its ubiquitylation are not fully understood. In this study, we demonstrate that the ubiquitin E3 ligase PIRH2 (p53-induced protein with a RING (Really Interesting New Gene)-H2 domain) interacts with CHK2 and mediates its polyubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation. We show that the deubiquitylating enzyme USP28 forms a complex with PIRH2 and CHK2 and antagonizes PIRH2-mediated polyubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of CHK2. We also provide evidence that CHK2 ubiquitylation by PIRH2 is dependent on its phosphorylation status. Cells deficient in Pirh2 displayed accumulation of Chk2 and enhanced hyperactivation of G1/S and G2/M cell-cycle checkpoints. This hyperactivation was, however, no longer observed in Pirh2−/−Chk2−/− cells, providing evidence for the importance of Chk2 regulation by Pirh2. These findings indicate that PIRH2 has central roles in the ubiquitylation of Chk2 and its turnover and in the regulation of its function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ATM:
-
ataxia telangiectasia mutated
- CHK2:
-
checkpoint kinase 2
- HA:
-
hemagglutinin
- ΔR:
-
mutant lacking the ring finger domain
- MEF:
-
mouse embryonic fibroblast
- PIRH2:
-
p53-induced protein with a RING (Really Interesting New Gene)-H2
- Ub:
-
ubiquitin
- USP28:
-
ubiquitin-specific-processing protease 28
- WT:
-
wild type
References
Leng RP, Lin Y, Ma W, Wu H, Lemmers B, Chung S et al. Pirh2, a p53-induced ubiquitin-protein ligase, promotes p53 degradation. Cell 2003; 112: 779–791.
Sheng Y, Laister RC, Lemak A, Wu B, Tai E, Duan S et al. Molecular basis of Pirh2-mediated p53 ubiquitylation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2008; 15: 1334–1342.
Wu H, Pomeroy SL, Ferreira M, Teider N, Mariani J, Nakayama KI et al. UBE4B promotes Hdm2-mediated degradation of the tumor suppressor p53. Nat Med 2011; 17: 347–355.
Hakem A, Bohgaki M, Lemmers B, Tai E, Salmena L, Matysiak-Zablocki E et al. Role of Pirh2 in mediating the regulation of p53 and c-Myc. PLoS Genet 2011; 7: e1002360.
Hattori T, Isobe T, Abe K, Kikuchi H, Kitagawa K, Oda T et al. Pirh2 promotes ubiquitin-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 10789–10795.
Maruyama S, Miyajima N, Bohgaki M, Tsukiyama T, Shigemura M, Nonomura K et al. Ubiquitylation of epsilon-COP by PIRH2 and regulation of the secretion of PSA. Mol Cell Biochem 2008; 307: 73–82.
Abe K, Hattori T, Isobe T, Kitagawa K, Oda T, Uchida C et al. Pirh2 interacts with and ubiquitylates signal recognition particle receptor beta subunit. Biomed Res 2008; 29: 53–60.
Jung YS, Liu G, Chen X . Pirh2 E3 ubiquitin ligase targets DNA polymerase eta for 20S proteasomal degradation. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 1041–1048.
Wu H, Zeinab RA, Flores ER, Leng RP . Pirh2, a ubiquitin E3 ligase, inhibits p73 transcriptional activity by promoting its ubiquitination. Mol Cancer Res 2011; 9: 1780–1790.
Jung YS, Qian Y, Chen X . The p73 tumor suppressor is targeted by Pirh2 RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligase for the proteasome-dependent degradation. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 35388–35395.
Stracker TH, Usui T, Petrini JH . Taking the time to make important decisions: the checkpoint effector kinases Chk1 and Chk2 and the DNA damage response. DNA Repair (Amst) 2009; 8: 1047–1054.
Matsuoka S, Rotman G, Ogawa A, Shiloh Y, Tamai K, Elledge SJ . Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated phosphorylates Chk2 in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 10389–10394.
Ahn JY, Schwarz JK, Piwnica-Worms H, Canman CE . Threonine 68 phosphorylation by ataxia telangiectasia mutated is required for efficient activation of Chk2 in response to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 5934–5936.
Melchionna R, Chen XB, Blasina A, McGowan CH . Threonine 68 is required for radiation-induced phosphorylation and activation of Cds1. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2: 762–765.
Ahn JY, Li X, Davis HL, Canman CE . Phosphorylation of threonine 68 promotes oligomerization and autophosphorylation of the Chk2 protein kinase via the forkhead-associated domain. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 19389–19395.
Lee CH, Chung JH . The hCds1 (Chk2)-FHA domain is essential for a chain of phosphorylation events on hCds1 that is induced by ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 30537–30541.
Xu X, Tsvetkov LM, Stern DF . Chk2 activation and phosphorylation-dependent oligomerization. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 4419–4432.
Antoni L, Sodha N, Collins I, Garrett MD . CHK2 kinase: cancer susceptibility and cancer therapy – two sides of the same coin? Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 925–936.
Tan Y, Raychaudhuri P, Costa RH . Chk2 mediates stabilization of the FoxM1 transcription factor to stimulate expression of DNA repair genes. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 1007–1016.
Stolz A, Ertych N, Kienitz A, Vogel C, Schneider V, Fritz B et al. The CHK2-BRCA1 tumour suppressor pathway ensures chromosomal stability in human somatic cells. Nat Cell Biol 2010; 12: 492–499.
Castedo M, Perfettini JL, Roumier T, Yakushijin K, Horne D, Medema R et al. The cell cycle checkpoint kinase Chk2 is a negative regulator of mitotic catastrophe. Oncogene 2004; 23: 4353–4361.
Lavin MF . Ataxia-telangiectasia: from a rare disorder to a paradigm for cell signalling and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 759–769.
Kass EM, Poyurovsky MV, Zhu Y, Prives C . Mdm2 and PCAF increase Chk2 ubiquitination and degradation independently of their intrinsic E3 ligase activities. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 430–437.
Lovly CM, Yan L, Ryan CE, Takada S, Piwnica-Worms H . Regulation of Chk2 ubiquitination and signaling through autophosphorylation of serine 379. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 5874–5885.
Feng L, Chen J . The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2012; 19: 201–206.
Kass EM, Ahn J, Tanaka T, Freed-Pastor WA, Keezer S, Prives C . Stability of checkpoint kinase 2 is regulated via phosphorylation at serine 456. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 30311–30321.
Zhang D, Zaugg K, Mak TW, Elledge SJ . A role for the deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 in control of the DNA-damage response. Cell 2006; 126: 529–542.
Popov N, Wanzel M, Madiredjo M, Zhang D, Beijersbergen R, Bernards R et al. The ubiquitin-specific protease USP28 is required for MYC stability. Nat Cell Biol 2007; 9: 765–774.
Hershko A, Ciechanover A . The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem 1998; 67: 425–479.
Grabbe C, Husnjak K, Dikic I . The spatial and temporal organization of ubiquitin networks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2011; 12: 295–307.
Li Q, Lin S, Wang X, Lian G, Lu Z, Guo H et al. Axin determines cell fate by controlling the p53 activation threshold after DNA damage. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 1128–1134.
Di Micco R, Fumagalli M, Cicalese A, Piccinin S, Gasparini P, Luise C et al. Oncogene-induced senescence is a DNA damage response triggered by DNA hyper-replication. Nature 2006; 444: 638–642.
Lukas C, Bartkova J, Latella L, Falck J, Mailand N, Schroeder T et al. DNA damage-activated kinase Chk2 is independent of proliferation or differentiation yet correlates with tissue biology. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 4990–4993.
Yu X, Chini CC, He M, Mer G, Chen J . The BRCT domain is a phospho-protein binding domain. Science 2003; 302: 639–642.
Lee SB, Kim SH, Bell DW, Wahrer DC, Schiripo TA, Jorczak MM et al. Destabilization of CHK2 by a missense mutation associated with Li-Fraumeni Syndrome. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 8062–8067.
Bartkova J, Falck J, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Skakkebaek NE, Lukas J, Bartek J . Chk2 tumour suppressor protein in human spermatogenesis and testicular germ-cell tumours. Oncogene 2001; 20: 5897–5902.
Wu X, Webster SR, Chen J . Characterization of tumor-associated Chk2 mutations. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 2971–2974.
Matsuoka S, Nakagawa T, Masuda A, Haruki N, Elledge SJ, Takahashi T . Reduced expression and impaired kinase activity of a Chk2 mutant identified in human lung cancer. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 5362–5365.
Henderson MJ, Munoz MA, Saunders DN, Clancy JL, Russell AJ, Williams B et al. EDD mediates DNA damage-induced activation of CHK2. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 39990–40000.
Munoz MA, Saunders DN, Henderson MJ, Clancy JL, Russell AJ, Lehrbach G et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase EDD regulates S-phase and G(2)/M DNA damage checkpoints. Cell Cycle 2007; 6: 3070–3077.
Hunter T . The age of crosstalk: phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and beyond. Mol Cell 2007; 28: 730–738.
Hirao A, Kong YY, Matsuoka S, Wakeham A, Ruland J, Yoshida H et al. DNA damage-induced activation of p53 by the checkpoint kinase Chk2. Science 2000; 287: 1824–1827.
Theunissen JW, Petrini JH . Methods for studying the cellular response to DNA damage: influence of the Mre11 complex on chromosome metabolism. Methods Enzymol 2006; 409: 251–284.
Acknowledgements
We thank V Stambolic, S Benchimol, C Arrowsmith, L Salmena, B Raught and the Hakem laboratory members for helpful discussions. We also thank Dr. T. Mak, Dr. S. Benchimol, Dr. S. Elledge and Dr. M. Eilers for providing reagents. This work was supported by the Canadian Institute of Health Research. RH was supported by a salary award from the Canadian Institute of Health Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by V Dixit
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bohgaki, M., Hakem, A., Halaby, M. et al. The E3 ligase PIRH2 polyubiquitylates CHK2 and regulates its turnover. Cell Death Differ 20, 812–822 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.7
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The RNA-binding protein HuR is a novel target of Pirh2 E3 ubiquitin ligase
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
SIRT1 modulates cell cycle progression by regulating CHK2 acetylation−phosphorylation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2020)
-
Targeting deubiquitinase USP28 for cancer therapy
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
High Expression of Pirh2 is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Glioma
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2017)
-
The emerging role of deubiquitinating enzymes in genomic integrity, diseases, and therapeutics
Cell & Bioscience (2016)