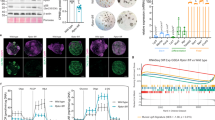
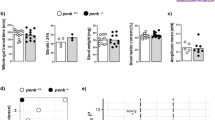
Abstract
Ribosome biogenesis is an essential cellular process. Its impairment is associated with developmental defects and increased risk of cancer. The in vivo cellular responses to defective ribosome biogenesis and the underlying molecular mechanisms are still incompletely understood. In particular, the consequences of impaired ribosome biogenesis within the intestinal epithelium in mammals have not been investigated so far. Here we adopted a genetic approach to investigate the role of Notchless (NLE), an essential actor of ribosome biogenesis, in the adult mouse intestinal lineage. Nle deficiency led to defects in the synthesis of large ribosomal subunit in crypts cells and resulted in the rapid elimination of intestinal stem cells and progenitors through distinct types of cellular responses, including apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and biased differentiation toward the goblet cell lineage. Similar observations were made using the rRNA transcription inhibitor CX-5461 on intestinal organoids culture. Importantly, we found that p53 activation was responsible for most of the cellular responses observed, including differentiation toward the goblet cell lineage. Moreover, we identify the goblet cell-specific marker Muc2 as a direct transcriptional target of p53. Nle-deficient ISCs and progenitors disappearance persisted in the absence of p53, underlying the existence of p53-independent cellular responses following defective ribosome biogenesis. Our data indicate that NLE is a crucial factor for intestinal homeostasis and provide new insights into how perturbations of ribosome biogenesis impact on cell fate decisions within the intestinal epithelium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BrdU:
-
Bromo-deoxyuridine
- CBC:
-
crypt base columnar
- cKO:
-
conditionnal Knock-out
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- IRES:
-
internal ribosome entry site
- Its:
-
internal spacer
- Nle:
-
Notchless
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- qPCR:
-
quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- PFA:
-
paraformaldehyde
- SC:
-
stem cell
- ISC:
-
intestinal stem cell
- TA:
-
transit-amplifying
- RE:
-
response element
References
Fromont-Racine M, Senger B, Saveanu C, Fasiolo F . Ribosome assembly in eukaryotes. Gene 2003; 313: 17–42.
Wild T, Horvath P, Wyler E, Widmann B, Badertscher L, Zemp I et al. A protein inventory of human ribosome biogenesis reveals an essential function of exportin 5 in 60S subunit export. PLoS Biol 2010; 8: e1000522.
Sloan KE, Mattijssen S, Lebaron S, Tollervey D, Pruijn GJM, Watkins NJ . Both endonucleolytic and exonucleolytic cleavage mediate ITS1 removal during human ribosomal RNA processing. J Cell Biol 2013; 200: 577–588.
Carron C, O'Donohue M-F, Choesmel V, Faubladier M, Gleizes P-E . Analysis of two human pre-ribosomal factors, bystin and hTsr1, highlights differences in evolution of ribosome biogenesis between yeast and mammals. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39: 280–291.
Tafforeau L, Zorbas C, Langhendries J-L, Mullineux S-T, Stamatopoulou V, Mullier R et al. The complexity of human ribosome biogenesis revealed by systematic nucleolar screening of Pre-rRNA processing factors. Mol Cell 2013; 51: 539–551.
Donati G, Peddigari S, Mercer CA, Thomas G . 5S ribosomal RNA is an essential component of a nascent ribosomal precursor complex that regulates the Hdm2-p53 checkpoint. Cell Rep 2013; 4: 87–98.
Zhang Y, Wolf GW, Bhat K, Jin A, Allio T, Burkhart WA et al. Ribosomal protein L11 negatively regulates oncoprotein MDM2 and mediates a p53-dependent ribosomal-stress checkpoint pathway. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 8902–8912.
Fumagalli S, Ivanenkov VV, Teng T, Thomas G . Suprainduction of p53 by disruption of 40S and 60S ribosome biogenesis leads to the activation of a novel G2/M checkpoint. Genes Dev 2012; 26: 1028–1040.
Armistead J, Triggs-Raine B . Diverse diseases from a ubiquitous process: the ribosomopathy paradox. FEBS Lett 2014; 588: 1491–1500.
Narla A, Ebert BL . Ribosomopathies: human disorders of ribosome dysfunction. Blood 2010; 115: 3196–3205.
McGowan KA, Li JZ, Park CY, Beaudry V, Tabor HK, Sabnis AJ et al. Ribosomal mutations cause p53-mediated dark skin and pleiotropic effects. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 963–970.
Dutt S, Narla A, Lin K, Mullally A, Abayasekara N, Megerdichian C et al. Haploinsufficiency for ribosomal protein genes causes selective activation of p53 in human erythroid progenitor cells. Blood 2011; 117: 2567–2576.
Stadanlick JE, Zhang Z, Lee S-Y, Hemann M, Biery M, Carleton MO et al. Developmental arrest of T cells in Rpl22-deficient mice is dependent upon multiple p53 effectors. J Immunol 2011; 187: 664–675.
McGowan KA, Pang WW, Bhardwaj R, Perez MG, Pluvinage JV, Glader BE et al. Reduced ribosomal protein gene dosage and p53 activation in low-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2011; 118: 3622–3633.
Pereboom TC, van Weele LJ, Bondt A, MacInnes AW . A zebrafish model of dyskeratosis congenita reveals hematopoietic stem cell formation failure resulting from ribosomal protein-mediated p53 stabilization. Blood 2011; 118: 5458–5465.
Jaako P, Flygare J, Olsson K, Quere R, Ehinger M, Henson A et al. Mice with ribosomal protein S19 deficiency develop bone marrow failure and symptoms like patients with Diamond-Blackfan anemia. Blood 2011; 118: 6087–6096.
Torihara H, Uechi T, Chakraborty A, Shinya M, Sakai N, Kenmochi N . Erythropoiesis failure due to RPS19 deficiency is independent of an activated Tp53 response in a zebrafish model of Diamond-Blackfan anaemia. Br J Haematol 2011; 152: 648–654.
Provost E, Wehner KA, Zhong X, Ashar F, Nguyen E, Green R et al. Ribosomal biogenesis genes play an essential and p53-independent role in zebrafish pancreas development. Development 2012; 139: 3232–3241.
Yadav GV, Chakraborty A, Uechi T, Kenmochi N . Ribosomal protein deficiency causes Tp53-independent erythropoiesis failure in zebrafish. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2014; 49: 1–7.
la Cruz de J, Sanz-Martínez E, Remacha M . The essential WD-repeat protein Rsa4p is required for rRNA processing and intra-nuclear transport of 60S ribosomal subunits. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: 5728–5739.
Ulbrich C, Diepholz M, Baszligler J, Kressler D, Pertschy B, Galani K et al. Mechanochemical Removal of Ribosome Biogenesis Factors from Nascent 60S Ribosomal Subunits. Cell 2009; 138: 911–922.
Matsuo Y, Granneman S, Thoms M, Manikas R-G, Tollervey D, Hurt E . Coupled GTPase and remodelling ATPase activities form a checkpoint for ribosome export. Nature 2014; 505: 112–116.
Le Bouteiller M, Souilhol C, Cormier S, Stedman A, Burlen-Defranoux O, Vandormael-Pournin S et al. Notchless-dependent ribosome synthesis is required for the maintenance of adult hematopoietic stem cells. J Exp Med 2013; 210: 2351–2369.
Cormier S, Le Bras S, Souilhol C, Vandormael-Pournin S, Durand B, Babinet C et al. The murine ortholog of notchless, a direct regulator of the notch pathway in Drosophila melanogaster, is essential for survival of inner cell mass cells. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 3541–3549.
van der Flier LG, van Gijn ME, Hatzis P, Kujala P, Haegebarth A, Stange DE et al. Transcription factor achaete scute-like 2 controls intestinal stem cell fate. Cell 2009; 136: 903–912.
Sato T, Vries RG, Snippert HJ, van de Wetering M, Barker N, Stange DE et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009; 459: 262–265.
Yang Q, Bermingham NA, Finegold MJ, Zoghbi HY . Requirement of Math1 for secretory cell lineage commitment in the mouse intestine. Science 2001; 294: 2155–2158.
Noah TK, Donahue B, Shroyer NF . Intestinal development and differentiation. Exp Cell Res 2011; 317: 2702–2710.
David A, Dolan BP, Hickman HD, Knowlton JJ, Clavarino G, Pierre P et al. Nuclear translation visualized by ribosome-bound nascent chain puromycylation. J Cell Biol 2012; 197: 45–57.
Drygin D, Lin A, Bliesath J, Ho CB, O'Brien SE, Proffitt C et al. Targeting RNA polymerase I with an oral small molecule CX-5461 inhibits ribosomal RNA synthesis and solid tumor growth. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 1418–1430.
Simeonova I, Lejour V, Bardot B, Bouarich-Bourimi R, Morin A, Fang M et al. Fuzzy tandem repeats containing p53 response elements may define species-specific p53 target genes. PLoS Genet 2012; 8: e1002731.
Li M, He Y, Dubois W, Wu X, Shi J, Huang J . Distinct regulatory mechanisms and functions for p53-activated and p53-repressed DNA damage response genes in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell 2012; 46: 30–42.
Inomata K, Aoto T, Binh NT, Okamoto N, Tanimura S, Wakayama T et al. Genotoxic stress abrogates renewal of melanocyte stem cells by triggering their differentiation. Cell 2009; 137: 1088–1099.
Wang J, Sun Q, Morita Y, Jiang H, Groß A, Lechel A et al. A differentiation checkpoint limits hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal in response to DNA damage. Cell 2012; 148: 1001–1014.
Ookawa K, Kudo T, Aizawa S, Saito H, Tsuchida S . Transcriptional activation of the MUC2 gene by p53. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 48270–48275.
Baßler J, Paternoga H, Holdermann I, Thoms M, Granneman S, Barrio-Garcia C et al. A network of assembly factors is involved in remodeling rRNA elements during preribosome maturation. J Cell Biol 2014; 207: 481–498.
Chantha S-C, Matton DP . Underexpression of the plant NOTCHLESS gene, encoding a WD-repeat protein, causes pleitropic phenotype during plant development. Planta 2007; 225: 1107–1120.
Royet J, Bouwmeester T, Cohen SM . Notchless encodes a novel WD40-repeat-containing protein that modulates Notch signaling activity. EMBO J 1998; 17: 7351–7360.
van Es JH, van Gijn ME, Riccio O, van den Born M, Vooijs M, Begthel H et al. Notch/gamma-secretase inhibition turns proliferative cells in intestinal crypts and adenomas into goblet cells. Nature 2005; 435: 959–963.
Fre S, Huyghe M, Mourikis P, Robine S, Louvard D, Artavanis-Tsakonas S . Notch signals control the fate of immature progenitor cells in the intestine. Nature 2005; 435: 964–968.
Riccio O, van Gijn ME, Bezdek AC, Pellegrinet L, van Es JH, Zimber-Strobl U et al. Loss of intestinal crypt progenitor cells owing to inactivation of both Notch1 and Notch2 is accompanied by derepression of CDK inhibitors p27Kip1 and p57Kip2. EMBO Rep 2008; 9: 377–383.
Guilmeau S, Flandez M, Bancroft L, Sellers RS, Tear B, Stanley P et al. Intestinal deletion of Pofut1 in the mouse inactivates notch signaling and causes enterocolitis. Gastroenterology 2008; 135: 849–860: 860.e1–6.
Pellegrinet L, Rodilla V, Liu Z, Chen S, Koch U, Espinosa L et al. Dll1- and dll4-mediated notch signaling are required for homeostasis of intestinal stem cells. Gastroenterology 2011; 140: 1230–1240.e1–7.
Donati G, Brighenti E, Vici M, Mazzini G, Treré D, Montanaro L et al. Selective inhibition of rRNA transcription downregulates E2F-1: a new p53-independent mechanism linking cell growth to cell proliferation. J Cell Sci. 2011; 124: 3017–3028.
Iadevaia V, Caldarola S, Biondini L, Gismondi A, Karlsson S, Dianzani I et al. PIM1 kinase is destabilized by ribosomal stress causing inhibition of cell cycle progression. Oncogene 2010; 29: 5490–5499.
Kurokawa M, Kim J, Geradts J, Matsuura K, Liu L, Ran X et al. A network of substrates of the E3 ubiquitin ligases MDM2 and HUWE1 control apoptosis independently of p53. Sci Signal 2013; 6: ra32.
Gu L, Zhu N, Zhang H, Durden DL, Feng Y, Zhou M . Regulation of XIAP translation and induction by MDM2 following irradiation. Cancer Cell 2009; 15: 363–375.
Yang J-Y, Zong CS, Xia W, Yamaguchi H, Ding Q, Xie X et al. ERK promotes tumorigenesis by inhibiting FOXO3a via MDM2-mediated degradation. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 138–148.
Teng T, Mercer CA, Hexley P, Thomas G, Fumagalli S . Loss of tumor suppressor RPL5/RPL11 does not induce cell cycle arrest but impedes proliferation due to reduced ribosome content and translation capacity. Mol Cell Biol 2013; 33: 4660–4671.
Morata G, Ripoll P . Minutes: mutants of drosophila autonomously affecting cell division rate. Dev Biol 1975; 42: 211–221.
Amoyel M, Bach EA . Cell competition: how to eliminate your neighbours. Development 2014; 141: 988–1000.
Zhang Q, Shalaby NA, Buszczak M . Changes in rRNA transcription influence proliferation and cell fate within a stem cell lineage. Science 2014; 343: 298–301.
Lai M-D, Xu J . Ribosomal proteins and colorectal cancer. Curr Genomics 2007; 8: 43–49.
Stumpf CR, Ruggero D . The cancerous translation apparatus. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2011; 21: 474–483.
Nieminen TT, O'Donohue M-F, Wu Y, Lohi H, Scherer SW, Paterson AD et al. Germline mutation of RPS20, encoding a ribosomal protein, causes predisposition to hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal carcinoma without DNA mismatch repair deficiency. Gastroenterology 2014; 147: 595–598.e5.
Brighenti E, Calabrese C, Liguori G, Giannone FA, Treré D, Montanaro L et al. Interleukin 6 downregulates p53 expression and activity by stimulating ribosome biogenesis: a new pathway connecting inflammation to cancer. Oncogene 2014; 33: 4396–4406.
El Marjou F, Janssen KP, Chang BH, Li M, Hindie V, Chan L et al. Tissue-specific and inducible Cre-mediated recombination in the gut epithelium. Genesis 2004; 39: 186–193.
Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M et al. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature 2007; 449: 1003–1007.
Jacks T, Remington L, Williams BO, Schmitt EM, Halachmi S, Bronson RT et al. Tumor spectrum analysis in p53-mutant mice. Curr Biol 1994; 4: 1–7.
Guo J, Longshore S, Nair R, Warner BW . Retinoblastoma protein (pRb), but not p107 or p130, is required for maintenance of enterocyte quiescence and differentiation in small intestine. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 134–140.
Léguillier T, Vandormael-Pournin S, Artus J, Houlard M, Picard C, Bernex F et al. Omcg1 is critically required for mitosis in rapidly dividing mouse intestinal progenitors and embryonic stem cells. Biol Open 2012; 1: 648–657.
O'Donohue M-F, Choesmel V, Faubladier M, Fichant G, Gleizes P-E . Functional dichotomy of ribosomal proteins during the synthesis of mammalian 40S ribosomal subunits. J Cell Biol 2010; 190: 853–866.
Fichelson P, Moch C, Ivanovitch K, Martin C, Sidor CM, Lepesant J-A et al. Live-imaging of single stem cells within their niche reveals that a U3snoRNP component segregates asymmetrically and is required for self-renewal in Drosophila. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 685–693.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the members of the histopathology unit and of B Romagnolo’s team and to A David and S El Messaoudi-Aubert for technical help and advices. We thank P Sansonetti for the Lgr5CreERT2-IRES-Gfp mouse line, B Romagnolo for the Olfm4 in situ probe and B Gayraud-Morel, L Le Cam, JC Marine for providing reagents. We thank B Romagnolo, P Jay and J Artus for critical reading of the manuscript, and all members of the GIstem consortium, S Tajbakhsh’s lab and the Mouse Functional Genetics unit for helpful discussions. Imaging was performed at the Imagopole and the histopathology Unit from Institut Pasteur. This work was supported by the Institut National du Cancer (INCa 2007-1-COL-6-IC-1 and PLBIO09-070), the Institut Pasteur, the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-10-LABX-73-01 REVIVE) and the Fondation ARC (Programme labellisé 2014). AS received support from the Fondation des Treilles.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by M Oren
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stedman, A., Beck-Cormier, S., Le Bouteiller, M. et al. Ribosome biogenesis dysfunction leads to p53-mediated apoptosis and goblet cell differentiation of mouse intestinal stem/progenitor cells. Cell Death Differ 22, 1865–1876 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2015.57
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2015.57
This article is cited by
-
Ribosome profiling analysis reveals the roles of DDX41 in translational regulation
International Journal of Hematology (2023)
-
Differential gene expression in iPSC-derived human intestinal epithelial cell layers following exposure to two concentrations of butyrate, propionate and acetate
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Translational control of stem cell function
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2021)
-
Co-expression network analysis identified key genes in association with mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation
Cell and Tissue Research (2019)
-
Differential regulated microRNA by wild type and mutant p53 in induced pluripotent stem cells
Cell Death & Disease (2016)