Abstract
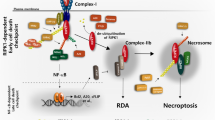
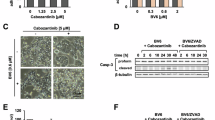
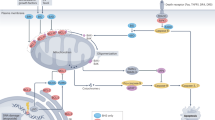
Peptido-mimetic inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) antagonists (Smac mimetics (SMs)) can kill tumour cells by depleting endogenous IAPs and thereby inducing tumour necrosis factor (TNF) production. We found that interferon-γ (IFNγ) synergises with SMs to kill cancer cells independently of TNF− and other cell death receptor signalling pathways. Surprisingly, CRISPR/Cas9 HT29 cells doubly deficient for caspase-8 and the necroptotic pathway mediators RIPK3 or MLKL were still sensitive to IFNγ/SM-induced killing. Triple CRISPR/Cas9-knockout HT29 cells lacking caspase-10 in addition to caspase-8 and RIPK3 or MLKL were resistant to IFNγ/SM killing. Caspase-8 and RIPK1 deficiency was, however, sufficient to protect cells from IFNγ/SM-induced cell death, implying a role for RIPK1 in the activation of caspase-10. These data show that RIPK1 and caspase-10 mediate cell death in HT29 cells when caspase-8-mediated apoptosis and necroptosis are blocked and help to clarify how SMs operate as chemotherapeutic agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y . Caspases: enemies within. Science 1998; 281: 1312–1316.
Gyrd-Hansen M, Meier P . IAPs: from caspase inhibitors to modulators of NF-kappaB, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 561–574.
Verhagen AM, Kratina TK, Hawkins CJ, Silke J, Ekert PG, Vaux DL . Identification of mammalian mitochondrial proteins that interact with IAPs via N-terminal IAP binding motifs. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 348–357.
Fulda S, Wick W, Weller M, Debatin KM . Smac agonists sensitize for Apo2L/TRAIL- or anticancer drug-induced apoptosis and induce regression of malignant glioma in vivo. Nat Med 2002; 8: 808–815.
Li L, Thomas RM, Suzuki H, De Brabander JK, Wang X, Harran PG . A small molecule Smac mimic potentiates TRAIL- and TNFalpha-mediated cell death. Science 2004; 305: 1471–1474.
Gaither A, Porter D, Yao Y, Borawski J, Yang G, Donovan J et al. A Smac mimetic rescue screen reveals roles for inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 11493–11498.
Petersen SL, Wang L, Yalcin-Chin A, Li L, Peyton M, Minna J et al. Autocrine TNFalpha signaling renders human cancer cells susceptible to Smac-mimetic-induced apoptosis. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 445–456.
Condon SM, Mitsuuchi Y, Deng Y, LaPorte MG, Rippin SR, Haimowitz T et al. Birinapant, a smac-mimetic with improved tolerability for the treatment of solid tumors and hematological malignancies. J Med Chem 2014; 57: 3666–3677.
Hsu H, Xiong J, Goeddel DV . The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa B activation. Cell 1995; 81: 495–504.
Micheau O, Tschopp J . Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 2003; 114: 181–190.
Wong WW, Gentle IE, Nachbur U, Anderton H, Vaux DL, Silke J . RIPK1 is not essential for TNFR1-induced activation of NF-kappaB. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 482–487.
Hsu H, Shu HB, Pan MG, Goeddel DV . TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell 1996; 84: 299–308.
Tokunaga F . Linear ubiquitination-mediated NF-kappaB regulation and its related disorders. J Biochem 2013; 154: 313–323.
Gerlach B, Cordier SM, Schmukle AC, Emmerich CH, Rieser E, Haas TL et al. Linear ubiquitination prevents inflammation and regulates immune signalling. Nature 2011; 471: 591–596.
Silke J . The regulation of TNF signalling: what a tangled web we weave. Curr Opin Immunol 2011; 23: 620–626.
Vercammen D, Brouckaert G, Denecker G, Van de Craen M, Declercq W, Fiers W et al. Dual signaling of the Fas receptor: initiation of both apoptotic and necrotic cell death pathways. J Exp Med 1998; 188: 919–930.
Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Vanden Berghe T, Kroemer G . Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 700–714.
Pop C, Oberst A, Drag M, Van Raam BJ, Riedl SJ, Green DR et al. FLIP(L) induces caspase 8 activity in the absence of interdomain caspase 8 cleavage and alters substrate specificity. Biochem J 2011; 433: 447–457.
Oberst A, Dillon CP, Weinlich R, McCormick LL, Fitzgerald P, Pop C et al. Catalytic activity of the caspase-8-FLIP(L) complex inhibits RIPK3-dependent necrosis. Nature 2011; 471: 363–367.
Murphy JM, Silke J . Ars Moriendi; the art of dying well—new insights into the molecular pathways of necroptotic cell death. EMBO Rep 2014; 15: 155–164.
Grell M, Zimmermann G, Gottfried E, Chen CM, Grunwald U, Huang DC et al. Induction of cell death by tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 2, CD40 and CD30: a role for TNF-R1 activation by endogenous membrane-anchored TNF. EMBO J 1999; 18: 3034–3043.
Wicovsky A, Henkler F, Salzmann S, Scheurich P, Kneitz C, Wajant H . Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-1 enhances proinflammatory TNF receptor-2 signaling and modifies TNFR1-TNFR2 cooperation. Oncogene 2009; 28: 1769–1781.
Salzmann S, Seher A, Trebing J, Weisenberger D, Rosenthal A, Siegmund D et al. Fibroblast growth factor inducible (Fn14)-specific antibodies concomitantly display signaling pathway-specific agonistic and antagonistic activity. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 13455–13466.
Vince JE, Chau D, Callus B, Wong WW, Hawkins CJ, Schneider P et al. TWEAK-FN14 signaling induces lysosomal degradation of a cIAP1-TRAF2 complex to sensitize tumor cells to TNFalpha. J Cell Biol 2008; 182: 171–184.
Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H, Hsu YM, Scott H, Hession C et al. TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 32401–32410.
Nakayama M, Kayagaki N, Yamaguchi N, Okumura K, Yagita H . Involvement of TWEAK in interferon gamma-stimulated monocyte cytotoxicity. J Exp Med 2000; 192: 1373–1380.
Darnell JE Jr., Kerr IM, Stark GR . Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994; 264: 1415–1421.
Beug ST, Tang VA, LaCasse EC, Cheung HH, Beauregard CE, Brun J et al. Smac mimetics and innate immune stimuli synergize to promote tumor death. Nat Biotechnol 2014; 32: 182–190.
Thapa RJ, Nogusa S, Chen P, Maki JL, Lerro A, Andrake M et al. Interferon-induced RIP1/RIP3-mediated necrosis requires PKR and is licensed by FADD and caspases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 18.
Taniguchi T, Lamphier MS, Tanaka N . IRF-1: the transcription factor linking the interferon response and oncogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1997; 1333: M9–17.
Maciejewski J, Selleri C, Anderson S, Young NS . Fas antigen expression on CD34+ human marrow cells is induced by interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha and potentiates cytokine-mediated hematopoietic suppression in vitro. Blood 1995; 85: 3183–3190.
Fulda S, Debatin KM . IFNgamma sensitizes for apoptosis by upregulating caspase-8 expression through the Stat1 pathway. Oncogene 2002; 21: 2295–2308.
Vince JE, Wong WW, Khan N, Feltham R, Chau D, Ahmed AU et al. IAP antagonists target cIAP1 to induce TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 2007; 131: 682–693.
Varfolomeev E, Blankenship JW, Wayson SM, Fedorova AV, Kayagaki N, Garg P et al. IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 2007; 131: 669–681.
Ahn EY, Pan G, Vickers SM, McDonald JM . IFN-gamma upregulates apoptosis-related molecules and enhances Fas-mediated apoptosis in human cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 2002; 100: 445–451.
Xu X, Fu XY, Plate J, Chong AS . IFN-gamma induces cell growth inhibition by Fas-mediated apoptosis: requirement of STAT1 protein for up-regulation of Fas and FasL expression. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 2832–2837.
Geserick P, Hupe M, Moulin M, Wong WW, Feoktistova M, Kellert B et al. Cellular IAPs inhibit a cryptic CD95-induced cell death by limiting RIP1 kinase recruitment. J Cell Biol 2009; 187: 1037–1054.
Kaiser WJ, Sridharan H, Huang C, Mandal P, Upton JW, Gough PJ et al. Toll-like receptor 3-mediated necrosis via TRIF, RIP3, and MLKL. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 31268–31279.
Fu Y, Comella N, Tognazzi K, Brown LF, Dvorak HF, Kocher O . Cloning of DLM-1, a novel gene that is up-regulated in activated macrophages, using RNA differential display. Gene 1999; 240: 157–163.
Upton JW, Kaiser WJ, Mocarski ES . DAI/ZBP1/DLM-1 complexes with RIP3 to mediate virus-induced programmed necrosis that is targeted by murine cytomegalovirus vIRA. Cell Host Microbe 2012; 11: 290–297.
Newton K, Dugger DL, Wickliffe KE, Kapoor N, de Almagro MC, Vucic D et al. Activity of protein kinase RIPK3 determines whether cells die by necroptosis or apoptosis. Science 2014; 343: 1357–1360.
Mandal P, Berger SB, Pillay S, Moriwaki K, Huang C, Guo H et al. RIP3 induces apoptosis independent of pronecrotic kinase activity. Mol Cell 2014; 56: 481–495.
Hildebrand JM, Tanzer MC, Lucet IS, Young SN, Spall SK, Sharma P et al. Activation of the pseudokinase MLKL unleashes the four-helix bundle domain to induce membrane localization and necroptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 15072–15077.
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N et al. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol 2005; 1: 112–119.
Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D, Lin S, Barretto R, Habib N et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 2013; 339: 819–823.
Aubrey BJ, Kelly GL, Kueh AJ, Brennan MS, O'Connor L, Milla L et al. An inducible lentiviral guide RNA platform enables the identification of tumor-essential genes and tumor-promoting mutations in vivo. Cell Rep 2015; 10: 1422–1432.
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Tinel A, LeBlanc H, Virmani A, Schow P et al. Death receptor recruitment of endogenous caspase-10 and apoptosis initiation in the absence of caspase-8. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 46639–46646.
Lamy L, Ngo VN, Emre NC, Shaffer AL, Yang Y, Tian E et al. Control of autophagic cell death by caspase-10 in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 2013; 23: 435–449.
Brumatti G, Ma C, Lalaoui N, Nguyen NY, Navarro M, Tanzer MC et al. The caspase-8 inhibitor emricasan combines with the SMAC mimetic birinapant to induce necroptosis and treat acute myeloid leukemia. Sci Transl Med 2016; 8: 339ra69.
Feoktistova M, Geserick P, Kellert B, Dimitrova DP, Langlais C, Hupe M et al. cIAPs block Ripoptosome formation, a RIP1/caspase-8 containing intracellular cell death complex differentially regulated by cFLIP isoforms. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 449–463.
Tencho T, Katiuscia B, Maurice D, Meike B, Claudia L, Fredrik W et al. The Ripoptosome, a signaling platform that assembles in response to genotoxic stress and loss of IAPs. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 432–438.
Kaiser WJ, Upton JW, Long AB, Livingston-Rosanoff D, Daley-Bauer LP, Hakem R et al. RIP3 mediates the embryonic lethality of caspase-8-deficient mice. Nature 2011; 471: 368–372.
Zhang H, Zhou X, McQuade T, Li J, Chan FK, Zhang J . Functional complementation between FADD and RIP1 in embryos and lymphocytes. Nature 2011; 471: 373–376.
Chawla-Sarkar M, Lindner DJ, Liu YF, Williams BR, Sen GC, Silverman RH et al. Apoptosis and interferons: role of interferon-stimulated genes as mediators of apoptosis. Apoptosis 2003; 8: 237–249.
Gao J, Shi LZ, Zhao H, Chen J, Xiong L, He Q et al. Loss of IFN-gamma pathway genes in tumor cells as a mechanism of resistance to anti-CTLA-4 therapy. Cell 2016; 167: 397–404 e399.
Zaretsky JM, Garcia-Diaz A, Shin DS, Escuin-Ordinas H, Hugo W, Hu-Lieskovan S et al. Mutations associated with acquired resistance to PD-1 blockade in melanoma. N Engl J Med 2016; 375: 819–829.
Ruiz-Ruiz C, Munoz-Pinedo C, Lopez-Rivas A . Interferon-gamma treatment elevates caspase-8 expression and sensitizes human breast tumor cells to a death receptor-induced mitochondria-operated apoptotic program. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 5673–5680.
Sprick MR, Rieser E, Stahl H, Grosse-Wilde A, Weigand MA, Walczak H . Caspase-10 is recruited to and activated at the native TRAIL and CD95 death-inducing signalling complexes in a FADD-dependent manner but can not functionally substitute caspase-8. EMBO J 2002; 21: 4520–4530.
Wang J, Chun HJ, Wong W, Spencer DM, Lenardo MJ . Caspase-10 is an initiator caspase in death receptor signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 13884–13888.
Etemadi N, Holien JK, Chau D, Dewson G, Murphy JM, Alexander WS et al. Lymphotoxin alpha induces apoptosis, necroptosis and inflammatory signals with the same potency as tumour necrosis factor. FEBS J 2013; 280: 5283–5297.
Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Kafri T, Green DR, Verma IM . Suppression of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB. Science 1996; 274: 787–789.
Acknowledgements
We thank Toru Okamoto for the pFTRE 3G construct, David Baltimore for lentiviral packaging constructs, Theo Mantamadiotis for the ERT2 construct, Robert Gerl for early work with the GAL4 ERT2 VP16 system, Henning Walczak for the TRAIL ligand, Tracy Putoczki for LIM2837, LIM1215, SW480, LIM2560, LIM2405, SW481 cells, Conor Kearney for MEWO, ME-RM, SK-Mel-28, ME4405, HT-144, Oliver Sieber for SKCO1, HCT116, OLDI, LIM2099 cells, Ben Kile for Ifnar−/− mouse tails, Paul Hertzog for Pkr−/−, PKR K271R and Ifnar−/− tails, Seth Masters for Casp1−/− tails, Andreas Strasser for Casp8−/−/Mlkl−/− tails, Hans-Uwe Simon for the pLKO.1 construct encoding for the shRNA ATG5, James Murphy and Guillaume Lessene for Compound 1 (MLKL inhibitor). Andrew Kueh and Stephen Wilcox for helping with the next-generation sequencing. J Silke is funded by the NHMRC (433013, 541901 and 541902). MC Tanzer is funded by the Victorian International Research Scholarship. Fc-TNFSF ligand DNA was provided by J Tschopp (University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland). We thank Wendy Cook and David Vaux for their input and guidance in editing this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
J Silke was variously a consultant and member of the Scientific Advisory Board and SM Condon, CA Benetatos, SK Chunduru and M McKinlay were employees of TetraLogic Pharmaceuticals Corporation over some of the course of this work. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by C Borner.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanzer, M., Khan, N., Rickard, J. et al. Combination of IAP antagonist and IFNγ activates novel caspase-10- and RIPK1-dependent cell death pathways. Cell Death Differ 24, 481–491 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.147
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.147
This article is cited by
-
TRAF2 and RIPK1 redundantly mediate classical NFκB signaling by TNFR1 and CD95-type death receptors
Cell Death & Disease (2025)
-
Necroptotic cell death consequences and disease relevance
Nature Immunology (2025)
-
Uncovering the rewired IAP-JAK regulatory axis as an immune-dependent vulnerability of LKB1-mutant lung cancer
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Immunogenic cell death in cancer: targeting necroptosis to induce antitumour immunity
Nature Reviews Cancer (2024)
-
An immunohistochemical atlas of necroptotic pathway expression
EMBO Molecular Medicine (2024)