Abstract
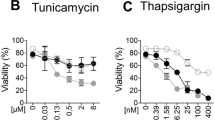
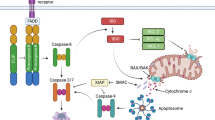
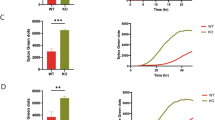
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response constitutes cellular reactions triggered by a wide variety of stimuli that disturb folding of proteins, often leading to apoptosis. ER stress-induced apoptotic cell death is thought to be an important contributor to many human pathological conditions. The molecular mechanism of this apoptosis process has been highly controversial with both the receptor and the mitochondrial pathways being implicated. Using knockout mouse models and RNAi-mediated gene silencing in cell lines, our group and others had demonstrated the importance of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in ER stress-induced cell death, particularly the role of the pro-apoptotic BH3-only BCL-2 family members, BIM and PUMA. However, a recent report suggested a central role for the death receptor, DR5, activated in a ligand-independent manner, and the initiator caspase, caspase-8, in ER stress-induced cell death. This prompted us to re-visit our previous observations and attempt to reproduce the newly published findings. Here we report that the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, activated by BH3-only proteins, is essential for ER stress-induced cell death and that, in contrast to the previous report, DR5 as well as caspase-8 are not required for this process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Weston RT, Puthalakath H . Endoplasmic reticulum stress and BCL-2 family members. Adv Exp Med Biol 2010; 687: 65–77.
Bravo R, Vicencio JM, Parra V, Troncoso R, Munoz JP, Bui M et al. Increased ER-mitochondrial coupling promotes mitochondrial respiration and bioenergetics during early phases of ER stress. J Cell Sci 2011; 124 (Pt 13): 2143–2152.
Kaufman RJ . Orchestrating the unfolded protein response in health and disease. J Clin Invest 2002; 110: 1389–1398.
Puthalakath H, O'Reilly LA, Gunn P, Lee L, Kelly PN, Huntington ND et al. ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein Bim. Cell 2007; 129: 1337–1349.
Reimertz C, Kogel D, Rami A, Chittenden T, Prehn JH . Gene expression during ER stress-induced apoptosis in neurons: induction of the BH3-only protein Bbc3/PUMA and activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. J Cell Biol 2003; 162: 587–597.
Li JLB, Lee AS . Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis: multiple pathways and activation of p53-up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) and NOXA by p53. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 7260–7270.
Lu M, Lawrence DA, Marsters S, Acosta-Alvear D, Kimmig P, Mendez AS et al. Cell death. Opposing unfolded-protein-response signals converge on death receptor 5 to control apoptosis. Science 2014; 345: 98–101.
Paton AW, Beddoe T, Thorpe CM, Whisstock JC, Wilce MC, Rossjohn J et al. AB5 subtilase cytotoxin inactivates the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP. Nature 2006; 443: 548–552.
Lindsten T, Ross AJ, King A, Zong WX, Rathmell JC, Shiels HA et al. The combined functions of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members bak and bax are essential for normal development of multiple tissues. Mol Cell 2000; 6: 1389–1399.
Jost PJ, Grabow S, Gray D, McKenzie MD, Nachbur U, Huang DC et al. XIAP discriminates between type I and type II FAS-induced apoptosis. Nature 2009; 460: 1035–1039.
Varfolomeev EE, Schuchmann M, Luria V, Chiannilkulchai N, Beckmann JS, Mett IL et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse Caspase 8 gene ablates cell death induction by the TNF receptors, Fas/Apo1, and DR3 and is lethal prenatally. Immunity 1998; 9: 267–276.
Kaufmann T, Jost PJ, Pellegrini M, Puthalakath H, Gugasyan R, Gerondakis S et al. Fatal hepatitis mediated by tumor necrosis factor TNFalpha requires caspase-8 and involves the BH3-only proteins Bid and Bim. Immunity 2009; 30: 56–66.
Puthalakath H, Strasser A . Keeping killers on a tight leash: transcriptional and post-translational control of the pro-apoptotic activity of BH3-only proteins. Cell Death Differ 2002; 9: 505–512.
Sarig R, Zaltsman Y, Marcellus RC, Flavell R, Mak TW, Gross A . BID-D59A is a potent inducer of apoptosis in primary embryonic fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 10707–10715.
Gangoda L, Doerflinger M, Srivastava R, Narayan N, Edgington LE, Orian J et al. Loss of Prkar1a leads to Bcl-2 family protein induction and cachexia in mice. Cell Death Differ 2014; 21: 1815–1824.
Aubrey BJ, Kelly GL, Kueh AJ, Brennan MS, O'Connor L, Milla L et al. An inducible lentiviral guide RNA platform enables the identification of tumor-essential genes and tumor-promoting mutations in vivo. Cell Rep 2015; 10: 1422–1432.
Acknowledgements
JG, CN and GM are supported by LTU PhD scholarship and this project was funded by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Project grant APP1085328 (to HP).
Author contributions
JG, MD, CN, IJ, GM and GB conducted the experiments. AK, DS, MJ and DH generated the CRISPR knockout cell lines. MJ, DH, AP, JP and HP designed the experiments and MD, JG and HP wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by G Melino
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glab, J., Doerflinger, M., Nedeva, C. et al. DR5 and caspase-8 are dispensable in ER stress-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 24, 944–950 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.53
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.53
This article is cited by
-
Targeting proteostasis for cancer therapy: current advances, challenges, and future perspectives
Molecular Cancer (2025)
-
IRE1 RNase controls CD95-mediated cell death
EMBO Reports (2024)
-
Trace elements and metal nanoparticles: mechanistic approaches to mitigating chemotherapy-induced toxicity—a review of literature evidence
BioMetals (2024)
-
When cell death goes wrong: inflammatory outcomes of failed apoptosis and mitotic cell death
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
Negligible role of TRAIL death receptors in cell death upon endoplasmic reticulum stress in B-cell malignancies
Oncogenesis (2023)