Abstract
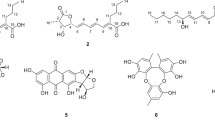
A new cytotoxic indole-3-ethenamide (1) and two known compounds, 7-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde (2) and emodin (3) were isolated and identified from the ethyl acetate extract of Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 in a hypersaline nutrient-rich medium. On the basis of spectroscopic analysis and amino-acid analysis, the new structure of 1 was determined to be (S,E)-3-methyl-2-(N- methylacetamido)-N-(2-(7-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)vinyl)butanamide within 3:1 ratio of rotamers along the acetamido single bond in DMSO-d6 at room temperature. Compound 1 showed moderate cytotoxicity against A-549 cells and weak cytotoxicity against HL-60 cells with the IC50 values of 3.0 and 27 μM, respectively. Compound 2 has been separated as natural product for the first time, and its NMR data were also reported for the first time in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lu, Z. Y. et al. Citrinin dimers from the halotolerant fungus Penicillium citrinum B-57. J. Nat. Prod. 71, 543–546 (2008).
Wang, W. L. et al. Two new cytotoxic quinone type compounds from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus variecolor. J. Antibiot. 60, 603–607 (2007).
Wang, W. L. et al. Isoechinulin-type alkaloids, variecolorin A-L, from halotolerant Aspergillus variecolor. J. Nat. Prod. 70, 1558–1564 (2007).
Wang, W. L. et al. Three novel, structurally unique spirocyclic alkaloids from the halotolerant B-17 fungus strain of Aspergillus variecolor. Chem. Biodiv. 4, 2913–2919 (2007).
Koch, A.L. Genetic response of microbes to extreme challenges. J. Theor. Biol. 160, 1–21 (1993).
Méjanelle, L., Lòpez, J. F., Gunde-Cimerman, N. & Grimalt, J. O. Ergosterol biosynthesis in novel melanized fungi from hypersaline environments. J. Lipid. Res. 42, 352–358 (2001).
Janin, Y. L. Peptides with anticancer use or potential. Amino Acids 25, 1–40 (2003).
Zheng, J. K. et al. Novel cyclic hexapeptides from marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. Org. Lett. 11, 5262–5265 (2009).
Zheng, J. K. et al. Cyclic tripeptides from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. J. Nat. Prod. 73, 1133–1137 (2010).
Liu, K., Wood, H. B. & Jones, A. B. Total synthesis of asterriquinone B-1. Tetrahedron Lett. 40, 5119–5122 (1999).
Cohen, P. A. & Towers, G. H. N. Anthraquinones and Phenanthroperylenequinones from Nephroma Laevigatum. J. Nat. Prod. 58, 520–526 (1995).
Dugave, C. & Demange, L. CisTrans isomerization of organic molecules and biomolecules: implications and applications. Chem. Rev. 103, 2475–2532 (2003).
Toske, S. G., Jensen, P. R., Kauffman, C. A. & Fenical, W. Aspergillamides A and B: modified cytotoxic tripeptides produced by a marine fungus of the genus Aspergillus. Tetrahedron 54, 13459–13466 (1998).
Marfey, P. Determination of D-amino acids. II. Use of a bifunctional reagent, 1,5-difluoro-2,4dinitrobenzene. Carlsberg Res. Commun. 49, 591–596 (1984).
Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Meth. 65, 55–63 (1983).
Skehan, P. et al. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer drug screening. J. Nat. Cancer Inst. 82, 1107–1112 (1990).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Major Program for Technique Development Research of New Drugs in China (No. 2009ZX09103-046), from Special Fund for Marine Scientific Research in the Public Interest of China (No. 2010418022-3), from National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2010CB833800), from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30470196 & 30670219), and from PCSIRT (No. IRT0944). The cytotoxicity assay was performed at the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The Journal of Antibiotics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zheng, JK., Qu, HJ. et al. A new cytotoxic indole-3-ethenamide from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. J Antibiot 64, 679–681 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2011.63
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2011.63
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Exploring Potential of Aspergillus sclerotiorum: Secondary Metabolites and Biotechnological Relevance
Mycological Progress (2023)
-
Fungi from the extremes of life: an untapped treasure for bioactive compounds
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2020)
-
Fungi in salterns
Journal of Microbiology (2019)
-
Screening and identification of Aspergillus activity against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and analysis of antimicrobial components
Journal of Microbiology (2019)
-
New rubrolides from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus OUCMDZ-1925
The Journal of Antibiotics (2014)