Abstract
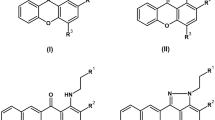
A new xanthone named sydoxanthone C (1) and a new alkaloid named acremolin B (2), together with 10 known compounds (3–12) were isolated from a deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO Ind09F01. The structures of compounds (1–12) were determined by the extensive 1D, 2D-NMR, High resolution mass spectra (HRESIMS) data. Compounds 7, 8, 11 and 12 showed significant selective cytotoxicities against HeLa, DU145 and U937 cell lines. In addition, compounds 7, 8 and 11 also exhibited COX-2 inhibitory activities with the prominent IC50 values of 2.4, 7.1 and 10.6 μM, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Blunt, J.W., Copp, B. R., Keyzers, R. A., Munro, M. H. & Prinsep, M. R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 31, 160–258 (2014).
Proksch, P., Putz, A., Ortlepp, S., Kjer, J. & Bayer, M. Bioactive natural products from marine sponges and fungal endophytes. Phytochem. Rev. 9, 475–489 (2010).
Rateb, M. E. & Ebel, R. Secondary metabolites of fungi from marine habitats. Nat. Prod. Rep. 28, 290–344 (2011).
Swathi, J., Narendra, K., Sowjanya, K. & Satya, A. K. Marine fungal metabolites as a rich source of bioactive compounds. Afr. J. Biochem. Res 7, 184–196 (2013).
Lin, X. et al. A new cytotoxic sesquiterpene quinone produced by Penicillium sp. F00120 isolated from a deep sea sediment sample. Mar. Drugs 10, 106–115 (2012).
Song, X. Q. et al. Xanthone derivatives from Aspergillus sydowii, an endophytic fungus from the liverwort Scapania ciliate S. Lac and their immunosuppressive activities. Phytochem. Lett 6, 318–321 (2013).
Yao, Q. et al. Cytotoxic polyketides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Engyodontium album DFFSCS021. Mar. Drugs 12, 5902–5915 (2014).
Hamasaki, T., Sato, Y. & Hatsuda, Y. Structure of sydowinin A, sydowinin B, and sydowinol, metabolites from Aspergillus sydowi.. Agri. Biol. Chem. 39, 2341–2345 (1975).
Januar, L. A. & Molinski, T. F. Acremolin from Acremonium strictum is N, 2, 3-Etheno-2′-isopropyl-1-methylguanine, not a 1 H-Azirine. Synthesis and Structural Revision. Org. Lett. 15, 2370–2373 (2013).
Yurchenko, A. N. et al. A new meroterpenoid from the marine fungus Aspergillus versicolor (Vuill.) Tirab. Russ. Chem. Bull. 59, 852–856 (2010).
Bunyapaiboonsri, T., Yoiprommarat, S., Intereya, K. & Kocharin, K. New diphenyl ethers from the insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps sp. BCC 1861. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 55, 304–307 (2007).
Chen, M. et al. Bioactive indole alkaloids and phenyl Ether derivatives from a marine-derived Aspergillus sp. fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 76, 547–553 (2013).
Gong, D. L. et al. Diphenyl etheric metabolites from Streptomyces sp. neau50. J. Antibiot. 64, 465–467 (2011).
Takenaka, Y., Hamada, N. & Tanahashi, T. Monomeric and dimeric dibenzofurans from cultured mycobionts of Lecanora iseana. Phytochemistry 66, 665–668 (2005).
Kim, H. S. et al. A novel dihydroxan-thenone, AGI-B4 with inhibition of VEGF-induced endothelial cell growth. J. Antibiot. 55, 669–672 (2002).
Bergeron, J. J. M., Brenner, M. B., Thomas, D.Y. & Williams, D. B. Calnexin: a membrane bound chaperone of the endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem. Sci. 19, 124–128 (1994).
Praveen Rao, P. N. & Edward, E. K. Evolution of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibition and beyond. J. Pharm. Pharmaceut. Sci 11, 81–110 (2008).
Blobaum, A. L. et al. The 2′-Trifluoromethyl analogue of indomethacin is a potent and selective COX-2 inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 4, 486–490 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Basic Research Program of China (973)’s Project (2011CB915503); the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program, 2012AA092104), Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA11030403), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31270402, 21172230, 41476135, 41376162, 41406187, 41406187); and Guangdong Marine Economic Development and Innovation of Regional Demonstration Project (GD2012-D01-001), Guangzhou Scientific Research Project (2014J4100212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The Journal of Antibiotics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Qin, X., Lin, X. et al. Sydoxanthone C and acremolin B produced by deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO Ind09F01. J Antibiot 68, 703–706 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2015.55
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2015.55
This article is cited by
-
Antarctic fungi produce pigment with antimicrobial and antiparasitic activities
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2024)
-
The intriguing chemistry and biology of sulfur-containing natural products from marine microorganisms (1987–2020)
Marine Life Science & Technology (2021)
-
Two New Quinazoline Derivatives from the Moss Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus sp. and Their Anti-inflammatory Activity
Natural Products and Bioprospecting (2021)
-
Systematic Review of Anti-inflammatory Agents from Aspergillus Species
Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia (2021)