Abstract
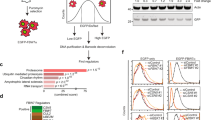
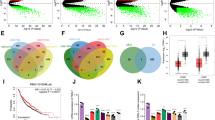
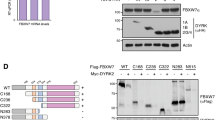
Fbxw7α is a member of the F-box family of proteins, which function as the substrate-targeting subunits of SCF (Skp1/Cul1/F-box protein) ubiquitin ligase complexes. Using differential purifications and mass spectrometry, we identified p100, an inhibitor of NF-κB signalling, as an interactor of Fbxw7α. p100 is constitutively targeted in the nucleus for proteasomal degradation by Fbxw7α, which recognizes a conserved motif phosphorylated by GSK3. Efficient activation of non-canonical NF-κB signalling is dependent on the elimination of nuclear p100 through either degradation by Fbxw7α or exclusion by a newly identified nuclear export signal in the carboxy terminus of p100. Expression of a stable p100 mutant, expression of a constitutively nuclear p100 mutant, Fbxw7α silencing or inhibition of GSK3 in multiple myeloma cells with constitutive non-canonical NF-κB activity results in apoptosis both in cell systems and xenotransplant models. Thus, in multiple myeloma, Fbxw7α and GSK3 function as pro-survival factors through the control of p100 degradation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Skaar, J. R., D’Angiolella, V., Pagan, J. K. & Pagano, M. S. F box proteins II. Cell 137, e1351–e1358 (2009).
Cardozo, T. & Pagano, M. The SCF ubiquitin ligase: insights into a molecular machine. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 739–751 (2004).
Petroski, M. D. & Deshaies, R. J. Function and regulation of cullin–RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 9–20 (2005).
Hoeck, J. D. et al. Fbw7 controls neural stem cell differentiation and progenitor apoptosis via Notch and c-Jun. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 1365–1372 (2010).
Welcker, M. & Clurman, B. E. FBW7 ubiquitin ligase: a tumour suppressor at the crossroads of cell division, growth and differentiation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 83–93 (2008).
Onoyama, I. et al. Conditional inactivation of Fbxw7 impairs cell-cycle exit during T cell differentiation and results in lymphomatogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 204, 2875–2888 (2007).
Thompson, B. J. et al. The SCFFBW7 ubiquitin ligase complex as a tumor suppressor in T cell leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 204, 1825–1835 (2007).
Rajagopalan, H. et al. Inactivation of hCDC4 can cause chromosomal instability. Nature 428, 77–81 (2004).
Millman, S. E. & Pagano, M. MCL1 meets its end during mitotic arrest. EMBO Rep. 12, 384–385 (2011).
Mavrakis, K. J. et al. A cooperative microRNA-tumor suppressor gene network in acute T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). Nat. Genet. 43, 673–678 (2011).
O’Neil, J. et al. FBW7 mutations in leukemic cells mediate NOTCH pathway activation and resistance to γ-secretase inhibitors. J. Exp. Med. 204, 1813–1824 (2007).
Akhoondi, S. et al. FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer Res. 67, 9006–9012 (2007).
Chapman, M. A. et al. Initial genome sequencing and analysis of multiple myeloma. Nature 471, 467–472 (2011).
Ghosh, S. & Karin, M. Missing pieces in the NF-κB puzzle. Cell 109 Suppl., S81–S96 (2002).
Senftleben, U. et al. Activation by IKKα of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-κB signaling pathway. Science 293, 1495–1499 (2001).
Dejardin, E. et al. The lymphotoxin- β receptor induces different patterns of gene expression via two NF-κB pathways. Immunity 17, 525–535 (2002).
Coope, H. J. et al. CD40 regulates the processing of NF-κB2 p100 to p52. EMBO J. 21, 5375–5385 (2002).
Weih, F. & Caamano, J. Regulation of secondary lymphoid organ development by the nuclear factor-κB signal transduction pathway. Immunol. Rev. 195, 91–105 (2003).
Ramakrishnan, P., Wang, W. & Wallach, D. Receptor-specific signaling for both the alternative and the canonical NF-κB activation pathways by NF-κB-inducing kinase. Immunity 21, 477–489 (2004).
Zarnegar, B. et al. Unique CD40-mediated biological program in B cell activation requires both type 1 and type 2 NF-κB activation pathways. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 8108–8113 (2004).
Basak, S. et al. A fourth IκB protein within the NF-κB signaling module. Cell 128, 369–381 (2007).
Mordmuller, B., Krappmann, D., Esen, M., Wegener, E. & Scheidereit, C. Lymphotoxin and lipopolysaccharide induce NF-κB-p52 generation by a co-translational mechanism. EMBO Rep. 4, 82–87 (2003).
Xiao, G., Harhaj, E. W. & Sun, S. C. NF-κB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-κB2 p100. Mol. Cell 7, 401–409 (2001).
Fong, A. & Sun, S. C. Genetic evidence for the essential role of β-transducin repeat-containing protein in the inducible processing of NF-κB2/p100. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22111–22114 (2002).
Bonizzi, G. et al. Activation of IKKα target genes depends on recognition of specific κB binding sites by RelB:p52 dimers. EMBO J. 23, 4202–4210 (2004).
Muller, J. R. & Siebenlist, U. Lymphotoxin β receptor induces sequential activation of distinct NF-κB factors via separate signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 12006–12012 (2003).
Staudt, L. M. Oncogenic activation of NF-κB. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2, a000109 (2010).
Annunziata, C. M. et al. Frequent engagement of the classical and alternative NF-κB pathways by diverse genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 12, 115–130 (2007).
Keats, J. J. et al. Promiscuous mutations activate the noncanonical NF-κB pathway in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 12, 131–144 (2007).
Razani, B. et al. Negative feedback in noncanonical NF-κB signaling modulates NIK stability through IKKα-mediated phosphorylation. Sci. Signal. 3, ra41 (2010).
Hao, B., Oehlmann, S., Sowa, M. E., Harper, J. W. & Pavletich, N. P. Structure of a Fbw7-Skp1-cyclin E complex: multisite-phosphorylated substrate recognition by SCF ubiquitin ligases. Mol. Cell 26, 131–143 (2007).
Orian, A. et al. SCF(β)(-TrCP) ubiquitin ligase-mediated processing of NF-κB p105 requires phosphorylation of its C-terminus by IκB kinase. EMBO J. 19, 2580–2591 (2000).
Sato, N., Meijer, L., Skaltsounis, L., Greengard, P. & Brivanlou, A. H. Maintenance of pluripotency in human and mouse embryonic stem cells through activation of Wnt signaling by a pharmacological GSK-3-specific inhibitor. Nat. Med. 10, 55–63 (2004).
Solan, N. J., Miyoshi, H., Carmona, E. M., Bren, G. D. & Paya, C. V. RelB cellular regulation and transcriptional activity are regulated by p100. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 1405–1418 (2002).
van Drogen, F. et al. Ubiquitylation of cyclin E requires the sequentialfunction of SCF complexes containing distinct hCdc4 isoforms. Mol. Cell 23, 37–48 (2006).
Sangfelt, O., Cepeda, D., Malyukova, A., van Drogen, F. & Reed, S. I. Both SCF(Cdc4 α) and SCF(Cdc4 γ) are required for cyclin E turnover in cell lines that do not overexpress cyclin E. Cell Cycle 7, 1075–1082 (2008).
Derudder, E. et al. RelB/p50 dimers are differentially regulated by tumor necrosis factor- α and lymphotoxin- β receptor activation: critical roles for p100. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 23278–23284 (2003).
Shih, V. F. et al. Kinetic control of negative feedback regulators of NF-κB/RelA determines their pathogen- and cytokine-receptor signaling specificity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 9619–9624 (2009).
Richardson, P. G. et al. Bortezomib or high-dose dexamethasone for relapsed multiple myeloma. New Engl. J. Med. 352, 2487–2498 (2005).
Shah, J. J. et al. Phase 1 dose-escalation study of MLN4924, a novel NAE inhibitor, in patients with multiple myeloma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 114, 735–736 (2009).
Thompson, B. J. et al. Control of hematopoietic stem cell quiescence by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Fbw7. J. Exp. Med. 205, 1395–1408 (2008).
Xie, P., Stunz, L. L., Larison, K. D., Yang, B. & Bishop, G. A. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 is a critical regulator of B cell homeostasis in secondary lymphoid organs. Immunity 27, 253–267 (2007).
Hoeflich, K. P. et al. Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase- 3β in cell survival and NF-κB activation. Nature 406, 86–90 (2000).
Milhollen, M. A. et al. MLN4924, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, is active in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma models: rationale for treatment of NF-κB-dependent lymphoma. Blood 116, 1515–1523 (2010).
Stransky, N. et al. The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science 333, 1157–1160 (2011).
Morin, R. D. et al. Frequent mutation of histone-modifying genes in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Nature 476, 298–303 (2011).
Busino, L. et al. Degradation of Cdc25A by β-TrCP during S phase and in response to DNA damage. Nature 426, 87–91 (2003).
Busino, L. et al. SCFFbxl3 controls the oscillation of the circadian clock by directing the degradation of cryptochrome proteins. Science 316, 900–904 (2007).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank I. Aifantis, H. J. Cho, G. Franzoso, W. M. Kuehl and A. Ventura for reagents; B. Aranda-Orgilles for her contribution; and I. Aifantis, G. Franzoso, K. Nakayama, S. Reed and J. R. Skaar for critically reading the manuscript. M.P. is grateful to T. M. Thor for continuous support. This work was supported in part by grant 5P30CA016087-33 from the National Cancer Institute, a fellowship from the American Italian Cancer Foundation and NIH 5T32HL007151-33 to L.B., NIH T32 CA009161 grant to S.M. and grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01-GM057587, R37-CA076584 and R21-CA161108) and the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation to M.P. M.P. is an Investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.B. conceived and directed the project. L.B. and S.E.M. designed and carried out most experiments. L.S. and O.O. helped with the mouse experiments. C.K. carried out the in vitro experiments shown in Fig. 1d,e and Supplementary Figs S2d and S5b. V.B. and K.S.E-J. carried out the mass spectrometry analysis of the Fbxw7α complex purified by L.B. A.H. provided constructs, cell lines and advice. M.P. coordinated the work and oversaw the results. L.B., S.M. and M.P. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 1777 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Supplementary Information (XLSX 50 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Busino, L., Millman, S., Scotto, L. et al. Fbxw7α- and GSK3-mediated degradation of p100 is a pro-survival mechanism in multiple myeloma. Nat Cell Biol 14, 375–385 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2463
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2463
This article is cited by
-
Clinical significance of FBXW7 loss of function in human cancers
Molecular Cancer (2022)
-
DNA damage-induced transcription stress triggers the genome-wide degradation of promoter-bound Pol II
Nature Communications (2022)
-
SCFβ-TrCP-mediated degradation of TOP2β promotes cancer cell survival in response to chemotherapeutic drugs targeting topoisomerase II
Oncogenesis (2020)
-
Oroxylin A alleviates immunoparalysis of CLP mice by degrading CHOP through interacting with FBXO15
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Loss of ELF5–FBXW7 stabilizes IFNGR1 to promote the growth and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer through interferon-γ signalling
Nature Cell Biology (2020)