Abstract
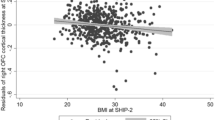
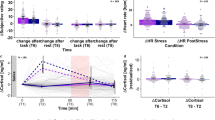
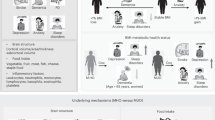
Stress is associated with alterations in neural motivational-reward pathways in the ventral striatum (VS), hormonal/metabolic changes, and weight increases. The relationship between these different factors is not well understood. We hypothesized that body mass index (BMI) status and hormonal/metabolic factors would be associated with VS activation. We used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to compare brain responses of overweight and obese (OW/OB: BMI ⩾25 kg/m2: N=27) individuals with normal weight (NW: BMI<18.5–24.9 kg/m2: N=21) individuals during exposure to personalized stress, alcohol cue, and neutral-relaxing situations using a validated, autobiographical, script-driven, guided-imagery paradigm. Metabolic factors, including fasting plasma glucose (FPG), insulin, and leptin, were examined for their association with VS activation. Consistent with previous studies, stress and alcohol cue exposure each increased activity in cortico-limbic regions. Compared with NW individuals, OW/OB individuals showed greater VS activation in the neutral-relaxing and stress conditions. FPG was correlated with VS activation. Significant associations between VS activation and metabolic factors during stress and relaxation suggest the involvement of metabolic factors in striatal dysfunction in OW/OB individuals. This relationship may contribute to non-homeostatic feeding in obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adam TC, Epel ES (2007). Stress, eating and the reward system. Physiol Behav 91: 449–458.
Block JP (2009). Psychosocial Stress and Change in Weight Among US Adults. American Journal of Epidemiology 170: 181–192.
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington HL et al (2003). Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science 301: 386–389.
Chambers RA, Taylor JR, Potenza MN (2003). Developmental neurocircuitry of motivation in Adolescents: A critical period of addiction vulnerability. Am J Psychiatry 160: 1041–1052.
Cox RW (1996). AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput Biomed Res 29: 162–173.
Dallman MF, Pecoraro N, Akana SF, la Fleur SE, Gomez F, Houshyar H et al (2003). Chronic stress and obesity: A new view of ‘comfort food’. PNAS 100: 11696–11701.
Desai RA, Manley M, Desai MM, Potenza MN (2009). Gender differences in the association between body mass index and psychopathology. CNS Spectr 14: 372–383.
Duncan JS, Papademetris X, Yang J, Jackowski M, Zeng X, Staib LH (2004). Geometric Strategies for Neuroanatomic Analysis from MRI. NeuroImage 23: 34–45.
Epel E, Jimenez S, Brownell K, Stroud L, Stoney C, Niaura R (2004). Are stress eaters at risk for the metabolic syndrome? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1032: 208–210.
Evans AC, Collins DL, Mills SR, Brown ED, Kelly RL, Peters TM (1993). 3D statistical neuroanatomical models from 305 MRI volumes, Proc. IEEE Nucl Sci Symp Med Imaging Conf 95: 1813–1817.
Figlewicz DP, Evans SB, Murphy J, Hoen M, Myers M, Baskin DG (2003). Expression of Receptors for Insulin and Leptin in the Ventral Tegmental Area/Substantia Nigra of the Rat. Brain Research 964: 107–115.
Finkelstein EA, Fieblkorn IC, Wang G (2003). National Medical Spending Attributable to Overweight and Obesity: How Much, And Who's Paying? Health Affairs (Suppl Web Exclusives): W3: 219–226.
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JB (1995). Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders—Non-Patient Edition (SCID-I/NP), version 2.0. New York State Psychiatric Institute, Biometrics Research: New York.
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR (2010). Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA 303: 235–241.
Frascella J, Potenza MN, Brown LL, Childress AR (2010). Shared brain vulnerabilities open the way for nonsubstance addictions: carving addiction at a new joint? Ann NY Acad Sci 1187: 294–315.
Gao Q, Horvath TL (2007). Neurobiology of feeding and energy expenditure. Annu Rev Neurosci 30: 367–398.
Hill JO, Peters JC (1998). Environmental contributions to the Obesity Epidemic. Science 280: 1371–1374.
Holmes CJ, Hoge R, Collins L, Woods R, Toga AW, Evans AC (1998). Enhancement of MR images using registration for signal averaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22: 324–333.
Kelley AE, Berridge KC (2002). The Neuroscience of Natural Rewards: Relevance to Addictive Drugs. J Neurosci 22: 3306–3311.
Kelley AE, Blado BA, Pratt WE, Will MJ (2005). Corticostriatal-hypothalamic circuitry and food motivation: Integration of energy, action and reward. Physiol Behav 86: 773–795.
Khani S, Tayek JA (2001). Cortisol increases gluconeogenesis in humans: its role in the metabolic syndrome. Clinical Science 101: 739–747.
Knutson B, Greer SM (2008). Anticipatory affect: neural correlates and consequences for choice. Philos Trans R Soc Lond, B, Biol Sci 363: 3771–3786.
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2008). Addiction and the Brain AntiReward System. Annu Rev Psychol 59: 29–53.
Lacadie CM, Fulbright RK, Rajeevan N, Constable RT, Papademetris X (2008). More accurate Talairach coordinates for neuroimaging using non-linear registration. Neuroimage 42: 717–725.
Levin BE, Routh VH, Kang L, Sanders N, Dunn-Meynell AA (2004). Neuronal Glucosensing What Do We Know After 50 Years? Diabetes 53: 2521–2528.
Li C-S, Kosten TR, Sinha R (2005). Sex differences in brain response to stress imagery in abstinent cocaine dependent individuals—an fMRI study. Biol Psychiatry 57: 487–494.
Miller GA, Levin DN, Kozak MJ, Cook III EW, McLean Jr A, Lang PJ (1987). Individual differences in imagery and the psychophysiology of emotion. Cognition and Emotion 1: 367–390.
McEwen B (2007). Physiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation: Central Role of the Brain. Physiol Rev 87: 873–904.
Molfino A, Fiorentini A, Tubani L, Martuscelli M, Rossi Fanelli F, Laviano A (2009). Body mass index is related to autonomic nervous system activity as measured by heart rate variability. Eur J Clin Nutr 63: 1263–1265.
Nolfe E, Voet T, Jacobs F, Dierckx R, Lemahieu I (2003). XMedCon- An open-source medical image conversion toolkit. Eur J Nucl Med 30 (Supp.2): S246.
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, McDowell MA, Flegal KM (2007). Obesity among adults in the United States—no change since 2003–2004. NCHS data brief no 1. National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD.
Pruessner JC, Champagne F, Meaney MJ, Dagher A (2004). Dopamine Release in Response to a Psychological Stress in Humans and Its Relationship to Early Life Maternal Care: A Positron Emission Tomography Study Using [11C]Raclopride. J Neurosci 24: 2825–2831.
Sandoval DA, Cota D, Seeley RJ (2008). The integrative role of CNS fuel-sensing mechanisms in energy balance and glucose regulation. Annu Rev Physiol 70: 513–535.
Schwartz MW, Figlewicz DP, Baskin DG, Woods SC, Porte D (1992). Insulin in the Brain: A Hormonal Regulator of Energy Balance. Endocr Rev 13: 387–414.
Shavel U, Yap J, Shaham Y (2001). Leptin Attenuates Acute Food Deprivation-Induced Relapse to Heroin Seeking. J Neurosci 21: RC129.
Sinha R (2001). How Does Stress Increase the Risk of Drug Abuse and Relapse? Psychopharmacology 158: 343–359.
Sinha R (2008). Chronic stress, drug use and vulnerability to addiction. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences: Addiction Reviews 1141: 105–130.
Sinha R (2009). Modeling stress and drug craving in the laboratory: Implications for addiction treatment development. Addict Biol 14: 84–98.
Sinha R, Fox HC, Hong KA, Bergquist K, Bhagwagar Z, Siedlarz KM (2009). Enhanced Negative Emotion and Alcohol Craving, and Altered Physiological Responses Following Stress and Cue Exposure in Alcohol Dependent Individuals. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 1198–1208.
Sinha R, Lacadie C, Skudlarski P, Wexler BE (2004). Neural circuits underlying emotional distress in humans. Ann NY Acad Sci 1032: 254–257.
Sinha R, Lacadie C, Skudlarski P, Fulbright RK, Kosten TR, Rounsaville BJ et al (2005). Neural activity associated with stress-induced cocaine craving: An fMRI study. Psychopharmacology 183: 171–180.
Sinha R, Lovallo WR, Parsons OA (1992). Cardiovascular differentiation of emotions. Psychosom Med 54: 422–435.
Sinha R, Talih M, Malison R, Cooney N, Anderson GM, Kreek MJ (2003). Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and sympatho-adreno-medullary responses during stress-induced and drug cue-induced cocaine craving states. Psychopharmacology 170: 62–72.
Stice E, Spoor S, Bohon C, Small DM (2008). Response to Food Is Moderated by TaqlA Allele. Science 322: 449–452.
Volkow ND, Wang G-J, Fowler JS, Telang F (2008). Overlapping neural circuits in addiction and obesity: evidence of systems pathology. Philos Trans R Soc 363: 3191–3200.
Volkow ND, Wise RA (2005). How can drug addiction help us understand obesity? Nat Neurosci 8: 555–560.
Von Deneen KM, Gold MS, Liu Y (2009). Food Addiction and Cues in Prader-Willi Syndrome. J Addict Med 3: 19–25.
Wang G-J, Volkow ND, Logan J, Pappas NR, Wong CT, Zhu W et al (2001). Brain dopamine and obesity. Lancet 357: 354–357.
Wang G-J, Volkow ND, Thanos PK, Fowler JS (2004). Similarity Between Obesity and Drug Addiction as Assessed by Neurofunctional Imaging: A Concept Review. J Addict Dis 23: 39–53.
Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Thanos PK, Fowler JS (2009). Imaging of brain dopamine pathways: implications for understanding obesity. J Addict Med 3: 8–18.
Woods SC, Seeley RJ (2000). Adiposity signals and the control of energy homeostasis. Ingestive Behavior and Obesity 16: 894–902.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIDDK/NIH T32 DK 07058 ‘Diabetes Mellitus and Disorders of Metabolism’, T32 DK 063703-07 ‘Training in Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes Research’, the NIH grants R01-AA013892, RL1AA017539, UL1-DE019586, UL1-RR024139 and the PL1-DA024859 and the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research Common Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that Ania M Jastreboff has provided clinical care for research volunteers in the Pfizer Clinical Research Unit in New Haven Connecticut. Marc N Potenza has received financial support or compensation for the following: Dr Potenza consults for and is an advisor to Boehringer Ingelheim; has consulted for and has financial interests in Somaxon; has received research support from the National Institutes of Health, Veteran's Administration, Mohegan Sun Casino, the National Center for Responsible Gaming and its affiliated Institute for Research on Gambling Disorders, and Forest Laboratories, Ortho-McNeil, Oy-Control/Biotie and Glaxo-SmithKline pharmaceuticals; has participated in surveys, mailings or telephone consultations related to drug addiction, impulse control disorders or other health topics; has consulted for law offices and the federal public defender's office in issues related to impulse control disorders; provides clinical care in the Connecticut Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services Problem Gambling Services Program; has performed grant reviews for the National Institutes of Health and other agencies; has guest-edited journal sections; has given academic lectures in grand rounds, CME events and other clinical or scientific venues; and has generated books or book chapters for publishers of mental health texts. Cheryl Lacadie: has nothing to disclose. Kwangik A. Hong: has nothing to disclose. Robert S. Sherwin: The authors declare that over the past three years Robert Sherwin has received compensation from Amylin, Biodel, Boehringer Ingelheim, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Mannkind, McKinsey & Company, Merck, Medtronic, Lily, and Ono Pharmacy. Rajita Sinha: The authors declare that Rajita Sinha is on the Scientific Advisory Board for Embera Neurotherapeutics and is also a consultant for Glaxo-Smith Kline, Pharmaceuticals. The authors report that they have no financial conflicts of interest with respect to the content of this paper.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jastreboff, A., Potenza, M., Lacadie, C. et al. Body Mass Index, Metabolic Factors, and Striatal Activation During Stressful and Neutral-Relaxing States: An fMRI Study. Neuropsychopharmacol 36, 627–637 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.194
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.194
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prenatal Cocaine Exposure and Adolescent Neural Responses to Appetitive and Stressful Stimuli
Neuropsychopharmacology (2014)
-
Saliency Processing and Obesity: A Preliminary Imaging Study of the Stop Signal Task
Obesity (2012)