Abstract
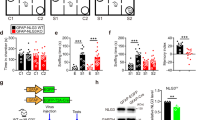
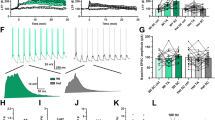
Neuroligins (NLGNs) are cell adhesion molecules that are important for proper synaptic formation and functioning, and are critical regulators of the balance between neural excitation/inhibition (E/I). Mutations in NLGNs have been linked to psychiatric disorders in humans involving social dysfunction and are related to similar abnormalities in animal models. Chronic stress increases the likelihood for affective disorders and has been shown to induce changes in neural structure and function in different brain regions, with the hippocampus being highly vulnerable to stress. Previous studies have shown evidence of chronic stress-induced changes in the neural E/I balance in the hippocampus. Therefore, we hypothesized that chronic restraint stress would lead to reduced hippocampal NLGN-2 levels, in association with alterations in social behavior. We found that rats submitted to chronic restraint stress in adulthood display reduced sociability and increased aggression. This occurs along with a reduction of NLGN-2, but not NLGN-1 expression (as shown with western blot, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy analyses), throughout the hippocampus and detectable in different layers of the CA1, CA3, and DG subfields. Furthermore, using synthetic peptides that comprise sequences in either NLGN-1 (neurolide-1) or NLGN-2 (neurolide-2) involved in the interaction with their presynaptic partner neurexin (NRXN)-1, intra-hippocampal administration of neurolide-2 led also to reduced sociability and increased aggression. These results highlight hippocampal NLGN-2 as a key molecular substrate regulating social behaviors and underscore NLGNs as promising targets for the development of novel drugs for the treatment of dysfunctional social behaviors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bessa JM, Ferreira D, Melo I, Marques F, Cerqueira JJ, Palha JA et al (2009). The mood-improving actions of antidepressants do not depend on neurogenesis but are associated with neuronal remodeling. Mol Psychiatry 14: 764–773.
Bisaz R, Schachner M, Sandi C (2011). Causal evidence for the involvement of the neural cell adhesion molecule, NCAM, in chronic stress-induced cognitive impairments. Hippocampus 21: 56–71.
Blundell J, Tabuchi K, Bolliger MF, Blaiss CA, Brose N, Liu X et al (2009). Increased anxiety-like behavior in mice lacking the inhibitory synapse cell adhesion molecule neuroligin-2. Genes Brain Behav 8: 114–126.
Blundell J, Blaiss CA, Etherton MR, Espinosa F, Tabuchi K, Walz C et al (2010). Neuroligin-1 deletion results in impaired spatial memory and increased repetitive behavior. J Neurosci 30: 2115–2129.
Budreck EC, Scheiffele P (2007). Neuroligin-3 is a neuronal adhesion protein at GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses. Eur J Neurosci 26: 1738–1748.
Cambon K, Venero C, Berezin V, Bock E, Sandi C (2003). Post-training administration of a synthetic peptide ligand of the neural cell adhesion molecule, C3d, attenuates long-term expression of contextual fear conditioning. Neuroscience 122: 183–191.
Chih B, Engelman H, Scheiffele P (2005). Control of excitatory and inhibitory synapse formation by neuroligins. Science 307: 1324–1328.
Dahlhaus R, Hines RM, Eadie BD, Kannangara TS, Hines DJ, Brown CE et al (2010). Overexpression of the cell adhesion molecule neuroligin-1 induces learning deficits and impairs synaptic plasticity by altering the ratio of excitation to inhibition in the hippocampus. Hippocampus 20: 305–322.
Donohue HS, Gabbott PL, Davies HA, Rodríguez JJ, Cordero MI, Sandi C et al (2006). Chronic restraint stress induces changes in synapse morphology in stratum lacunosum-moleculare CA1 rat hippocampus: a stereological and three-dimensional ultrastructural study. Neuroscience 140: 597–606.
Foley AG, Hartz BP, Gallagher HC, Rønn LC, Berezin V, Bock E et al (2000). A synthetic peptide ligand of neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) IgI domain prevents NCAM internalization and disrupts passive avoidance learning. J Neurochem 74: 2607–2613.
Gao Y, Bezchlibnyk YB, Sun X, Wang JF, McEwen BS, Young LT (2006). Effects of restraint stress on the expression of proteins involved in synaptic vesicle exocytosis in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 141: 1139–1148.
Gauthier J, Siddiqui TJ, Huashan P, Yokomaku D, Hamdan FF, Champagne N et al (2011). Truncating mutations in NRXN2 and NRXN1 in autism spectrum disorders and schizophrenia. Hum Genet 130: 563–573.
Gilabert-Juan J, Castillo-Gomez E, Pérez-Rando M, Moltó MD, Nacher J (2011). Chronic stress induces changes in the structure of interneurons and in the expression of molecules related to neuronal structural plasticity and inhibitory neurotransmission in the amygdala of adult mice. Exp Neurol 232: 33–40.
Gjørlund MD, Nielsen J, Pankratova S, Li S, Korshunova I, Bock E et al (2012). Neuroligin-1 induces neurite outgrowth through interaction with neurexin-1β and activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor-1. FASEB J 26: 4174–4186.
Gogolla N, Leblanc JJ, Quast KB, Südhof TC, Fagiolini M, Hensch TK (2009). Common circuit defect of excitatory-inhibitory balance in mouse models of autism. J Neurodev Disord 1: 172–181.
Graf ER, Zhang X, Jin SX, Linhoff MW, Craig AM (2004). Neurexins induce differentiation of GABA and glutamate postsynaptic specializations via neuroligins. Cell 119: 1013–1026.
Grønli J, Fiske E, Murison R, Bjorvatn B, Sørensen E, Ursin R et al (2007). Extracellular levels of serotonin and GABA in the hippocampus after chronic mild stress in rats. A microdialysis study in an animal model of depression. Behav Brain Res 181: 42–51.
Harrison PJ, Weinberger DR (2005). Schizophrenia genes, gene expression, and neuropathology: on the matter of their convergence. Mol Psychiatry 10: 40–68.
Hines RM, Wu L, Hines DJ, Steenland H, Mansour S, Dahlhaus R et al (2008). Synaptic imbalance, stereotypies, and impaired social interactions in mice with altered neuroligin 2 expression. J Neurosci 28: 6055–6067.
Hu W, Zhang M, Czéh B, Flügge G, Zhang W (2010). Stress impairs GABAergic network function in the hippocampus by activating nongenomic glucocorticoid receptors and affecting the integrity of the parvalbumin-expressing neuronal network. Neuropsychopharmacology 35: 1693–1707.
Jamain S, Radyushkin K, Hammerschmidt K, Granon S, Boretius S, Varoqueaux F et al (2008). Reduced social interaction and ultrasonic communication in a mouse model of monogenic heritable autism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 1710–1715.
Jedlicka P, Hoon M, Papadopoulos T, Vlachos A, Winkels R, Poulopoulos A et al (2011). Increased dentate gyrus excitability in neuroligin-2-deficient mice in vivo. Cereb Cortex 21: 357–367.
Joëls M, Karst H, Alfarez D, Heine VM, Qin Y, van Riel E et al (2004). Effects of chronic stress on structure and cell function in rat hippocampus and hypothalamus. Stress 7: 221–231.
Karst H, Joëls M (2003). Effect of chronic stress on synaptic currents in rat hippocampal dentate gyrus neurons. J Neurophysiol 89: 625–633.
Kleen JK, Sitomer MT, Killeen PR, Conrad CD (2006). Chronic stress impairs spatial memory and motivation for reward without disrupting motor ability and motivation to explore. Behav Neurosci 120: 842–851.
Koehnke J, Jin X, Budreck EC, Posy S, Scheiffele P, Honig B et al (2008). Crystal structure of the extracellular cholinesterase-like domain from neuroligin-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 1873–1888.
Kogan JH, Frankland PW, Silva AJ (2000). Long-term memory underlying hippocampus-dependent social recognition in mice. Hippocampus 10: 47–56.
Kohl C, Riccio O, Grosse J, Zanoletti O, Fournier C, Schmidt MV et al (2013). Hippocampal neuroligin-2 overexpression leads to reduced aggression and inhibited novelty reactivity in rats. PLoS One 8: e56871.
Kolkova K, Novitskaya V, Pedersen N, Berezin V, Bock E (2000). Neural cell adhesion molecule-stimulated neurite outgrowth depends on activation of protein kinase C and the Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Neurosci 20: 2238–2246.
Kompagne H, Bárdos G, Szénási G, Gacsályi I, Hársing LG, Lévay G (2008). Chronic mild stress generates clear depressive but ambiguous anxiety-like behaviour in rats. Behav Brain Res 193: 311–314.
Kraev I, Henneberger C, Rossetti C, Conboy L, Kohler LB, Fantin M et al (2011). A peptide mimetic targeting trans-homophilic NCAM binding sites promotes spatial learning and neural plasticity in the hippocampus. PLoS One 6: e23433.
Lee T, Jarome T, Li SJ, Kim JJ, Helmstetter FJ (2009). Chronic stress selectively reduces hippocampal volume in rats: a longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroreport 20: 1554–1558.
Leuner B, Shors TJ (2012). Stress, anxiety, and dendritic spines: What are the connections? Neuroscience 251: 108–119.
Levinson JN, El-Husseini A (2005). Building excitatory and inhibitory synapses: balancing neuroligin partnerships. Neuron 48: 171–174.
Maaswinkel H, Gispen WH, Spruijt BM (1997). Executive function of the hippocampus in social behavior in the rat. Behav Neurosci 111: 777–784.
Magariños AM, McEwen BS (1995). Stress-induced atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA3c neurons: involvement of glucocorticoids secretion and excitatory amino acid receptors. Neuroscience 69: 89–98.
McEwen BS (2005). Glucocorticoids, depression, and mood disorders: structural remodeling in the brain. Metabolism 54: 20–23.
McEwen BS (2012). The ever-changing brain: cellular and molecular mechanisms for the effects of stressful experiences. Dev Neurobiol 72: 878–890.
Pavlides C, Nivón LG, McEwen BS (2002). Effects of chronic stress on hippocampal long-term potentiation. Hippocampus 12: 245–257.
Popov VI, Davies HA, Rogachevsky VV, Patrushev IV, Errington ML, Gabbot PL et al (2004). Remodelling of synaptic morphology but unchanged synaptic density during late phase long-term potentiation (LTP): a serial section electron micrograph study in the dentate gyrus in the aneasthetised rat. Neuroscience 128: 251–262.
Reagan LP, Rosell DR, Wood GE, Spedding M, Muñoz C, Rothstein J et al (2004). Chronic restraint stress up-regulates GLT-1 mRNA and protein expression in the rat hippocampus: reversal by tianeptine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 2179–2184.
Sandi C (2004). Stress, cognitive impairment and cell adhesion molecules. Nat Rev Neurosci 5: 917–930.
Sousa N, Madeira MD, Paula-Barbosa MM (1997). Structural alterations of the hippocampal formation of adrenalectomized rats: an unbiased stereological study. J Neurocytol 26: 423–438.
Sousa N, Lukoyanov NV, Madeira MD, Almeida OF, Paula-Barbosa MM (2000). Reorganization of the morphology of hippocampal neurites and synapses after stress-induced damage correlates with behavioral improvement. Neuroscience 97: 253–266.
Stewart MG, Davies HA, Sandi C, Kraev IV, Rogachevsky VV, Peddie CJ et al (2005). Stress suppresses and learning induces plasticity in CA3 of rat hippocampus: a three-dimensional ultrastructural study of thorny excrescences and their postsynaptic densities. Neuroscience 131: 43–54.
Südhof TC (2008). Neuroligins and neurexins link synaptic function to cognitive disease. Nature 455: 903–911.
Sun C, Cheng MC, Qin R, Liao DL, Chen TT, Koong FJ et al (2011). Identification and functional characterization of rare mutations of the neuroligin-2 gene (NLGN2) associated with schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 20: 3042–3051.
Tabuchi K, Blundell J, Etherton MR, Hammer RE, Liu X, Powell CM et al (2007). A neuroligin-3 mutation implicated in autism increases inhibitory synaptic transmission in mice. Science 318: 71–76.
Toth I, Neumann ID (2013). Animal models of social avoidance and social fear. Cell Tissue Res 354: 107–118.
Uekita T, Okanoya K (2011). Hippocampus lesions induced deficits in social and spatial recognition in Octodon degus. Behav Brain Res 219: 302–309.
Wöhr M, Silverman JL, Scattoni ML, Turner SM, Harris MJ, Saxena R et al (2012). Developmental delays and reduced pup ultrasonic vocalizations but normal sociability in mice lacking the postsynaptic cell adhesion protein neuroligin2. Behav Brain Res 251: 50–64.
Wood GE, Young LT, Reagan LP, McEwen BS (2003). Acute and chronic restraint stress alter the incidence of social conflict in male rats. Horm Behav 43: 205–213.
Wood GE, Norris EH, Waters E, Stoldt JT, McEwen BS (2008). Chronic immobilization stress alters aspects of emotionality and associative learning in the rat. Behav Neurosci 122: 282–292.
Yang M, Silverman JL, Crawley JN (2011). Automated three-chambered social approach task for mice. Curr Protoc Neurosci 8: 8.26.
Yizhar O, Fenno LE, Prigge M, Schneider F, Davidson TJ, O'Shea DJ et al (2011). Neocortical excitation/inhibition balance in information processing and social dysfunction. Nature 477: 171–178.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Kooij, M., Fantin, M., Kraev, I. et al. Impaired Hippocampal Neuroligin-2 Function by Chronic Stress or Synthetic Peptide Treatment is Linked to Social Deficits and Increased Aggression. Neuropsychopharmacol 39, 1148–1158 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.315
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.315
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The within-subject application of diffusion tensor MRI and CLARITY reveals brain structural changes in Nrxn2 deletion mice
Molecular Autism (2019)
-
The susceptibility to chronic social defeat stress is related to low hippocampal extrasynaptic NMDA receptor function
Neuropsychopharmacology (2019)
-
Bidirectional Regulation of Aggression in Mice by Hippocampal Alpha-7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
Neuropsychopharmacology (2018)
-
Neuroligin-2 Expression in the Prefrontal Cortex is Involved in Attention Deficits Induced by Peripubertal Stress
Neuropsychopharmacology (2016)
-
Mechanisms of stress in the brain
Nature Neuroscience (2015)