Abstract
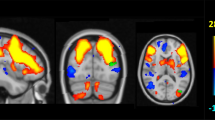
As the Apolipoprotein E (APOE) ɛ4 allele is a major genetic risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which has been suggested as a disconnection syndrome manifested by the disruption of white matter (WM) integrity and functional connectivity (FC), elucidating the subtle brain structural and functional network changes in cognitively normal ɛ4 carriers is essential for identifying sensitive neuroimaging based biomarkers and understanding the preclinical AD-related abnormality development. We first constructed functional network on the basis of resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging and a structural network on the basis of diffusion tensor image. Using global, local and nodal efficiencies of these two networks, we then examined (i) the differences of functional and WM structural network between cognitively normal ɛ4 carriers and non-carriers simultaneously, (ii) the sensitivity of these indices as biomarkers, and (iii) their relationship to behavior measurements, as well as to cholesterol level. For ɛ4 carriers, we found reduced global efficiency significantly in WM and marginally in FC, regional FC dysfunctions mainly in medial temporal areas, and more widespread for WM network. Importantly, the right parahippocampal gyrus (PHG.R) was the only region with simultaneous functional and structural damage, and the nodal efficiency of PHG.R in WM network mediates the APOE ɛ4 effect on memory function. Finally, the cholesterol level correlated with WM network differently than with the functional network in ɛ4 carriers. Our results demonstrated ɛ4-specific abnormal structural and functional patterns, which may potentially serve as biomarkers for early detection before the onset of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Achard S, Bullmore E (2007). Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Comput Biol 3: e17.
Bai F, Watson DR, Yu H, Shi Y, Yuan Y, Zhang Z (2009). Abnormal resting-state functional connectivity of posterior cingulate cortex in amnestic type mild cognitive impairment. Brain Res 1302: 167–174.
Bartzokis G, Lu PH, Mintz J (2007). Human brain myelination and amyloid beta deposition in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 3: 122–125.
Bateman RJ, Xiong C, Benzinger TL, Fagan AM, Goate A, Fox NC et al (2012). Clinical and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med 367: 795–804.
Bookheimer S, Burggren A (2009). APOE-4 genotype and neurophysiological vulnerability to Alzheimer's and cognitive aging. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 5: 343–362.
Brown JA, Terashima KH, Burggren AC, Ercoli LM, Miller KJ, Small GW et al (2011). Brain network local interconnectivity loss in aging APOE-4 allele carriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: 20760–20765.
Burgmans S, van Boxtel M, van den Berg K, Gronenschild E, Jacobs H, Jolles J et al (2011). The posterior parahippocampal gyrus is preferentially affected in age-related memory decline. Neurobiol Aging 32: 1572–1578.
Chen K, Reiman E, Alexander G, Caselli R, Gerkin R, Bandy D et al (2007). Correlations between apolipoprotein E ɛ4 gene dose and whole brain atrophy rates. Am J Psych 164: 916–921.
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW et al (1993). Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science 261: 921–923.
Davatzikos C, Resnick SM (2002). Degenerative age changes in white matter connectivity visualized in vivo using magnetic resonance imaging. Cereb Cortex 12: 767–771.
Dehouck B, Fenart L, Dehouck MP, Pierce A, Torpier G, Cecchelli R (1997). A new function for the LDL receptor: transcytosis of LDL across the blood-brain barrier. J Cell Biol 138: 877–889.
Delbeuck X, Van der Linden M, Collette F (2003). Alzheimer' Disease as a disconnection syndrome? Neuropsychol Rev 13: 79–92.
Dik MG, Jonker C, Bouter LM, Geerlings MI, van Kamp GJ, Deeg DJ (2000). APOE-epsilon4 is associated with memory decline in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurology 54: 1492–1497.
Donix M, Burggren AC, Scharf M, Marschner K, Suthana NA, Siddarth P et al (2013). APOE associated hemispheric asymmetry of entorhinal cortical thickness in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Psych Res 214: 212–220.
Eichenbaum H, Otto T, Cohen NJ (1994). Two functional components of the hippocampal memory system. Behav Brain Sci 17: 449–471.
Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JL, Hyman B, Kukull WA, Mayeux R et al (1997). Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA 278: 1349–1356.
Felsky D, Voineskos AN, Lerch JP, Nazeri A, Shaikh SA, Rajji TK et al (2012). Myelin-associated glycoprotein gene and brain morphometry in schizophrenia. Front Psych 3: 40.
Fleisher AS, Chen K, Quiroz YT, Jakimovich LJ, Gomez MG, Langois CM et al (2012). Florbetapir PET analysis of amyloid-beta deposition in the presenilin 1 E280A autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease kindred: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol 11: 1057–1065.
Geroldi C, Pihlajamäki M, Laakso M, DeCarli C, Beltramello A, Bianchetti A et al (1999). APOE-ɛ4 is associated with less frontal and more medial temporal lobe atrophy in AD. Neurology 53: 1825–1825.
Gong G, He Y, Concha L, Lebel C, Gross DW, Evans AC et al (2009). Mapping anatomical connectivity patterns of human cerebral cortex using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cereb Cortex 19: 524–536.
Hamanaka H, Katoh-Fukui Y, Suzuki K, Kobayashi M, Suzuki R, Motegi Y et al (2000). Altered cholesterol metabolism in human apolipoprotein E4 knock-in mice. Human Mol Genet 9: 353–361.
Hashimoto M, Yasuda M, Tanimukai S, Matsui M, Hirono N, Kazui H et al (2001). Apolipoprotein E ɛ4 and the pattern of regional brain atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 57: 1461–1466.
Hayes AF (2013) Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. Guilford Press.
Honea RA, Vidoni E, Harsha A, Burns JM (2009). Impact of APOE on the healthy aging brain: a voxel-based MRI and DTI study. J Alzheimer's Dis 18: 553–564.
Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR, Barnes CL (1984). Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science 225: 1168–1170.
Ignatius MJ, Shooter EM, Pitas RE, Mahley RW (1987). Lipoprotein uptake by neuronal growth cones in vitro. Science 236: 959–962.
Jiang Q, Lee CY, Mandrekar S, Wilkinson B, Cramer P, Zelcer N et al (2008). ApoE promotes the proteolytic degradation of Abeta. Neuron 58: 681–693.
Kohler S, Black SE, Sinden M, Szekely C, Kidron D, Parker JL et al (1998). Memory impairments associated with hippocampal versus parahippocampal-gyrus atrophy: an MR volumetry study in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychologia 36: 901–914.
Kordower JH, Chu Y, Stebbins GT, DeKosky ST, Cochran EJ, Bennett D et al (2001). Loss and atrophy of layer II entorhinal cortex neurons in elderly people with mild cognitive impairment. Annals Neurol 49: 202–213.
Liu Y-H, Jiao S-S, Wang Y-R, Bu X-L, Yao X-Q, Xiang Y et al (2014). Associations between ApoEɛ4 carrier status and serum BDNF levels—new insights into the molecular mechanism of ApoEɛ4 actions in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 1–7.
Lo CY, Wang PN, Chou KH, Wang J, He Y, Lin CP (2010). Diffusion tensor tractography reveals abnormal topological organization in structural cortical networks in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 30: 16876–16885.
Machulda MM, Jones DT, Vemuri P, McDade E, Avula R, Przybelski S et al (2011). Effect of APOE epsilon4 status on intrinsic network connectivity in cognitively normal elderly subjects. Arch Neurol 68: 1131–1136.
Mahley RW, Weisgraber KH, Huang Y (2006). Apolipoprotein E4: a causative factor and therapeutic target in neuropathology, including Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 5644–5651.
Masliah E, Mallory M, Alford M, Veinbergs I, Roses A (1996). Apolipoprotein E role in maintaining the integrity of the aging central nervous system. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s Disease. Springer: Berlin Heidelberg. pp 59–73.
Masliah E, Mallory M, Ge N, Alford M, Veinbergs I, Roses AD (1995). Neurodegeneration in the central nervous system of apoE-deficient mice. Exp Neurol 136: 107–122.
Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, van Zijl PC (1999). Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 45: 265–269.
Murray EA (1996). What have ablation studies told us about the neural substrates of stimulus memory? Semin Neurosci 8: 13–22.
Nichols LM, Masdeu JC, Mattay VS, Kohn P, Emery M, Sambataro F et al (2012). Interactive effect of apolipoprotein e genotype and age on hippocampal activation during memory processing in healthy adults. Arch Gen Psych 69: 804–813.
Nierenberg J, Pomara N, Hoptman MJ, Sidtis JJ, Ardekani BA, Lim KO (2005). Abnormal white matter integrity in healthy apolipoprotein E epsilon4 carriers. Neuroreport 16: 1369–1372.
Persson J, Lind J, Larsson A, Ingvar M, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C et al (2006). Altered brain white matter integrity in healthy carriers of the APOE epsilon4 allele: a risk for AD? Neurology 66: 1029–1033.
Rapp A, Gmeiner B, Huttinger M (2006). Implication of apoE isoforms in cholesterol metabolism by primary rat hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. Biochimie 88: 473–483.
Reiman EM, Caselli RJ, Chen K, Alexander GE, Bandy D, Frost J (2001). Declining brain activity in cognitively normal apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 heterozygotes: a foundation for using positron emission tomography to efficiently test treatments to prevent Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 3334–3339.
Reiman EM, Caselli RJ, Yun LS, Chen K, Bandy D, Minoshima S et al (1996). Preclinical evidence of Alzheimer's disease in persons homozygous for the epsilon 4 allele for apolipoprotein E. N Engl J Med 334: 752–758.
Reiman EM, Chen K, Langbaum JB, Lee W, Reschke C, Bandy D et al (2010). Higher serum total cholesterol levels in late middle age are associated with glucose hypometabolism in brain regions affected by Alzheimer's disease and normal aging. NeuroImage 49: 169–176.
Resnick SM, Pham DL, Kraut MA, Zonderman AB, Davatzikos C (2003). Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging studies of older adults: a shrinking brain. J Neurosci 23: 3295–3301.
Riddell DR, Zhou H, Atchison K, Warwick HK, Atkinson PJ, Jefferson J et al (2008). Impact of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) polymorphism on brain ApoE levels. J Neurosci 28: 11445–11453.
Rubinov M, Sporns O (2010). Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. NeuroImage 52: 1059–1069.
Ryan L, Walther K, Bendlin BB, Lue LF, Walker DG, Glisky EL (2011). Age-related differences in white matter integrity and cognitive function are related to APOE status. NeuroImage 54: 1565–1577.
Sheline YI, Morris JC, Snyder AZ, Price JL, Yan Z, D'Angelo G et al (2010). APOE4 allele disrupts resting state fMRI connectivity in the absence of amyloid plaques or decreased CSF Abeta42. J Neurosci 30: 17035–17040.
Shu N, Liang Y, Li H, Zhang J, Li X, Wang L et al (2012). Disrupted topological organization in white matter structural networks in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: relationship to subtype. Radiology 265: 518–527.
Sparks DL (1997). Coronary artery disease, hypertension, ApoE, and cholesterol: a link to Alzheimer's disease? Annals NY Acad Sci 826: 128–146.
Stam C, Jones B, Nolte G, Breakspear M, Scheltens P (2007). Small-world networks and functional connectivity in Alzheimer's disease. Cereb Cortex 17: 92–99.
Tanaka J, Horiike Y, Matsuzaki M, Miyazaki T, Ellis-Davies GC, Kasai H (2008). Protein synthesis and neurotrophin-dependent structural plasticity of single dendritic spines. Science 319: 1683–1687.
Van Hoesen GW, Augustinack JC, Dierking J, Redman SJ, Thangavel R (2000). The parahippocampal gyrus in Alzheimer's disease. Clinical and preclinical neuroanatomical correlates. Annals NY Acad Sci 911: 254–274.
Van Hoesen GW, Hyman BT, Damasio AR (1991). Entorhinal cortex pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Hippocampus 1: 1–8.
Verghese PB, Castellano JM, Holtzman DM (2011). Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's disease and other neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol 10: 241–252.
Wang C, Stebbins GT, Medina DA, Shah RC, Bammer R, Moseley ME et al (2012). Atrophy and dysfunction of parahippocampal white matter in mild Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 33: 43–52.
Wang J, Zuo X, Dai Z, Xia M, Zhao Z, Zhao X et al (2013). Disrupted functional brain connectome in individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease. Biol Psych 73: 472–481.
Zhang J, Wang J, Wu Q, Kuang W, Huang X, He Y et al (2011). Disrupted brain connectivity networks in drug-naive, first-episode major depressive disorder. Biol Psych 70: 334–342.
Zhou Y, Dougherty JH Jr., Hubner KF, Bai B, Cannon RL, Hutson RK (2008). Abnormal connectivity in the posterior cingulate and hippocampus in early Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Dement 4: 265–270.
Zhuang L, Wen W, Zhu W, Trollor J, Kochan N, Crawford J et al (2010). White matter integrity in mild cognitive impairment: a tract-based spatial statistics study. NeuroImage 53: 16–25.
Acknowledgements
ZZ had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. ZZ and EMR conceived the original idea for the study, supervised in the conception and revised the manuscript. YC, JZ, XL, NS, and JW recruited the study population and conducted the neuropsychological tests. YC and KC analyzed the data. YC, KC, and ZZ drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Chen, K., Zhang, J. et al. Disrupted Functional and Structural Networks in Cognitively Normal Elderly Subjects with the APOE ɛ4 Allele. Neuropsychopharmacol 40, 1181–1191 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.302
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.302
This article is cited by
-
Environmental effects on brain functional networks in a juvenile twin population
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Dyslipidemia induced large-scale network connectivity abnormality facilitates cognitive decline in the Alzheimer’s disease
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
Metabolic connectivity in Alzheimer’s diseases
Clinical and Translational Imaging (2020)
-
Early brain connectivity alterations and cognitive impairment in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy (2018)
-
Liver X receptors regulate cerebrospinal fluid production
Molecular Psychiatry (2016)