Abstract
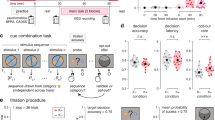
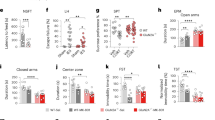
Antidepressant activity of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists and negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) has led to increased investigation of their behavioral pharmacology. NMDA antagonists, such as ketamine, impair cognition in multiple species and in multiple cognitive domains. However, studies with NR2B subtype-selective NAMs have reported mixed results in rodents including increased impulsivity, no effect on cognition, impairment or even improvement of some cognitive tasks. To date, the effects of NR2B-selective NAMs on cognitive tests have not been reported in nonhuman primates. The current study evaluated two selective NR2B NAMs, CP101,606 and BMT-108908, along with the nonselective NMDA antagonists, ketamine and AZD6765, in the nonhuman primate Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB) list-based delayed match to sample (list-DMS) task. Ketamine and the two NMDA NR2B NAMs produced selective impairments in memory in the list-DMS task. AZD6765 impaired performance in a non-specific manner. In a separate cohort, CP101,606 impaired performance of the nonhuman primate CANTAB visuo-spatial Paired Associates Learning (vsPAL) task with a selective impairment at more difficult conditions. The results of these studies clearly show that systemic administration of a selective NR2B NAM can cause transient cognitive impairment in multiple cognitive domains.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abdallah CG, Averill LA, Krystal JH (2015). Ketamine as a promising prototype for a new generation of rapid-acting antidepressants. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1344: 66–77.
Bachevalier J, Mishkin M (1986). Visual recognition impairment follows ventromedial but not dorsolateral prefrontal lesions in monkeys. Behav Brain Res 20: 249–261.
Buccafusco JJ, Terry AV Jr. (2009). A reversible model of the cognitive impairment associated with schizophrenia in monkeys: potential therapeutic effects of two nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists. Biochem Pharmacol 78: 852–862.
Cardinal RN, Aitken MR (2010). Whisker: a client-server high-performance multimedia research control system. Behav Res Methods 42: 1059–1071.
Coyle CM, Laws KR (2015). The use of ketamine as an antidepressant: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Psychopharmacol 30: 152–163.
Duman RS, Li N, Liu RJ, Duric V, Aghajanian G (2012). Signaling pathways underlying the rapid antidepressant actions of ketamine. Neuropharmacology 62: 35–41.
Graef JD, Newberry K, Newton A, Pieschl R, Shields E, Luan FN et al (2015). Effect of acute NR2B antagonist treatment on long-term potentiation in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res 1609: 31–39.
Guscott MR, Clarke HF, Murray F, Grimwood S, Bristow LJ, Hutson PH (2003). The effect of (+/-)-CP-101,606, an NMDA receptor NR2B subunit selective antagonist, in the Morris watermaze. Eur J Pharmacol 476: 193–199.
Hanson JE, Weber M, Meilandt WJ, Wu T, Luu T, Deng L et al (2013). GluN2B antagonism affects interneurons and leads to immediate and persistent changes in synaptic plasticity, oscillations, and behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 38: 1221–1233.
Hetem LA, Danion JM, Diemunsch P, Brandt C (2000). Effect of a subanesthetic dose of ketamine on memory and conscious awareness in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 152: 283–288.
Higgins GA, Ballard TM, Enderlin M, Haman M, Kemp JA (2005). Evidence for improved performance in cognitive tasks following selective NR2B NMDA receptor antagonist pre-treatment in the rat. Psychopharmacology 179: 85–98.
Higgins GA, Ballard TM, Huwyler J, Kemp JA, Gill R (2003). Evaluation of the NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonist Ro 63-1908 on rodent behaviour: evidence for an involvement of NR2B NMDA receptors in response inhibition. Neuropharmacology 44: 324–341.
Johnson K, Shah A, Jaw-Tsai S, Baxter J, Prakash C (2003). Metabolism, pharmacokinetics, and excretion of a highly selective N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, traxoprodil, in human cytochrome P450 2D6 extensive and poor metabolizers. Drug Metab Dispos 31: 76–87.
Kos T, Nikiforuk A, Rafa D, Popik P (2011). The effects of NMDA receptor antagonists on attentional set-shifting task performance in mice. Psychopharmacology 214: 911–921.
Krystal JH, Karper LP, Bennett A, D'Souza DC, Abi-Dargham A, Morrissey K et al (1998). Interactive effects of subanesthetic ketamine and subhypnotic lorazepam in humans. Psychopharmacology 135: 213–229.
Li N, Lee B, Liu RJ, Banasr M, Dwyer JM, Iwata M et al (2010). mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 329: 959–964.
Li N, Liu RJ, Dwyer JM, Banasr M, Lee B, Son H et al (2011). Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists rapidly reverse behavioral and synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress exposure. Biol Psychiatry 69: 754–761.
Mealing GA, Lanthorn TH, Murray CL, Small DL, Morley P (1999). Differences in degree of trapping of low-affinity uncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor antagonists with similar kinetics of block. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288: 204–210.
Menniti FS, Shah AK, Williams SA, Wilner KD, White WF, Chenard BL (1998). CP-101,606: an NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonist. CNS Drug Rev 4: 307–322.
Merchant RE, Bullock MR, Carmack CA, Shah AK, Wilner KD, Ko G et al (1999). A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of CP-101,606 in patients with a mild or moderate traumatic brain injury. Ann N Y Acad Sci 890: 42–50.
Morgan CJ, Curran HV (2006). Acute and chronic effects of ketamine upon human memory: a review. Psychopharmacology 188: 408–424.
Morgan CJ, Mofeez A, Brandner B, Bromley L, Curran HV (2004). Acute effects of ketamine on memory systems and psychotic symptoms in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 29: 208–218.
Neill JC, Barnes S, Cook S, Grayson B, Idris NF, McLean SL et al (2010). Animal models of cognitive dysfunction and negative symptoms of schizophrenia: focus on NMDA receptor antagonism. Pharmacol Ther 128: 419–432.
Newcomer JW, Farber NB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Selke G, Melson AK, Hershey T et al (1999). Ketamine-induced NMDA receptor hypofunction as a model of memory impairment and psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 20: 106–118.
Newcomer JW, Krystal JH (2001). NMDA receptor regulation of memory and behavior in humans. Hippocampus 11: 529–542.
NRC (2011). National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th edn. National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA.
Nutt JG, Gunzler SA, Kirchhoff T, Hogarth P, Weaver JL, Krams M et al (2008). Effects of a NR2B selective NMDA glutamate antagonist, CP-101,606, on dyskinesia and Parkinsonism. Mov Disord 23: 1860–1866.
Okiyama K, Smith DH, White WF, Richter K, McIntosh TK (1997). Effects of the novel NMDA antagonists CP-98,113, CP-101,581 and CP-101,606 on cognitive function and regional cerebral edema following experimental brain injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma 14: 211–222.
Owen AM, Sahakian BJ, Semple J, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1995). Visuo-spatial short-term recognition memory and learning after temporal lobe excisions, frontal lobe excisions or amygdalo-hippocampectomy in man. Neuropsychologia 33: 1–24.
Passingham R (1975). Delayed matching after selective prefrontal lesions in monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Brain Res 92: 89–102.
Preskorn SH, Baker B, Kolluri S, Menniti FS, Krams M, Landen JW (2008). An innovative design to establish proof of concept of the antidepressant effects of the NR2B subunit selective N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, CP-101,606, in patients with treatment-refractory major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol 28: 631–637.
Roberts BM, Seymour PA, Schmidt CJ, Williams GV, Castner SA (2010). Amelioration of ketamine-induced working memory deficits by dopamine D1 receptor agonists. Psychopharmacology 210: 407–418.
Sanacora G, Schatzberg AF (2015). Ketamine: promising path or false prophecy in the development of novel therapeutics for mood disorders? Neuropsychopharmacology 40: 259–267.
Sanacora G, Smith MA, Pathak S, Su HL, Boeijinga PH, McCarthy DJ et al (2014). Lanicemine: a low-trapping NMDA channel blocker produces sustained antidepressant efficacy with minimal psychotomimetic adverse effects. Mol Psychiatry 19: 978–985.
Shipton OA, Paulsen O (2014). GluN2A and GluN2B subunit-containing NMDA receptors in hippocampal plasticity. Philos Trans R SocLond B Biol Sci 369: 20130163.
Smith JW, Gastambide F, Gilmour G, Dix S, Foss J, Lloyd K et al (2011). A comparison of the effects of ketamine and phencyclidine with other antagonists of the NMDA receptor in rodent assays of attention and working memory. Psychopharmacology 217: 255–269.
Taffe MA, Davis SA, Gutierrez T, Gold LH (2002a). Ketamine impairs multiple cognitive domains in rhesus monkeys. Drug Alcohol Depend 68: 175–187.
Taffe MA, Weed MR, Gutierrez T, Davis SA, Gold LH (2002b). Differential muscarinic and NMDA contributions to visuo-spatial paired-associate learning in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 160: 253–262.
Wang M, Yang Y, Wang CJ, Gamo NJ, Jin LE, Mazer JA et al (2013). NMDA receptors subserve persistent neuronal firing during working memory in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Neuron 77: 736–749.
Weed MR, Taffe MA, Polis I, Roberts AC, Robbins TW, Koob GF et al (1999). Performance norms for a rhesus monkey neuropsychological testing battery: acquisition and long-term performance. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 8: 185–201.
Zarate CA Jr., Mathews D, Ibrahim L, Chaves JF, Marquardt C, Ukoh I et al (2013). A randomized trial of a low-trapping nonselective N-methyl-D-aspartate channel blocker in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 74: 257–264.
Zhang XH, Liu SS, Yi F, Zhuo M, Li BM (2013). Delay-dependent impairment of spatial working memory with inhibition of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in hippocampal CA1 region of rats. Mol Brain 6: 13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weed, M., Bookbinder, M., Polino, J. et al. Negative Allosteric Modulators Selective for The NR2B Subtype of The NMDA Receptor Impair Cognition in Multiple Domains. Neuropsychopharmacol 41, 568–577 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.184
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.184
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor modulators in psychiatry
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Ketamine exerts neurotoxic effects on the offspring of pregnant rats via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2020)
-
Antagonism at the NR2B subunit of NMDA receptors induces increased connectivity of the prefrontal and subcortical regions regulating reward behavior
Psychopharmacology (2018)