Abstract
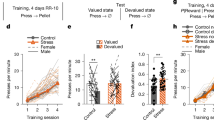
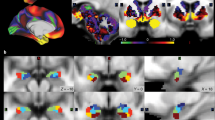
Stress is assumed to cause a shift from flexible 'cognitive' memory to more rigid 'habit' memory. In the spatial memory domain, stress impairs place learning depending on the hippocampus whereas stimulus-response learning based on the striatum appears to be improved. While the neural basis of this shift is still unclear, previous evidence in rodents points towards cortisol interacting with the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) to affect amygdala functioning. The amygdala is in turn assumed to orchestrate the stress-induced shift in memory processing. However, an integrative study testing these mechanisms in humans is lacking. Therefore, we combined functional neuroimaging of a spatial memory task, stress-induction, and administration of an MR-antagonist in a full-factorial, randomized, placebo-controlled between-subjects design in 101 healthy males. We demonstrate that stress-induced increases in cortisol lead to enhanced stimulus-response learning, accompanied by increased amygdala activity and connectivity to the striatum. Importantly, this shift was prevented by an acute administration of the MR-antagonist spironolactone. Our findings support a model in which the MR and the amygdala play an important role in the stress-induced shift towards habit memory systems, revealing a fundamental mechanism of adaptively allocating neural resources that may have implications for stress-related mental disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Acheson DT, Gresack JE, Risbrough VB (2012). Hippocampal dysfunction effects on context memory: possible etiology for posttraumatic stress disorder. Neuropharmacology 62: 674–685.
Arnsten AFT (2009). Stress signalling pathways that impair prefrontal cortex structure and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 10: 410–422.
Cornelisse S, Joels M, Smeets T (2011). A randomized trial on mineralocorticoid receptor blockade in men: effects on stress responses, selective attention, and memory. Neuropsychopharmacology 36: 2720–2728.
de Kloet ER, Joels M, Holsboer F (2005). Stress and the brain: From adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 6: 463–475.
de Oliveira AR, Reimer AE, Brandão ML (2014). Mineralocorticoid receptors in the ventral tegmental area regulate dopamine efflux in the basolateral amygdala during the expression of conditioned fear. Psychoneuroendocrinology 43: 114–125.
Doeller CF, Burgess N (2008a). Distinct error-correcting and incidental learning of location relative to landmarks and boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105: 5909–5914.
Doeller CF, King JA, Burgess N (2008b). Parallel striatal and hippocampal systems for landmarks and boundaries in spatial memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 5915–5920.
Elliott AE, Packard MG (2008). Intra-amygdala anxiogenic drug infusion prior to retrieval biases rats towards the use of habit memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90: 616–623.
Henckens M, van Wingen GA, Joels M, Fernandez G (2010). Time-dependent effects of corticosteroids on human amygdala processing. J Neurosci 30: 12725–12732.
Henckens MJAG, van Wingen GA, Joëls M, Fernández G (2012). Corticosteroid induced decoupling of the amygdala in men. Cereb Cortex 22: 2336–2345.
Herman CP, Polivy J (1975). Anxiety, restraint, and eating behavior. J Abnorm Psychol 84: 666–672.
Hermans EJ, Battaglia FP, Atsak P, de Voogd LD, Fernández G, Roozendaal B (2014). How the amygdala affects emotional memory by altering brain network properties. Neurobiol Learn Mem 37: 304–314.
Iaria G, Petrides M, Dagher A, Pike B, Bohbot VD (2003). Cognitive strategies dependent on the hippocampus and caudate nucleus in human navigation: variability and change with practice. J Neurosci 23: 5945–5952.
Joëls M, Baram TZ (2009). The neuro-symphony of stress. Nat Rev Neurosci 10: 459–466.
Joëls M, Fernandez G, Roozendaal B (2011). Stress and emotional memory: a matter of timing. Trends Cogn Sci 15: 280–288.
Joëls M, Sarabdjitsingh RA, Karst H (2012). Unraveling the time domains of corticosteroid hormone influences on brain activity: rapid, slow, and chronic modes. Pharmacol Rev 64: 901–938.
Karst H, Berger S, Erdmann G, Schutz G, Joels M (2010). Metaplasticity of amygdalar responses to the stress hormone corticosterone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 14449–14454.
Kim JJ, Lee HJJ, Han JS, Packard MG (2001). Amygdala is critical for stress-induced modulation of hippocampal long-term potentiation and learning. J Neurosci 21: 5222–5228.
Morris RGM, Garrud P, Rawlins JNP, O'Keefe J (1982). Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 297: 681–683.
Otte C, Moritz S, Yassouridis A, Koop M, Madrischewski AM, Wiedemann K et al (2007). Blockade of the mineralocorticoid receptor in healthy men: Effects on experimentally induced panic symptoms, stress hormones, and cognition. Neuropsychopharmacology 32: 232–238.
Otto AR, Raio CM, Chiang A, Phelps EA, Daw ND (2013). Working-memory capacity protects model-based learning from stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110: 20941–20946.
Packard MG, Teather LA (1998). Amygdala modulation of multiple memory systems: hippocampus and caudate-putamen. Neurobiol Learn Mem 69: 163–203.
Packard MG, Wingard JC (2004). Amygdala and ‘emotional’ modulation of the relative use of multiple memory systems. Neurobiol Learn Mem 82: 243–252.
Porcelli AJ, Delgado MR (2009). Acute stress modulates risk taking in financial decision making. Psychol Sci 20: 278–283.
Pruessner JC, Kirschbaum C, Meinlschmid G, Hellhammer DH (2003). Two formulas for computation of the area under the curve represent measures of total hormone concentration versus time-dependent change. Psychoneuroendocrinology 28: 916–931.
Qian X, Droste SK, Gutièrrez-Mecinas M, Collins A, Kersanté F, JMHM Reul et al (2011). A rapid release of corticosteroid-binding globulin from the liver restrains the glucocorticoid hormone response to acute stress. Endocrinology 152: 3738–3748.
Schane HP, Potts GO (1978). Oral progestational activity of spironolactone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 47: 691–694.
Schwabe L, Dalm S, Schachinger H, Oitzl MS (2008a). Chronic stress modulates the use of spatial and stimulus-response learning strategies in mice and man. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90: 495–503.
Schwabe L, Haddad L, Schachinger H (2008b). HPA axis activation by a socially evaluated cold-pressor test. Psychoneuroendocrinology 33: 890–895.
Schwabe L, Höffken O, Tegenthoff M, Wolf OT (2011). Preventing the stress-induced shift from goal-directed to habit action with a β-adrenergic antagonist. J Neurosci 31: 17317–17325.
Schwabe L, Oitzl MS, Philippsen C, Richter S, Bohringer A, Wippich W et al (2007). Stress modulates the use of spatial versus stimulus-response learning strategies in humans. Learn Mem 14: 109–116.
Schwabe L, Schachinger H, de Kloet ER, Oitzl MS (2010). Corticosteroids operate as a switch between memory systems. J Cogn Neurosci 22: 1362–1372.
Schwabe L, Tegenthoff M, Höffken O, Wolf OT (2013a). Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade prevents stress-induced modulation of multiple memory systems in the human brain. Biol Psychiatry 74: 801–808.
Schwabe L, Wolf OT (2013b). Stress and multiple memory systems: from ‘thinking’ to ‘doing’. Trends Cogn Sci 17: 60–68.
Taube JS (1998). Head direction cells and the neurophysiological basis for a sense of direction. Prog Neurobiol 55: 225–256.
Ter Horst JP, Kentrop J, Arp M, Hubens CJ, de Kloet ER, Oitzl MS (2013). Spatial learning of female mice: a role of the mineralocorticoid receptor during stress and the estrous cycle. Front Behav Neurosci 7: 56.
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N et al (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15: 273–289.
van Ast VA, Cornelisse S, Meeter M, Joels M, Kindt M (2013). Time-dependent effects of cortisol on the contextualization of emotional memories. Biol Psychiatry 74: 809–816.
van Marle HJF, Hermans EJ, Qin SZ, Fernandez G (2010). Enhanced resting-state connectivity of amygdala in the immediate aftermath of acute psychological stress. Neuroimage 53: 348–354.
Vogel S, Klumpers F, Kroes MC, Oplaat KT, Krugers HJ, Oitzl MS et al (2015a). A stress-induced shift from trace to delay conditioning depends on the mineralocorticoid receptor. Biol Psychiatry 78: 830–839.
Vogel S, Klumpers F, Krugers HJ, Fang Z, Oplaat KT, Oitzl MS et al (2015b). Blocking the mineralocorticoid receptor in humans prevents the stress-induced enhancement of centromedial amygdala connectivity with the dorsal striatum. Neuropsychopharmacology 40: 947–956.
Weiss F, Ciccocioppo R, Parsons LH, Katner S, Liu XIU, Zorrilla EP et al (2001). Compulsive drug-seeking behavior and relapse. Ann N Y Acad Sci 937: 1–26.
Wilton LA, Baird AL, Muir JL, Honey RC, Aggleton JP (2001). Loss of the thalamic nuclei for ‘head direction’ impairs performance on spatial memory tasks in rats. Behav Neurosci 115: 861–869.
Wingard JC, Packard MG (2008). The amygdala and emotional modulation of competition between cognitive and habit memory. Behav Brain Res 193: 126–131.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Sabine Kooijman, Sanne Tops, Monique H.M. Timmer, Dirk Geurts, Niels ter Huurne, Atsuko Takashima, and Daphne Everaerd for their help acquiring data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Methods and Results accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vogel, S., Klumpers, F., Schröder, T. et al. Stress Induces a Shift Towards Striatum-Dependent Stimulus-Response Learning via the Mineralocorticoid Receptor. Neuropsychopharmacol 42, 1262–1271 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2016.262
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2016.262
This article is cited by
-
Brain activation and heart rate variability as markers of autonomic function under stress
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Stress-related cellular pathophysiology as a crosstalk risk factor for neurocognitive and psychiatric disorders
BMC Neuroscience (2023)
-
Glucocorticoids and cognitive function: a walkthrough in endogenous and exogenous alterations
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2023)
-
Chronic stress causes striatal disinhibition mediated by SOM-interneurons in male mice
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Interactive relations between maternal prenatal stress, fetal brain connectivity, and gestational age at delivery
Neuropsychopharmacology (2021)