Abstract
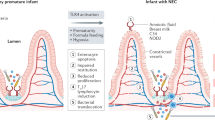
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is the leading cause of death from gastrointestinal disease in the preterm infant. The dismal results of current treatment for NEC highlight the urgent need for greater understanding of the pathogenesis of this disease, and the importance of discovering novel, molecular-specific therapies for it. Current dogma indicates that NEC development reflects an abnormal response by the premature infant to the microbial flora that colonizes the gastrointestinal tract, although the mechanisms that mediate these abnormal bacterial-enterocyte interactions and the reasons for the particularly increased susceptibility of the premature infant to the development of NEC remain incompletely explained. Recent evidence has shed light on an emerging role for the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) of the innate immune system as central players in the pathways that signal in response to enteric bacteria resulting in the development of NEC. We now review recent advances in the field of NEC and identify several exciting potential avenues for novel treatments by focusing on abnormal TLR4 signaling in the premature intestine in the pathogenesis of NEC. In so doing, we seek to offer new hope to the patients and their families who are affected by this devastating disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- NEC:
-
necrotizing enterocolitis
- PAF:
-
platelet-activating factor
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
References
Luig M, Lui K, NSW & ACT NICUS Group 2005 Epidemiology of necrotizing enterocolitis—part I: changing regional trends in extremely preterm infants over 14 years. J Paediatr Child Health 41: 169–173
Gagliardi L, Bellu R, Cardilli V, De Curtis M, Network Neonatale Lombardo 2008 Necrotising enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants in Italy: incidence and non-nutritional risk factors. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 47: 206–210
Mizrahi A, Barlow O, Berdon W, Blanc WA, Silverman WA 1965 Necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants. J Pediatr 66: 697–705
Blakely ML, Lally KP, McDonald S, Brown RL, Barnhart DC, Ricketts RR, Thompson WR, Scherer LR, Klein MD, Letton RW, Chwals WJ, Touloukian RJ, Kurkchubasche AG, Skinner MA, Moss RL, Hilfiker ML; Network NECSotNNR 2005 Postoperative outcomes of extremely low birth-weight infants with necrotizing enterocolitis or isolated intestinal perforation: a prospective cohort study by the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Ann Surg 241: 984–989; discussion 989–994.
Lin HC, Su BH, Chen AC, Lin TW, Tsai CH, Yeh TF, Oh W 2005 Oral probiotics reduce the incidence and severity of necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 115: 1–4
Grave GD, Nelson SA, Walker WA, Moss RL, Dvorak B, Hamilton FA, Higgins R, Raju TN 2007 New therapies and preventive approaches for necrotizing enterocolitis: report of a research planning workshop. Pediatr Res 62: 510–514
Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R 2010 Regulation of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Science 327: 291–295
Wynn J, Cornell TT, Wong HR, Shanley TP, Wheeler DS 2010 The host response to sepsis and developmental impact. Pediatrics 125: 1031–1041
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA Jr 1997 A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature 388: 394–397
Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA 1996 The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spätzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell 86: 973–983
Roach JC, Glusman G, Rowen L, Kaur A, Purcell MK, Smith KD, Hood LE, Aderem A 2005 The evoluation of vertebrate Toll-like receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 9577–9582
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B 1998 Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 282: 2085–2088
Hotta T, Yoshida N, Yoshikawa T, Sugino S, Kondo M 1986 Lipopolysaccharide-induced colitis in rabbits. Res Exp Med (Berl) 186: 61–69
Feng J, El-Assal ON, Besner GE 2005 Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg 14: 167–174
Feng J, Besner GE 2007 Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor promotes enterocyte migration and proliferation in neonatal rats with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 42: 214–220
Kruis W, Schussler P, Weinzierl M, Galanos C, Eisenburg J 1984 Circulating lipid A antibodies despite absence of systemic endotoxemia in patients with Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci 29: 502–507
Caradonna L, Amati L, Lella P, Jirillo E, Caccavo D 2000 Phagocytosis, killing, lymphocyte-mediated antibacterial activity, serum autoantibodies, and plasma endotoxins in inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 95: 1495–1502
Noerr B 2003 Current controversies in the understanding of necrotizing enterocolitis. Adv Neonatal Care 3: 107–120
Sharma R, Tepas JJ III, Hudak ML, Mollitt DL, Wludyka PS, Teng RJ, Premachandra BR 2007 Neonatal gut barrier and multiple organ failure: role of endotoxin and proinflammatory cytokines in sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 42: 454–461
Duffy LC, Zielezny MA, Carrion V, Griffiths E, Dryja D, Hilty M, Rook C, Morin F III 1997 Concordance of bacterial cultures with endotoxin and interleukin-6 in necrotizing enterocolitis. Dig Dis Sci 42: 359–365
Leaphart CL, Cavallo JC, Gribar SC, Cetin S, Li J, Branca MF, Dubowski TD, Sodhi CP, Hackam DJ 2007 A critical role for TLR4 in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis by modulating intestinal injury and repair. J Immunol 179: 4808–4820
Jilling T, Simon D, Lu J, Meng FJ, Li D, Schy R, Thomson RB, Soliman A, Arditi M, Caplan MS 2006 The roles of bacteria and TLR4 in rat and murine models of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Immunol 177: 3273–3282
Chan KL, Wong KF, Luk JM 2009 Role of LPS/CD14/TLR4-mediated inflammation in necrotizing enterocolitis: pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. World J Gastroenterol 15: 4745–4752
Richardson WM, Sodhi CP, Russo A, Siggers RH, Afrazi A, Gribar SC, Neal MD, Dai S, Prindle TJ, Branca M, Ma C, Ozolek J, Hackam DJ 2010 Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-2 inhibits Toll like receptor-4 signaling in the intestinal epithelium. Gastroenterology 139: 904–917
Sodhi CP, Shi XH, Richardson WM, Grant ZS, Shapiro RA, Prindle TJ, Branca M, Russo A, Gribar SC, Ma C, Hackam DJ 2010 Toll-like receptor-4 inhibits enterocyte proliferation via impaired beta-catenin signaling in necrotizing enterocolitis. Gastroenterology 138: 185–196
Qureshi FG, Leaphart C, Cetin S, Li J, Grishin A, Watkins S, Ford HR, Hackam DJ 2005 Increased expression and function of integrins in enterocytes by endotoxin impairs epithelial restitution. Gastroenterology 128: 1012–1022
Wolfs TG, Derikx JP, Hodin CM, Vanderlocht J, Driessen A, de Bruïne AP, Bevins CL, Lasitschka F, Gassler N, van Gemert WG, Buurman WA 2010 Localization of the lipopolysaccharide recognition complex in the human healthy and inflamed premature and adult gut. Inflamm Bowel Dis 16: 68–75
Liu Y, Zhu L, Fatheree NY, Liu X, Pacheco SE, Tatevian N, Rhoads JM 2009 Changes in intestinal Toll-like receptors and cytokines precede histological injury in a rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297: G442–G450
Lu J, Jilling T, Li D, Caplan MS 2007 Polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation alters proinflammatory gene expression and reduces the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in a neonatal rat model. Pediatr Res 61: 427–432
Cetin S, Ford HR, Sysko LR, Agarwal C, Wang J, Neal MD, Baty C, Apodaca G, Hackam DJ 2004 Endotoxin inhibits intestinal epithelial restitution through activation of Rho-GTPase and increased focal adhesions. J Biol Chem 279: 24592–24600
Dai S, Sodhi CP, Cetin S, Richardson W, Branca M, Neal MD, Prindle T, Ma C, Shapiro RA, Li B, Wang JH, Hackam DJ 2010 Extracellular high mobility group box1 (HMGB1) inhibits enterocyte migration via activation of Toll like receptor 4 and increased cell-matrix adhesiveness. J Biol Chem 285: 4995–5002
Zheng L, Riehl TE, Stenson WF 2009 Regulation of colonic epithelial repair in mice by Toll-like receptors and hyaluronic acid. Gastroenterology 137: 2041–2051
Fukata M, Chen A, Klepper A, Krishnareddy S, Vamadevan AS, Thomas LS, Xu R, Inoue H, Arditi M, Dannenberg AJ, Abreu MT 2006 Cox-2 is regulated by Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) signaling: role in proliferation and apoptosis in the intestine. Gastroenterology 131: 862–877
Fukata M, Michelsen KS, Eri R, Thomas LS, Hu B, Lukasek K, Nast CC, Lechago J, Xu R, Naiki Y, Soliman A, Arditi M, Abreu MT 2005 Toll-like receptor-4 is required for intestinal response to epithelial injury and limiting bacterial translocation in a murine model of acute colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288: G1055–G1065
Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S, Medzhitov R 2004 Recognition of commensal microflora by Toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell 118: 229–241
Fukata M, Hernandez Y, Conduah D, Cohen J, Chen A, Breglio K, Goo T, Hsu D, Xu R, Abreu MT 2009 Innate immune signaling by Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) shapes the inflammatory microenvironment in colitis-associated tumors. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15: 997–1006
Lotz M, Gutle D, Walther S, Menard S, Bogdan C, Hornef MW 2006 Postnatal acquisition of endotoxin tolerance in intestinal epithelial cells. J Exp Med 203: 973–984
Wang J, Ford HR, Grishin AV 2010 NF-kappaB-mediated expression of MAPK phosphatase-1 is an early step in desensitization to TLR ligands in enterocytes. Mucosal Immunol 3: 523–534
Wang J, Ouyang Y, Guner Y, Ford HR, Grishin AV 2009 Ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 promotes tolerance to lipopolysaccharide in enterocytes. J Immunol 183: 1384–1392
Gribar SC, Sodhi CP, Richardson WM, Anand RJ, Gittes GK, Branca MF, Jakub A, Shi XH, Shah S, Ozolek JA, Hackam DJ 2009 Reciprocal expression and signaling of TLR4 and TLR9 in the pathogenesis and treatment of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Immunol 182: 636–646
Borzutzky A, Fried A, Chou J, Bonilla FA, Kim S, Dedeoglu F 2010 NOD2-associated diseases: bridging innate immunity and autoinflammation. Clin Immunol 134: 251–261
Shindou H, Ishii N, Uozumi T, Shimizu T 2000 Roles of cytosolic phospholipase A2 and platelet-activating factor receptor in the Ca-induced biosynthesis of PAF. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 271: 812–817
Svetlov SI, Liu H, Chao W, Olson MS 1997 Regulation of platelet-activating factor (PAF) biosynthesis via coenzyme A-independent transacylase in the macrophage cell line IC-21 stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1346: 120–130
Izumi T, Shimizu T 1995 Platelet-activating factor receptor: gene expression and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta 1259: 317–333
Muguruma K, Gray PW, Tjoelker LW, Johnston JM 1997 The central role of PAF in necrotizing enterocolitis development. Adv Exp Med Biol 407: 379–382
Amer MD, Hedlund E, Rochester J, Caplan MS 2004 Platelet-activating factor concentration in the stool of human newborns: effects of enteral feeding and neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Biol Neonate 85: 159–166
Caplan MS, Hedlund E, Adler L, Lickerman M, Hsueh W 1997 The platelet activating factor receptor antagonist WEB 2170 prevents neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis in rats. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 24: 296–301
Caplan MS, Lickerman M, Adler L, Dietsch GN, Yu A 1997 The role of recombinant platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase in a neonatal rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Res 42: 779–783
Worthen GS, Seccombe JF, Clay KL, Guthrie LA, Johnston RB Jr 1988 The priming of neutrophils by lipopolysaccharide for production of intracellular platelet-activating factor: potential role in mediation of enhanced superoxide secretion. J Immunol 140: 3553–3559
Milla PJ, Fenton TR 1983 Small intestinal motility patterns in the perinatal period. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2: S141–S144
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Grants DK083752 and GM078238 from the National Institutes of Health and The Hartwell Foundation, Memphis, TN.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afrazi, A., Sodhi, C., Richardson, W. et al. New Insights Into the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Toll-Like Receptors and Beyond. Pediatr Res 69, 183–188 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182093280
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182093280
This article is cited by
-
IL-17-related signature genes linked to human necrotizing enterocolitis
BMC Research Notes (2021)
-
Sialylated human milk oligosaccharides prevent intestinal inflammation by inhibiting toll like receptor 4/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in necrotizing enterocolitis rats
Nutrition & Metabolism (2021)
-
Surfactant protein A reduces TLR4 and inflammatory cytokine mRNA levels in neonatal mouse ileum
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Irf5 deficiency in myeloid cells prevents necrotizing enterocolitis by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization
Mucosal Immunology (2019)
-
Single-Immunoglobulin Interleukin-1-Related Receptor regulates vulnerability to TLR4-mediated necrotizing enterocolitis in a mouse model
Pediatric Research (2018)