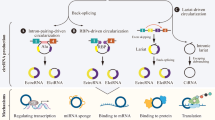
Abstract
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a malignant tumor of the head and neck with a high prevalence in Southeast Asia. Although radiotherapy remains the primary treatment modality, resistance to radiation in a subset of patients with advanced-stage disease significantly limits therapeutic outcomes, and the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. In this study, we identified the circular RNA circSETD3 as a critical regulator of radioresistance in NPC. Functional assays in both in vitro and in vivo models demonstrated that circSETD3 enhances radioresistance by suppressing autophagy and apoptosis. Mechanistically, circSETD3 binds to the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of PDIA6 mRNA, stabilizing the transcript and increasing PDIA6 protein expression and its localization to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Elevated PDIA6 promotes the refolding of radiation-induced misfolded proteins, maintains ER proteostasis, and suppresses the unfolded protein response (UPR). This alleviation of ER stress reduces radiation-induced autophagy and apoptosis, ultimately enhancing NPC cell survival under radiotherapeutic stress. Together, these findings reveal a pivotal role for circSETD3 in promoting NPC radioresistance via PDIA6-mediated modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress, and they provide a novel mechanistic framework and promising therapeutic target for improving radiotherapy efficacy in NPC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Tang LL, Chen YP, Chen CB, Chen MY, Chen NY, Chen XZ, et al. The Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Commun. 2021;41:1195–227.
Chen LL. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21:475–90.
Qu H, Wang Y, Yan Q, Fan C, Zhang X, Wang D, et al. CircCDYL2 bolsters radiotherapy resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by promoting RAD51 translation initiation for enhanced homologous recombination repair. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024;43:122.
Wang D, Tang L, Chen M, Gong Z, Fan C, Qu H, et al. Nanocarriers targeting circular RNA ADARB1 boost radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through synergically promoting ferroptosis. ACS Nano. 2024;18:31055–75.
Ge J, Meng Y, Guo J, Chen P, Wang J, Shi L, et al. Human papillomavirus-encoded circular RNA circE7 promotes immune evasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2024;15:8609.
Wang D, Zuo S, Ge J, Qu H, Wu J, Yi N, et al. circTP63-N suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via engaging with HSP90AB1 to modulate the YAP1/Hippo signaling pathway. Sci China Life Sci. 2025;68:689–705.
Peng M, Zhang S, Wu P, Hou X, Wang D, Ge J, et al. Circular RNA circCLASP2 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression through binding to DHX9 to enhance PCMT1 translation. Mol cancer. 2025;24:67.
Fan C, Tan F, Wu J, Zeng Z, Guo W, Huang H, et al. CircCCNB1 inhibits vasculogenic mimicry by sequestering NF90 to promote miR-15b-5p and miR-7-1-3p processing in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 2025;19:1876–93.
Yang Y, Wang Y, Qu H, Wang D, Ge J, Wu P, et al. CircCDYL promotes glycolysis to drive the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Adv Res. 2025;26:S2090–1232.
Wang D, Mendoza JJ, Xiang P, Zhang Y, Tang L, Zhang J, et al. circADARB1 enhances ZEB1 expression in an m(6)A-dependent manner to promote the invasion and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025;318:145187.
Zeng H, Ge J, Meng Y, Wang Q, Yang M, Zeng Z, et al. Research progress on the role and mechanism of circular RNA in drug resistance of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024;7:31.
Tang L, Xiong W, Zhang L, Wang D, Wang Y, Wu Y, et al. circSETD3 regulates MAPRE1 through miR-615-5p and miR-1538 sponges to promote migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene. 2021;40:307–21.
Lv X, Lu X, Cao J, Luo Q, Ding Y, Peng F, et al. Modulation of the proteostasis network promotes tumor resistance to oncogenic KRAS inhibitors. Science. 2023;381:eabn4180.
Wu Y, Song Y, Wang R, Wang T. Molecular mechanisms of tumor resistance to radiotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2023;22:96.
Bai Y, Liu X, Qi X, Liu X, Peng F, Li H, et al. PDIA6 modulates apoptosis and autophagy of non-small cell lung cancer cells via the MAP4K1/JNK signaling pathway. EBioMedicine. 2019;42:311–25.
Lee S, Min Kim S, Dotimas J, Li L, Feener EP, Baldus S, et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein regulates protein disulfide isomerases and endoplasmic reticulum stress. EMBO Mol Med. 2014;6:732–43.
Mestre-Farràs N, Guerrero S, Bley N, Rivero E, Coll O, Borràs E, et al. Melanoma RBPome identification reveals PDIA6 as an unconventional RNA-binding protein involved in metastasis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:8207–25.
Rosell R, Karachaliou N. Disulfide isomerase family-6 mediates cisplatin resistance by interfering with apoptosis and autophagy. EBioMedicine. 2019;42:20–21.
Tufo G, Jones AW, Wang Z, Hamelin J, Tajeddine N, Esposti DD, et al. The protein disulfide isomerases PDIA4 and PDIA6 mediate resistance to cisplatin-induced cell death in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21:685–95.
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, Mo Y, Fan C, Xiong F, et al. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:79.
Yang X, Yang Y, Sun BF, Chen YS, Xu JW, Lai WY, et al. 5-methylcytosine promotes mRNA export - NSUN2 as the methyltransferase and ALYREF as an m(5)C reader. Cell Res. 2017;27:606–25.
Warminski M, Mamot A, Depaix A, Kowalska J, Jemielity J. Chemical modifications of mRNA ends for therapeutic applications. Acc Chem Res. 2023;56:2814–26.
Chen X, Cubillos-Ruiz JR. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21:71–88.
Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:89–102.
Marciniak SJ, Chambers JE, Ron D. Pharmacological targeting of endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022;21:115–40.
Oakes SA, Papa FR. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol. 2015;10:173–94.
Salaroglio IC, Panada E, Moiso E, Buondonno I, Provero P, Rubinstein M, et al. PERK induces resistance to cell death elicited by endoplasmic reticulum stress and chemotherapy. Mol cancer. 2017;16:91.
Ngo LH, Bert AG, Dredge BK, Williams T, Murphy V, Li W, et al. Nuclear export of circular RNA. Nature. 2024;627:212–20.
Liu D, Dredge BK, Bert AG, Pillman KA, Toubia J, Guo W, et al. ESRP1 controls biogenesis and function of a large abundant multiexon circRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;52:1387–403.
Liang Y, Cen J, Huang Y, Fang Y, Wang Y, Shu G, et al. CircNTNG1 inhibits renal cell carcinoma progression via HOXA5-mediated epigenetic silencing of Slug. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:224.
Xu L, Feng X, Hao X, Wang P, Zhang Y, Zheng X, et al. CircSETD3 (Hsa_circ_0000567) acts as a sponge for microRNA-421 inhibiting hepatocellular carcinoma growth. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:98.
Huang Y, Dai Y, Wen C, He S, Shi J, Zhao D, et al. circSETD3 contributes to acquired resistance to gefitinib in non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting the miR-520h/ABCG2 pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:885–99.
Tian Y, Gao P, Dai D, Chen L, Chu X, Mei X. Circular RNA circSETD3 hampers cell growth, migration, and stem cell properties in bladder cancer through sponging miR-641 to upregulate PTEN. Cell Cycle. 2021;20:1589–602.
Chen Q, Deng Q, Pan Y, Ding X, Liu J. Hypoxia-induced miR-653 enhances colorectal cancer progression by targeting circSETD3/KLF6 axis. J Cancer. 2023;14:163–73.
Fessart D, Robert J, Hartog C, Chevet E, Delom F, Babin G. The Anterior GRadient (AGR) family proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40:271.
Shergalis AG, Hu S, Bankhead A 3rd, Neamati N. Role of the ERO1-PDI interaction in oxidative protein folding and disease. Pharm Ther. 2020;210:107525.
Duncan RM, Reyes L, Moats K, Robinson RM, Murphy SA, Kaur B, et al. ATF3 coordinates antitumor synergy between epigenetic drugs and protein disulfide isomerase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2020;80:3279–91.
Liu Y, Ji W, Shergalis A, Xu J, Delaney AM, Calcaterra A, et al. Activation of the unfolded protein response via inhibition of protein disulfide isomerase decreases the capacity for DNA repair to sensitize glioblastoma to radiotherapy. Cancer Res. 2019;79:2923–32.
Ma Y, Liu E, Fan H, Li C, Huang P, Cui M, et al. RBM47 promotes cell proliferation and immune evasion by upregulating PDIA6: a novel mechanism of pancreatic cancer progression. J Transl Med. 2024;22:1164.
Wu P, Zhang H, Qi L, Tang Q, Tang Y, Xie Z, et al. Identification of ERp29 as a biomarker for predicting nasopharyngeal carcinoma response to radiotherapy. Oncol Rep. 2012;27:987–94.
Niu X, You Q, Hou K, Tian Y, Wei P, Zhu Y, et al. Autophagy in cancer development, immune evasion, and drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2025;78:101170.
Wang Z, Ren X, Li Y, Qiu L, Wang D, Liu A, et al. Reactive oxygen species amplifier for apoptosis-ferroptosis mediated high-efficiency radiosensitization of tumors. ACS Nano. 2024;18:10288–301.
Mizushima N, Levine B. Autophagy in human diseases. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1564–76.
Debnath J, Gammoh N, Ryan KM. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24:560–75.
Wang L, Klionsky DJ, Shen HM. The emerging mechanisms and functions of microautophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24:186–203.
Mace PD, Day CL. A massive machine regulates cell death. Science. 2023;379:1093–4.
Yuan J, Ofengeim D. A guide to cell death pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25:379–95.
Czabotar PE, Garcia-Saez AJ. Mechanisms of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24:732–48.
Liu K, Chen H, Li Y, Wang B, Li Q, Zhang L, et al. Autophagy flux in bladder cancer: cell death crosstalk, drug and nanotherapeutics. Cancer Lett. 2024;591:216867.
Urra H, Dufey E, Avril T, Chevet E, Hetz C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the hallmarks of cancer. Trends Cancer. 2016;2:252–62.
Meng B, Xu M, Chen Z, You J, Zhou R, Guan J, et al. SIRT7 sustains tumor development and radioresistance by repressing endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in cutaneous melanoma. Cell Signal. 2024;116:111058.
Song L, Liu H, Ma L, Zhang X, Jiang Z, Jiang C. Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA enhances endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 2013;6:1031–8.
Zheng X, Jin X, Liu X, Liu B, Li P, Ye F, et al. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced autophagy promotes the killing effect of X-rays on sarcoma in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;522:612–7.
Feng X, Lv W, Wang S, He Q. miR‑495 enhances the efficacy of radiotherapy by targeting GRP78 to regulate EMT in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2018;40:1223–32.
Eletto D, Eletto D, Dersh D, Gidalevitz T, Argon Y. Protein disulfide isomerase A6 controls the decay of IRE1α signaling via disulfide-dependent association. Mol Cell. 2014;53:562–76.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge BioRender (www.biorender.com) for the creation of Fig. 7C.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82503155, 82472711, 82302979 and U21A20382), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2025JJ60500, 2025JJ20099, 2025JJ50590 and 2024JJ3036), the Key Research Development Program of Hunan Province (2024PT5102 and 2024DK2007) and the Central South University Graduate Research and Innovation Project (2024ZZTS0859).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WX and DW conceived and designed the project. PX completed most experiments and wrote the manuscript. LT, YZ, and JJM performed some of the experiments. QY and LS collected tissue samples. BX and ZZ revised the manuscript. PC performed the data analysis. DW and WX are responsible for research supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, P., Tang, L., Zhang, Y. et al. circSETD3 confers radiotherapy resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by attenuating ER stress-induced autophagy and apoptosis via PDIA6 upregulation. Oncogene 45, 368–382 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03652-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03652-1