Abstract
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) play important roles in human physiology. GPCRs are involved in immunoregulation including regulation of the inflammatory response. Chemotaxis of phagocytes and lymphocytes is mediated to a great extent by the GPCRs for chemoattractants including myriads of chemokines. Accumulation and activation of phagocytes at the site of inflammation contribute to local inflammatory response. A handful of GPCRs have been found to transduce anti-inflammatory signals that promote resolution of inflammation. These GPCRs interact with selected metabolites of arachdonic acid, such as lipoxins, and of omega-3 essential fatty acids, such as resolvins and protectins. Despite mounting evidence for the in vivo functions of these anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving ligands paired with their respective GPCRs, the underlying signaling mechanisms have not been fully delineated. The present review summarizes what we have learned about these GPCRs, their structures and signaling pathways and the prospect of targeting these receptors for novel anti-inflammatory therapies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Inflammation is a self-limiting process consisting of an initiation phase marked by capillary dilatation, leukocytic infiltration, and inflammatory mediator production, followed by the cessation of microvasculature dilation, reduction in inflammatory mediator generation and, finally, the removal of infiltrated neutrophils, which is termed the resolution phase [1]. The resolution of inflammation was initially considered a passive process, but in the past two decades, evidence has emerged indicating that the resolution of inflammation is an active process driven by active mediators that promote the reestablishment of homeostasis in inflamed tissue [2]. Anti-inflammatory therapies have been traditionally focused on the interruption of proinflammatory factor production, involving, for example, the inhibition of key enzymes, such as cyclooxygenases that are critical for the generation of proinflammatory prostanoids [3]. With the understanding that anti-inflammation and pro-resolution functions are actively orchestrated through special ligands and receptors, the usual strategy of antagonizing receptors of chemoattractants, such as leukotrienes is now complemented with the activation of pro-resolving signaling pathways through a selective set of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) with pro-resolving ligands. This article provides a brief review of the roles of these GPCRs in anti-inflammatory vs. pro-resolving signaling, with a major focus on formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2).
Anti-inflammatory vs. pro-resolving activities through GPCRs
GPCRs constitute the largest family of cell surface receptors, with more than 800 identified members in humans [4]. GPCR signaling establishes important physiological functions such as vision, olfaction, taste, neurotransmission, and immunity. Immune cells such as phagocytes and lymphocytes express a large number of Gi-coupled GPCRs that mediate directed migration of these highly mobile cells to tissues, where they eliminate invading microorganisms and attach to infected cells [5]. Major signaling pathways downstream of these GPCRs lead to the suppression of intracellular cAMP accumulation, generation of key second messengers, such as inositol phosphates and calcium ions, and reorganization of the cytoskeleton (Fig. 1). Through chemotaxis, these signaling events lead to the recruitment of leukocytes to the inflammation site, where the cells contribute to the inflammatory response by producing arachidonic acid (AA) and, in specialized cells such as phagocytes, releasing proteolytic enzymes stored in granules, and generating reactive oxygen species [6]. The pharmacological blockade of receptors for classic chemoattractants (e.g., leukotriene B4, C5a, and formylated peptides) and chemokines (e.g., CXCL8 and CCL2) prevents the accumulation and activation of leukocytes, thereby reducing inflammation. Inhibition of cyclooxygenases also reduces the production of inflammatory prostanoids such as prostaglandin D2 and E2 [7]. All chemotactic GPCRs identified thus far are able to couple to the Gi class of heterotrimeric G proteins. Upon agonist binding, the Giα subunits separate from the Gβγ subunits, resulting in the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by the Giα protein subunits and activation of the phospholipase Cβ pathway by the Gβγ subunits. The activation of phospholipase Cβ leads to the accumulation of inositol phosphate IP3 and diacylglycerol. These second messengers, along with the subsequently released Ca2+ from intracellular stores, stimulate the activation of conventional PKC, which is required for the activation of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase (Nox2) for generating superoxide. In addition, Ca2+ flux is required for granule enzyme release. In comparison, the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by activated Giα subunits results in reduced cellular cAMP concentration [6]. Since cAMP is well known for its inhibitory effect on NF-κB activation, which is critical for the transcription of a plethora of proinflammatory cytokine genes [8, 9], a reduction in cAMP level facilitates NF-κB activation and favors the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. GPCR-dependent activation of NF-κB has been well documented and is known to contribute to the inflammatory response [10, 11]. Taken together, the activation of Gi-coupled chemotactic receptors generates an overall proinflammatory effect through multiple signaling pathways (Fig. 1).
Proinflammatory ligands of FPR2 (e.g., SAA and WKYMVm) activate FPR2 signaling mainly through the Gi class of heterotrimeric G proteins. Upon separation, the Giα and Gβγ subunits activate two different pathways, leading to reduced cAMP accumulation and enhanced activities of the small GTPases Rac, ERK, and PKC; these signaling molecules contribute to the production of reactive oxygen radicals. Release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores is key to the degranulation of neutrophils, whereas Rac is critical to both oxidant production and the chemotaxis of leukocytes. Since cAMP inhibits NF-κB, which is critical for the induced expression of many inflammatory cytokines [8, 9], a reduced cAMP level contributes to increased inflammatory cytokine production. Solid arrows indicate established signaling pathways, while dashed arrows indicate proposed signaling pathways.
Whereas intervention of proinflammatory signaling has been a mainstream approach to anti-inflammatory therapy, the recent identification of a class of lipid mediators with pro-resolving activities has led to a new proposal suggesting that the resolution of inflammation is an active process driven by special ligands. Through work conducted in the past three decades, a major class of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) was identified. These SPMs are lipids derived from essential fatty acids such as AA, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), including the AA metabolites lipoxins (LXs) and aspirin-triggered lipoxins (ATLs), and the EPA and DHA metabolites resolvins, protectins, and maresins [12]. A large number of published reports documented the in vivo functions of these SPMs in various models of acute and chronic inflammatory diseases [2]. By definition, pro-resolving action is not equivalent to the anti-inflammatory process because specialized mediators serve as ligands to activate the nonphlogistic responses of macrophages to promote the resolution of inflammation and repair of tissue. An example of this pro-resolving response is efferocytosis, which refers to macrophage phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils in this context. Removal of excess neutrophils is necessary for healing and tissue repair. The transition of the macrophage M1 phenotype to the M2 phenotype, which favors efferocytosis, has been associated with several SPMs [13]. IL-10 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine with important functions in limiting inflammation [14]. Increased IL-10 production has been reported in cells stimulated with some SPMs [2]. Of interest, several GPCRs in the class A subfamily have been associated with the functions of SPMs (Table 1). Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) and its aspirin-triggered analog 15-epi-LXA4 (an ATL) are known ligands of FPR2 [15, 16], which also binds proinflammatory agonists such as serum amyloid A (SAA) and formyl peptides [6]. In addition, FPR2 is reported to be the receptor of resolvin D1 (RvD1) and RvD3 [17]. One of the leukotriene B4 receptors, BLT1, is also a receptor of RvE1 and RvE2 [17]. Chemokine-like receptor 1 (CMKLR1, also known as ChemR23) serves as a receptor for RvE1 and RvE2 [17]. In addition, GPR32 is known as a receptor of RvD1, RvD3, and RvD5 [17], and GPR18 has recently been identified as a receptor of RvD2 [18]. GPR37 has been shown to bind neuroprotectins (e.g., NPD1) to promote macrophage phagocytosis and the resolution of inflammatory pain [19]. LGR6, another class A GPCR, has been reported to bind maresin 1 (MaR1) and promote phagocytosis, efferocytosis, and phosphorylation of ERK and cAMP response element-binding protein [20]. As some of these receptors have been previously reported to bind chemotactic peptides such as SAA and chemerin, which lead to proinflammatory signaling, it remains unclear how one receptor can transduce both pro- and anti-inflammatory signals. The identification of the signaling pathways leading to anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving activities is of high importance. The remainder of this review focuses on LXA4 and FPR2 as examples to delineate the possible signaling mechanisms for their anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving activities and for identifying the structural basis of ligand-biased signaling.
Mechanisms of anti-inflammatory signaling induced by LXs
Appreciation for the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of LXs dates back to the early 1980s. LXA4 was first identified as an AA metabolite with anti-inflammatory activity [21, 22]. ATL is an epimer of LXA4 that is simulated by aspirin [23]. Both LXA4 and ATL show anti-inflammatory activity in vivo, but the 15-epimer is more stable than LXA4 [24]. Specific lipoxin recognition sites were identified using radiolabeled LXA4 in human neutrophils [25]. This approach led to the identification of FPR2, an FPR1 homolog with low affinity for the formylated tripeptide fMet-Leu-Phe, which is a receptor of LXA4 [15]. The basic features of the receptor in relation to LXA4 include high affinity binding (Kd = 1.7 nM with the recombinant receptor in transfected CHO cells vs. a Kd of 0.7 nM in neutrophils), stimulation of GTPase activity in GTP hydrolysis assays, induced expression of the receptor in HL-60 cells, and competitive binding of the same receptor by LTD4 with a Ki of 80 nM. In addition, LXA4 is able to stimulate the release of esterified arachidonate from FPR2 cDNA-transfected CHO cells. Pertussis toxin, which inactivates the Gi protein through ADP-ribosylation, disrupted the LXA4-induced activity in transfected CHO cells [15]. Subsequent studies led to the identification of additional activities of LXA4 and its 15-epimer ATL through FPR2, including Ca2+ mobilization [26] and ligand-induced internalization of the receptor [26, 27]. In 2009, an international panel of experts recommended that the IUPHAR Nomenclature Committee name this receptor FPR2/ALX [6]. Research on the LXA4 interaction with and signaling through FPR2, however, has led to questions after several groups reported failed attempts to repeat LXA4-induced activity, such as Ca2+ mobilization [28,29,30]. Under the same experimental conditions, various FPR2 agonists, including the synthetic peptide WKYMVm, SAA, LL-37 and several formyl peptides, were able to induce the expected signaling events [28,29,30].
To bridge the gap in knowledge on LXA4 signaling and address how FPR2 transduces both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals, Cooray and coworkers investigated the signaling bias of FPR2 from the perspective of receptor dimerization [31]. Their study design involved the use of a Renilla luciferase (Rluc)-tagged FPR2 construct (FPR2-Rluc) and an EYFP-tagged FPR2 construct (FPR2-EYFP) that, when cotransfected into HEK293 cells and induced to be in proximity after ligand-induced dimerization, could generate bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET). Similarly, HA-tagged and FLAG-tagged FPR1, FPR2, and FPR3 were generated for a coimmunoprecipitation study. As reported, these authors found constitutive dimerization of the FPRs. Specifically, homodimerization of FPR2 was enhanced by annexin A1 (AnxA1, 10−8 M), Ac2–26 (10−5 M) or LXA4 (10−7 M), but not by SAA, a proinflammatory ligand of FPR2 [32, 33]. This enhanced FPR2 homodimerization led to the production of IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, through a signaling pathway involving the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and Hsp27 (Fig. 2). In addition to receptor homodimerization, FPR1–FPR2 heterodimers were identified, and the formation of these heterodimers was stimulated by the same ligands, including AnxA1, Ac2–26, and LXA4. However, heterodimer formation was not associated with anti-inflammatory activity. In contrast, Ac2–26 stimulation of the FPR1–FPR2 heterodimer led to JNK phosphorylation and neutrophil apoptosis [31] (Fig. 2).
The signaling mechanisms of anti-inflammatory ligands (e.g., Annexin A1), as proposed by Cooray et al. [31], are shown. Annexin A1, Ac2–26, or LXA4, but not SAA, can enhance the homodimerization of FPR2 (FPR2/ALX). Receptor dimerization leads to p38 MAPK phosphorylation, which is thought to be mediated by β-arrestins. β-arrestin recruitment is also observed with proinflammatory ligands but to a lesser extent. The signaling is followed by the activation of Hsp27 and the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. When FPR2 and FPR1 form heterodimers, a different signaling pathway leading to JNK activation and cell apoptosis is activated. Based on the work by Gooray and coworkers [31]. Solid arrows indicate established signaling pathways, while dashed arrows indicate proposed signaling pathways.
These results from living cells provide evidence for an association between conformational changes resulting from FPR2 homodimer formation and anti-inflammatory signaling. The underlying principle of these findings is that FPR2 can distinguish between agonists having distinct and somewhat opposing biological properties and thus rearrange its conformation through the formation of FPR2 homodimers and FPR1–FPR2 heterodimers. However, it is unclear how these observations compare with available structural data demonstrating the ability of a GPCR monomer to form complexes with heterotrimeric G proteins or β-arrestins for biased signaling. Moreover, the same ligand–receptor combination can enhance both FPR2 homodimer formation, which leads to anti-inflammatory signaling, and FPR1–FPR2 heterodimer formation, which leads to JNK pathway-induced apoptosis, making it difficult to comprehend the structure–function relationship. Ac2–26, the N-terminal peptide of AnxA1, displays anti-inflammatory potential, yet it can also induce Ca2+ mobilization and other cellular activities common to the proinflammatory ligands of FPR2 at 100 nM or greater. Clearly, there is a need for alternative explanations for the observed ligand recognition and signaling bias of FPR2.
In 2003, He et al. reported that LXA4 could diminish SAA-induced signaling leading to CXCL8 (IL-8) production [33], raising the possibility that anti-inflammatory ligands of FPR2 may alter the signaling capability of another ligand with proinflammatory activity. In vivo studies have shown that proinflammatory factors and anti-inflammatory factors often coexist at different stages of an inflammatory response, and focusing exclusively on the ability of one ligand to induce biased signaling may lead to an incomplete understanding and partial conclusions. Considering this complicated situation, Ge et al. recently investigated the effect of ATL on CXCL8 production by differentiated HL-60 cells stimulated with WKYMVm, a potent agonist of FPR2 and FPR1 [34]. A 30-min incubation with ATL reduced CXCL8 production by 20% in WKYMVm-stimulated dHL-60 cells, with maximal inhibition observed at 100 pM and 1 nM ATL [34]. To determine whether ATL can induce conformational changes in FPR2, a single-molecule fluorescent resonance energy transfer (smFRET) approach was taken with a prepared fluorescent biosensor of FPR2. Incubation with ATL reduced smFRET efficiency by as much as 40%, while incubation with WKYMVm enhanced smFRET efficiency, suggesting that these two ligands induced opposite changes in receptor conformation [34]. When HEK293 cells expressing the FPR2 biosensor were first incubated with ATL and then stimulated with WKYMVm, the responses to WKYMVm were reduced in terms of Ca2+ mobilization and cAMP accumulation and increased with respect to β-arrestin2 membrane translocation, with maximal effects obtained at 100 pM ATL. These results suggested that ATL skewed the WKYMVm-induced signaling pathway away from G protein signaling and towards β-arrestin2 signaling (Fig. 3). Collectively, the experimental data revealed a previously undetected function of ATL to induce FPR2 conformational changes at picomolar concentrations to produce a negative and possibly allosteric effect on WKYMVm-induced signaling. ATL at picomolar concentrations did not mobilize β-arrestin2, nor did it induce Ca2+ mobilization, alter cAMP accumulation or compete with WKYMVm for binding to the receptor [34], suggesting biased allosteric modulation. At higher concentrations, ATL alone was able to induce the inhibition of cAMP accumulation at levels of 100 pM and the Ca2+ mobilization at levels >1 µM. The mechanism for these differences in dose responses is currently unclear.
FPR2 is at its lowest energy level in the inactive state (blue dotted line in a), whereas binding of an agonist,such as WKYMVm overcomes the energy barrier and activates the receptor for downstream signaling through both G proteins and β-arrestins (a, red dotted line). Binding of ATL at picomolar or nanomolar concentrations increases the energy threshold for G protein activation by WKYMVm (b), while lowering the energy level required for β-arrestin activation (c). Therefore, ATL binding modulates FPR2 with a bias towards β-arrestin activation. This model is based on the work by Ge et al. [34].
The data collected thus far suggest the presence of at least two mechanisms for biased signaling through FPR2. The work by Cooray et al. emphasizes the FPR2 homodimer, but not the FPR1–FPR2 heterodimer, for anti-inflammatory signaling. A number of ligands with anti-inflammatory properties (AnxA1, Ac2-26, LXA4, and Cpd43) can increase FPR2 homodimerization and stimulate the p38 MAPK–Hsp27–IL-10 pathway (Fig. 2). The agonist concentration required for the activation of this mechanism varies between AnxA1 (10−8 M), Ac2–26 (10−5 M), and LXA4 (10−7 M). Interestingly, the proinflammatory ligand SAA fails to induce FPR2 homodimerization [31]. In the study by Ge et al. FPR2 was studied as a monomer through the use of smFRET. FPR2 conformational changes were observed with ATL concentrations as low as 1 pM and peaked at 100 pM. By altering the FPR2 conformation, ATL exerted a negative modulatory effect on G protein activation but promoted β-arrestin2 signaling [34] (Fig. 3). The ATL-induced FPR2 conformational change was consistent with the reduced CXCL8 production observed in the WKYMVm-stimulated dHL-60 cells after pre-exposure to ATL.
Structural analysis of the lipoxin interaction with FPR2
Recent developments in the structural determination of membrane proteins have greatly accelerated the understanding of GPCR signaling, with more than 60 structures of GPCRs and GPCRs complexed with G proteins or arrestins determined to date [35]. To understand the structural basis for FPR interaction with its diverse ligands, traditional ligand-binding assays combined with chimeric receptor and DNA mutagenesis approaches were adopted in initial studies [36, 37]. These approaches led to the initial appreciation for the requirements of high-affinity binding of fMet-Leu-Phe, which involves the charged amino acids Arg842.63 and Lys852.64 [38]. This result was confirmed in a study by Mills et al., who employed a site-specific fluorescent photoaffinity probe and mass spectrometry [39]. Using formyl peptide ligands of different sequences and FPR1 mutants, Mills et al. also identified Asp1063.33 and Arg2015.38 as key residues for hydrogen bonding established between FPR1 and the formamide group of fMLF [36]. Human FPR2 shares 69% sequence identity with human FPR1; however, it interacts with the formylated tripeptide fMLF with 100–500-fold lower affinity than FPR1 [6]. A sequence alignment showed that Arg842.63 and Lys852.64 at the membrane boundary were missing in FPR2 and were replaced with Ser842.63 and Lys852.64, thus contributing to the low affinity binding of fMLF. Using the CXCR4 crystal structure as a template for molecular docking, He et al. found that Asp2817.32 was crucial for the FPR2 interaction with certain formyl peptides [40]. This study also confirmed the important role of Arg2055.42 in the activation of both FPR2 and FPR1 by formyl peptides. An appreciation of these results from early studies may help to understand how FPR2 is activated to its full capacity and how LXs may bind FPR2 through different contact points.
Two recently published papers reported the cryo-electron microscopy structure of human FPR2 in complex with a Gi protein [41] and the crystal structure of FPR2 at a resolution of 2.8 Å [42]. Both studies used the potent pan-agonist WKYMVm for binding. The results are very consistent and demonstrate that WKYMVm-bound FPR2 assumes an active conformation with multiple hydrogen bonds formed between the peptide ligands and FPR2. WKYMVm penetrates the FPR2-binding cavity, with its C terminus occupying a deeper site within the receptor transmembrane helical bundle (Fig. 4a). The vertical pose of WKYMVm in FPR2 differs from the pose projected for the formyl peptide binding of FPR1 in that the N-terminus of fMLF is inserted deeply into the receptor-binding pocket [36, 40] (Fig. 4b). WKYMVm also forms hydrogen bonds with Arg2015.38 and Arg2055.42. Amino acid substitutions of V1053.32F, L1093.36A, F1103.37A, V1133.40A, L164W, F178A, F180A, W2546.48A, F2576.51A, and M271A completely abolished the binding of FPR2 to the fluorescently labeled WK(FITC)YMVm and the resulting production of inositol phosphate, possibly by decreasing the conformational stability of the ligand-binding pocket [42]. More importantly, alanine substitutions at V1133.40 and W2546.48 may relay signals communicating the agonist-induced conformational changes in the ligand-binding pocket to the cytoplasmic domain, thus impairing the global conformational rearrangement that is required for receptor activation [42].
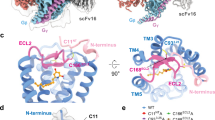
The structure of FPR2-WKYMVm was downloaded from the Protein Data Bank with accession code 6LW5 [42]. After removing WKYMVm based on the atomic coordinates of the complex, the crystal structure of FPR2 was treated as a receptor in the molecular docking analysis. The 3D structure of lipoxin A4 (LXA4) was generated and optimized using the LigPrep tool of the Schrodinger Suite. Docking of LXA4 to FPR2 was performed with AutoDock Vina as previously described [40]. The final pose of every docked peptide was selected based on the top-scoring conformations. a Side view of the FPR2-WKYMVm structure. FPR2 is colored marine blue. The N-terminus and the extracellular loops, ECL1, ECL2, and ECL3, of the receptor are colored cyan, blue, red, and purple, respectively. b Side view of the FPR2-fMLFII structure. c Side view of LXA4 bound to FPR2. The ligand LXA4 is shown as spheres with carbons in orange. d Extracellular view of LXA4 bound to FPR2.
Molecular docking of LXA4 to FPR2 has been performed for this review. The ligand LXA4 binds to FPR2 in a pocket surrounded by the receptor helices III, V, VI, and VII (Fig. 4c, d). LXA4 penetrates the binding cavity, occupying a shallow site within the receptor transmembrane helical bundle, which differs from the binding sites in the WKYMVm-bound FPR2 structure. The residues L812.60, H1023.29, V1053.32, V1093.36, F1103.37, V1604.60, W2546.48, F2576.51, L2847.35, and F2927.43 in helices II, III, IV, VI, and VII form hydrophobic contacts with LXA4. In addition, residues D1063.33, R2015.38, and R2055.42 establish a hydrogen-bond network with the end-terminal COO− group of LXA4. A comparison of the FPR2-LXA4 and FPR2-WKYMVm models revealed major differences in the interaction mode. In the predicted binding mode of LXA4 to FPR2, LXA4 occupies only a part of the binding pocket of FPR2 (Fig. 5a). Interactions between the polar moieties of FPR2 and LXA4 involve residues D1063.33, R2015.38, and R2055.42 (Fig. 5b). In the binding mode showing WKYMVm to FPR2, significant impairment of WK(FITC)YMVm binding and fewer IP products were found upon the introduction of D1063.33A, R2015.38A, and R2055.42A substitutions, indicating that these polar interactions are critical for the recognition of the peptide ligand and its agonistic potency. The predicted binding of LXA4 does not seem to involve an interaction with V1133.40, which is located at the bottom of the FPR2-binding pocket (Fig. 5c).
The ligand LXA4 binds to FPR2 in a pocket near helices III, V, VI, and VII of the receptor. LXA4 penetrates into binding cavity, occupying a shallow site with the receptor transmembrane helical bundle, which differs from the binding sites for WKYMVm with FPR2. a Binding pocket of LXA4 in FPR2. The receptor in FPR2–LXA4 is marine blue in the cartoon representation. The ligand LXA4 is shown as an orange strand. b Schematic representation of interactions between FPR2 and LXA4 is analyzed using the LigPlot+ program [55]. Hydrogen bonds are shown as green dashed lines. The stick drawings of FPR2 and LXA4 are colored orange and blue, respectively. c Comparison of LXA4 ligand-binding sites in the WKYMVm-bound FPR2 structure. WKYMVm (green) and LXA4 (orange) are shown as sticks. The hydrophobic clusters that form interactions with LXA4 and FPR2 are shown in d, e purple sticks. f Polar interactions formed between LXA4 and D106, R201, and R205 in FPR2 shown as cyan sticks.
The horizontal pose of LXA4, but not the vertical insertion of WKYMVm (as observed by comparing Fig. 4c with 4a), suggests different modes for receptor activation. Nevertheless, LXA4 occupies a part of the same ligand-binding pocket in FPR2, consistent with previously published binding data [15, 16]. Therefore, it is conceivable that LXA4 may trigger FPR2 conformational changes that affect the binding and signaling of WKYMVm, as shown in the study by Ge et al. The mode of LXA4 interaction with FPR2 involves several amino acids (Fig. 5d–f) and will need to be confirmed with mutagenesis experiments.
Concluding remarks
The delineation of the FPR2 structure has enabled a deeper understanding of the structural basis for FPR2 interactions with a variety of ligands possessing distinct chemical features. In addition to the SPMs that use FPR2 as a signaling receptor, small-molecule ligands, such as Quin-C1 [43, 44], Cpd43 [45, 46], and Cpd17b [47] have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory and possibly pro-resolving properties upon binding with FPR2. Further understanding of the anti-inflammatory effect of FPR2 and its structure–function relationship may aid in the rational design of molecules with biased signaling properties. In addition to FPR2, other GPCRs that mediate the pro-resolving actions of resolvins, protectins, and maresins are potential targets for drug development aiming at reducing inflammatory responses and promoting resolution and healing. Clinical evaluation of SPMs and their derivatives will be of importance for the development of this new class of anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving agents.
References
Blake DR, Allen R. Inflammation: basic principles and clinical correlates. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988;47:792.
Serhan CN, Levy BD. Resolvins in inflammation: emergence of the pro-resolving superfamily of mediators. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:2657–69.
Bacchi S, Palumbo P, Sponta A, Coppolino MF. Clinical pharmacology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a review. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2012;11:52–64.
Perez DM. From plants to man: the GPCR “tree of life”. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;67:1383–4.
Ley K, Hoffman HM, Kubes P, Cassatella MA, Zychlinsky A, Hedrick CC, et al. Neutrophils: new insights and open questions. Sci Immunol. 2018;3:eaat4579.
Ye RD, Boulay F, Wang JM, Dahlgren C, Gerard C, Parmentier M, et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXIII. Nomenclature for the formyl peptide receptor (FPR) family. Pharmacol Rev. 2009;61:119–61.
Ricciotti E, FitzGerald GA. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31:986–1000.
Ollivier V, Parry GC, Cobb RR, de Prost D, Mackman N. Elevated cyclic AMP inhibits NF-kappaB-mediated transcription in human monocytic cells and endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20828–35.
Fan J, Ye RD, Malik AB. Transcriptional mechanisms of acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001;281:L1037–50.
Grabiner BC, Blonska M, Lin PC, You Y, Wang D, Sun J, et al. CARMA3 deficiency abrogates G protein-coupled receptor-induced NF-{kappa}B activation. Genes Dev. 2007;21:984–96.
Ye RD. Regulation of nuclear factor kappaB activation by G-protein-coupled receptors. J Leukoc Biol. 2001;70:839–48.
Serhan CN. Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature. 2014;510:92–101.
Dalli J, Zhu M, Vlasenko NA, Deng B, Haeggstrom JZ, Petasis NA, et al. The novel 13S,14S-epoxy-maresin is converted by human macrophages to maresin 1 (MaR1), inhibits leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H), and shifts macrophage phenotype. FASEB J. 2013;27:2573–83.
Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O’Garra A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:683–765.
Fiore S, Maddox JF, Perez HD, Serhan CN. Identification of a human cDNA encoding a functional high affinity lipoxin A4 receptor. J Exp Med. 1994;180:253–60.
Chiang N, Fierro IM, Gronert K, Serhan CN. Activation of lipoxin A(4) receptors by aspirin-triggered lipoxins and select peptides evokes ligand-specific responses in inflammation. J Exp Med. 2000;191:1197–208.
Chiang N, Serhan CN. Structural elucidation and physiologic functions of specialized pro-resolving mediators and their receptors. Mol Asp Med. 2017;58:114–29.
Chiang N, Dalli J, Colas RA, Serhan CN. Identification of resolvin D2 receptor mediating resolution of infections and organ protection. J Exp Med. 2015;212:1203–17.
Bang S, Xie YK, Zhang ZJ, Wang Z, Xu ZZ, Ji RR. GPR37 regulates macrophage phagocytosis and resolution of inflammatory pain. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:3568–82.
Chiang N, Libreros S, Norris PC, de la Rosa X, Serhan CN. Maresin 1 activates LGR6 receptor promoting phagocyte immunoresolvent functions. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:5294–311.
Serhan CN, Hamberg M, Samuelsson B. Lipoxins: novel series of biologically active compounds formed from arachidonic acid in human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1984;81:5335–9.
Colgan SP, Serhan CN, Parkos CA, Delp-Archer C, Madara JL. Lipoxin A4 modulates transmigration of human neutrophils across intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1993;92:75–82.
Claria J, Serhan CN. Aspirin triggers previously undescribed bioactive eicosanoids by human endothelial cell–leukocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:9475–9.
@Serhan CN. Lipoxins and novel aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxins (ATL): a jungle of cell–cell interactions or a therapeutic opportunity? Prostaglandins. 1997;53:107–37.
Fiore S, Ryeom SW, Weller PF, Serhan CN. Lipoxin recognition sites. Specific binding of labeled lipoxin A4 with human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:16168–76.
Maddox JF, Hachicha M, Takano T, Petasis NA, Fokin VV, Serhan CN. Lipoxin A4 stable analogs are potent mimetics that stimulate human monocytes and THP-1 cells via a G-protein-linked lipoxin A4 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:6972–8.
Maderna P, Cottell DC, Toivonen T, Dufton N, Dalli J, Perretti M, et al. FPR2/ALX receptor expression and internalization are critical for lipoxin A4 and annexin-derived peptide-stimulated phagocytosis. FASEB J. 2010;24:4240–9.
Forsman H, Dahlgren C. Lipoxin A(4) metabolites/analogues from two commercial sources have no effects on TNF-alpha-mediated priming or activation through the neutrophil formyl peptide receptors. Scand J Immunol. 2009;70:396–402.
Forsman H, Onnheim K, Andreasson E, Dahlgren C. What formyl peptide receptors, if any, are triggered by compound 43 and lipoxin A4? Scand J Immunol. 2011;74:227–34.
Hanson J, Ferreiros N, Pirotte B, Geisslinger G, Offermanns S. Heterologously expressed formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2/ALX) does not respond to lipoxin A(4). Biochem Pharm. 2013;85:1795–802.
Cooray SN, Gobbetti T, Montero-Melendez T, McArthur S, Thompson D, Clark AJ, et al. Ligand-specific conformational change of the G-protein-coupled receptor ALX/FPR2 determines proresolving functional responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:18232–7.
Su SB, Gong W, Gao JL, Shen W, Murphy PM, Oppenheim JJ, et al. A seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor, FPRL1, mediates the chemotactic activity of serum amyloid A for human phagocytic cells. J Exp Med. 1999;189:395–402.
He R, Sang H, Ye RD. Serum amyloid A induces IL-8 secretion through a G protein-coupled receptor, FPRL1/LXA4R. Blood. 2003;101:1572–81.
Ge Y, Zhang S, Wang J, Xia F, Wan JB, Lu J, et al. Dual modulation of formyl peptide receptor 2 by aspirin-triggered lipoxin contributes to its anti-inflammatory activity. FASEBJ. 2020;34:6920–33.
Hilger D, Masureel M, Kobilka BK. Structure and dynamics of GPCR signaling complexes. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018;25:4–12.
Mills JS, Miettinen HM, Cummings D, Jesaitis AJ. Characterization of the binding site on the formyl peptide receptor using three receptor mutants and analogs of Met-Leu-Phe and Met-Met-Trp-Leu-Leu. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:39012–7.
Quehenberger O, Prossnitz ER, Cavanagh SL, Cochrane CG, Ye RD. Multiple domains of the N-formyl peptide receptor are required for high-affinity ligand binding. Construction and analysis of chimeric N-formyl peptide receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:18167–75.
Quehenberger O, Pan ZK, Prossnitz ER, Cavanagh SL, Cochrane CG, Ye RD. Identification of an N-formyl peptide receptor ligand binding domain by a gain-of-function approach. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;238:377–81.
Mills JS, Miettinen HM, Barnidge D, Vlases MJ, Wimer-Mackin S, Dratz EA, et al. Identification of a ligand binding site in the human neutrophil formyl peptide receptor using a site-specific fluorescent photoaffinity label and mass spectrometry. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:10428–35.
He HQ, Troksa EL, Caltabiano G, Pardo L, Ye RD. Structural determinants for the interaction of formyl peptide receptor 2 with peptide ligands. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:2295–306.
Zhuang Y, Liu H, Edward Zhou X, Kumar Verma R, de Waal PW, Jang W, et al. Structure of formylpeptide receptor 2-Gi complex reveals insights into ligand recognition and signaling. Nat Commun. 2020;11:885.
Chen T, Xiong M, Zong X, Ge Y, Zhang H, Wang M, et al. Structural basis of ligand binding modes at the human formyl peptide receptor 2. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1208.
He M, Cheng N, Gao WW, Zhang M, Zhang YY, Ye RD, et al. Characterization of Quin-C1 for its anti-inflammatory property in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced lung injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011;32:601–10.
Nanamori M, Cheng X, Mei J, Sang H, Xuan Y, Zhou C, et al. A novel nonpeptide ligand for formyl peptide receptor-like 1. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;66:1213–22.
Kao W, Gu R, Jia Y, Wei X, Fan H, Harris J, et al. A formyl peptide receptor agonist suppresses inflammation and bone damage in arthritis. Br J Pharmacol. 2014;171:4087–96.
Burli RW, Xu H, Zou X, Muller K, Golden J, Frohn M, et al. Potent hFPRL1 (ALXR) agonists as potential anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006;16:3713–8.
Qin CX, May LT, Li R, Cao N, Rosli S, Deo M, et al. Small-molecule-biased formyl peptide receptor agonist compound 17b protects against myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14232.
Krishnamoorthy S, Recchiuti A, Chiang N, Yacoubian S, Lee CH, Yang R, et al. Resolvin D1 binds human phagocytes with evidence for proresolving receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:1660–5.
Arnardottir HH, Dalli J, Norling LV, Colas RA, Perretti M, Serhan CN. Resolvin D3 is dysregulated in arthritis and reduces arthritic inflammation. J Immunol. 2016;197:2362–8.
Chiang N, Fredman G, Backhed F, Oh SF, Vickery T, Schmidt BA, et al. Infection regulates pro-resolving mediators that lower antibiotic requirements. Nature. 2012;484:524–8.
Dalli J, Winkler JW, Colas RA, Arnardottir H, Cheng CY, Chiang N, et al. Resolvin D3 and aspirin-triggered resolvin D3 are potent immunoresolvents. Chem Biol. 2013;20:188–201.
Arita M, Bianchini F, Aliberti J, Sher A, Chiang N, Hong S, et al. Stereochemical assignment, antiinflammatory properties, and receptor for the omega-3 lipid mediator resolvin E1. J Exp Med. 2005;201:713–22.
Arita M, Ohira T, Sun YP, Elangovan S, Chiang N, Serhan CN. Resolvin E1 selectively interacts with leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 and ChemR23 to regulate inflammation. J Immunol. 2007;178:3912–7.
Oh SF, Pillai PS, Recchiuti A, Yang R, Serhan CN. Pro-resolving actions and stereoselective biosynthesis of 18S E-series resolvins in human leukocytes and murine inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:569–81.
Laskowski RA, Swindells MB. LigPlot+: multiple ligand–protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J Chem Inf Model. 2011;51:2778–86.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Fundo para o Desenvolvimento das Ciências e da Tecnologia (FDCT 072/2015/A2) and from the University of Macau (MYRG2016-00246-ICMS-QRCM). YJG and RDY were supported by the President Fund of the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen. QWL was supported by the Ganghong Young Scholar Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, Yj., Liao, Qw., Xu, Yc. et al. Anti-inflammatory signaling through G protein-coupled receptors. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41, 1531–1538 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-00523-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-00523-1
This article is cited by
-
A review of gut failure as a cause and consequence of critical illness
Critical Care (2025)
-
Oral FPR2/ALX modulators tune myeloid cell activity to ameliorate mucosal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2025)
-
Unlocking therapeutic potential in traumatic brain injury: exploring microenvironmental targets, signaling pathways and translational hurdles
Inflammopharmacology (2025)
-
Specialized pro-resolution mediators in the bladder: effects of resolvin E1 on diabetic bladder dysfunction in the type 1 diabetic male Akita mouse model
BMC Urology (2024)
-
Disease clusters subsequent to anxiety and stress-related disorders and their genetic determinants
Nature Communications (2024)