Abstract
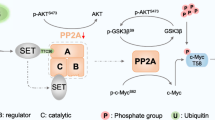
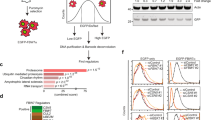
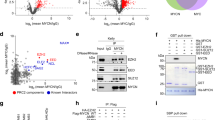
c-Myc (Myc) is a master transcription factor that is often deregulated and highly expressed by at least 50% of cancers. In many cases, Myc protein levels correlate with resistance to therapy and poor prognosis. However, effective direct inhibition of Myc by pharmacologic approaches has remained unachievable. Here, we identify MAP3K13 as a positive regulator of Myc to promote tumor development. Our findings show that MAP3K13 upregulation is predictive of poor outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Mechanistically, MAP3K13 phosphorylates the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM25 at Ser12 to decrease its polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. This newly stabilized TRIM25 then directly ubiquitinates Lys412 of FBXW7α, a core subunit of the SKP1-Cullin-F-box (SCF) ubiquitin ligase complex involved in Myc ubiquitination, thereby stabilizing Myc. Together, these results reveal a novel regulatory pathway that supervises Myc protein stability via the MAP3K13-TRIM25-FBXW7α signaling axis. In addition, they provide a potential therapeutic target in Myc over-expressing human cancers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Mehta A, Herrera H, Block T. Glycosylation and liver cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2015;126:257–9.
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108.
El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–27.
Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–55.
Villanueva A, Hernandez-Gea V, Llovet JM. Medical therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: a critical view of the evidence. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:34–42.
Thorgeirsson SS, Grisham JW. Molecular pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2002;31:339–46.
Liu P, Ge M, Hu J, Li X, Che L, Sun K, et al. A functional mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling is indispensable for c-Myc-driven hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 2017;66:167–81.
Shachaf CM, Kopelman AM, Arvanitis C, Karlsson A, Beer S, Mandl S, et al. MYC inactivation uncovers pluripotent differentiation and tumour dormancy in hepatocellular cancer. Nature. 2004;431:1112–7.
Dang CV, O’Donnell KA, Zeller KI, Nguyen T, Osthus RC, Li F. The c-Myc target gene network. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:253–64.
Grim JE, Gustafson MP, Hirata RK, Hagar AC, Swanger J, Welcker M, et al. Isoform- and cell cycle-dependent substrate degradation by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase. J Cell Biol. 2008;181:913–20.
Welcker M, Orian A, Jin J, Grim JE, Harper JW, Eisenman RN, et al. The Fbw7 tumor suppressor regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylation-dependent c-Myc protein degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:9085–90.
Yada M, Hatakeyama S, Kamura T, Nishiyama M, Tsunematsu R, Imaki H, et al. Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of c-Myc is mediated by the F-box protein Fbw7. EMBO J. 2004;23:2116–25.
Spruck CH, Strohmaier H, Sangfelt O, Muller HM, Hubalek M, Muller-Holzner E, et al. hCDC4 gene mutations in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4535–9.
Welcker M, Orian A, Grim JE, Eisenman RN, Clurman BE. A nucleolar isoform of the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase regulates c-Myc and cell size. Curr Biol. 2004;14:1852–7.
Masaki M, Ikeda A, Shiraki E, Oka S, Kawasaki T. Mixed lineage kinase LZK and antioxidant protein-1 activate NF-kappaB synergistically. Eur J Biochem. 2003;270:76–83.
Ikeda A, Hasegawa K, Masaki M, Moriguchi T, Nishida E, Kozutsumi Y, et al. Mixed lineage kinase LZK forms a functional signaling complex with JIP-1, a scaffold protein of the c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase pathway. J Biochem. 2001;130:773–81.
Sakuma H, Ikeda A, Oka S, Kozutsumi Y, Zanetta JP, Kawasaki T. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding a new member of mixed lineage protein kinase from human brain. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:28622–9.
Edwards ZC, Trotter EW, Torres-Ayuso P, Chapman P, Wood HM, Nyswaner K, et al. Survival of head and neck cancer cells relies upon LZK kinase-mediated stabilization of mutant p53. Cancer Res. 2017;77:4961–72.
Jing HZ, Qiu F, Chen SZ, Su L, Qu C. [Tripartite-motif protein 25 and pyruvate kinase M2 protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015;35:437–41.
Qin Y, Cui H, Zhang H. Overexpression of TRIM25 in lung cancer regulates tumor cell progression. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2016;15:707–15.
Zhu Z, Wang Y, Zhang C, Yu S, Zhu Q, Hou K, et al. TRIM25 blockade by RNA interference inhibited migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells through TGF-beta signaling. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19070.
Sakuma M, Akahira J, Suzuki T, Inoue S, Ito K, Moriya T, et al. Expression of estrogen-responsive finger protein (Efp) is associated with advanced disease in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;99:664–70.
Sun N, Xue Y, Dai T, Li X, Zheng N. Tripartite motif containing 25 promotes proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through TGF-beta signaling. Biosci Rep. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20170805.
Suzuki T, Urano T, Tsukui T, Horie-Inoue K, Moriya T, Ishida T, et al. Estrogen-responsive finger protein as a new potential biomarker for breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:6148–54.
Li YH, Zhong M, Zang HL, Tian XF. Mechanism of TRIM25 mediated ubiquitination of metastasis associated protein (MTA) 1 in normal liver cells. Exp Cell Res. 2018;371:250–4.
Han H, Chen Y, Cheng L, Prochownik EV, Li Y. microRNA-206 impairs c-Myc-driven cancer in a synthetic lethal manner by directly inhibiting MAP3K13. Oncotarget. 2016;7:16409–19.
Kim SY, Herbst A, Tworkowski KA, Salghetti SE, Tansey WP. Skp2 regulates Myc protein stability and activity. Mol Cell. 2003;11:1177–88.
von der Lehr N, Johansson S, Wu S, Bahram F, Castell A, Cetinkaya C, et al. The F-box protein Skp2 participates in c-Myc proteosomal degradation and acts as a cofactor for c-Myc-regulated transcription. Mol Cell. 2003;11:1189–200.
Fang X, Zhou W, Wu Q. Deubiquitinase USP13 maintains glioblastoma stem cells by antagonizing FBXL14-mediated Myc ubiquitination. J Exp Med. 2017;214:245–67.
Gupta S, Yla-Anttila P. Herpesvirus deconjugases inhibit the IFN response by promoting TRIM25 autoubiquitination and functional inactivation of the RIG-I signalosome. PLoS Pathog. 2018;14:e1006852.
Meroni G, Diez-Roux G. TRIM/RBCC, a novel class of ‘single protein RING finger’ E3 ubiquitin ligases. Bioessays. 2005;27:1147–57.
Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807.
Hershko A, Ciechanover A, Varshavsky A. Basic Medical Research Award. The ubiquitin system. Nat Med. 2000;6:1073–81.
Min SH, Lau AW, Lee TH, Inuzuka H, Wei S, Huang P, et al. Negative regulation of the stability and tumor suppressor function of Fbw7 by the Pin1 prolyl isomerase. Mol Cell. 2012;46:771–83.
Welcker M, Larimore EA, Swanger J, Bengoechea-Alonso MT, Grim JE, Ericsson J, et al. Fbw7 dimerization determines the specificity and robustness of substrate degradation. Genes Dev. 2013;27:2531–6.
Akhoondi S, Sun D, von der Lehr N, Apostolidou S, Klotz K, Maljukova A, et al. FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:9006–12.
Coleman WB. Mechanisms of human hepatocarcinogenesis. Curr Mol Med. 2003;3:573–88.
Fletcher S, Prochownik EV. Small-molecule inhibitors of the Myc oncoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1849:525–43.
Chen J, Shin JH, Zhao R, Phan L, Wang H, Xue Y, et al. CSN6 drives carcinogenesis by positively regulating Myc stability. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5384.
Hassan QN 2nd, Alinari L, Byrd JC. PLK1: a promising and previously unexplored target in double-hit lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:5206–8.
Horiuchi D, Camarda R, Zhou AY, Yau C, Momcilovic O, Balakrishnan S, et al. PIM1 kinase inhibition as a targeted therapy against triple-negative breast tumors with elevated MYC expression. Nat Med. 2016;22:1321–9.
Gack MU, Shin YC, Joo CH, Urano T, Liang C, Sun L, et al. TRIM25 RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase is essential for RIG-I-mediated antiviral activity. Nature. 2007;446:916–20.
Lee NR, Choi JY, Yoon IH, Lee JK, Inn KS. Positive regulatory role of c-Src-mediated TRIM25 tyrosine phosphorylation on RIG-I ubiquitination and RIG-I-mediated antiviral signaling pathway. Cell Immunol. 2018;332:94–100.
Han H, Sun D, Li W, Shen H, Zhu Y, Li C, et al. A c-Myc-MicroRNA functional feedback loop affects hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 2013;57:2378–89.
Shevchenko A, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mann M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem. 1996;68:850–8.
Subramanian A, Kuehn H, Gould J, Tamayo P, Mesirov JP. GSEA-P: a desktop application for Gene Set Enrichment Analysis. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:3251–3.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC1302300) and National Nature Science Foundation of China (81772609, 81802782).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QZ and YL designed the study, analyzed and interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. QZ, XL, CL, KC, MW, and YL performed most of the experiments. QZ,YL, and EP wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by D. Guardavaccaro
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Li, X., Cui, K. et al. The MAP3K13-TRIM25-FBXW7α axis affects c-Myc protein stability and tumor development. Cell Death Differ 27, 420–433 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0363-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0363-0
This article is cited by
-
QAL333’s antitumor activity and predictive modeling: integrated transcriptomic-bioinformatic analysis reveals selective cytotoxicity and sensitivity determinants
Scientific Reports (2026)
-
DCST1-AS1 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression via regulating the miR-582-5p/HMGB2 axis
Journal of Translational Medicine (2025)
-
Acetylation-dependent USP7-TRIM25 axis drives oncogenic progression in non-small cell lung cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2025)
-
KMT2D/ZNF460-induced COL9A1-mediated extracellular matrix stiffness maintains the cancer stem cell pool to promote colorectal cancer progression
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2025)
-
Targeting the TRIB3–MYC axis in cancer: mechanistic insights and therapeutic disruption strategies
Investigational New Drugs (2025)