Abstract
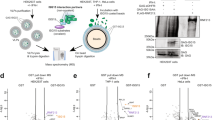
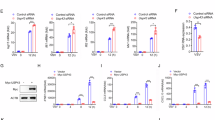
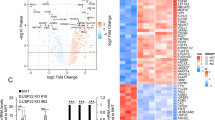
STAT1 is a master regulator that orchestrates type 1 and 2 interferon (IFN)-induced IFN-stimulated gene (ISG) expression. The mechanisms by which STAT1 is phosphorylated and activated upon IFN signaling remain elusive. Our work demonstrated that ubiquitination of STAT1 mediated by the E3 ligase RNF220 contributed significantly to STAT1 activation and innate immune responses. Rnf220 gene deficiency resulted in the downregulation of IFN signaling and decreased expression of ISGs in response to type 1 and 2 IFNs stimulation and Acinetobacter baumannii and HSV-1 infection. Mechanistically, RNF220 interacted with STAT1 and mediated the K63-linked polyubiquitination of STAT1 at residue K110, which promoted the interaction between STAT1 and the kinase JAK1. The expression of RNF220 was induced by pathogenic infection and IFN signaling. RNF220 promoted STAT1 ubiquitination and phosphorylation through a positive feedback loop. RNF220 haploinsufficiency impaired IFN signaling, and RNF220-defective mice were more susceptible to A. baumannii and HSV-1 infection than WT mice. Our work offers novel insights into the mechanisms of STAT1 modulation and provides potential therapeutic targets against bacterial and viral infection and inflammatory diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ivashkiv LB, Donlin LT. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:36–49.
Chen K, Liu J, Cao X. Regulation of type I interferon signaling in immunity and inflammation: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2017;83:1–11.
Li S, Wang L, Berman M, Kong Y-Y, Dorf Martin E. Mapping a dynamic innate immunity protein interaction network regulating type I interferon production. Immunity. 2011;35:426–40.
Li F, Li Y, Liang H, Xu T, Kong Y, Huang M, et al. HECTD3 mediates TRAF3 polyubiquitination and type I interferon induction during bacterial infection. J Clin Investig. 2018;128:4148–62.
González-Navajas JM, Lee J, David M, Raz E. Immunomodulatory functions of type I interferons. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:125–35.
Hu X, Ivashkiv LB. Cross-regulation of signaling pathways by interferon-gamma: implications for immune responses and autoimmune diseases. Immunity. 2009;31:539–50.
Begitt A, Droescher M, Meyer T, Schmid CD, Baker M, Antunes F, et al. STAT1-cooperative DNA binding distinguishes type 1 from type 2 interferon signaling. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:168.
Majoros A, Platanitis E, Kernbauer-Hölzl E, Rosebrock F, Müller M, Decker T. Canonical and non-canonical aspects of JAK–STAT signaling: lessons from interferons for cytokine responses. Front Immunol. 2017;8:29.
Majoros A, Platanitis E, Szappanos D, Cheon H, Vogl C, Shukla P, et al. Response to interferons and antibacterial innate immunity in the absence of tyrosine-phosphorylated STAT1. EMBO Rep. 2016;17:367–82.
Grönholm J, Vanhatupa S, Ungureanu D, Väliaho J, Laitinen T, Valjakka J, et al. Structure-function analysis indicates that sumoylation modulates DNA-binding activity of STAT1. BMC Biochem. 2012;13:20.
Begitt A, Droescher M, Knobeloch K-P, Vinkemeier U. SUMO conjugation of STAT1 protects cells from hyperresponsiveness to IFNγ. Blood. 2011;118:1002–7.
Kim TK, Maniatis T. Regulation of interferon-γ-activated STAT1 by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Science. 1996;273:1717–9.
Yuan C, Qi J, Zhao X, Gao C. Smurf1 protein negatively regulates interferon-γ signaling through promoting STAT1 protein ubiquitination and degradation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:17006–15.
Yeh H-M, Yu C-Y, Yang H-C, Ko S-H, Liao C-L, Lin Y-L. Ubiquitin-specific protease 13 regulates IFN signaling by stabilizing STAT1. J Immunol. 2013;191:3328–36.
Ren Y, Zhao P, Liu J, Yuan Y, Cheng Q, Zuo Y, et al. Deubiquitinase USP2a sustains interferons antiviral activity by restricting ubiquitination of activated STAT1 in the nucleus. PLOS Pathog. 2016;12:e1005764.
Lawrence DW, Kornbluth J. E3 ubiquitin ligase NKLAM ubiquitinates STAT1 and positively regulates STAT1-mediated transcriptional activity. Cell Signal. 2016;28:1833–41.
Liu S, Jiang M, Wang W, Liu W, Song X, Ma Z, et al. Nuclear RNF2 inhibits interferon function by promoting K33-linked STAT1 disassociation from DNA. Nat Immunol. 2018;19:41–52.
Kong Q, Zeng W, Wu J, Hu W, Li C, Mao B. RNF220, an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets Sin3B for ubiquitination. Biochemical Biophysical Res Commun. 2010;393:708–13.
Jiang X, Wang X, Zhang X, Xiao Z, Zhang C, Liu X, et al. A homozygous RNF220 mutation leads to male infertility with small-headed sperm. Gene. 2019;688:13–18.
Ma P, Yang X, Kong Q, Li C, Yang S, Li Y, et al. The ubiquitin ligase RNF220 enhances canonical Wnt signaling through USP7-mediated deubiquitination of β-catenin. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34:4355–66.
Ma P, Song N, Xu Y, Gao X, Ding Y, Mao B. RNF220 mediated K-63 linked ubiquitination induces sequestration of Gli to pattern the ventral neural tube. Mechanisms Dev. 2017;145:S100–S101.
Ma P, Song N-N, Li Y, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Zhang L, et al. Fine-tuning of Shh/Gli signaling gradient by non-proteolytic ubiquitination during neural patterning. Cell Rep. 2019;28:541–e544.
Ma P, Song N-N, Cheng X, Zhu L, Zhang Q, Zhang L, et al. ZC4H2 stabilizes RNF220 to pattern ventral spinal cord through modulating Shh/Gli signaling. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019;12:337–44.
Kim J, Choi T-I, Park S, Kim MH, Kim C-H, Lee S. Rnf220 cooperates with Zc4h2 to specify spinal progenitor domains. Development. 2018;145:dev165340.
Li Y, Guo X, Hu C, Du Y, Guo C, Di W, et al. Type I IFN operates pyroptosis and necroptosis during multidrug-resistant A. baumannii infection. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:1304–18.
Sadzak I, Schiff M, Gattermeier I, Glinitzer R, Sauer I, Saalmüller A, et al. Recruitment of Stat1 to chromatin is required for interferon-induced serine phosphorylation of Stat1 transactivation domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:8944–9.
Ungureanu D, Vanhatupa S, Grönholm J, Palvimo JJ, Silvennoinen O. SUMO-1 conjugation selectively modulates STAT1-mediated gene responses. Blood. 2005;106:224–6.
Krämer OH, Knauer SK, Greiner G, Jandt E, Reichardt S, Gührs K-H, et al. A phosphorylation-acetylation switch regulates STAT1 signaling. Genes Dev. 2009;23:223–35.
Cheon H, Stark GR. Unphosphorylated STAT1 prolongs the expression of interferon-induced immune regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:9373–8.
Vanhatupa S, Ungureanu D, Paakkunainen M, Silvennoinen O. MAPK-induced Ser727 phosphorylation promotes SUMOylation of STAT1. Biochem J. 2008;409:179–85.
Qi X, Man SM, Malireddi RKS, Karki R, Lupfer C, Gurung P, et al. Cathepsin B modulates lysosomal biogenesis and host defense against Francisella novicida infection. J Exp Med. 2016;213:2081–97.
Jin L, Guo X, Shen C, Hao X, Sun P, Li P, et al. Salivary factor LTRIN from Aedes aegypti facilitates the transmission of Zika virus by interfering with the lymphotoxin-β receptor. Nat Immunol. 2018;19:342–53.
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Gao (Shandong University School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jinan) for mutated Stat1 plasmids; X. Cao (Nankai University, Tianjin) for Stat1–/– L929 cells; C. Chen (Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming) for ubiquitin plasmids; J. Zhou (Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming) for HSV-1; S.-Z. Duan (Institute for Nutritional Sciences, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai) for L929 cells. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0500300), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB13000000 and HXDTZX-2019-1), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31970896, 31871483, 31671521, 31500847, 31701134, and 81701578) and Yunnan Province (2019FJ008, 2018FA038, 2018FB127, 2018FB131, HXDT-2019-2, and AMHD-2018-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XQ and BM designed the study; XG, PM, YL, YY, CW, TX, HW, CL, BM, and XQ performed experiments and analyzed the data; XQ wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by M. Piacentini
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Ma, P., Li, Y. et al. RNF220 mediates K63-linked polyubiquitination of STAT1 and promotes host defense. Cell Death Differ 28, 640–656 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00609-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00609-7
This article is cited by
-
Identification of the E3 ligase TRIM21 as a crucial regulator of STAT1 in metabolic dysfunction—associated steatohepatitis
Cell Communication and Signaling (2026)
-
Inhibition of MBTPS1 enhances antitumor immunity and potentiates anti-PD-1 immunotherapy
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Cardiomyocyte-derived USP13 protects hearts from hypertrophy via deubiquitinating and stabilizing STAT1 in male mice
Nature Communications (2025)
-
RNF220 mediates K63-linked polyubiquitination of STAT3 and aggravates pathological cardiac hypertrophy
Cell Death & Differentiation (2025)
-
WASH regulates B cell signaling, metabolism and function through STAT1
Cell Death & Differentiation (2025)