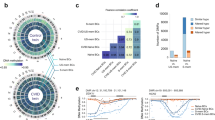
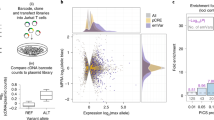
Abstract
Ciliogenesis proteins orchestrate vesicular trafficking pathways that regulate immune synapse (IS) assembly in the non-ciliated T-cells. We hypothesized that ciliogenesis-related genes might be disease candidates for common variable immunodeficiency with impaired T-cell function (T-CVID). We identified a heterozygous, predicted pathogenic variant in the ciliogenesis protein CCDC28B present with increased frequency in a large CVID cohort. We show that CCDC28B participates in IS assembly by regulating polarized T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) recycling. This involves the CCDC28B-dependent, FAM21-mediated recruitment of the actin regulator WASH to retromer at early endosomes to promote actin polymerization. The CVID-associated CCDC28BR25W variant failed to interact with FAM21, leading to impaired synaptic TCR recycling. CVID T cells carrying the ccdc28b 211 C > T allele displayed IS defects mapping to this pathway that were corrected by overexpression of the wild-type allele. These results identify a new disease gene in T-CVID and pinpoint CCDC28B as a new player in IS assembly.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Resnick ES, Cunningham-Rundles C. The many faces of the clinical picture of common variable immune deficiency. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;12:595–601.
Yazdani R, Hakemi MG, Sherkat R, Homayouni V, Farahani R. Genetic defects and the role of helper T-cells in the pathogenesis of common variable immunodeficiency. Adv Biomed Res. 2014;3:2.
Orange JS, Glessner JT, Resnick E, Sullivan KE, Lucas M, Ferry B, et al. Genome-wide association identifies diverse causes of common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127:1360–1367 e1366.
Abolhassani H, Hammarstrom L, Cunningham-Rundles C. Current genetic landscape in common variable immune deficiency. Blood. 2020;135:656–67.
Grimbacher B, Hutloff A, Schlesier M, Glocker E, Warnatz K, Drager R, et al. Homozygous loss of ICOS is associated with adult-onset common variable immunodeficiency. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:261–8.
Lougaris V, Baronio M, Gazzurelli L, Lorenzini T, Fuoti M, Moratto D, et al. A de novo monoallelic CTLA-4 deletion causing pediatric onset CVID with recurrent autoimmune cytopenias and severe enteropathy. Clin Immunol. 2018;197:186–8.
Fischer MB, Wolf HM, Hauber I, Eggenbauer H, Thon V, Sasgary M, et al. Activation via the antigen receptor is impaired in T cells, but not in B cells from patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26:231–7.
Majolini MB, D’Elios MM, Boncristiano M, Galieni P, Del Prete G, Telford JL, et al. Uncoupling of T-cell antigen receptor and downstream protein tyrosine kinases in common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1997;84:98–102.
Boncristiano M, Majolini MB, D’Elios MM, Pacini S, Valensin S, Ulivieri C, et al. Defective recruitment and activation of ZAP-70 in common variable immunodeficiency patients with T cell defects. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30:2632–8.
Paccani SR, Boncristiano M, Patrussi L, Ulivieri C, Wack A, Valensin S, et al. Defective Vav expression and impaired F-actin reorganization in a subset of patients with common variable immunodeficiency characterized by T-cell defects. Blood. 2005;106:626–34.
Capitani N, Ariani F, Amedei A, Pezzicoli A, Matucci A, Vultaggio A, et al. Vav1 haploinsufficiency in a common variable immunodeficiency patient with defective T-cell function. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012;25:811–7.
Dustin ML, Choudhuri K. Signaling and polarized communication across the T cell immunological synapse. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2016;32:303–25.
Finetti F, Paccani SR, Riparbelli MG, Giacomello E, Perinetti G, Pazour GJ, et al. Intraflagellar transport is required for polarized recycling of the TCR/CD3 complex to the immune synapse. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:1332–9.
Finetti F, Patrussi L, Galgano D, Cassioli C, Perinetti G, Pazour GJ, et al. The small GTPase Rab8 interacts with VAMP-3 to regulate the delivery of recycling T-cell receptors to the immune synapse. J Cell Sci. 2015;128:2541–52.
Onnis A, Finetti F, Patrussi L, Gottardo M, Cassioli C, Spano S, et al. The small GTPase Rab29 is a common regulator of immune synapse assembly and ciliogenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22:1687–99.
Vivar OI, Masi G, Carpier JM, Magalhaes JG, Galgano D, Pazour GJ, et al. IFT20 controls LAT recruitment to the immune synapse and T-cell activation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:386–91.
Badano JL, Leitch CC, Ansley SJ, May-Simera H, Lawson S, Lewis RA, et al. Dissection of epistasis in oligogenic Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Nature. 2006;439:326–30.
Cardenas-Rodriguez M, Osborn DP, Irigoin F, Grana M, Romero H, Beales PL, et al. Characterization of CCDC28B reveals its role in ciliogenesis and provides insight to understand its modifier effect on Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Hum Genet. 2013;132:91–105.
Soares H, Lasserre R, Alcover A. Orchestrating cytoskeleton and intracellular vesicle traffic to build functional immunological synapses. Immunol Rev. 2013;256:118–32.
Onnis A, Baldari CT. Orchestration of immunological synapse assembly by vesicular trafficking. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:110.
Das V, Nal B, Dujeancourt A, Thoulouze MI, Galli T, Roux P, et al. Activation-induced polarized recycling targets T cell antigen receptors to the immunological synapse; involvement of SNARE complexes. Immunity. 2004;20:577–88.
Granger E, McNee G, Allan V, Woodman P. The role of the cytoskeleton and molecular motors in endosomal dynamics. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014;31:20–29.
Martin-Cofreces NB, Sanchez-Madrid F. Sailing to and docking at the immune synapse: role of tubulin dynamics and molecular motors. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1174.
Seaman MN, Gautreau A, Billadeau DD. Retromer-mediated endosomal protein sorting: all WASHed up! Trends Cell Biol. 2013;23:522–8.
Gomez TS, Billadeau DD. A FAM21-containing WASH complex regulates retromer-dependent sorting. Dev Cell. 2009;17:699–711.
Derivery E, Sousa C, Gautier JJ, Lombard B, Loew D, Gautreau A. The Arp2/3 activator WASH controls the fission of endosomes through a large multiprotein complex. Dev Cell. 2009;17:712–23.
Wang J, Fedoseienko A, Chen B, Burstein E, Jia D, Billadeau DD. Endosomal receptor trafficking: Retromer and beyond. Traffic. 2018;19:578–90.
Jia D, Gomez TS, Billadeau DD, Rosen MK. Multiple repeat elements within the FAM21 tail link the WASH actin regulatory complex to the retromer. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23:2352–61.
Harbour ME, Breusegem SY, Seaman MN. Recruitment of the endosomal WASH complex is mediated by the extended ‘tail’ of Fam21 binding to the retromer protein Vps35. Biochem J. 2012;442:209–20.
Carter SP, Blacque OE. Membrane retrieval, recycling and release pathways that organise and sculpt the ciliary membrane. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019;59:133–9.
Radha Rama Devi A, Naushad SM, Lingappa L. Clinical and molecular diagnosis of joubert syndrome and related disorders. Pediatr Neurol. 2020;106:43–49.
Barroso-Gil M, Powell L, Sayer JA. RE: clinical and molecular diagnosis of joubert syndrome and related disorders. Pediatr Neurol. 2020;112:10.
Tsyklauri O, Niederlova V, Forsythe E, Prasai A, Drobek A, Kasparek P, et al. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome ciliopathy is linked to altered hematopoiesis and dysregulated self-tolerance. EMBO Rep 2021;22:e50785.
Romberg N, Lawrence MG. Birds of a feather: common variable immune deficiencies. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;123:461–7.
Capitani N, Baldari CT. F-actin dynamics in the regulation of endosomal recycling and immune synapse assembly. Front Immunol. 2021;9:670882. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.670882.
Cassioli C, Baldari CT. A Ciliary View of the Immunological Synapse. Cells 2019;8:789.
Gawden-Bone CM, Frazer GL, Richard AC, Ma CY, Strege K, Griffiths GM. PIP5 kinases regulate membrane phosphoinositide and actin composition for targeted granule secretion by cytotoxic lymphocytes. Immunity. 2018;49:427–37.
Cassioli C, Onnis A, Finetti F, Capitani C, Brunetti J, Compeer EB. et al. The Bardet-Biedl Syndrome complex component BBS1 regulates proteasome-dependent F-actin clearance from the centrosome to enable its translocation to the T cell immune synapse. Pre-print bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.30.403980.
Finetti F, Patrussi L, Masi G, Lucherini OM, Onnis A, Pazour GJ, et al. Immune synapse targeting of specific recycling receptors by the intraflagellar transport system. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:1924–37.
Tangye SG, Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, Chatila T, Cunningham-Rundles C, Etzioni A, et al. Human inborn errors of immunity: 2019 update on the classification from the international union of immunological societies expert committee. J Clin Immunol. 2020;40:24–64.
Yates AD, Achuthan P, Akanni W, Allen J, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, et al. Ensembl 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:D682–8.
Genomes Project C, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Garrison EP, Kang HM, et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature. 2015;526:68–74.
Karczewski KJ, Francioli LC, Tiao G, Cummings BB, Alfoldi J, Wang Q, et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature. 2020;581:434–43.
Manders EM, Stap J, Brakenhoff GJ, van Driel R, Aten JA. Dynamics of three-dimensional replication patterns during the S-phase, analysed by double labelling of DNA and confocal microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1992;103Pt 3:857–62.
Esquerre M, Tauzin B, Guiraud M, Muller S, Saoudi A, Valitutti S. Human regulatory T cells inhibit polarization of T helper cells toward antigen-presenting cells via a TGF-beta-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:2550–5.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Claire Hivroz for critical reading of the manuscript and Vincenzo Sorrentino for useful advice.
Funding
This work was carried out with the support of Fondazione Telethon, Italy (Grant GGP16003) to CTB. The support of ERC Synergy (grant 951329) to CTB is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NC, AO, FF, CC, and CTB designed research and analyzed and interpreted data; NC, AO, FF, CC, JB, AT, and CDB carried out the experiments; AP, SDE, MB, LG, DDB, MMD, and VL contributed vital reagents; NC and CTB drafted the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Experiments were performed after approval by the institutional review board of the Universities of Florence and Brescia. Peripheral blood was obtained after informed consent according to the Declaration of Helsinki, and sample size was kept small according to the guidelines of the ethics committee.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by G. Melino
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capitani, N., Onnis, A., Finetti, F. et al. A CVID-associated variant in the ciliogenesis protein CCDC28B disrupts immune synapse assembly. Cell Death Differ 29, 65–81 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00837-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00837-5
This article is cited by
-
A novel coiled-coil domain containing-related gene signature for predicting prognosis and treatment effect of breast cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)