Abstract
Allylation of nucleophiles with highly reactive electrophiles like allyl halides can be conducted without metal catalysts. Less reactive electrophiles, such as allyl esters and carbonates, usually require a transition metal catalyst to facilitate the allylation. Herein, we report a unique transition-metal-free allylation strategy with allyl ether electrophiles. Reaction of a host of allyl ethers with 2-azaallyl anions delivers valuable homoallylic amine derivatives (up to 92%), which are significant in the pharmaceutical industry. Interestingly, no deprotonative isomerization or cyclization of the products were observed. The potential synthetic utility and ease of operation is demonstrated by a gram scale telescoped preparation of a homoallylic amine. In addition, mechanistic studies provide insight into these C(sp3)–C(sp3) bond-forming reactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
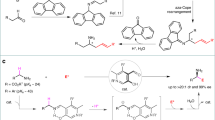
Since the importance of the medicinal chemistry concept “escaping from the flatlands” gained appreciation, greater research efforts have been devoted to the formation of bonds between two C(sp3) carbons1,2. The allylation of nucleophilic carbon centers is one of the most useful methods for the formation of C(sp3)–C(sp3) linkages3,4,5,6,7,8. As a result, it has been widely applied in the synthesis of bioactive compounds and natural products9,10,11,12,13,14,15. For decades, tremendous effort has been devoted to developing new and efficient methods for allylic alkylation. Most allylic alkylations fall into one of the two classes based on the nature of the allylic electrophile. When the electrophile possesses a potent leaving group, such as an allylic halide or pseudohalide, allylation reactions can be conducted in the absence of a catalyst. The drawback of these reactions, however, is the high reactivity of the electrophile, making selective reactions difficult. In cases where the allylic electrophile is less reactive, such as allylic acetates or carbonates, allylic alkylations can be performed with the assistance of a catalyst. This latter method has the advantage of more stable electrophilic substrates and has been widely employed with enantioenriched transition-metal catalysts16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25, most notably in the Tsuji-Trost reaction26,27,28,29,30,31,32. The shortcoming of this approach is it generally relies on precious metal catalysts. Recent advances on radical allylation reactions have also been reported33.
Allylic alkylation of carbanions can be used to prepare homoallylic amines. In particular Kauffmann and co-workers have prepared homoallylic amines by allylation of 2-azaallyl anions using allyl bromide as an electrophile34. Homoallylic amines are incredibly useful precursors for the synthesis of a vast number of biologically active molecules11,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48. Economical methods to prepare homoallylic amines remain in demand. The use of allylic alkylations49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56 or decarboxylative allylic alkylation reactions56,57,58,59,60,61 to prepare homoallylic amines has been demonstrated with various transition-metal catalysts, including Ni, Pd, Cu, Zn, Ir, Rh, and Yb (Fig. 1a, b).
Our team62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70 and other groups71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84 have been interested in the functionalization of 2-azaallyl anions through an umpolung strategy. Recently, we discovered and developed a unique radical generation approach85 for the transition-metal-free C(sp3)–C(sp2) (Fig. 2a) and C(sp3)–C(sp3) bond formations enabled by 2-azaallyl species86,87. We found that deprotonation of N-benzyl imines 1 generated semi-stabilized 2-azaallyl anions that readily undergo single electron transfer (SET) with a variety of electrophiles85, generating 2-azaallyl anion intermediates that are persistent radicals88. These species have now been isolated and characterized by electrochemical methods and X-ray crystallography69. Inspired by the work of Murphy and co-workers on organic super electron donors (SEDs)89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96, we demonstrated that 2-azaallyl anions served as SEDs and enabled transition-metal-free C−C bond formation via reduction of aryl or alkyl iodides followed by radical recombination with the resulting 2-azaallyl radical (Fig. 2a). This SED approach was further used for the preparation of benzofurylethylamines (Fig. 2b) and isochromene derivatives via SET from the 2-azaallyl anion, radical cyclization, and finally intermolecular radical–radical coupling reactions97,98. Based on the unusual reactivity of 2-azaallyl anions, we were curious about their ability to react with allyl electrophiles that bear leaving groups that were generally categorized as poor in both organic chemistry and in the presence of transition-metal allylation catalysts99,100,101,102,103.
Herein, we report a rare transition-metal-free C(sp3)–C(sp3) coupling of allyl phenyl ethers with 2-azaallyl anions (Fig. 2c). Specifically, we describe coupling of 2-azaallyl species with allyl phenyl ether electrophiles to furnish SN2- and SN2ʹ-type allylation products in good yields. This allylation approach enables the synthesis of homoallylic amines bearing various functional groups (38 examples, up to 92% yield). It is noteworthy that the simple combination of base and solvent enable the transition-metal-free allylation to proceed efficiently. Furthermore, no deprotonation and isomerization or cyclization of products was detected. Mechanistic studies provide insight into these C(sp3)–C(sp3) coupling reactions and suggest that reactions can proceed by either polar or radical mechanisms, depending on the substitution pattern of the electrophile.
Results
Reaction optimization
We initiated our reaction optimization using N-benzyl benzophenone imine 1a and commercial allyl phenyl ether 2a as coupling partners with 3.0 equiv. NaN(SiMe3)2 in MTBE (methyl tert-butyl ether) at room temperature for 12 h. To our delight, the allylation product 3aa was generated in 64% assay yield (AY, as determined by 1H NMR integration against an internal standard Table 1, entry 1). We previously discovered that solvent can play an important role in modulating reactivity of 2-azaallyl anions by coordination to the main group cation of the base69. Therefore, a variety of solvents, including DME (1,2-dimethoxyethane), CPME (cyclopentyl methyl ether), THF (tetrahydrofuran), 1,4-dioxane, DMSO, DMF, and toluene, were examined (entries 2–8). CPME and toluene provided the target product 3aa in 74% and 84% AY, respectively, while other solvents either gave reduced yields or led to no reaction. Using toluene, we next screened bases (LiOtBu, NaOtBu, KOtBu, LiN(SiMe3)2 and KN(SiMe3)2, entries 9–13). Of these, only LiN(SiMe3)2 and KN(SiMe3)2 afforded product 3aa in 23% and 8% AY. Other bases did not result in the desired product. When 2.0 equiv. of NaN(SiMe3)2 (entry 14) was employed, the yield dropped to 74%. However, the yield increased to 89% (with 86% isolated yield) when 4.0 equiv. of NaN(SiMe3)2 (entry 15) was used. Further decreasing the amount of 1a (from 2.0 to 1.5 equiv.), reaction time (from 12 h to 6 h), and concentration (from 0.2 M to 0.1 M) led to a decrease of yields to 63–73% (entries 16–18). Based on this optimization, the standard conditions for the allylic alkylation are those in entry 15 of Table 1.
Following the reaction optimization with allyl phenyl ether, we surveyed other allylic electrophiles. Under the optimized conditions, allyl substrates possessing leaving groups, such as allyl methyl ether (18% AY), allyl benzyl ether (14% AY), allyl benzoate (0% AY), allyl acetate (19% AY), allyl bromide (66% AY), allyl tert-butyl silyl ether (16% AY), and allyl tert-butyl diphenylsilyl (14% AY) provided the desired product in lower AY than allyl phenyl ether (89% AY). Thus, we selected allyl phenyl ether 2a as the allylating agent, which was easily synthesized from phenol.
Reaction scope of imines
With the optimized conditions in hand (Table 1, entry 15), we initiated investigation of the scope of N-benzyl ketimines 1 (Fig. 3a). In general, we found that a wide variety of ketimines with neutral, electron-rich, and electron-deficient Ar groups provided good to excellent yields. Electron-donating substituents 4-Me (1b) and 4-tBu (1c) generated allylic products 3ba and 3ca in 83% and 78% yields, respectively. 4-Methoxy and 3,4-methylenedioxy groups (1d and 1e) delivered products 3da and 3ea in 63% and 70% yields, respectively. N-benzyl ketimines bearing electronegative and electron-withdrawing groups, such as 4-F, 4-Cl, 4-Br, and 3-CF3, were also suitable coupling partners, providing the products 3fa, 3ga, 3ha, and 3ia in 73%, 45%, 35%, and 54% yields, respectively. Coupling with a ketimine possessing a biphenyl group (1j) produced the product 3ja in 59% yield. The influence of more sterically hindered N-benzyl ketimines was explored. Interestingly, 1-naphthyl (1k) and 2-Tol (1l) ketimines reacted with the allyl ether in good yields (92% and 73%, respectively), despite the increased steric hindrance. Finally, the heterocyclic ketimine bearing a 3-pyridyl (1m) and 2-thiophenyl (2n) were also competent coupling partners, furnishing product 3ma at 60 °C in 64% yield and 3na in 32% yield. With imines bearing 4-C6H4-CN, 4-C6H4-COOMe, 2-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl, or 2-thiazolyl were employed, no reaction occurred and the allyl ethers were recovered in >90% yields. In addition to the allylation products in Fig. 3a, minor regioisomeric allylation products 3aaʹ–3maʹ were detected in these reactions with yields ranging from 7% to 18% (see Supplementary information for details). This phenomenon is similar to the transition-metal-free arylation of 2-azaallyls reported previously by our group63.
In an effort to fully explore the scope of this transformation, we next investigated aldimine substrates. In our past work, the aldimines have generally proven to be inferior starting materials to their ketimine isomers, despite generating the identical 2-azaallyl anions. This is attributed to the challenging deprotonation of the more hindered diphenylmethyl C–H bond. The advantage of aldimines, however, is that there are many commercially available benzaldehyde precursors67. As shown in Fig. 3b, the optimized conditions for ketimines accommodated aldimines bearing various substituted aryl groups in yields slightly below those reported in Fig. 3a. The parent aldimine (1aʹ) and those with Ar groups supporting alkyl substituents, such as 4-Me (1bʹ) and 4-tBu (1cʹ), furnished the desired products 3aa, 3ba, and 3ca in 86%, 63%, and 53% yields, respectively. Aldimine substrates bearing electron-donating (4-OMe and dioxol), electronegative (4-F, 4-Cl, and 4-Br) and electron-withdrawing (3-CF3) groups led to products 3da, 3ea, 3fa, 3ga, 3ha, and 3ia in 31–66% yields. Coupling with biphenyl substrate (1jʹ) proceeded in 59% yield. The sterically hindered 1-naphthyl and 2-Me derivatives reacted with allyl phenyl ether to form the desired products 3ka and 3la in 89% and 84% yields. The higher yield of the aldimine 1lʹ over its ketimine counterpart 1l may be due to the increased steric hindrance about the benzylic C–H’s of the ketimine 1l, causing a lower conversion to the 2-azaallyl anion and subsequent yield of the products. Similarly, a few regioisomeric allylation products with yields ranging from 6% to 23% were obtained when aldimines were used as 2-azaallyl anion sources (see Supplementary information for details).
Encouraged by the results with ketimine and aldimine substrates, we turned our attention to surveying the scope in the allyl phenyl ether-coupling partner. Although the substrates examined were more sterically hindered and required higher temperature (110 °C), the scope was found to be broad (Fig. 4). Mono- or 1,1-disubstituted allyl ethers, such as 2-methylbut-3-en-2-yl (2b), 1-vinylcyclohexyl (2c), 2-methylallyl (2d), but-3-en-2-yl (2e), and pent-1-en-3-yl (2f) groups, were coupled with N-benzyl ketimine 1a at the least hindered position of the allyl ether to generate coupling products 3ab, 3ac, 3ad, 3ae, and 3af in 82%, 79%, 88%, 85%, and 64% yields, respectively. 1,2-Disubstituted allyl ethers, such as 3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl (2g), E-4-methylpent-2-en-1-yl (2h), E-2-methylpent-2-en-1-yl (2i), and E-but-2-en-1-yl (2j) groups, furnished linear coupling products 3ab, 3ah, 3ai, and 3ae in 76%, 64%, 71%, and 83% yields, respectively. Interestingly, the 1,2-disubstituted allyl bromide 3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl (2gʹ) provided product 3ab in a lower yield (44%) compared to the phenolic electrophile (76% yield). Allyl ethers with substituents both on the terminal and allylic positions, such as (E)-5-methylhex-3-en-2-yl (2k), (E)-3-methylpent-3-en-2-yl (2l), and (E)-1-cyclohexylbut-2-en-1-yl (2m) provided the less sterically hindered coupling products 3ak, 3al, and 3am in 43%, 52%, and 64% yields, respectively. The moderate yields may be due to increased steric hindrance in the C–C bond-forming step. In addition, regioisomeric allylation products 3abʹ and 3ahʹ were obtained with yields in 7% and 23%, respectively (see Supplementary Information for details). Notably, deprotonative isomerization or cyclization of allylated products was not detected for any of the coupling reactions in Figs. 3 and 4.
It is vital for a synthetic approach to be straightforward and scalable. Hence, we explored the scalability of this coupling reaction by a telescoped imine preparation/allylation process on gram scale (Fig. 5a). Treatment of the benzyl amine with benzophenone imine in DCM at room temperature for 12 h was followed by removal of the solvent under reduced pressure to form N-benzyl ketimine 1a. Next, the unpurified 1a was coupled with allyl phenyl ether 2a following the standard procedure. After 12 h at room temperature, workup, and purification 1.18 g of 3aa (76% over 2 steps) and 3aaʹ (109.0 mg, 7%) were generated. Hydrolysis of the allylated product 3aa was performed to deliver the homoallylic amine 4aa in 89% yield (Fig. 5b).
Mechanistic studies
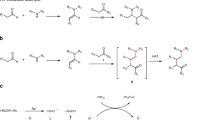
To obtain insight into the allylation reaction pathway, we carried out preliminary mechanistic investigations. In order to isolate the leaving group, we switched to an allyl aryl ether that would generate a less volatile phenolic product. When an allyl ether bearing a 2-naphthyl group 5a was employed for coupling with N-benzyl ketimine 1a, naphthalen-2-ol 6a was isolated in 90% yield together with the allylated products 3aa and 3aaʹ in 82% and 7% yields, respectively. This result indicates that 2-napthoxide was generated under the reaction conditions, followed by protonation upon workup (Fig. 6a).
To further probe the mechanism of the allylation reaction, a Hammett study was performed using intermolecular competition experiments (Fig. 6b). At the outset of these experiments, we were aware that the correlation of the relative rates might be impacted by concurrent reaction mechanisms (SN2, SN2ʹ, and radical). In the event, the Hammett plots show a loose correlation with typical polar substituent constant parameters (R2 = 0.55 for σ, R2 = 0.53 for σ−). The fit was improved by employing the σ• parameter (R2 = 0.62) (see Supplementary information for details). The experimental data could be better fitted to a two-parameter Hammett relationship104,105,106,107,108,109. For example, plotting log(krel) versus a combination of σ (33%) and σ• (67%) provided a better fit (R2 = 0.70) (Fig. 6c), which reflects the character of the selectivity-determining and rate-limiting step that might be expected from a combination of radical character with polar influences. The ρ value determined (ρ = +1.4), with this combination of σ scales, is smaller than would be expected for a SET mechanism, though still consistent with the buildup of negative charge105.
To probe the presence of radical intermediates in the allylation reaction, two radical-clock-containing cyclopropanes were prepared (see Supplementary Information, Synthesis of radical clock 7a and 11a for details). In the case of allylic ether radical clock 7a, the SN2 and SN2ʹ reaction pathways are hindered by the bulky substituents. The reaction of the cyclopropane radical clock 7a (2.0 mmol) with ketimine 1a in the presence of NaN(SiMe3)2 provided the allylated product 8aa in 32% and the cyclopropane ring-opened product 9aa in 15% yield (Fig. 7a). It is noteworthy that radical clock 7a is expected to favor ring-closed products, because ring opening produces a high-energy primary radical (Fig. 7a). Nonetheless, these results suggest that the coupling of hindered allyl phenyl ethers proceed, at least in part, through radical intermediates. A control experiment was carried out with 7a at 110 °C and NaN(SiMe3)2, but in the absence of ketimine 1a. Only the Claisen rearrangement product 10a was obtained (96% yield, Fig. 7b). No ring-opened product was observed. This result suggests that NaN(SiMe3)2 alone is not reacting as a reducing agent and the ketimine is necessary to generate radical intermediates.
The radical clock 11a was designed with a terminal double bond to facilitate the SN2ʹ reaction and with a phenyl cyclopropyl moiety that would give a benzylic radical if this substrate proceeded through radical ring-opened intermediates. When 11a (2.0 mmol) was subjected to ketimine 1a and NaN(SiMe3)2 at 110 °C, the allylated product 12aa was afforded in 83% yield with the cyclopropane intact. This observation suggests that, in the case of unhindered pathways for SN2ʹ, the two-electron process prevails. The cyclopropane ring-opened product 13aa was isolated in 15% yield (Fig. 8a). Crystals were obtained of the minor product 13aa and the structure confirmed by X-ray crystallography (CCDC 2039076).
A proposed mechanism for the formation of 13aa is provided in Fig. 8b. Based on DFT calculations, we previously proposed that the 2-azaallyl anion (S1) could undergo SET with ketimine 1a to generate the 2-azaallyl radical (S3) and the ketiminyl radical anion (S2). Here, the resulting 2-azaallyl radical (S3) undergoes addition to the double bond to generate a C–C bond and a new radical (S4). This radical can eliminate the phenoxy radical, which can abstract H• from the benzylic hydrogen in S4. Formation of phenol is accompanied by generation of radical S5 and its resonance form S6. The radical character in S6 can add to the π-system of the newly formed double bond to generate S7. This addition places the radical alpha to the cyclopropyl group, which opens to give the stabilized benzylic radical S8. Intermediate S8 then gains a hydrogen and an electron, possibly through reduction of the benzylic radical by the ketiminyl anion (S2) and proton transfer from HN(SiMe3)2. This mechanism is reminiscent of our previous work85, in which vinyl bromides reacted with 2-azaallyl species via either an anionic substitution pathway with the 2-azaallyl anion or a radical pathway with the 2-azaallyl radical.
In order to probe this system for radical behavior, an additional set of experiments were performed (Fig. 9a). First, the allylation product 3aa (0.4 mmol) was reacted in the presence of NaN(SiMe3)2 (4.0 equiv.) for 0.5 h at room temperature (Fig. 9a). This resulted in the formation of a dark purple solution, consistent with deprotonation of the ketimine to generate the 2-azaallyl anion. Next, ketimine 1a was added at 110 °C. After heating at this temperature for 12 h, the reaction was worked up following the standard procedure. Dihydropyrrole product 14aa was isolated in 38% yield. A proposed mechanism for the formation of 14aa is provided that is based on the notion that the 2-azaallyl anion can undergo SET with ketimine 1a to generate the ketiminyl anion and 2-azaallyl radical, as we previously reported85. One could imagine that the ketimines and aldimines are in equilibrium with the 2-azaallyl anions. Under such circumstances, SET from 2-azaallyl anion S9 to ketimine 1a would generate ketiminyl anion S2 and the 2-azaallyl radical (S10). Resonance form S11 could then undergo addition to the double bond to generate a C–C bond and a new radical (S12). Intermediate S12 gains a hydrogen and an electron, possibly via HAT from S2 to form the dihydropyrrole 14aa. While the exact mechanism of this transformation is not clear, it does have the hallmarks of a radical process rather than a two-electron addition of the 2-azaallyl anion to the double bond, which would give rise to a primary carbanion. When the reaction is carried out by combining both 3aa and 1a at the same time, the yield of the dihydropyrrole increased to 47%. We note that when the reaction is conducted in the absence of 1a, no major product is observed and less than 5% 14aa is detected by NMR.
a Mechanistic experiment with allylation product 3aa. b EPR experimental conditions. c X-band EPR spectrum of the PBN-trapped carbon-centered radical (T = 298 K; microwave frequency: 9.462390 GHz; power: 0.2 mW; center field: 336.00 mT; sweep width: 15.0 mT; modulation frequency, 100 kHz; modulation amplitude, 100 μT). SET, single electron transfer. EPR, electron paramagnetic resonance.
Spin trapping experiments using phenyl N-tert-butylnitrone (PBN) as the spin trap support the proposed radical-type mechanism. Heating a mixture of 1a, 2g, NaN(SiMe3)2 in the presence of PBN led to the formation of a PBN-trapped carbon-centered radical, as detected by EPR spectroscopy (Fig. 9b, c). The resulting EPR signal (g = 2.0040, AN = 14.9 G, AH = 2.4 G) is strong and similar to other reported PBN-trapped carbon-centered radicals110,111. The cationic signal of radical 15 can be detected in the reaction mixtures by high-resolution mass spectroscopy (HRMS calculated for C16H24NO•+ 246.1852, found 246.1851 [M]•+).
Discussion
We have outlined reactivity of 2-azaallyl anions that is founded in their ability to behave as super electron donors. This chemistry represents a unique transition-metal-free allylation of 2-azaallyls with allyl ethers to prepare homoallylic amine derivatives, which are of value in the pharmaceutical industry. In this reaction, simple, readily prepared allyl phenyl ethers coupled with azaallyl anions or azaallyl radicals to construct new C(sp3)–C(sp3) bonds in excellent yields. Notably, the simple combination of base and solvent enabled the metal-free allylation to proceed efficiently, in which no deprotonative isomerization or cyclization of products was detected. A gram-scale telescoped homoallylic amine preparation was carried out, demonstrating the potential synthetic utility of this chemistry. In addition, mechanistic studies provide insight into these C(sp3)–C(sp3) bond-forming reactions and support substrate-dependent radical and anionic pathways. Unlike past advances, this allylation approach enables the synthesis of a diverse array of homoallylic amines without the addition of transition-metal catalysts, photocatalysts, or organometallic reagents. These attributes increase the attractiveness of this method for applications in the pharmaceutical industry112.
Methods
General procedure
An oven-dried 8 mL reaction vial equipped with a stir bar was charged with ketimine 1 (1.2 mmol) or aldimine 1ʹ (1.2 mmol) and allyl phenyl ether 2 (0.6 mmol) under a nitrogen atmosphere in a glove box. A solution of NaN(SiMe3)2 (2.4 mmol) in 3 mL dry toluene was added to the reaction vial. The reaction mixture turned to a dark purple solution. Then the vial was sealed with a cap, removed from the glove box, and stirred for 12 h at room temperature (Fig. 3) or 110 °C (Fig. 4). The room temperature reaction mixture was opened to air, quenched with three drops of H2O, diluted with 3 mL of ethyl acetate, and filtered over a 2 cm pad of MgSO4 and deactivated silica. The pad was rinsed with ethyl acetate (3 × 2 mL), and the combined organic solutions were concentrated in vacuo. The crude material was purified on an Agilent HPLC 1260 system using acetonitrile:H2O (75:25 vol./vol.) as the mobile phase and flow rate of 3.5 mL/min with monitoring at 254 nm to give product 3.
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary information files. For the experimental procedures and spectroscopic and physical data of compounds, see Supplementary Methods. For 1H and 13C{1H} NMR spectra of compounds, see Supplementary Figs. 1–127. The X-ray crystallographic coordinates for structures reported in this study have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC), under deposition numbers of CCDC 2039076. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.
References
Lovering, F., Bikker, J. & Humblet, C. Escape from flatland: increasing saturation as an approach to improving clinical success. J. Med. Chem. 52, 6752–6756 (2009).
Lovering, F. Escape from flatland 2: complexity and promiscuity. Med. Chem. Commun. 4, 515–519 (2013).
Masse, C. E. & Panek, J. S. Diastereoselective reactions of chiral allyl- and allenylsilanes with activated C=X π-bonds. Chem. Rev. 95, 1293–1316 (1995).
Bower, J. F., Kim, I. S., Patman, R. L. & Krische, M. J. Catalytic carbonyl addition through transfer hydrogenation: a departure from preformed organometallic reagents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 34–46 (2009).
Ketcham, J. M. et al. Evaluation of chromane-based bryostatin analogues prepared via hydrogen-mediated C−C bond formation: potency does not confer bryostatin-like biology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 13415–13423 (2016).
Xu, B. & Tambar, U. K. Remote allylation of unactivated C(sp3)–H bonds triggered by photogenerated amidyl radicals. ACS Catal. 9, 4627–4631 (2019).
Tanabe, S., Mitsunuma, H. & Kanai, M. Catalytic allylation of aldehydes using unactivated alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 12374–12381 (2020).
Cartwright, K. C. & Tunge, J. A. Organophotoredox/palladium dual catalytic decarboxylative Csp3–Csp3 coupling of carboxylic acids and π-electrophiles. Chem. Sci. 11, 8167–8175 (2020).
Trost, B. M. & Toste, F. D. Enantioselective total synthesis of (-)-galanthamine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 11262–11263 (2000).
Trost, B. M., Thiel, O. R. & Tsui, H. C. DYKAT of baylis-hillman adducts: concise total synthesis of furaquinocin E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 11616–11617 (2002).
Yus, M., Gonzalez-Gomez, J. C. & Foubelo, F. Diastereoselective allylation of carbonyl compounds and imines: application to the synthesis of natural products. Chem. Rev. 113, 5595–5698 (2013).
Bailey, A. M., Wolfrum, S. & Carreira, E. M. Biological investigations of (+)-danicalipin A enabled through synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 639–643 (2016).
Cabrera, J. M. & Krische, M. J. Total synthesis of clavosolide avia asymmetric alcohol-mediated carbonyl allylation: beyond protecting groups or chiral auxiliaries in polyketide construction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 10718–10722 (2019).
Clementson, S., Jessing, M., Pedersen, H., Vital, P. & Kristensen, J. L. Enantioselective total synthesis of (+)-dihydro-β-erythroidine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 8783–8786 (2019).
Komine, K. et al. Formal synthesis of (-)-haliclonin A: stereoselective construction of an azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane ring system by a tandem radical reaction. Org. Lett. 22, 5046–5050 (2020).
Watson, I. D. G., Styler, S. A. & Yudin, A. K. Unusual selectivity of unprotected aziridines in palladium-catalyzed allylic amination enables facile preparation of branched aziridines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 5086–5087 (2004).
Alexakis, A., Bäckvall, J. E., Krause, N., Pàmies, O. & Diéguez, M. Enantioselective copper-catalyzed conjugate addition and allylic substitution reactions. Chem. Rev. 108, 2796–2823 (2008).
Harutyunyan, S. R., Hartog, T., Geurts, K., Minnaard, A. J. & Feringa, B. L. Catalytic asymmetric conjugate addition and allylic alkylation with grignard reagents. Chem. Rev. 108, 2824–2852 (2008).
Lu, Z. & Ma, S. Metal-catalyzed enantioselective allylation in asymmetric synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 258–297 (2008).
Weaver, J. D., Recio, A. 3rd, Grenning, A. J. & Tunge, J. A. Transition metal-catalyzed decarboxylative allylation and benzylation reactions. Chem. Rev. 111, 1846–1913 (2011).
Sha, S. C., Zhang, J., Carroll, P. J. & Walsh, P. J. Raising the pKa limit of “soft” nucleophiles in palladium-catalyzed allylic substitutions: application of diarylmethane pronucleophiles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 17602–17609 (2013).
Trost, B. M. Metal catalyzed allylic alkylation: its development in the trost laboratories. Tetrahedron 71, 5708–5733 (2015).
Tsuji, J. Dawn of organopalladium chemistry in the early 1960s and a retrospective overview of the research on palladium-catalyzed reactions. Tetrahedron 71, 6330–6348 (2015).
Haruki, H., Yasuda, S., Nagao, K. & Ohmiya, H. Dehydrative allylation between aldehydes and allylic alcohols through synergistic N-heterocyclic carbene/palladium catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 25, 724–727 (2019).
Bag, S. et al. Palladium-catalyzed meta-C−H allylation of arenes: a unique combination of a pyrimidine-based template and hexafluoroisopropanol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 12453–12466 (2020).
Trost, B. M. Asymmetric transition metal-catalyzed allylic alkylations. Chem. Rev. 96, 395–422 (1996).
Trost, B. M. & Crawley, M. L. Asymmetric transition-metal-catalyzed allylic alkylations: applications in total synthesis. Chem. Rev. 103, 2921–2943 (2003).
Trost, B. M. Asymmetric allylic alkylation, an enabling methodology. J. Org. Chem. 69, 5813–5837 (2004).
Trost, B. M., Machacek, M. R. & Aponick, A. Predicting the stereochemistry of diphenylphosphino benzoic acid (DPPBA)-based palladium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic alkylation reactions: a working model. Acc. Chem. Res. 39, 747–760 (2006).
Trost, B. M. & Thaisrivongs, D. A. Palladium-catalyzed regio-, diastereo-, and enantioselective benzylic allylation of 2-substituted pyridines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 12056–12057 (2009).
Trost, B. M., Xu, J. & Schmidt, T. Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative asymmetric allylic alkylation of enol carbonates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 18343–18357 (2009).
Trost, B. M., Thaisrivongs, D. A. & Hartwig, J. Palladium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic alkylations of polynitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 12439–12441 (2011).
Huang, H., Bellotti, P. & Glorius, F. Transition metal-catalysed allylic functionalization reactions involving radicals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 6186–6197 (2020).
Kauffmann, T., Berg, H., Kiippelmann, E. & Kuhlmann, D. New reagents. I. Nucleophilic aminomethylation of ketones and organic halides with 1,1-diphenyl-2-azaallyllithium. Chem. Ber. 110, 2659–2664 (1977).
Umezawa, I. et al. A new antitumor antibiotic, stubomycin. J. Antibiot. 34, 259–265 (1981).
Sandgren, V. et al. Highly potent macrocyclic BACE-1 inhibitors incorporating a hydroxyethylamine core: design, synthesis and X-ray crystal structures of enzyme inhibitor complexes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20, 4377–4389 (2012).
Wright, D. L., Schulte, J. P. II & Page, M. A. An imine addition/ring-closing metathesis approach to the spirocyclic core of halichlorine and pinnaic acid. Org. Lett. 2, 1847–1850 (2000).
Puentes, C. O. & Kouznetsov, V. Recent advancements in the homoallylamine chemistry. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 39, 595–614 (2002).
Gille, S., Ferry, A., Billard, T. & Langlois, B. R. Synthesis of α-trifluoromethylated nitrogen heterocycles. J. Org. Chem. 68, 8932–8935 (2003).
Danieli, B. et al. Total enantioselective synthesis of (−)-cytisine. Org. Lett. 6, 493–496 (2004).
Ramachandran, P. V., Burghardt, T. E. & Bland-Berry, L. Chiral synthesis of functionalized tetrahydropyridines: γ-aminobutyric acid uptake inhibitor analogues. J. Org. Chem. 70, 7911–7918 (2005).
Hernandez, E., Canales, E., Gonzalez, E. & Soderquist, J. A. Asymmetric synthesis with the robust and versatile 10-substituted 9-borabicyclo[3.3.2]decanes: homoallylic amines from aldimines. Pure Appl. Chem. 78, 1389–1395 (2006).
Ramachandran, P. V. & Burghardt, T. E. Recent developments in the chiral synthesis of homoallylic amines via organoboranes. Pure Appl. Chem. 78, 1397–1406 (2006).
Chandrasekhar, S. & Tiwari, B. Synthesis of the C10–C24 fragment of (+)-cannabisativine. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 20, 1924–1929 (2009).
Batey, R. & Ramadhar, T. Allylation of imines and their derivatives with organoboron reagents: stereocontrolled synthesis of homoallylic amines.Synthesis 2011, 1321–1346 (2011).
Medjahdi, M., González-Gómez, J.C., Foubelo, F. & Yus, M. Concise route to (-)- and (+)-aphanorphine.Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 2230–2234 (2011).
Yus, M., Gonzalez-Gomez, J. C. & Foubelo, F. Catalytic enantioselective allylation of carbonyl compounds and imines. Chem. Rev. 111, 7774–7854 (2011).
Teh, W. P. & Michael, F. E. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling of N-sulfonylaziridines and alkenylboronic acids: stereospecific synthesis of homoallylic amines with di- and trisubstituted alkenes. Org. Lett. 19, 1738–1740 (2017).
Li, Z., Zhang, L., Nishiura, M. & Hou, Z. Copper-catalyzed umpolung of imines through carbon-to-nitrogen boryl migration. ACS Catal. 9, 4388–4393 (2019).
Li, W. S. et al. Enantioselective rhodium-catalyzed allylation of aliphatic imines: synthesis of chiral C-aliphatic homoallylic amines. Org. Lett. 22, 5675–5679 (2020).
Wang, Y., Deng, L. F., Zhang, X. & Niu, D. Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of α-tetrasubstituted α-trifluoromethyl homoallylic amines by Ir-catalyzed umpolung allylation of imines. Org. Lett. 21, 6951–6956 (2019).
Barros, O. S., Sirvent, J. A., Foubelo, F. & Yus, M. Diastereoselective allylation and crotylation of N-tert-butanesulfinyl imines with allylic alcohols. Chem. Commun. 50, 6898–6901 (2014).
Zhao, L. M., Zhang, S. Q., Jin, H. S., Wan, L. J. & Dou, F. Zinc-mediated highly α-regioselective prenylation of imines with prenyl bromide. Org. Lett. 14, 886–889 (2012).
Qiao, X. C., Zhu, S. F., Chen, W. Q. & Zhou, Q. L. Palladium-catalyzed asymmetric umpolung allylation of imines with allylic alcohols. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 21, 1216–1220 (2010).
Yamanaka, M., Nishida, A. & Nakagawa, M. Ytterbium(III) triflate/TMSCl: efficient catalyst for imino ene reaction. Org. Lett. 2, 159–161 (2000).
Liu, C. et al. Nickel-catalyzed decarboxylative generation and asymmetric allylation of 2-azaallyl anions. J. Org. Chem. 84, 10102–10110 (2019).
Yeagley, A. A. & Chruma, J. J. C−C bond-forming reactions via Pd-mediated decarboxylative α-imino anion generation. Org. Lett. 9, 2879–2882 (2007).
Yeagley, A. A., Lowder, M. A. & Chruma, J. J. Tandem C−C bond-forming processes: interception of the Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative allylation of allyl diphenylglycinate imines with activated olefins. Org. Lett. 11, 4022–4025 (2009).
Qian, X. et al. Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative generation and asymmetric allylation of α-imino anions. Org. Lett. 16, 5228–5231 (2014).
Wang, X., Zeng, X., Lin, Q., Li, M. & Chruma, J. J. Palladium-catalysed decarboxylative generation and regiodivergent prenylation of 2-azaallyl anions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 361, 3751–3757 (2019).
Burger, E. C. & Tunge, J. A. Synthesis of homoallylic amines via the palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling of amino acid derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 10002–10003 (2006).
Shelp, R. A. & Walsh, P. J. Synthesis of BCP benzylamines from 2-azaallyl anions and [1.1.1]propellane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 15857–15861 (2018).
Li, M. et al. Transition-metal-free radical C(sp3)-C(sp2) and C(sp3)-C(sp3) coupling enabled by 2-azaallyls as super-electron-donors and coupling-partners. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 16327–16333 (2017).
Li, M. et al. Palladium-catalyzed C−H arylation of α,β-unsaturated imines: catalyst-controlled synthesis of enamine and allylic amine derivatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 2825–2829 (2016).
Li, M. et al. Umpolung synthesis of diarylmethylamines via palladium-catalyzed arylation of N-benzyl aldimines. Adv. Synth. Catal. 358, 1910–1915 (2016).
Li, M., Yucel, B., Adrio, J., Bellomo, A. & Walsh, P. J. Synthesis of diarylmethylamines via palladium-catalyzed regioselective arylation of 1,1,3-triaryl-2-azaallyl anions. Chem. Sci. 5, 2383–2391 (2014).
Li, M., Berritt, S. & Walsh, P. J. Palladium-catalyzed regioselective arylation of 1,1,3-triaryl-2-azaallyl anions with aryl chlorides. Org. Lett. 16, 4312–4315 (2014).
Wang, J. et al. Transition metal-free synthesis of α-aminophosphine oxides through C(sp3)−P coupling of 2-azaallyls. Adv. Synth. Catal. 362, 2268–2273 (2020).
Panetti, G. B. et al. Synthesis of an elusive, stable 2-azaallyl radical guided by electrochemical and reactivity studies of 2-azaallyl anions. Chem. Sci. 12, 4405–4410 (2021).
Zhang, L. et al. Transition-metal-free C(sp3)-H coupling of cycloalkanes enabled by single-electron transfer and hydrogen atom transfer. Org. Lett. 23, 1714–1719 (2021).
Matsumoto, Y. et al. Amino acid schiff base bearing benzophenone imine as a platform for highly congested unnatural α-amino acid synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 8498–8505 (2020).
Burger, E. C. & Tunge, J. A. Synthesis of homoallylic amines via the palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling of amino acid derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 10002–10003 (2006).
Zhu, Y. & Buchwald, S. L. Ligand-controlled asymmetric arylation of aliphatic α-amino anion equivalents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 4500–4503 (2014).
Wu, Y., Hu, L., Li, Z. & Deng, L. Catalytic asymmetric umpolung reactions of imines. Nature 523, 445–450 (2015).
Liu, J., Cao, C. G., Sun, H. B., Zhang, X. & Niu, D. Catalytic asymmetric umpolung allylation of imines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 13103–13106 (2016).
Liu, Y. E. et al. Enzyme-inspired axially chiral pyridoxamines armed with a cooperative lateral amine chain for enantioselective biomimetic transamination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 10730–10733 (2016).
Niwa, T., Yorimitsu, H. & Oshima, K. Palladium-catalyzed benzylic arylation of N-benzylxanthone imine. Org. Lett. 10, 4689–4691 (2008).
Fields, W. H. & Chruma, J. J. Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative benzylation of diphenylglycinate imines. Org. Lett. 12, 316–319 (2010).
Daniel, P. E., Weber, A. E. & Malcolmson, S. J. Umpolung synthesis of 1,3-amino alcohols: stereoselective addition of 2-azaallyl anions to epoxides. Org. Lett. 19, 3490–3493 (2017).
Tang, S., Zhang, X., Sun, J., Niu, D. & Chruma, J. J. 2-Azaallyl anions, 2-azaallyl cations, 2-azaallyl radicals, and azomethine ylides. Chem. Rev. 118, 10393–10457 (2018).
Reddy, L. R. et al. Umpolung synthesis of vicinal diamines: diastereoselective addition of 2-azaallyl anions to Davis-Ellman’s imines. Org. Lett. 20, 5423–5426 (2018).
Cao, C. G., He, B., Fu, Z. & Niu, D. Synthesis of β3-amino esters by iridium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic alkylation reaction. Org. Process Res. Dev. 23, 1758–1761 (2019).
Wang, Y. et al. 2-Azaallyl anion initiated ring-opening polymerization of N-sulfonyl aziridines: one-pot synthesis of primary amine-ended telechelic polyaziridines. Macromolecules 52, 3888–3896 (2019).
Niwa, T., Suehiro, T., Yorimitsu, H. & Oshima, K. Carbon–carbon bond formations at the benzylic positions of N-benzylxanthone imines and N-benzyldi-1-naphthyl ketone imine. Tetrahedron 65, 5125–5131 (2009).
Li, M. et al. Transition-metal-free chemo- and regioselective vinylation of azaallyls. Nat. Chem. 9, 997–1004 (2017).
Wang, Q., Poznik, M., Li, M., Walsh, P. J. & Chruma, J. J. 2-Azaallyl anions as light-tunable super-electron-donors: coupling with aryl fluorides, chlorides, and bromides. Adv. Synth. Catal. 360, 2854–2868 (2018).
Liu, Z. et al. Transition-metal-free C(sp3)–H/C(sp3)–H dehydrogenative coupling of saturated heterocycles with N-benzyl imines. Chem. Sci. 11, 7619–7625 (2020).
Leifert, D. & Studer, A. The persistent radical effect in organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 59, 74–108 (2020).
Farwaha, H. S., Bucher, G. & Murphy, J. A. A novel neutral organic electron donor with record half-wave potential. Org. Biomol. Chem. 11, 8073–8081 (2013).
Doni, E. & Murphy, J. A. Evolution of neutral organic super-electron-donors and their applications. Chem. Commun. 50, 6073–6087 (2014).
Murphy, J. A. Discovery and development of organic super-electron-donors. J. Org. Chem. 79, 3731–3746 (2014).
Zhou, S. et al. Identifying the roles of amino acids, alcohols and 1,2-diamines as mediators in coupling of haloarenes to arenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 17818–17826 (2014).
Doni, E., Zhou, S. & Murphy, J. A. Electron transfer-induced coupling of haloarenes to styrenes and 1,1-diphenylethenes triggered by diketopiperazines and potassium tert-butoxide. Molecules 20, 1755–1774 (2015).
Anderson, G. M., Cameron, I., Murphy, J. A. & Tuttle, T. Predicting the reducing power of organic super electron donors. RSC Adv. 6, 11335–11343 (2016).
Barham, J. P. et al. KOtBu: a privileged reagent for electron transfer reactions? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 7402–7410 (2016).
Barham, J. P. et al. Dual roles for potassium hydride in haloarene reduction: CSNAr and single electron transfer reduction via organic electron donors formed in benzene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 11510–11518 (2018).
Deng, G. et al. Synthesis of benzofuran derivatives through cascade radical cyclization/intermolecular coupling of 2-azaallyls. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 2826–2830 (2019).
Yu, K. et al. An efficient route to isochromene derivatives via cascade radical cyclization and radical–radical coupling. Adv. Synth. Catal. 361, 4354–4359 (2019).
Suzuki, N., Kondakov, D. Y. & Takahashi, T. Zirconium-catalyzed highly regioselective carbon–carbon bond formation reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 8485–8486 (1993).
Lalic, G., Blum, S. A. & Bergman, R. G. Zirconium-mediated SN2′ substitution of allylic ethers: regio- and stereospecific formation of protected allylic amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 16790–16791 (2005).
Perez, M. et al. Asymmetric allylic alkylation of acyclic allylic ethers with organolithium reagents. Chem. Eur. J. 18, 11880–11883 (2012).
Huo, X. et al. Hydrogen-bond-activated palladium-catalyzed allylic alkylation via allylic alkyl ethers: challenging leaving groups. Org. Lett. 16, 1570–1573 (2014).
Butt, N. A. & Zhang, W. Transition metal-catalyzed allylic substitution reactions with unactivated allylic substrates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 7929–7967 (2015).
Hikawa, H., Mori, Y., Kikkawa, S. & Azumaya, I. A radical pathway for direct substitution of benzyl alcohols with water-soluble copper catalyst in water. Adv. Synth. Catal. 358, 765–773 (2016).
Hedstrom, A., Izakian, Z., Vreto, I., Wallentin, C. J. & Norrby, P. O. On the radical nature of iron-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. Chem. Eur. J. 21, 5946–5953 (2015).
Maestre, L., Sameera, W. M., Diaz-Requejo, M. M., Maseras, F. & Perez, P. J. A general mechanism for the copper- and silver-catalyzed olefin aziridination reactions: concomitant involvement of the singlet and triplet pathways. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 1338–1348 (2013).
Liu, J., Hu, L., Wang, L., Chen, H. & Deng, L. An iron(II) ylide complex as a masked open-shell iron alkylidene species in its alkylidene-transfer reactions with alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 3876–3888 (2017).
Bagchi, V. et al. Comparative nitrene-transfer chemistry to olefinic substrates mediated by a library of anionic Mn(II) triphenylamido-amine reagents and M(II) congeners (M=Fe, Co, Ni) favoring aromatic over aliphatic alkenes. ACS Catal. 8, 9183–9206 (2018).
Dust, J. M. & Arnold, D. R. Substituent effects on benzyl radical ESR hyperfine coupling constants. The σα• scale based upon spin delocalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105, 1221–1227 (2002).
Das, B. G., Chirila, A., Tromp, M., Reek, J. N. & Bruin, B. Co(III)-carbene radical approach to substituted 1H-indenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 8968–8975 (2016).
Buettner, G. R. Spin trapping: ESR parameters of spin adducts. Free Radic. Bio. Med. 3, 259–303 (1987).
Garrett, C. E. & Prasad, K. The art of meeting palladium specifications in active pharmaceutical ingredients produced by Pd-catalyzed reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 346, 889–900 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFE0109200), NSFC (U1702286), Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Teams in Universities (IRT17R94), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M663581), the NSF of Yunnan Province (2019FY003010 and 202005AB160003), the YunLing Scholar Programs and IRTSTYN. P.J.W. thanks the US National Science Foundation (CHE-1902509) for financial support. We thank Prof. Chengfeng Xia for the help with EPR equipments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.D. and S.D. contributed equally to this work. X.Y. conceived of the project. H.Z. and P.J.W. designed the experiments. G.D., S.D., J.W., Z.C., T.L., and W.C. performed the research. X.Y. and P.J.W. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks Junmin Zhang and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, G., Duan, S., Wang, J. et al. Transition-metal-free allylation of 2-azaallyls with allyl ethers through polar and radical mechanisms. Nat Commun 12, 3860 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24027-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24027-6
This article is cited by
-
Catalytic asymmetric α C(sp3)–H addition of benzylamines to aldehydes
Nature Catalysis (2022)