Fig. 1: Associations among HMV, serum susceptibility, and gene mutation frequency in the Kp clinical isolates.
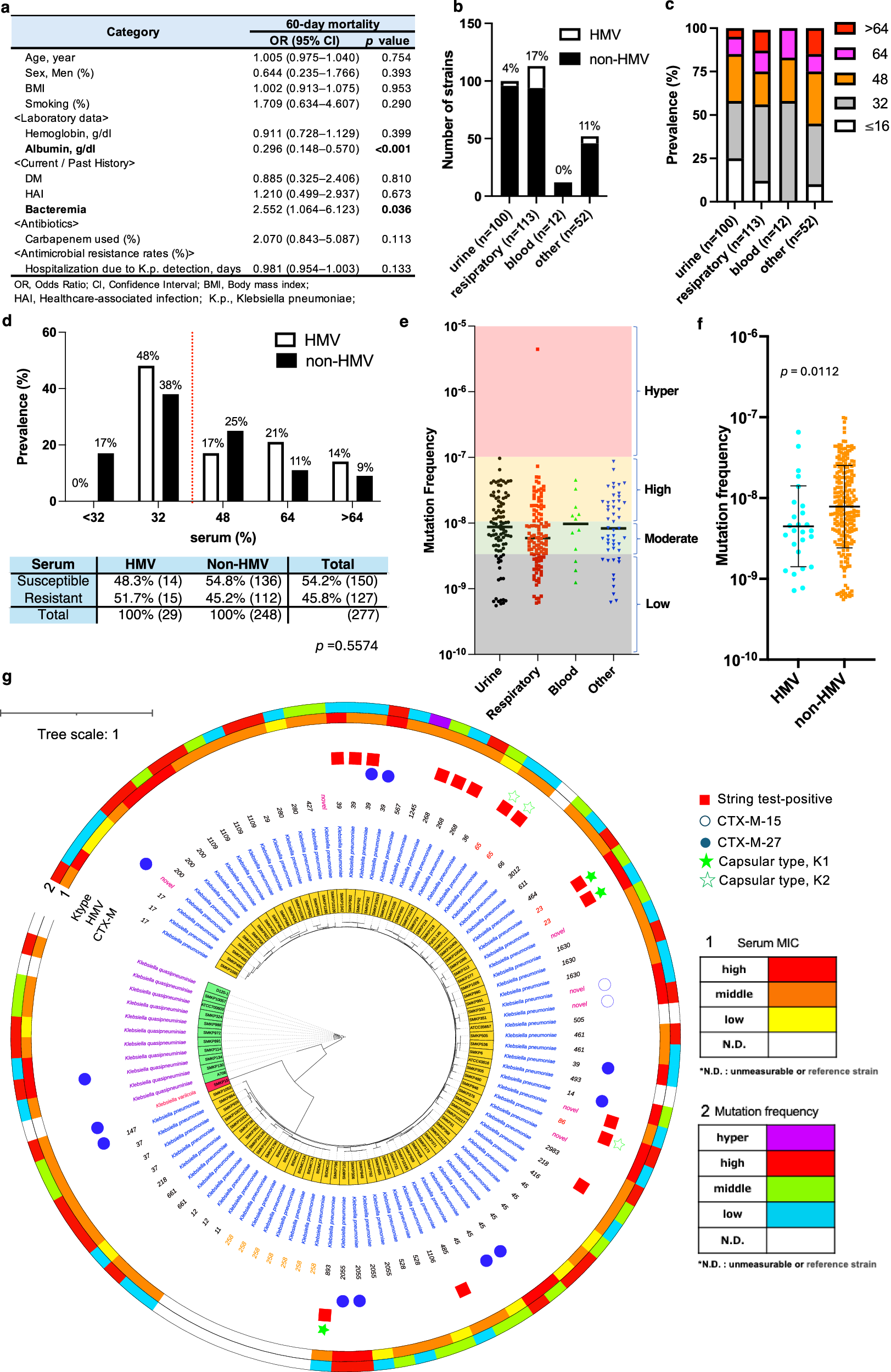
a Influence of bacteraemia caused by Kp infection on 60-day mortality. Multivariate logistic regression analysis (two-sided) demonstrated that Kp bacteraemia was associated with increased 60-day mortality independent of these confounders. No multiple-comparison adjustments were applied. A p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. b Numbers of HMV-Kp and non-HMV-Kp isolates derived from clinical specimens. The percentage indicates the prevalence of HMV-Kp isolates. c Susceptibility of human serum. The values indicate the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of human serum (%, vol/vol in MHBII). d Distribution of serum MICs. The y-axis shows the prevalence of isolates among the HMV and non-HMV groups. The dotted red line indicates the breakpoint of serum resistance. No significant difference in serum resistance was observed between the HMV and non-HMV groups by two-sided Fisher’s exact test (p = 0.5574). e Frequency of gene mutation in the Kp clinical isolates determined via the rifampicin assay. We defined mutators as low (< 5 × 10−8), moderate (from 5 × 10−9 to 10−8), high (from 10−8 to 10−7), and hyper (> 10−7) according to their mutation. A hypermutator was identified from a clinical respiratory sample (non-HMV isolate SMKP590; mutation frequency: 4.43 × 10−6). The geometric means were indicated, and no significant differences in gene mutation frequency were detected among each isolation site by the two-sided Kruskal‒Wallis test (p = 0.2519). f Comparison of the mutation frequencies of the HMV-Kp (n = 26) and non-HMV-Kp (n = 241) clinical isolates. The value of the hypermutator non-HMV strain was removed to evaluate the majority. The geometric means and geometric standard deviations are given, and a two-sided Student’s t test was used for the statistical analysis. g Core genome SNP analysis of respiratory Kp clinical isolates. The 84 Kp clinical isolates identified by the MALDI Biotyper were 75 Kp strains, eight Klebsiella quasipneumoniae strains, and one Klebsiella variicola strain, as determined by average nucleotide identity (ANI) analysis. HMV (string test-positive) isolates were classified into several STs (ST23, ST39, ST65, ST86, ST218, ST268, ST458, ST893, and some novel STs) and are shown in the red square. We included the carbapenem-resistant Kp strains of ST258 from the NCBI database (shown in orange) as references.
