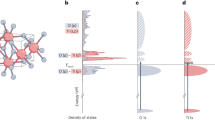
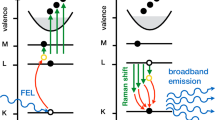
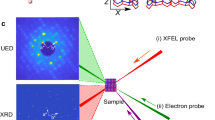
Abstract
Time-resolved resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (tr-RIXS) is a powerful technique for probing quasiparticle interactions in quantum materials under nonequilibrium conditions. Here, we implement tr-RIXS at the carbon K-edge to investigate the ultrafast dynamics of core excitons coupled to vibrational modes in graphite. Using femtosecond X-ray pulses from a free-electron laser, we monitor the temporal evolution of vibronically dressed excitons and their interaction with symmetry-selective optical phonons. By tuning the incident photon energy across the 1s → σ* resonance and analyzing the integrated inelastic sideband intensity, we reveal a detuning-controlled crossover between two complementary dynamical regimes. Phenomenological modeling and first-principles calculations reproduce both the magnitude and detuning dependence of the spectral-weight changes. In this work, enabled by the unique capabilities of X-ray free-electron lasers, we demonstrate how tr-RIXS can access coupled electronic and lattice dynamics with elemental and symmetry specificity, opening new routes to control vibronic interactions in light-element and low-dimensional quantum materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study, including raw and processed RIXS spectra, XAS profiles, and analysis outputs, are publicly available in the Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste S.C.p.A. repository under the title Dataset of Ultrafast dynamics of vibronically dressed core excitons in graphite at https://doi.org/10.34965/i53456. Source data for Figs. 1-4 and Supplementary Figs. are provided with the paper.
Code availability
All analysis scripts and fitting routines used in this study are available in the same repository at https://doi.org/10.34965/i53456under a CC-BY-SA-4.0 license.
References
Yu, P. Y. & Cardona, M. Fundamentals of semiconductors, physics and materials properties. Grad. Texts Phys. 1–15 https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-26475-2_1 (2005).
Ahuja, R. et al. Theoretical and experimental study of the graphite 1s X-ray absorption edges. Phys. Rev. B 54, 14396–14404 (1996).
Zhang, L. et al. Electronic band structure of graphene from resonant soft X-ray spectroscopy: the role of core-hole effects. Phys. Rev. B 86, 245430 (2012).
Wessely, O., Katsnelson, M. I. & Eriksson, O. Ab initio theory of dynamical core-hole screening in graphite from X-ray absorption spectra. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 167401 (2005).
Veenendaal, M. V. & Carra, P. Excitons and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering in graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 2839–2842 (1997).
Brühwiler, P. A. et al. π* and σ* excitons in C 1s absorption of graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 614–617 (1995).
Skytt, P. & Ma, Y. Angle-resolved soft-x-ray fluorescence and absorption study of graphite. Phys. Rev. B 50, 10457–10461 (1994).
Ma, Y. et al. Core excitons and vibronic coupling in diamond and graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 3725–3728 (1993).
Sette, F. et al. Lifetime and screening of the C 1s photoemission in graphite. Phys. Rev. B 41, 9766–9770 (1990).
Weng, X., Rez, P. & Ma, H. Carbon K-shell near-edge structure: multiple scattering and band-theory calculations. Phys. Rev. B 40, 4175–4178 (1989).
Mele, E. J. & Ritsko, J. J. Fermi-level lowering and the core exciton spectrum of intercalated graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 43, 68–71 (1979).
Feng, X. et al. Disparate exciton-phonon couplings for zone-center and boundary phonons in solid-state graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 116401 (2020).
Gilmore, K. Quantifying vibronic coupling with resonant inelastic X-ray scattering. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 25, 217–231 (2022).
Dashwood, C. D. et al. Probing electron-phonon interactions away from the Fermi level with resonant inelastic X-ray scattering. Phys. Rev. X 11, 041052 (2021).
Geondzhian, A. & Gilmore, K. Generalization of the Franck-Condon model for phonon excitations by resonant inelastic x-ray scattering. Phys. Rev. B 101, 214307 (2020).
Harada, Y. et al. Dynamical symmetry breaking under core excitation in graphite: polarization correlation in soft X-ray recombination emission. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 017401 (2004).
Attekum, P. M. T. M. V. & Wertheim, G. K. Excitonic effects in core-hole screening. Phys. Rev. Lett. 43, 1896–1898 (1979).
Dean, M. P. M. et al. Ultrafast energy- and momentum-resolved dynamics of magnetic correlations in the photo-doped Mott insulator Sr2IrO4. Nat. Mater. 15, 601–605 (2016).
Cao, Y. et al. Ultrafast dynamics of spin and orbital correlations in quantum materials: an energy- and momentum-resolved perspective. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 377, 20170480 (2019).
Mazzone, D. G. et al. Laser-induced transient magnons in Sr3Ir2O7 throughout the Brillouin zone. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 118, 2103696118 (2021).
Paris, E. et al. Probing the interplay between lattice dynamics and short-range magnetic correlations in CuGeO3 with femtosecond RIXS. npj Quantum Mater. 6, 51 (2021).
Mitrano, M., Johnston, S., Kim, Y.-J. & Dean, M. P. M. Exploring quantum materials with resonant inelastic X-Ray scattering. Phys. Rev. X 14, 040501 (2024).
Thielemann-Kühn, N. et al. Optical control of 4f orbital state in rare-earth metals. Sci. Adv. 10, 9522 (2024).
Xu, C. & Zong, A. Time-domain study of coupled collective excitations in quantum materials. npj Quantum Mater. 10, 21 (2025).
Freibert, A., Mendive-Tapia, D., Huse, N. & Vendrell, O. Time-dependent resonant inelastic X-ray scattering of pyrazine at the nitrogen K-edge: a quantum dynamics approach. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 20, 2167–2180 (2024).
Monney, C., Patthey, L., Razzoli, E. & Schmitt, T. Static and time-resolved resonant inelastic X-ray scattering: Recent results and future prospects. X Ray Spectrom. 52, 216–225 (2023).
Ishioka, K. et al. Ultrafast electron-phonon decoupling in graphite. Phys. Rev. B 77, 121402 (2008).
Pomarico, E. et al. Enhanced electron-phonon coupling in graphene with periodically distorted lattice. Phys. Rev. B 95, 024304 (2017).
Erhardt, N. G. et al. Ultrafast Nonequilibrium Enhancement of Electron-Phonon Interaction in 2H-MoTe2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 135, 146904 (2025).
Pan, Y. et al. Momentum-resolved signatures of carrier screening effects on electron-phonon coupling in MoS2. ACS Nano 19, 11381–11389 (2025).
Ament, L. J. P., Veenendaal, M. V., Devereaux, T. P., Hill, J. P. & Brink, J. V. D. Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering studies of elementary excitations. Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 705–767 (2011).
Carlisle, J. A. et al. Probing the graphite band structure with resonant soft-X-ray fluorescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 1234–1237 (1994).
Gel’mukhanov, F., Sałek, P., Privalov, T. & Ågren, H. Duration of x-ray Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. A 59, 380–389 (1999).
Yavaş, H. et al. Observation of phonons with resonant inelastic x-ray scattering. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22, 485601 (2010).
Mainwood, A. & Stoneham, A. M. A comparison of the core exciton and nitrogen donor in diamond. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 6, 4917 (1994).
Gel’mukhanov, F. & Ågren, H. Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering with symmetry-selective excitation. Phys. Rev. A 49, 4378–4389 (1994).
Geondzhian, A. & Gilmore, K. Demonstration of resonant inelastic x-ray scattering as a probe of exciton-phonon coupling. Phys. Rev. B 98, 214305 (2018).
Malvestuto, M. et al. The MagneDyn beamline at the FERMI free electron laser. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 93, 115109 (2022).
Xu, S. et al. Energy dependence of electron lifetime in graphite observed with femtosecond photoemission spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 483–486 (1996).
Breusing, M. et al. Ultrafast nonequilibrium carrier dynamics in a single graphene layer. Phys. Rev. B 83, 153410 (2011).
Spataru, C. D. et al. Anomalous quasiparticle lifetime in graphite: band structure effects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 246405 (2001).
Piscanec, S., Lazzeri, M., Mauri, F., Ferrari, A. C. & Robertson, J. Kohn anomalies and electron-phonon interactions in graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 185503 (2004).
Park, C.-H., Giustino, F., Spataru, C. D., Cohen, M. L. & Louie, S. G. First-principles study of electron linewidths in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 076803 (2009).
Park, C.-H., Giustino, F., Cohen, M. L. & Louie, S. G. Velocity renormalization and carrier lifetime in graphene from the electron-phonon interaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 086804 (2007).
Johannsen, J. C. et al. Direct view of hot carrier dynamics in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 027403 (2013).
Caruso, F., Novko, D. & Draxl, C. Photoemission signatures of nonequilibrium carrier dynamics from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 101, 035128 (2020).
Novko, D. & Kralj, M. Phonon-assisted processes in the ultraviolet-transient optical response of graphene. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 3, 48 (2019).
Duvel, M. et al. Far-from-equilibrium electron-phonon interactions in optically excited graphene. Nano Lett. 22, 4897–4904 (2022).
Girotto, N. & Novko, D. Dynamical phonons following electron relaxation stages in photoexcited graphene. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14, 8709–8716 (2023).
Sidiropoulos, T. P. H. et al. Probing the energy conversion pathways between light, carriers, and lattice in real time with attosecond core-level spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. X 11, 041060 (2021).
Breusing, M., Ropers, C. & Elsaesser, T. Ultrafast carrier dynamics in graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 086809 (2008).
Kampfrath, T., Perfetti, L., Schapper, F., Frischkorn, C. & Wolf, M. Strongly coupled optical phonons in the ultrafast dynamics of the electronic energy and current relaxation in graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 187403 (2005).
Ritsko, J. J. Valence- and core-electronic excitations in potassium-intercalated graphite. Phys. Rev. B 25, 6452–6459 (1982).
Carlisle, J. A. et al. Crystal-momentum-resolved electronic structure of solids using resonant soft-X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 110, 323–334 (2000).
Skytt, P. et al. Probing symmetry breaking upon core excitation with resonant x-ray fluorescence. Phys. Rev. A 52, 3572–3576 (1995).
Skytt, P. et al. Quenching of symmetry breaking in resonant inelastic X-ray scattering by detuned excitation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 5035–5038 (1996).
Ma, Y. et al. Soft-x-ray resonant inelastic scattering at the C K edge of diamond. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2598–2601 (1992).
Brühwiler, P. A., Kuiper, P., Eriksson, O., Ahuja, R. & Svensson, S. Core hole effects in resonant inelastic X-ray scattering of graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 1761–1761 (1996).
Margine, E. R. & Giustino, F. Two-gap superconductivity in heavily n-doped graphene: Ab initio Migdal-Eliashberg theory. Phys. Rev. B 90, 014518 (2014).
Mazzola, F. et al. Strong electron-phonon coupling in the σ band of graphene. Phys. Rev. B 95, 075430 (2017).
Gel’mukhanov, F., Privalov, T. & Agren, H. Collapse of vibrational structure in spectra of resonant x-ray Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. A 56, 256 (1997).
Yang, J.-A., Parham, S., Dessau, D. & Reznik, D. Novel electron-phonon relaxation pathway in graphite revealed by time-resolved Raman scattering and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 7, 40876 (2017).
Ulstrup, S. et al. Ultrafast electron dynamics in epitaxial graphene investigated with time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 27, 164206 (2015).
Gierz, I. et al. Snapshots of non-equilibrium Dirac carrier distributions in graphene. Nat. Mater. 12, 1119–1124 (2013).
Na, M. X. et al. Direct determination of mode-projected electron-phonon coupling in the time domain. Science 366, 1231–1236 (2019).
Harb, M. et al. Picosecond dynamics of laser-induced strain in graphite. Phys. Rev. B 84, 045435 (2011).
Carbone, F., Baum, P., Rudolf, P. & Zewail, A. H. Structural preablation dynamics of graphite observed by ultrafast electron crystallography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 035501 (2008).
Carbone, F. The interplay between structure and orbitals in the chemical bonding of graphite. Chem. Phys. Lett. 496, 291–295 (2010).
Stern, M. J. et al. Mapping momentum-dependent electron-phonon coupling and nonequilibrium phonon dynamics with ultrafast electron diffuse scattering. Phys. Rev. B 97, 165416 (2018).
Nordgren, J. & Guo, J. Instrumentation for soft X-ray emission spectroscopy. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 110, 1–13 (2000).
Danailov, M. B. et al. Towards jitter-free pump-probe measurements at seeded free electron laser facilities. Opt. Express 22, 12869 (2014).
Sigalotti, P. et al. Ultrafast laser synchronization at the FERMI@Elettra FEL. In Proc. SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 8778 (SPIE, 2013).
Giannozzi, P. et al. Advanced capabilities for materials modelling with quantum ESPRESSO. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 29, 465901 (2017).
Baroni, S., Gironcoli, S. D., Corso, A. D. & Giannozzi, P. Phonons and related crystal properties from density-functional perturbation theory. Rev. Mod. Phys. 73, 515–562 (2001).
Lee, H. et al. Electron-phonon physics from first principles using the EPW code. npj Comput. Mater. 9, 156 (2023).
Marzari, N., Mostofi, A. A., Yates, J. R., Souza, I. & Vanderbilt, D. Maximally localized Wannier functions: theory and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 1419–1475 (2012).
Giustino, F. Electron-phonon interactions from first principles. Rev. Mod. Phys. 89, 015003 (2017).
Pagliara, S. et al. Photoinduced π − pi* band gap renormalization in graphite. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 6318–6322 (2011)..
Williams, P. F., Rousseau, D. L. & Dworetsky, S. H. Resonance fluorescence and resonance raman scattering: lifetimes in molecular iodine. Phys. Rev. Lett. 32, 196–199 (1974).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the assistance of the staff at FERMI during the beamtimes 20209081 and 20214052. M.M. thanks Dr. Carlo Alberto Brondin (ISM-CNR) for the preparation of graphite crystals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.M., A.C., R.B., and S.L. carried out the experiment, collected the data, and contributed to the preliminary analysis. B.V. and E.B. participated in the data analysis. The theoretical investigation was conducted by D.N., M.M., and A.C. were responsible for the MagneDyn endstation. P.R., E.M.A., A.D.B., L.G., D.G., and F.S. optimized the accelerator and provided the FEL beam. M.Ma., A.S., and M.Z. optimized the optical transport of the MagneDyn beamline and characterized the FEL pulses. A.C., A.D., and P.S. optimized the optical laser system. S.L., D.N., and F.P. contributed to the revision of the manuscript. M.M. wrote the manuscript, which all authors discussed. M.M. proposed and led the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks MengXing (Ketty) Na, and the other anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Malvestuto, M., Volpato, B., Babici, E. et al. Ultrafast dynamics of vibronically dressed core excitons in graphite: a femtosecond RIXS perspective. Nat Commun (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-67919-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-67919-7