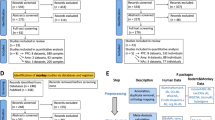
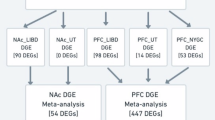
Abstract
Regulation of gene expression is a highly coordinated process in both the healthy and pathological brain with unique patterns across a multitude of cell types. Here we present a multi-omic single nucleus study of ~175,000 nuclei from 50 donors with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and control donors without AUD, profiling cell type specific gene expression and chromatin accessibility in the human central amygdala. We identify all major CNS cell types and neuronal subtypes and find inhibitory neurons are particularly affected by AUD. We find high numbers of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) including GABRA2, GRM8, and NCAM1 and show significant enrichment for AUD risk genes within these DEGs. We identified 51,431 cell type-specific, disease associated candidate cis-regulatory elements including an interneuron-associated set of chromatin loops at the AUD risk gene CALN1. Transcription factor footprinting identified Kruppel-like factors upstream of AUD GWAS genes and DEGs. Finally, we also perform cell type-specific fine mapping for AUD GWAS to prioritize variants within functional genomic elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The snMultiome data generated in this study have been deposited in the Zenodo database [https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17656668]. Datasets are available from the corresponding author and requests may also be submitted to https://www.research.va.gov/programs/tissue_banking/ptsd/ and referencing this paper. The processed data generated in this study are provided in the Supplementary Information/Source Data file. Source data are provided with this paper.
Code availability
All code used in this study is freely available online and can be found at https://github.com/mjgirgenti/AUDsnCEA.
References
Hart, A. B. & Kranzler, H. R. Alcohol Dependence Genetics: Lessons Learned From Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) and Post-GWAS Analyses. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 39, 1312–1327 (2015).
Reilly, M. T., Noronha, A., Goldman, D. & Koob, G. F. Genetic studies of alcohol dependence in the context of the addiction cycle. Neuropharmacology 122, 3–21 (2017).
Enoch, M. A. & Goldman, D. The genetics of alcoholism and alcohol abuse. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 3, 144–151 (2001).
Agrawal, A. & Lynskey, M. T. Are there genetic influences on addiction: evidence from family, adoption and twin studies. Addiction 103, 1069–1081 (2008).
Verhulst, B., Neale, M. C. & Kendler, K. S. The heritability of alcohol use disorders: a meta-analysis of twin and adoption studies. Psychol. Med. 45, 1061–1072 (2015).
Tawa, E. A., Hall, S. D. & Lohoff, F. W. Overview of the Genetics of Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol Alcohol 51, 507–514 (2016).
Augier, E. et al. A molecular mechanism for choosing alcohol over an alternative reward. Science 360, 1321–1326 (2018).
Yang, W., Singla, R., Maheshwari, O., Fontaine, C. J. & Gil-Mohapel, J. Alcohol Use Disorder: Neurobiology and Therapeutics. Biomedicines 10, 1192 (2022).
Koob, G. F. Dynamics of neuronal circuits in addiction: reward, antireward, and emotional memory. Pharmacopsychiatry 42, S32–S41 (2009).
Goodman, J. & Packard, M. G. Memory Systems and the Addicted Brain. Front. Psychiatry 7, 24 (2016).
Robbins, T. W., Ersche, K. D. & Everitt, B. J. Drug addiction and the memory systems of the brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1141, 1–21 (2008).
Farris, S. P., Arasappan, D., Hunicke-Smith, S., Harris, R. A. & Mayfield, R. D. Transcriptome organization for chronic alcohol abuse in human brain. Mol. Psychiatry 20, 1438–1447 (2015).
Walters, R. K. et al. Transancestral GWAS of alcohol dependence reveals common genetic underpinnings with psychiatric disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 21, 1656–1669 (2018).
Kranzler, H. R. et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol consumption and use disorder in 274,424 individuals from multiple populations. Nat. Commun. 10, 1499 (2019).
Zhou, H. et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of problematic alcohol use in 435,563 individuals yields insights into biology and relationships with other traits. Nat. Neurosci. 23, 809–818 (2020).
Zhou, H. et al. Multi-ancestry study of the genetics of problematic alcohol use in over 1 million individuals. Nat. Med. 29, 3184–3192 (2023).
Gelernter, J. & Polimanti, R. Genetics of substance use disorders in the era of big data. Nat. Rev. Genet. 22, 712–729 (2021).
Andrade-Brito, D. E. et al. Neuronal-specific methylome and hydroxymethylome analysis reveal significant loci associated with alcohol use disorder. Front. Genet. 15, 1345410 (2024).
Nestler, E. J. & Lüscher, C. The Molecular Basis of Drug Addiction: Linking Epigenetic to Synaptic and Circuit Mechanisms. Neuron 102, 48–59 (2019).
Lüscher, C. The Emergence of a Circuit Model for Addiction. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 39, 257–276 (2016).
Kapoor, M. et al. Analysis of whole genome-transcriptomic organization in brain to identify genes associated with alcoholism. Transl. Psychiatry 9, 89 (2019).
Hitzemann, R. et al. Sex Differences in the Brain Transcriptome Related to Alcohol Effects and Alcohol Use Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 91, 43–52 (2022).
Ponomarev, I., Wang, S., Zhang, L., Harris, R. A. & Mayfield, R. D. Gene coexpression networks in human brain identify epigenetic modifications in alcohol dependence. J. Neurosci. 32, 1884–1897 (2012).
Zhang, H. et al. Differentially co-expressed genes in postmortem prefrontal cortex of individuals with alcohol use disorders: influence on alcohol metabolism-related pathways. Hum. Genet. 133, 1383–1394 (2014).
Ducci, F. & Goldman, D. Genetic approaches to addiction: genes and alcohol. Addiction 103, 1414–1428 (2008).
Spanagel, R. Alcoholism: a systems approach from molecular physiology to addictive behavior. Physiol. Rev. 89, 649–705 (2009).
Abernathy, K., Chandler, L. J. & Woodward, J. J. Alcohol and the prefrontal cortex. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 91, 289–320 (2010).
Moorman, D. E. The role of the orbitofrontal cortex in alcohol use, abuse, and dependence. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 87, 85–107 (2018).
Gorka, S. M., Fitzgerald, D. A., King, A. C. & Phan, K. L. Alcohol attenuates amygdala-frontal connectivity during processing social signals in heavy social drinkers: a preliminary pharmaco-fMRI study. Psychopharmacology 229, 141–154 (2013).
Mbarek, H. et al. The genetics of alcohol dependence: Twin and SNP-based heritability, and genome-wide association study based on AUDIT scores. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 168, 739–748 (2015).
Sanchez-Roige, S. et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol use disorder identification test (AUDIT) scores in 20 328 research participants of European ancestry. Addict. Biol. 24, 121–131 (2019).
Sanchez-Roige, S. et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Meta-Analysis of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) in Two Population-Based Cohorts. Am. J. Psychiatry 176, 107–118 (2019).
Yang, C. et al. Exploring the genetic architecture of alcohol dependence in African-Americans via analysis of a genomewide set of common variants. Hum. Genet. 133, 617–624 (2014).
Hwang, A. et al. Single-cell transcriptomic and chromatin dynamics of the human brain in PTSD. Nature 643, 744–754 (2025).
Xu, S., Lee, C. Y., Zhang, J. & Girgenti, M. J. Central amygdala single-nucleus atlas reveals chromatin and gene transcription dynamics in human alcohol use disorder. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17656668 (2025).
Beyeler, A. & Dabrowska, J. Neuronal diversity of the amygdala and the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Handb Behav Neurosci 26, 63–100 (2020).
Yu, B. et al. Molecular and cellular evolution of the amygdala across species analyzed by single-nucleus transcriptome profiling. Cell Discov 9, 19 (2023).
Tran, M. N. et al. Single-nucleus transcriptome analysis reveals cell-type-specific molecular signatures across reward circuitry in the human brain. Neuron 109, 3088–3103.e5 (2021).
Finak, G. et al. MAST: a flexible statistical framework for assessing transcriptional changes and characterizing heterogeneity in single-cell RNA sequencing data. Genome Biol 16, 278 (2015).
Li, B. et al. Cumulus provides cloud-based data analysis for large-scale single-cell and single-nucleus RNA-seq. Nat Methods 17, 793–798 (2020).
Love, M. I., Huber, W. & Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15, 550 (2014).
Flores-Bonilla, A. & Richardson, H. N. Sex Differences in the Neurobiology of Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol Res 40, 04 (2020).
Grace, S. et al. Sex differences in the neuroanatomy of alcohol dependence: hippocampus and amygdala subregions in a sample of 966 people from the ENIGMA Addiction Working Group. Transl. Psychiatry 11, 156 (2021).
Varodayan, F. P. & Harrison, N. L. HSF1 transcriptional activity mediates alcohol induction of Vamp2 expression and GABA release. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 7, 89 (2013).
Krystal, J. H., Petrakis, I. L., Mason, G., Trevisan, L. & D’Souza, D. C. N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptors and alcoholism: reward, dependence, treatment, and vulnerability. Pharmacol. Ther. 99, 79–94 (2003).
Burnett, E. J., Chandler, L. J. & Trantham-Davidson, H. Glutamatergic plasticity and alcohol dependence-induced alterations in reward, affect and cognition. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 65, 309–320 (2016).
Joffe, M. E., Centanni, S. W., Jaramillo, A. A., Winder, D. G. & Conn, P. J. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Alcohol Use Disorder: Physiology, Plasticity, and Promising Pharmacotherapies. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 9, 2188–2204 (2018).
Zhang, Y. et al. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol 9, R137 (2008).
Fullard, J. F. et al. An atlas of chromatin accessibility in the adult human brain. Genome Res 28, 1243–1252 (2018).
Przybycien-Szymanska, M. M., Rao, Y. S., Prins, S. A. & Pak, T. R. Parental binge alcohol abuse alters F1 generation hypothalamic gene expression in the absence of direct fetal alcohol exposure. PLoS One 9, e89320 (2014).
Schep, A. N., Wu, B., Buenrostro, J. D. & Greenleaf, W. J. chromVAR: inferring transcription-factor-associated accessibility from single-cell epigenomic data. Nat. Methods 14, 975–978 (2017).
Dilly, G. A., Kittleman, C. W., Kerr, T. M., Messing, R. O. & Mayfield, R. D. Cell-type specific changes in PKC-delta neurons of the central amygdala during alcohol withdrawal. Transl. Psychiatry 12, 289 (2022).
Wang, G., Sarkar, A., Carbonetto, P. & Stephens, M. A simple new approach to variable selection in regression, with application to genetic fine mapping. J. R. Stat. Soc. Series B Stat. Methodol. 82, 1273–1300 (2020).
Zhou, H. et al. Multi-ancestry study of the genetics of problematic alcohol use in >1 million individuals. medRxiv (2023) https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.24.23284960.
Squair, J. W. et al. Confronting false discoveries in single-cell differential expression. Nat. Commun. 12, 5692 (2021).
Lee, M. R. et al. Striatal adenosine signaling regulates EAAT2 and astrocytic AQP4 expression and alcohol drinking in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 38, 437–445 (2013).
Roland, A. V. et al. Acute and chronic alcohol modulation of extended amygdala calcium dynamics. Alcohol 116, 53–64 (2024).
Tanaka, A. et al. Heavy Alcohol Consumption is Associated with Impaired Endothelial Function. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 23, 1047–1054 (2016).
Erickson, E. K., Blednov, Y. A., Harris, R. A. & Mayfield, R. D. Glial gene networks associated with alcohol dependence. Scientific Reports 9, 1–13 (2019).
Astrocytes and Alcohol Throughout the Lifespan. Biological Psychiatry (2025) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2025.04.013.
Drug dependence stress and dysregulation of brain reward pathways. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 51, 23–47 (1998).
Turner, N. & Grose, R. Fibroblast growth factor signalling: from development to cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer 10, 116–129 (2010).
Giardino, W. J. & Pomrenze, M. B. Extended Amygdala Neuropeptide Circuitry of Emotional Arousal: Waking Up on the Wrong Side of the Bed Nuclei of Stria Terminalis. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 15, 613025 (2021).
Ehrlich, I. et al. Amygdala inhibitory circuits and the control of fear memory. Neuron 62, 757–771 (2009).
Racz, I. et al. The opioid peptides enkephalin and beta-endorphin in alcohol dependence. Biol. Psychiatry 64, 989–997 (2008).
de Laat, B. et al. The Kappa Opioid Receptor Is Associated With Naltrexone-Induced Reduction of Drinking and Craving. Biol. Psychiatry 86, 864–871 (2019).
Volpicelli, J. R., Clay, K. L., Watson, N. T. & Volpicelli, L. A. Naltrexone and the Treatment of Alcohol Dependence. Alcohol Health Res. World 18, 272–278 (1994).
Roberto, M., Gilpin, N. W. & Siggins, G. R. The central amygdala and alcohol: role of γ-aminobutyric acid, glutamate, and neuropeptides. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2, a012195 (2012).
Xiong, X. et al. Epigenomic dissection of Alzheimer’s disease pinpoints causal variants and reveals epigenome erosion. Cell 186, 4422–4437.e21 (2023).
Hsieh, P. N., Fan, L., Sweet, D. R. & Jain, M. K. The Krüppel-Like Factors and Control of Energy Homeostasis. Endocr. Rev. 40, 137–152 (2019).
Oishi, Y. & Manabe, I. Krüppel-Like Factors in Metabolic Homeostasis and Cardiometabolic Disease. Front Cardiovasc Med 5, 69 (2018).
MacDonald, M. et al. Divergent gene expression patterns in alcohol and opioid use disorders lead to consistent alterations in functional networks within the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. bioRxiv (2024) https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.04.29.591734.
Lu, X.-J., Shi, Y., Chen, J.-L. & Ma, S. Krüppel-like factors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol 36, 533–541 (2015).
Green, N. C. et al. Integrated single-cell multiomic profiling of caudate nucleus suggests key mechanisms in alcohol use disorder. Nat. Commun. 16, 9070 (2025).
Van Booven, D. et al. Alcohol use disorder causes global changes in splicing in the human brain. Transl. Psychiatry 11, 2 (2021).
Farris, S. P. et al. Applying the new genomics to alcohol dependence. Alcohol 49, 825–836 (2015).
van den Oord, E. J. C. G., Xie, L. Y., Zhao, M., Aberg, K. A. & Clark, S. L. A single-nucleus transcriptomics study of alcohol use disorder in the nucleus accumbens. Addict. Biol. 28, e13250 (2023).
Brenner, E. et al. Single cell transcriptome profiling of the human alcohol-dependent brain. Hum. Mol. Genet. 29, 1144–1153 (2020).
Mai, J. K., Majtanik, M. & Paxinos, G. Atlas of the Human Brain. (Elsevier Science, 2015).
Ma, S. et al. Molecular and cellular evolution of the primate dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Science 377, eabo7257 (2022).
Andrijevic, D. et al. Cellular recovery after prolonged warm ischaemia of the whole body. Nature 608, 405–412 (2022).
Franjic, D. et al. Transcriptomic taxonomy and neurogenic trajectories of adult human, macaque, and pig hippocampal and entorhinal cells. Neuron 110, 452–469.e14 (2022).
Franklin, K. B. J. & Paxinos, G. Paxinos and Franklin’s the Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Compact: The Coronal Plates and Diagrams. (Academic Press, 2019).
Lim, M. M., Hammock, E. A. D. & Young, L. J. A method for acetylcholinesterase staining of brain sections previously processed for receptor autoradiography. Biotech. Histochem. 79, 11–16 (2004).
Maynard, K. R. et al. dotdotdot: an automated approach to quantify multiplex single molecule fluorescent in situ hybridization (smFISH) images in complex tissues. Nucleic Acids Res 48, e66 (2020).
Stuart, T., Srivastava, A., Madad, S., Lareau, C. A. & Satija, R. Single-cell chromatin state analysis with Signac. Nat. Methods 18, 1333–1341 (2021).
Wolock, S. L., Lopez, R. & Klein, A. M. Scrublet: Computational Identification of Cell Doublets in Single-Cell Transcriptomic Data. Cell Syst 8, 281–291.e9 (2019).
Xi, N. M. & Li, J. J. Benchmarking Computational Doublet-Detection Methods for Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data. Cell Syst 12, 176–194.e6 (2021).
Granja, J. M. et al. ArchR is a scalable software package for integrative single-cell chromatin accessibility analysis. Nat. Genet. 53, 403–411 (2021).
Bulik-Sullivan, B. K. et al. LD Score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 47, 291–295 (2015).
Zhang, X., Jiang, W. & Zhao, H. Integration of Expression QTLs with fine mapping via SuSiE. medRxiv (2023) https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.10.03.23294486.
1000 Genomes Project Consortium et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 526, 68–74 (2015).
Purcell, S. et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 559–575 (2007).
Kent, W. J. et al. The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res 12, 996–1006 (2002).
Karolchik, D. et al. The UCSC Table Browser data retrieval tool. Nucleic Acids Res 32, D493–496 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the National Center for PTSD Brain Bank, the University of Pittsburgh Brain Tissue Donation Program, and the NIH NeuroBioBank whose efforts led to the donation of the postmortem tissue used in these studies. We are also indebted to the generosity of the families of the decedents, who donated the brain tissue used in these studies. The research reported here was supported by the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veteran Health Administration, VISN1 Career Development Award, a Brain and Behavior Research Foundation Young Investigator Award, an American Foundation for Suicide Prevention Young Investigator Award, NIH grants R01AA031017 and DP1DA060811 to M.J.G., R01HG012572, R01DA063316 to J.Z. and P50AA012870 J.H.K. We thank the Keck Microarray Shared Resource (KMSR) and Yale Center for Genome Analysis (YCGA) at Yale university for their assistance with snMultiome sequencing. This work was supported with resources and use of facilities at the VA Connecticut Health Care System, West Haven, CT, the Durham VA Healthcare System, Durham NC, and the VA Boston Healthcare System, Boston, MA, USA and the National Center for PTSD, U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. This work was funded in part by the State of Connecticut, Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services. The views expressed here are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the position or policy of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) or the U.S. government or the views of the Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services or the State of Connecticut.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.L., J.Z., and M.J.G. conceived the project and designed the experiments. C.L. and M.J.G. wrote the manuscript. C.D., M.S., R.T., D.M., J.L., G.T., J.C., and A-N.S., generated all of the data. C.L., A.H., X.Z., S.X., J.W., T.N., Y.Liu., H.L., Y.D., Z.D., Y.Lei., Y. Lin, K.X., H.Z., J.Z., and M.J.G. oversaw all bioinformatics analyses. H.Zhou and J.G. contributed GWAS summary data and analysis. J.R.G., D.A.L, P.E.H., J.H.K., H.Zhou, S.T., J.T. and A.C. contributed to study design. All authors contributed to the preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
J.H.K. has consulting agreements (less than US$10,000 per year) with the following: Aptinyx, Inc. Biogen, Idec, MA, Bionomics, Limited (Australia), Boehringer Ingelheim International, Epiodyne, Inc., EpiVario, Inc., Janssen Research & Development, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc., Spring Care, Inc., Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; is the co-founder for Freedom Biosciences, Inc.; serves on the scientific advisory boards of Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc. (Clinical Advisory Board), Cerevel Therapeutics, LLC, Delix Therapeutics, Inc., Eisai, Inc., EpiVario, Inc., Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Neumora Therapeutics, Inc., Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, PsychoGenics, Inc., Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Tempero Bio, Inc., Terran Biosciences, Inc..; has stock options with Biohaven Pharmaceuticals Medical Sciences, Cartego Therapeutics, Damona Pharmaceuticals, Delix Therapeutics, EpiVario, Inc., Neumora Therapeutics, Inc., Rest Therapeutics, Tempero Bio, Inc., Terran Biosciences, Inc., Tetricus, Inc.; and is editor of Biological Psychiatry with income greater than $10,000. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Source data
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C.Y., Hwang, A., McRiley, D. et al. Central amygdala single-nucleus atlas reveals chromatin and gene transcription dynamics in human alcohol use disorder. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68351-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68351-1