Abstract
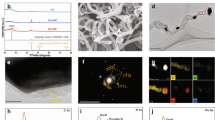
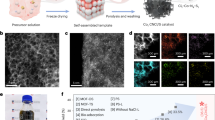
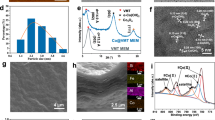
Co(IV) = O-mediated Fenton-like processes show great potential for water remediation but are fundamentally limited by the “oxo-wall” effect, which imposes prohibitive activation energies for Co(IV) = O bond formation and stabilization. Herein, by unifying thermodynamic analysis with the “oxo-wall” constraint mechanism, we establish the comprehensive theoretical framework for Co(IV) = O-dominated non-radical Fenton-like oxidation pathways. We design a Ce-Co tetra-(4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin framework (Ce-Co TCPP), where Ce(IV)-based oxide linkers induce long-range electronic modulation, enhancing electronic delocalization at Co–N4 sites. This significantly reduces electron occupancy in Co–O antibonding orbitals, thereby effectively circumventing “oxo-wall” constraints. Combined experimental and computational analyses confirm that Co(IV) = O species dominate in the Ce-Co TCPP/peroxymonosulfate (PMS) system, where synergistic electron transfer and proton transfer processes significantly lower activation barriers. Practically, the lamellar Ce-Co TCPP membrane/PMS system achieves desirable water permeability (126.97 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1 (LMHB)), high pollutant degradation efficiency (0.0717 ms−1), robust anti-interference capability, and long-term operational stability (95 h), which can be attributed to the shortened mass transport pathways and the approximately 1000-fold enrichment of Co(IV) = O complexes within membrane nanoconfined channels. This work offers an innovative strategy for sustainable Co(IV) = O-mediated advanced oxidation processes in water treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated in this study are provided in the Supplementary Materials/source data file. All the raw data relevant to the study are available from the corresponding author upon request. Source data are provided with this paper. The optimized DFT computational models and molecular dynamics trajectories generated in this study are publicly available on GitHub: https://github.com/JomerMatirays/Breakingtheoxo-wallforCo-IV--oxospeciesandtheirnanoconfinedcatalyticperformancewithinCe-Comembrane/. These data are also permanently archived in the Zenodo repository (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17895247). Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Duan, P. J. et al. Polymeric products deactivate carbon-based catalysts in catalytic oxidation reactions. Nat. Water. 3, 178–190 (2025).
Li, S., Zhu, Y., Zhong, G., Huang, Y. & Jones, K. C. Comprehensive assessment of environmental missions, fate, and risks of veterinary antibiotics in China: an environmental fate modeling approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 58, 5534–5547 (2024).
Zhao, X. & Zhang, Z. Heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate-based advanced oxidation mechanisms: new wine in old bottles? Environ. Sci. Technol. 59, 5913–5924 (2025).
Gu, C. H. et al. Tuning electronic structure of metal-free dual-site catalyst enables exclusive singlet oxygen production and in-situ utilization. Nat. Commun. 15, 5771 (2024).
Chen, Z. et al. Organic carbon transfer process in advanced oxidation systems for water clean-up. Nat. Water. 3, 334–344 (2025).
Chen, T. et al. Robust Fe-N4-C6O2 single atom sites for efficient PMS activation and enhanced FeIV=O reactivity. Nat. Commun. 16, 2402 (2025).
Wu, Z. et al. Long-range interactions driving neighboring Fe-N4 sites in Fenton-like reactions for sustainable water decontamination. Nat. Commun. 15, 7775 (2024).
Wang, Z. et al. Aqueous iron(IV)-oxo complex: an emerging powerful reactive oxidant formed by iron(II)-based advanced oxidation processes for oxidative water treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 1492–1509 (2022).
Huang, M. et al. Facilely tuning the intrinsic catalytic sites of the spinel oxide for peroxymonosulfate activation: from fundamental investigation to pilot-scale demonstration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2202682119 (2022).
Wu, Q. Y., Yang, Z. W., Wang, Z. W. & Wang, W. L. Oxygen doping of cobalt-single-atom coordination enhances peroxymonosulfate activation and high-valent cobalt-oxo species formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 120, e2219923120 (2023).
Jiang, J. et al. Nitrogen vacancy-modulated peroxymonosulfate nonradical activation for organic contaminant removal via high-valent cobalt-oxo species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 5611–5619 (2022).
Song, J. et al. Asymmetrically coordinated CoB1N3 moieties for selective generation of high-valence Co-oxo species via coupled electron-proton transfer in Fenton-like reactions. Adv. Mater. 35, 2209552 (2023).
Shi, Z. et al. High-entropy effect breaking the oxo wall for selective high-valent metal−oxo species generation. ACS Catal 14, 14796–14806 (2024).
Li, X. et al. CoN1O2 Single-atom catalyst for efficient peroxymonosulfate activation and selective cobalt(IV)=O generation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202303267 (2023).
Andris, E. et al. M−O bonding beyond the oxo wall: spectroscopy and reactivity of cobalt(III)-oxyl and cobalt(III)-oxo complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 9619–9624 (2019).
Larson, V. A., Battistella, B., Ray, K., Lehnert, N. & Nam, W. Iron and manganese oxo complexes, oxo wall and beyond. Nat. Rev. Chem 4, 404–419 (2020).
Guo, J. et al. Fenton-like activity and pathway modulation via single-atom sites and pollutants comediates the electron transfer process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 121, e2313387121 (2023).
Shang, Y., Xu, X., Gao, B., Wang, S. & Duan, X. Single-atom catalysis in advanced oxidation processes for environmental remediation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 5281–5322 (2021).
Wei, S. et al. Self-carbon-thermal-reduction strategy for boosting the Fenton-like activity of single Fe-N4 sites by carbon-defect engineering. Nat. Commun. 14, 7549 (2023).
Zhang, Y. et al. The role of long-range interactions between high-entropy single-atoms in catalyzing sulfur conversion reactions. Adv. Mater. 37, 2413653 (2025).
Qi, Z., Zhou, Y., Guan, R., Fu, Y. & Baek, J. B. Tuning the coordination environment of carbon-based single-atom catalysts via doping with multiple heteroatoms and their applications in electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 35, 2210575 (2023).
Lu, Y. et al. Recent advances in bonding regulation of metalloporphyrin-modified carbon-based catalysts for accelerating energy electrocatalytic applications. Small 20, 2406180 (2024).
Lv, N. et al. Electrocatalytic porphyrin/phthalocyanine-based organic frameworks: building blocks, coordination microenvironments, structure-performance relationships. Adv. Sci. 10, 2206239 (2023).
Yang, C. et al. Incorporation of atomically dispersed cobalt in the 2D metal-organic framework of a lamellar membrane for highly efficient peroxymonosulfate activation. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 325, 122344 (2023).
Jin, Z. et al. Ultrafast photogenerated charge dynamics driven by synergistic dual-metal atomic sites in porphyrinic metal-organic frameworks. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 379, 125670 (2025).
Zhang, Y., Guan, X., Meng, Z. & Jiang, H. L. Supramolecular built local electric field microenvironment around cobalt phthalocyanine in covalent organic frameworks for enhanced photocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 147, 3776–3785 (2025).
Wang, Q. et al. Modulating active center microenvironment in phthalocyanine-based covalent organic frameworks for enhanced electrocatalytic CO2 to CH3OH. Adv. Mater. 37, 2502644 (2025).
Zhang, J. et al. Suppressing the hydrogen bonding interaction with *OOH toward efficient H2O2 electrosynthesis via remote electronic tuning of Co-N4. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 358, 124448 (2024).
Huang, M. et al. Linkage microenvironment and oxygen electroreduction reaction performance correlationship of iron phthalocyanine-based polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64, e202501506 (2025).
Jacobsen, J., Ienco, A., D’Amato, R., Costantino, F. & Stock, N. The chemistry of Ce-based metal-organic frameworks. Dalton Trans 49, 16551–16586 (2020).
Ma, Y. et al. Design of hierarchical CeO2@Co-Ni3S2 catalyst for rapid high-valent Ni3+ generation and optimized organic adsorption toward enhanced biomass conversion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 35, e12292 (2025).
Zhang, Y. L. et al. Electronic delocalization regulates the occupancy and energy level of Co 3dz2 orbitals to enhance bifunctional oxygen catalytic activity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2209499 (2022).
Jiang, Z. W. et al. Controllable synthesis of porphyrin-based 2D lanthanide metal-organic frameworks with thickness and metal-node-dependent photocatalytic performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 3300–3306 (2020).
Jian, M. et al. Ultrathin water-stable metal-organic framework membranes for ion separation. Sci. Adv. 6, eaay3998 (2020).
Wang, J. et al. Light-responsive and ultrapermeable two-dimensional metal-organic framework membrane for efficient ionic energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 15, 2125 (2024).
Zhang, Y. et al. Bidirectional light-driven ion transport through porphyrin metal-organic framework-based van der Waals heterostructures via pH-induced band alignment inversion. CCS Chem 4, 3329–3341 (2022).
Li, M. et al. Ce-induced differentiated regulation of Co sites via gradient orbital coupling for bifunctional water-splitting reactions. Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 2301162 (2023).
Wu, J. H. & Yu, H. Q. Confronting the mysteries of oxidative reactive species in advanced oxidation processes: an elephant in the room. Environ. Sci. Technol. 58, 18496–18507 (2024).
Lei, Y. et al. Assessing the use of probes and quenchers for understanding the reactive species in advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 5433–5444 (2023).
Zong, Y. et al. High-valent cobalt-oxo species triggers hydroxyl radical for collaborative environmental decontamination. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 300, 120722 (2022).
Pei, J. et al. Manipulating high-valent cobalt-oxo generation on Co/N cooped carbon beads via PMS activation for micropollutants degradation. ACS EST Eng 3, 1997–2007 (2023).
Tian, M. et al. Overcoming the permeability-selectivity challenge in water purification using two-dimensional cobalt-functionalized vermiculite membrane. Nat. Commun. 15, 391 (2024).
Zou, Y. et al. Unveiling the long-range interaction of sulfur in the second shell of Fe-N4 single-atom sites for highly selective generation of high-valent iron-oxo species in peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 505, 159684 (2025).
Cao, P. et al. Breaking symmetry for better catalysis: insights into single-atom catalyst design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 54, 3848–3905 (2025).
Fu, S. et al. Iron single-atom catalyst actuates PMS/O3 activation process: nonradical generation path for synergistic multi-peroxides. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 3, 202–213 (2025).
Lin, Y. et al. Coordination engineering of heterogeneous high-valent Fe(IV)-oxo for safe removal of pollutants via powerful Fenton-like reactions. Nat. Commun. 15, 10032 (2024).
Zhang, J., Liu, Y. & Zhang, Z. Nanoconfined catalytic water purification within CoFeCu LDH-assembled membrane nanochannels. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 357, 124290 (2024).
Li, Y. et al. Peracetic acid-induced nanoengineering of Fe-based metallic glass ribbon in application of efficient drinking water treatment. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 355, 124161 (2024).
Jiang, J. et al. Angstrom confinement-triggered adaptive spin state transition of CoMn dual single atoms for efficient singlet oxygen generation. Adv. Mater. 37, 2417834 (2025).
Meng, C. et al. Angstrom-confined catalytic water purification within Co-TiOx laminar membrane nanochannels. Nat. Commun. 13, 4010 (2022).
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52170041, Z.Z.), Tsinghua SIGS Cross-disciplinary Research and Innovation Fund (JC2022006, Z.Z.), the Committee of Science and Technology Innovation of Shenzhen (JCYJ20230807111705011, Z.Z.), and the Guangdong Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (2024B1515020085, Z.Z.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.Z. conceived the project. M.T. synthesized and characterized the nanosheets and membranes and performed the catalytic activity experiments. L.L. and Z.C. helped with experiments and result analysis. C.Y. performed the XAFS analysis. H.Z. and Y.L. performed the theoretical calculations. M.T. and Z.Z. analyzed the results and wrote the manuscript. Z.Z. revised the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Source data
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, M., Zhang, H., Liu, Y. et al. Breaking the oxo-wall for Co(IV)-oxo species and their nanoconfined catalytic performance within Ce-Co lamellar membrane. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68471-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68471-8