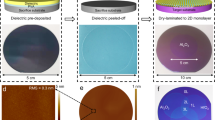
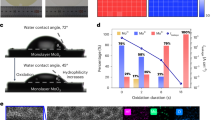
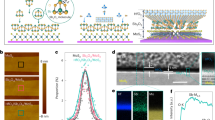
Abstract
High-κ gate dielectrics are indispensable in modern transistor technology and play a pivotal role in efficient capacitive gating and suppression of leakage currents. However, the realization of industry-compatible high-κ gate dielectrics at a sub-5-Å equivalent oxide thickness (EOT) remains challenging. Here we report the realization of 1.3-nm thick hafnium oxide (HfO2) dielectrics via an industry-compatible multiple oxidation atomic layer deposition process at 200 °C. A low EOT down to 2.5 Å is demonstrated for 1.3-nm thick HfO2 dielectrics on metal gates with a low leakage current of 10−6 A/cm2 and a robust breakdown electric field of ~22.3 MV/cm. Remarkably, such low EOT high-κ/metal gates can be directly implanted into emerging two-dimensional (2D) transistors and low-power logic circuits on 8-inch wafer scale to showcase their potentials. The as-fabricated molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) transistors exhibit a large on-state current density of 260 µA/µm at source-drain bias of 0.5 V, a high on/off ratio of 108, an average subthreshold slope (SS) of 75 mV/dec, and small capacitance equivalent thickness (CET) values of 0.34 nm for gate-first transistors and 0.50 nm for gate-last transistors. Our ultra-scaled dielectrics hold significant promise for advanced semiconductor fabrication processes towards the angstrom era.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Relevant data supporting the key findings of this study are available within the article and the Supplementary Information file. All raw data generated during the current study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Cao, W. et al. The future transistors. Nature 620, 501–515 (2023).
Mistry, K. et al. A 45 nm logic technology with high-k+metal gate transistors, strained silicon, 9 Cu interconnect layers, 193 nm dry patterning, and 100% Pb-free packaging. In 2007 IEEE Int. Electron Devices Meeting 247–250 (IEEE, 2007).
Lundstrom, M. S. et al. Moore’s law: the journey ahead. Science 378, 722–723 (2022).
Först, C. J. et al. The interface between silicon and a high-κ oxide. Nature 427, 53–56 (2004).
Datta, S. et al. Toward attojoule switching energy in logic transistors. Science 378, 733–740 (2022).
Li, N. et al. Large-scale flexible and transparent electronics based on monolayer molybdenum disulfide field-effect transistors. Nat. Electron. 3, 711–717 (2020).
Tang, J. et al. In situ oxygen doping of monolayer MoS2 for novel electronics. Small 16, 2004276 (2020).
O’Brien, K. P. et al. Process integration and future outlook of 2D transistors. Nat. Commun. 14, 6400 (2023).
Sicard, E. et al. Introducing 3-nm nano-sheet FET technology in microwind. ffhal-03377556f (2021).
Xu, Y. et al. Scalable integration of hybrid high-κ dielectric materials on two-dimensional semiconductors. Nat. Mater. 22, 1078–1084 (2023).
Cheema, S. S. et al. Ultrathin ferroic HfO2–ZrO2 superlattice gate stack for advanced transistors. Nature 604, 65–71 (2022).
IEEE. International roadmap for devices and systems. https://irds.ieee.org/editions (2022).
Jin, Y. et al. Controllable oxidation of ZrS2 to prepare high-κ, single-crystal m-ZrO2 for 2D electronics. Adv. Mater. 35, e2212079 (2023).
Li, W. et al. Uniform and ultrathin high-κ gate dielectrics for two-dimensional electronic devices. Nat. Electron. 2, 563–571 (2019).
Huang, J.-K. et al. High-κ perovskite membranes as insulators for two-dimensional transistors. Nature 605, 262–267 (2022).
Illarionov, Y. Y. et al. Ultrathin calcium fluoride insulators for two-dimensional field-effect transistors. Nat. Electron. 2, 230–235 (2019).
Liu, K. et al. A wafer-scale van der Waals dielectric made from an inorganic molecular crystal film. Nat. Electron. 4, 906–913 (2021).
Zhang, Y. et al. A single-crystalline native dielectric for two-dimensional semiconductors with an equivalent oxide thickness below 0.5 nm. Nat. Electron. 5, 643–649 (2022).
Chen, J. et al. Vertically grown ultrathin Bi2SiO5 as high-κ single-crystalline gate dielectric. Nat. Commun. 14, 4406 (2023).
Lau, C. S. et al. Dielectrics for two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenide applications. ACS Nano 17, 9870–9905 (2023).
Ye, K. et al. An overview of advanced methods for the characterization of oxygen vacancies in materials. Trends Anal. Chem. 116, 102–108 (2019).
Mora-Fonz, D. et al. Disorder-induced electron and hole trapping in amorphous TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 102, 054205 (2020).
Kaewmeechai, C. et al. Electronic structure and properties of trapped holes in crystalline and amorphous Ga2O3. Phys. Rev. B 111, 035203 (2025).
El-Sayed, A. et al. Nature of intrinsic and extrinsic electron trapping in SiO2. Phys. Rev. B 89, 125201 (2014).
Akinwande, D. et al. Graphene and two-dimensional materials for silicon technology. Nature 573, 507–518 (2019).
Das, S. et al. Transistors based on two-dimensional materials for future integrated circuits. Nat. Electron. 4, 786–799 (2021).
Li, T. et al. A native oxide high-κ gate dielectric for two-dimensional electronics. Nat. Electron. 3, 473–478 (2020).
Luo, P. et al. Molybdenum disulfide transistors with enlarged van der Waals gaps at their dielectric interface via oxygen accumulation. Nat. Electron. 5, 849–858 (2022).
PangC.-S. et al. Sub-1nm EOT WS2-FET with IDS >600μA/μm at VDS=1V and SS <70mV/dec at LG=40nm. In 2020 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 3.4.1–3.4.4 (IEEE, 2020).
Xu, W. et al. Single-crystalline high-κ GdOCl dielectric for two-dimensional field-effect transistors. Nat. Commun. 15, 9469 (2024).
Yin, L. et al. High-κ monocrystalline dielectrics for low-power two-dimensional electronics. Nat. Mater. 24, 197–204 (2025).
Zhu, C.-Y. et al. Magnesium niobate as a high-κ gate dielectric for two-dimensional electronics. Nat. Electron. 7, 1137–1146 (2024).
Yi, K. et al. Integration of high-κ native oxides of gallium for two-dimensional transistors. Nat. Electron. 7, 1126–1136 (2024).
Zhu, K. et al. The development of integrated circuits based on two-dimensional materials. Nat. Electron. 4, 775–785 (2021).
Li, M.-Y. et al. How 2D semiconductors could extend Moore’s law. Nature 567, 169–170 (2019).
Liu, Y. et al. Promises and prospects of two-dimensional transistors. Nature 591, 43–53 (2021).
Li, W. et al. Approaching the quantum limit in two-dimensional semiconductor contacts. Nature 613, 274–279 (2023).
English, C. D. et al. Approaching ballistic transport in monolayer MoS2 transistors with self-aligned 10 nm top gates. In 2016 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 5.6.1–5.6.4 (IEEE, 2016).
Fu, Z. et al. Low-temperature controlled growth of 2D LaOCl with enhanced dielectric properties for advanced electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 35, 2501136 (2025).
Yu, H. et al. Eight in. Wafer-scale epitaxial monolayer MoS2. Adv. Mater. 36, e2402855 (2024).
Strand, J. et al. Intrinsic charge trapping in amorphous oxide films: status and challenges. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 30, 233001 (2018).
Thompson, A. P. et al. LAMMPS - a flexible simulation tool for particle-based materials modeling at the atomic, meso, and continuum scales. Comput. Phys. Commun. 271, 108171 (2022).
Shan, T.-R. et al. Charge-optimized many-body potential for the hafnium/hafnium oxide system. Phys. Rev. B 81, 125328 (2009).
Li, P. et al. Large-scale ab initio simulations based on systematically improvable atomic basis. Comput. Mater. Sci. 112, 503–517 (2016).
Chen, M. et al. Systematically improvable optimized atomic basis sets for ab initio calculations. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22, 445501 (2010).
Perdew, J. et al. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996).
Hamann, D. R. Optimized norm-conserving Vanderbilt pseudopotentials. Phys. Rev. B 88, 085117 (2013).
Lin, P. et al. Strategy for constructing compact numerical atomic orbital basis sets by incorporating the gradients of reference wavefunctions. Phys. Rev. B 103, 235131 (2021).
Acknowledgements
G.Z. acknowledges the support by the National Key Research and Development Program (Grant No. 2021YFA1202904), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Grant No. 62488201), and the Guangdong Major Project of Basic and Applied Basic Research (2021B0301030002). N.L. acknowledges the support of the NFSC (Grant No. 12574200). H.Y. acknowledges the support of the NFSC (Grant No. 62404145). S.W. acknowledges the support by the National Key Research and Development Program (Grant No. 2022YFA1402500). C.S. acknowledges the support by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant No: 2025ZNSFSC0881). L.D. acknowledges the support by the NFSC (Grant No. 12274447). L.X. acknowledges the support by the NFSC (Grant No. 62341404), Hangzhou Tsientang Education Foundation and the Max Planck Partner group program. X.T. acknowledges the support by Innovation and Technology Commission of Hong Kong SAR Government (No. MRP/020/21) and Research Grants Council Theme-based Research Scheme (TRS) 2024/25 (No. T42-513/24-R).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.Z. and N.L. co-supervised the project. S.Z. performed the HfO2 film growth, device fabrication, characterizations, and electrical measurements. T.Z., H.G., and L.X. performed DFT calculations. X.L., T.L., and C.C. assisted with the device fabrication and electrical measurements. H.Y., S.W., L.H., and Y.Z. contributed to the 8-inch MoS2 growth and characterizations. S.W., D.Z., L.B., S.L., C.S., W.Y., L.D., D.S., X.T., and Y.C. were involved in data analysis. S.Z., N.L., and G.Z. wrote, and all authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Theresia Knobloch, Tania Roy, and the other, anonymous, reviewer for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Zhang, T., Yu, H. et al. Wafer-scale high-κ HfO2 dielectric films with sub-5-Å equivalent oxide thickness for 2D MoS2 transistors. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68584-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68584-0